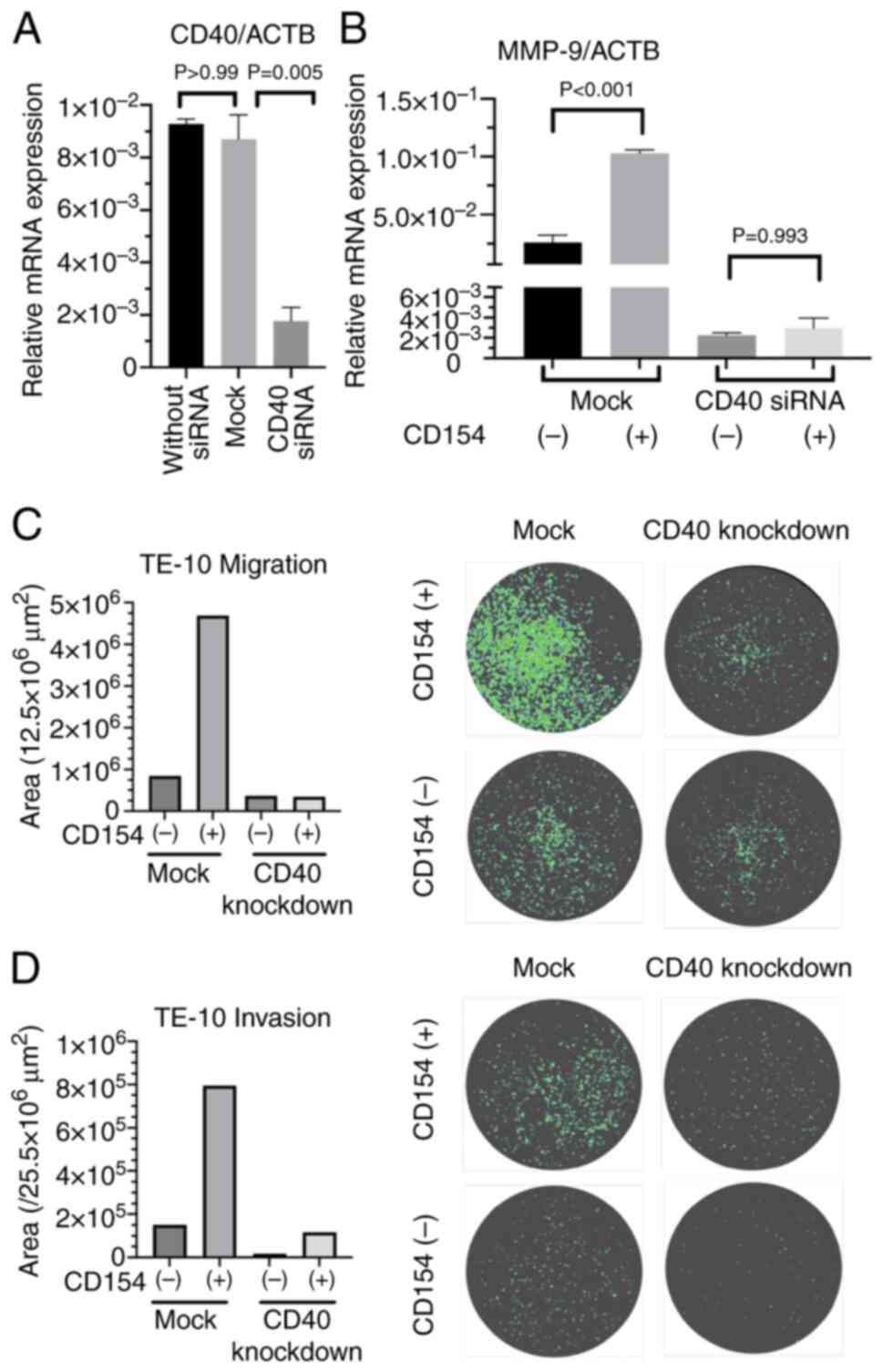
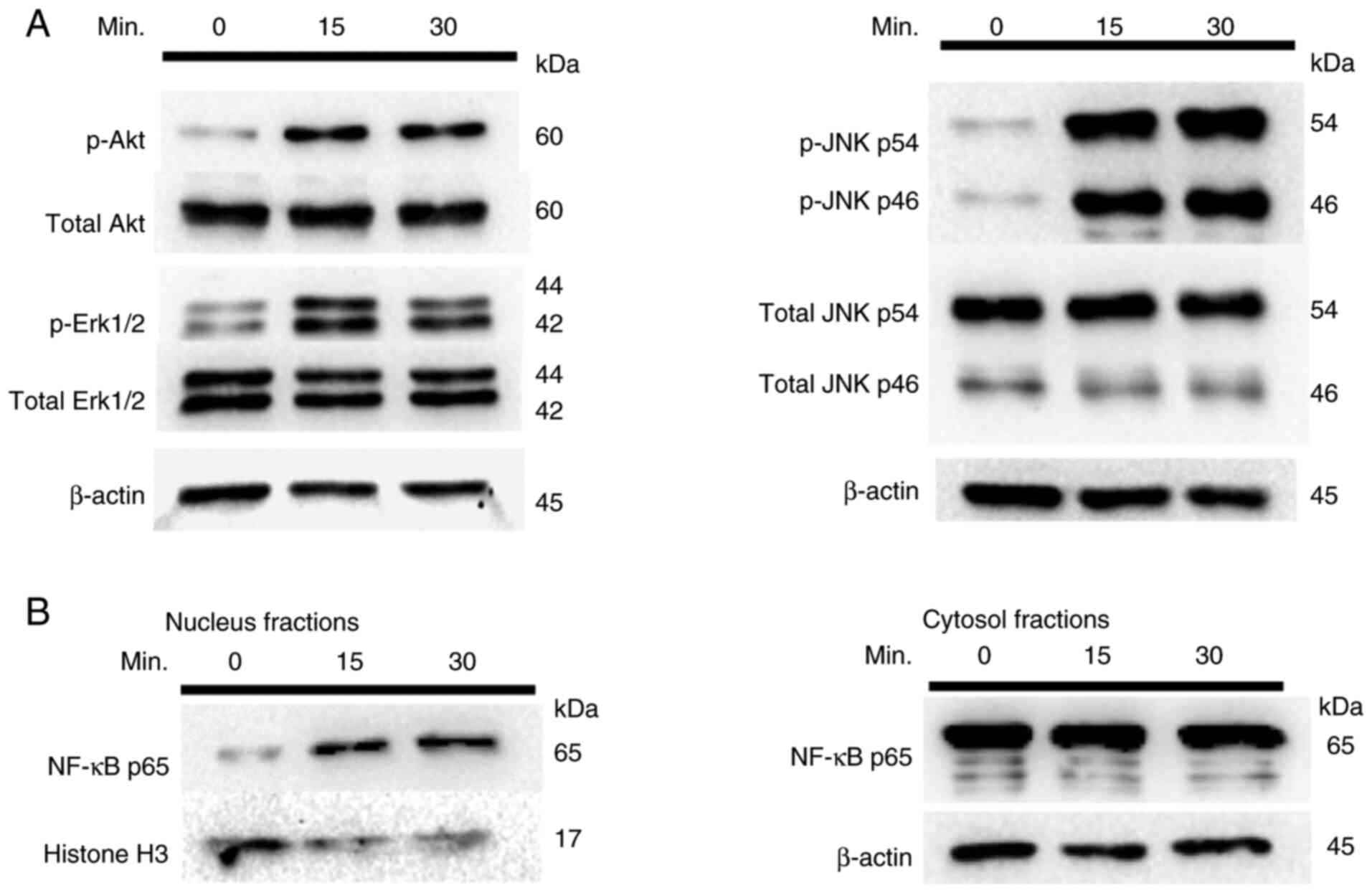
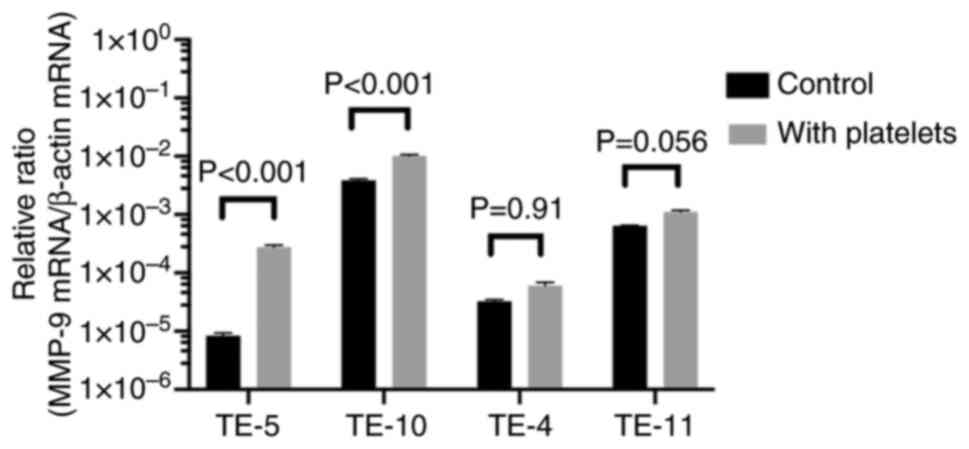
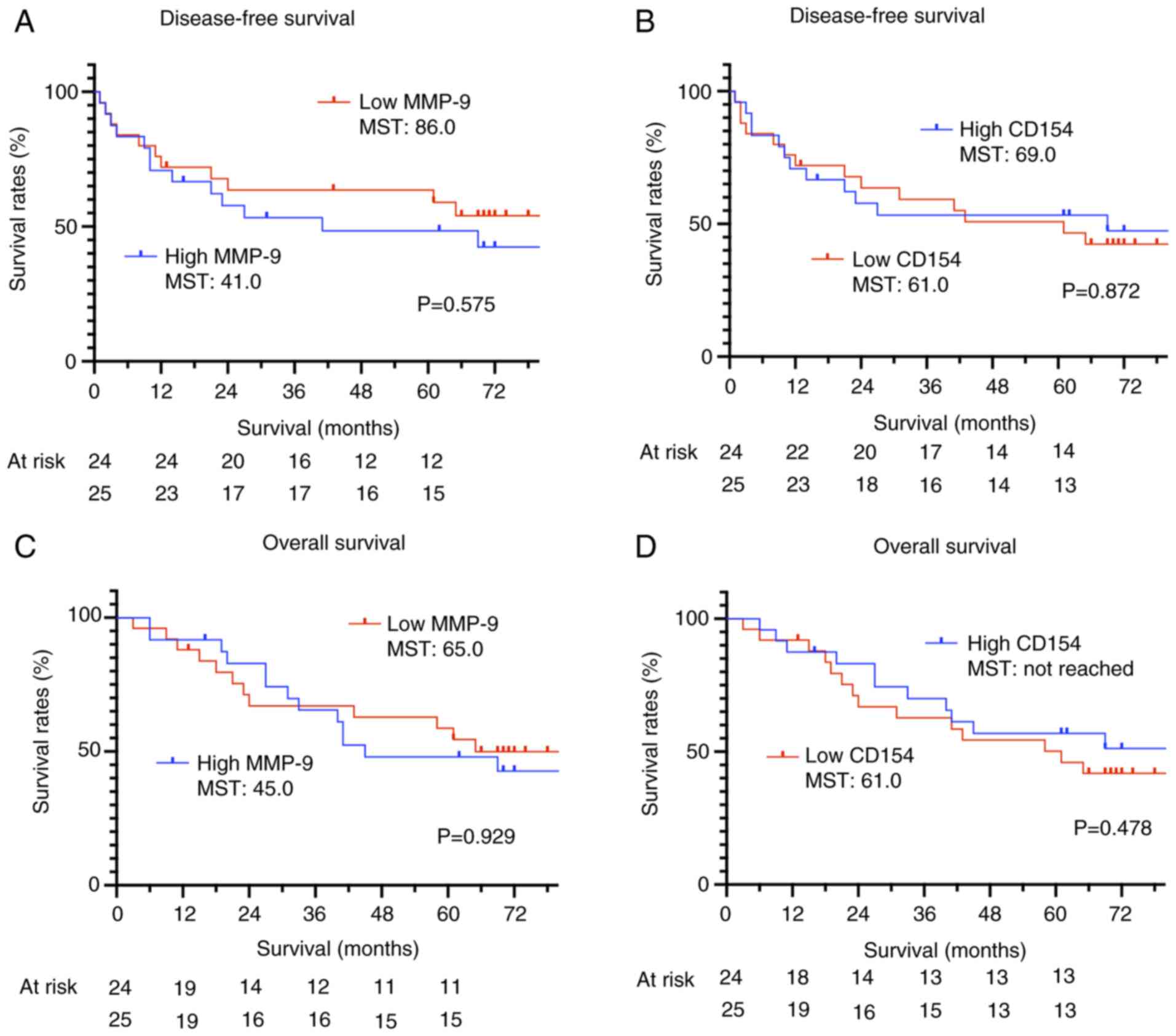
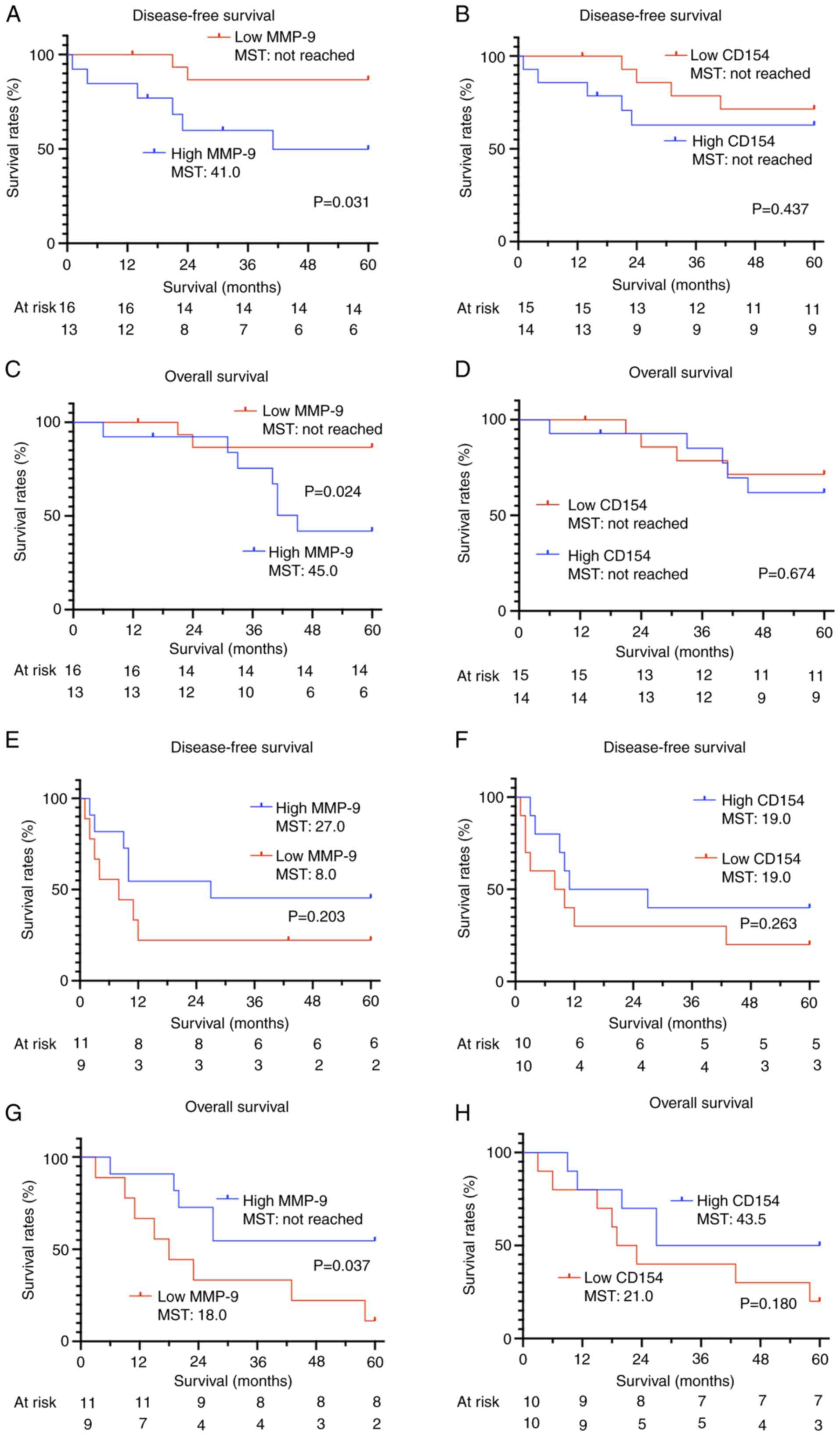
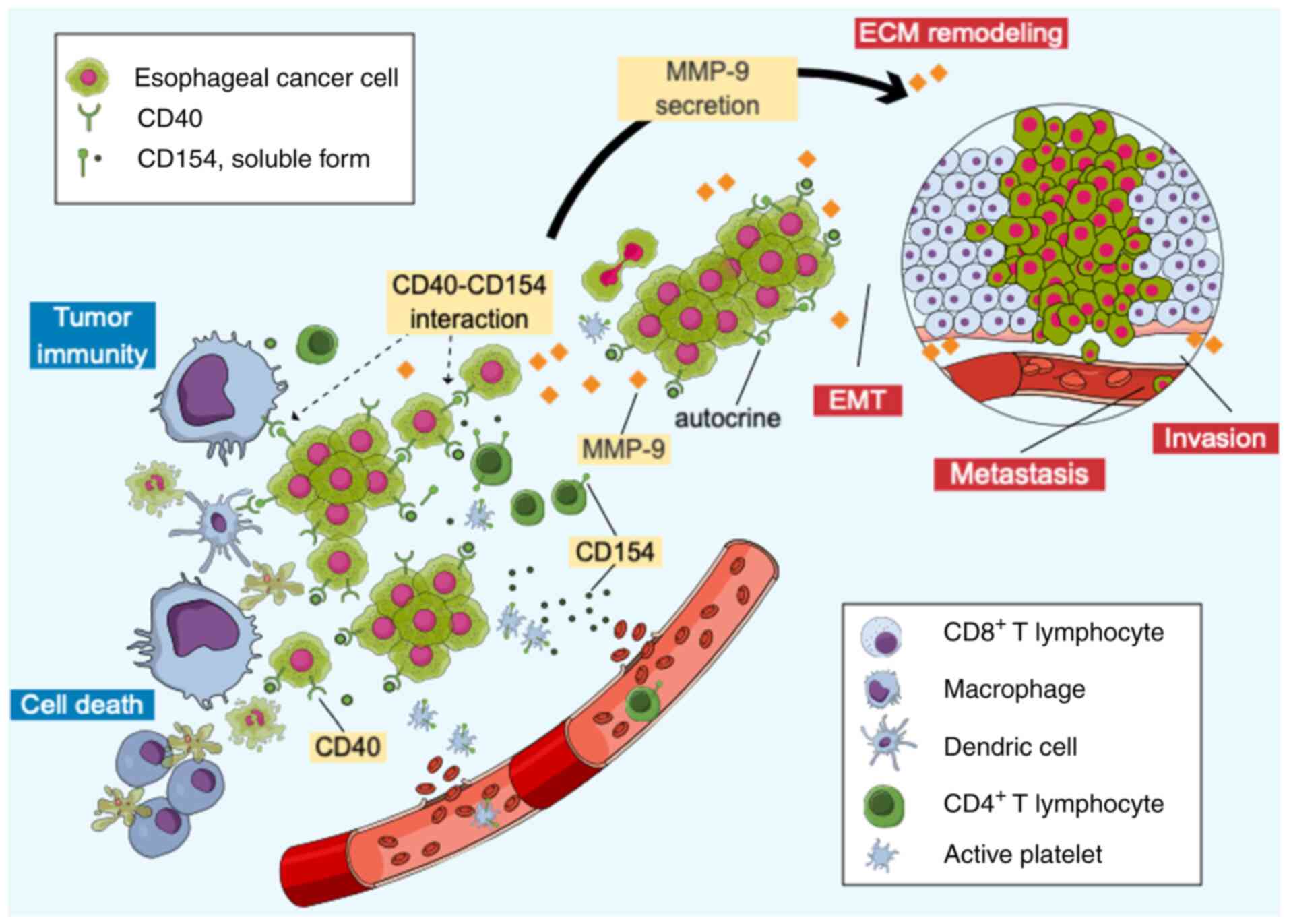
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Kooten C and Banchereau J: CD40-CD40
ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 67:2–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schonbeck U and Libby P: The CD40/CD154
receptor/ligand dyad. Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:4–43. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richards DM, Sefrin JP, Gieffers C, Hill O
and Merz C: Concepts for agonistic targeting of CD40 in
immuno-oncology. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 16:377–387. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu W, Li Y, Yuan WW, Yin Y, Song WW, Wang
Y, Huang QQ, Zhao WH and Wu JQ: Membrane-bound CD40L promotes
senescence and initiates senescence-associated secretory phenotype
via NF-κB activation in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
48:1793–1803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim CY, Chang JH, Lee WS, Kim J and Park
IY: CD40 agonists alter the pancreatic cancer microenvironment by
shifting the macrophage phenotype toward M1 and suppress human
pancreatic cancer in organotypic slice cultures. Gut and Liver.
16:645–659. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bishop GA, Moore CR, Xie P, Stunz LL and
Kraus ZJ: TRAF proteins in CD40 signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol.
597:131–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van den Oord JJ, Maes A, Stas M, Nuyts J,
Battocchio S, Kasran A, Garmyn M, De Wever I and De Wolf-Peeters C:
CD40 is a prognostic marker in primary cutaneous malignant
melanoma. Am J Pathol. 149:1953–1961. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sabel MS, Yamada M, Kawaguchi Y, Chen FA,
Takita H and Bankert RB: CD40 expression on human lung cancer
correlates with metastatic spread. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
49:101–108. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li R, Chen WC, Pang XQ, Hua C, Li L and
Zhang XG: Expression of CD40 and CD40L in gastric cancer tissue and
its clinical significance. Int J Mol Sci. 10:3900–3917. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ishikawa K, Miyamoto M, Yoshioka T, Kato
T, Kaji M, Ohbuchi T, Hirano S, Itoh T, Dosaka-Akita H and Kondo S:
Up-regulation of CD40 with juxtacrine activity in human nonsmall
lung cancer cells correlates with poor prognosis. Cancer.
113:530–541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cooke PW, James ND, Ganesan R, Wallace M,
Burton A and Young LS: CD40 expression in bladder cancer. J Pathol.
188:38–43. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shoji Y, Miyamoto M, Ishikawa K, Yoshioka
T, Mishra R, Ichinokawa K, Matsumura Y, Itoh T, Shinohara T, Hirano
S and Kondo S: The CD40-CD154 interaction would correlate with
proliferation and immune escape in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 103:230–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsumura Y, Hiraoka K, Ishikawa K, Shoji
Y, Noji T, Hontani K, Itoh T, Nakamura T, Tsuchikawa T, Shichinohe
T and Hirano S: CD40 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
Carcinoma is associated with tumor progression and lymph node
metastasis. Anticancer Res. 36:4467–4475. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Davidson B, Reich R, Risberg B and Nesland
JM: The biological role and regulation of matrix metalloproteinases
(MMP) in cancer. Arkh Patol. 64:47–53. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rhee JS and Coussens LM: RECKing MMP
function: Implications for cancer development. Trends Cell Biol.
12:209–211. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dagouassat M, Suffee N, Hlawaty H, Haddad
O, Charni F, Laguillier C, Vassy R, Martin L, Schischmanoff PO,
Gattegno L, et al: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)/CCL2
secreted by hepatic myofibroblasts promotes migration and invasion
of human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer. 126:1095–1108. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakamura T, Kuwai T, Kim JS, Fan D, Kim SJ
and Fidler IJ: Stromal metalloproteinase-9 is essential to
angiogenesis and progressive growth of orthotopic human pancreatic
cancer in parabiont nude mice. Neoplasia. 9:979–986. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rigothier C, Daculsi R, Lepreux S, Auguste
P, Villeneuve J, Dewitte A, Doudnikoff E, Saleem M, Bourget C,
Combe C and Ripoche J: CD154 induces matrix metalloproteinase-9
secretion in human podocytes. J Cell Biochem. 117:2737–2747. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takeuchi S, Baghdadi M, Tsuchikawa T, Wada
H, Nakamura T, Abe H, Nakanishi S, Usui Y, Higuchi K, Takahashi M,
et al: Chemotherapy-derived inflammatory responses accelerate the
formation of immunosuppressive myeloid cells in the tissue
microenvironment of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.
75:2629–2640. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C, RBrierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumours. 8th ed. Oxford:
Wiley-Blackwell; 2017
|
|
25
|
Tone M, Tone Y, Fairchild PJ, Wykes M and
Waldmann H: Regulation of CD40 function by its isoforms generated
through alternative splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:1751–1756.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schlesinger M: Role of platelets and
platelet receptors in cancer metastasis. J Hematol Oncol.
11:1252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haemmerle M, Stone RL, Menter DG,
Afshar-Kharghan V and Sood AK: The platelet lifeline to cancer:
Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Cell. 33:965–983. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gay LJ and Feldin-Habermann B:
Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:123–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Goubran H, Sabry W, Kotb R, Seghatchian J
and Burnouf T: Platelet microparticles and cancer: An intimate
cross-talk. Transfus Apher Sci. 53:168–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blair TA and Frelinger AL: 3rd: Platelet
surface marker analysis by mass cytometry. Platelets. 31:633–640.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chatzigeorgiou A, Lyberi M, Chatzilymperis
G, Nezos A and Kamper E: CD40/CD40L signaling and its implication
in health and disease. Biofactors. 35:474–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bussolati B, Russo S, Deambrosis I,
Cantaluppi V, Volpe A, Ferrando U and Camussi G: Expression of
CD154 on renal cell carcinomas and effect on cell proliferation,
motility and platelet-activating factor synthesis. Int J Cancer.
100:654–661. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grazia GA, Bastos DR and Villa LL:
CD40/CD40L expression and its prognostic value in cervical cancer.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 56:e130472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pantel K and Brakenhoff RH: Dissecting the
metastatic cascade. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:448–456. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|