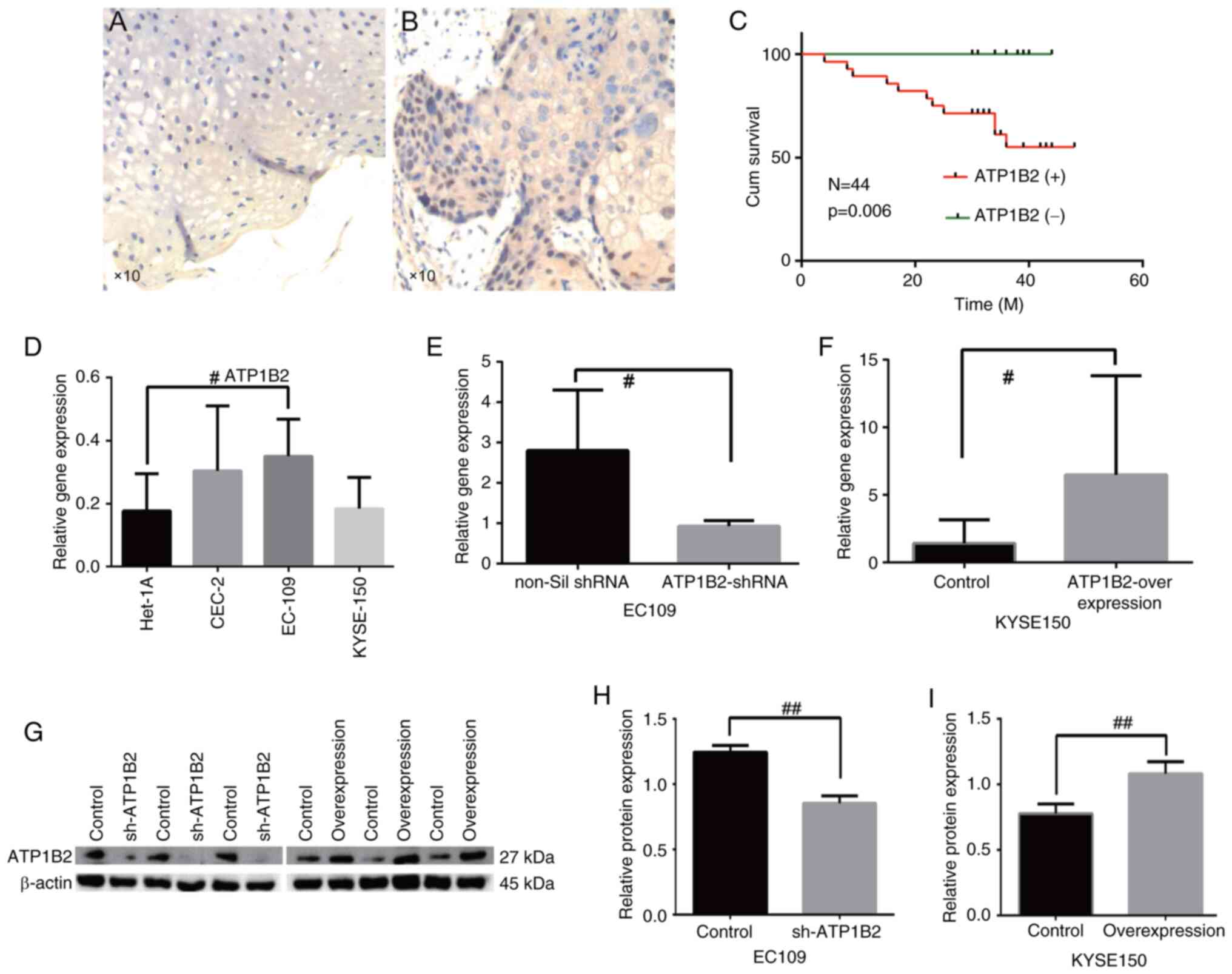
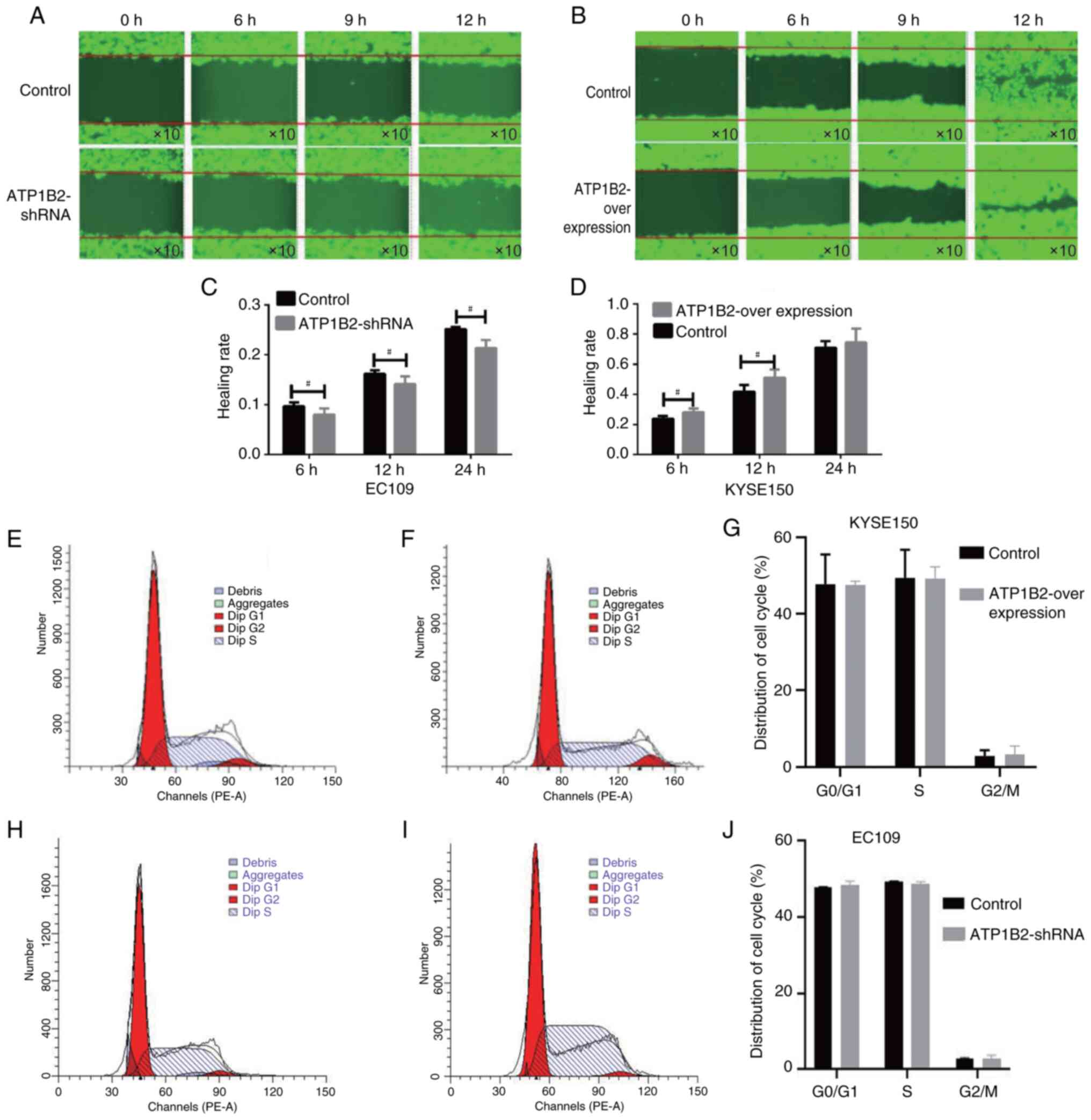
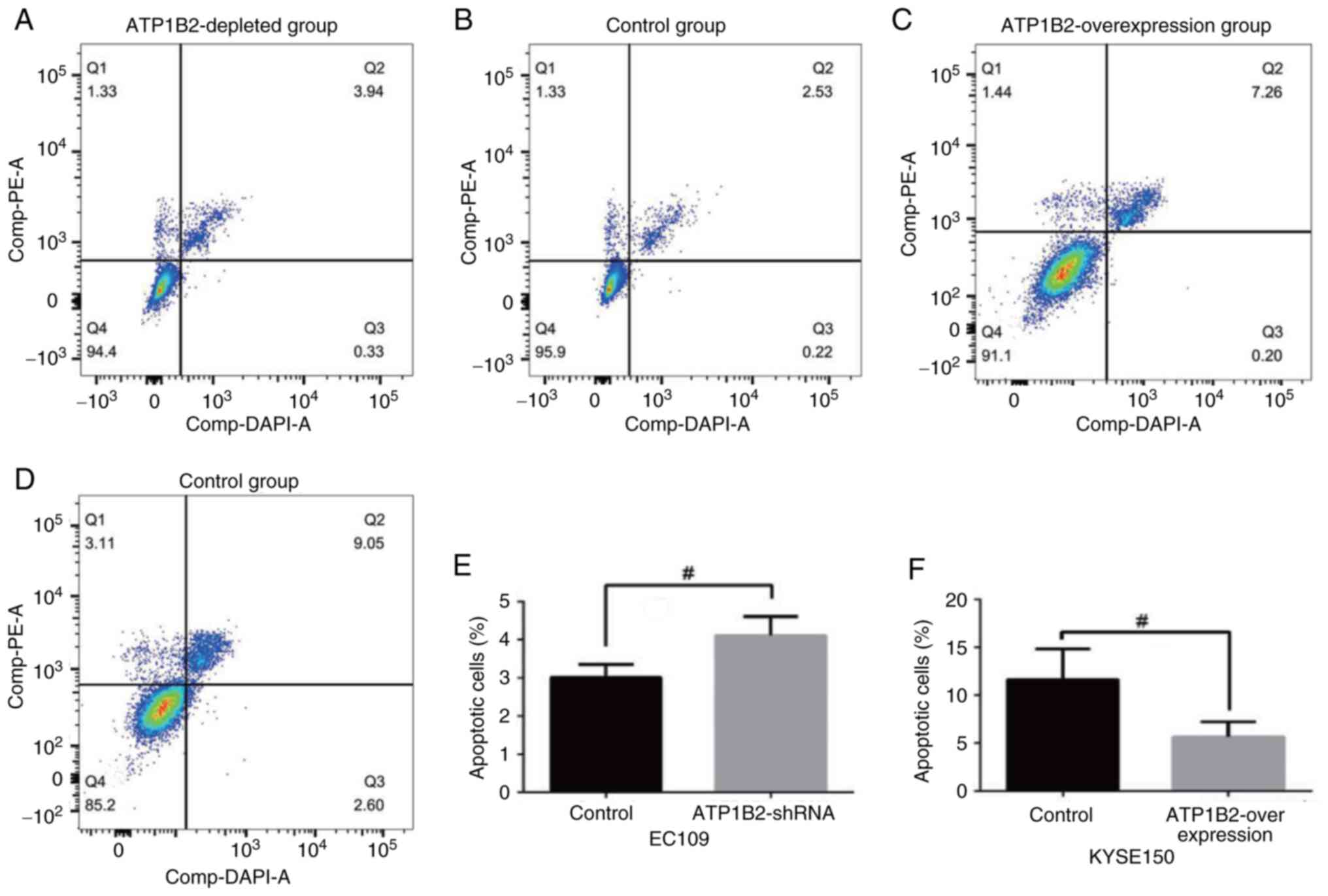
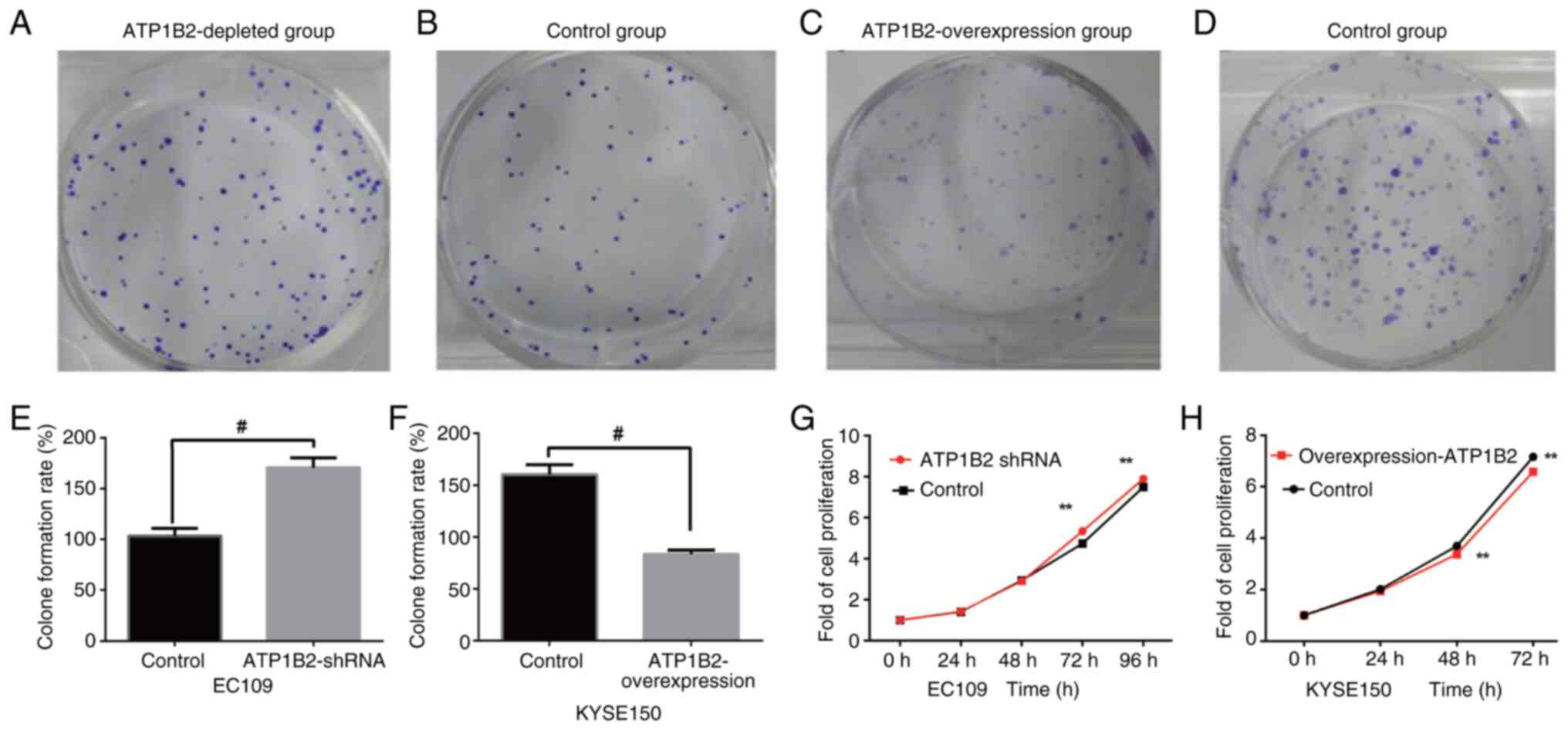
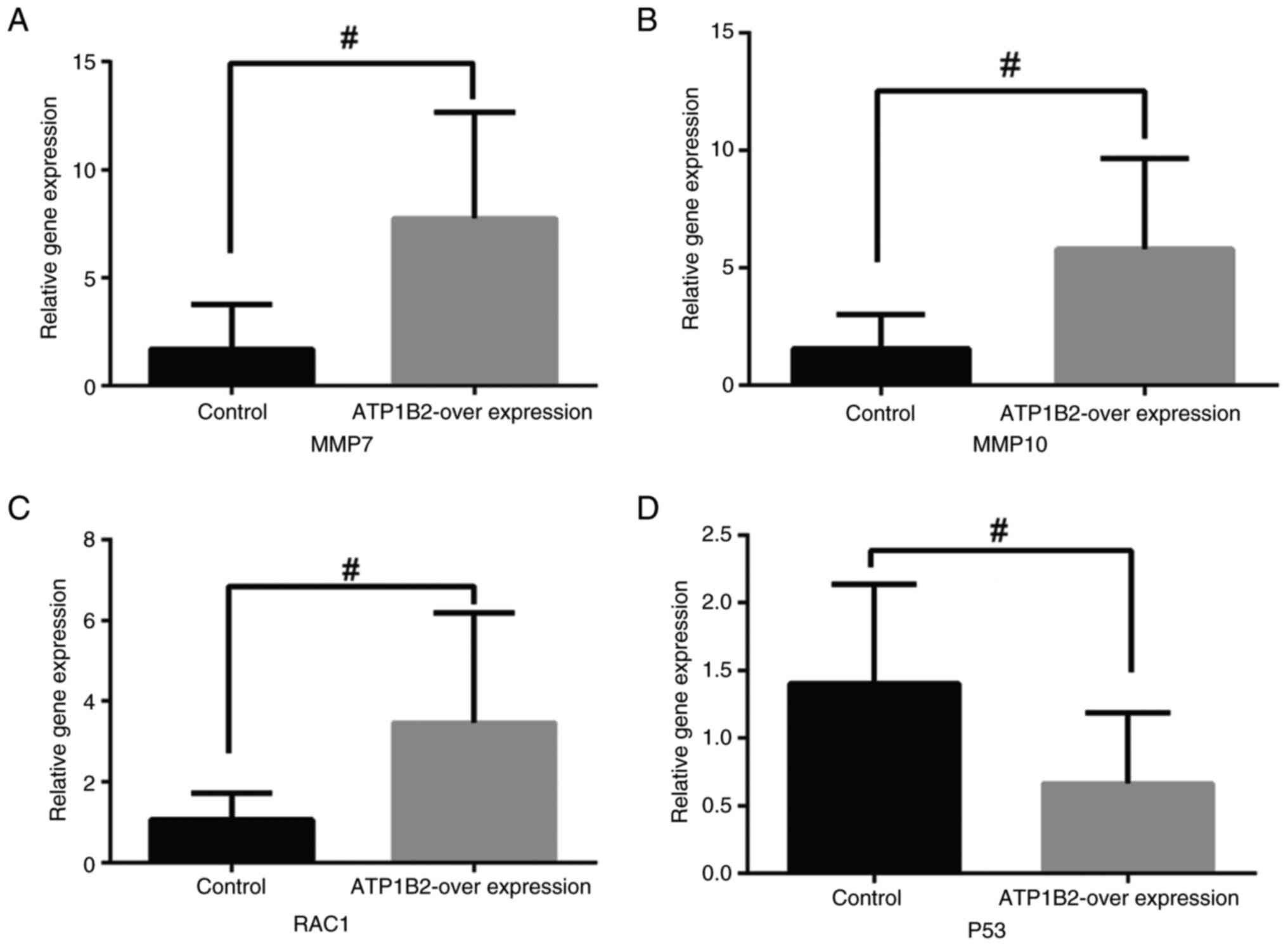
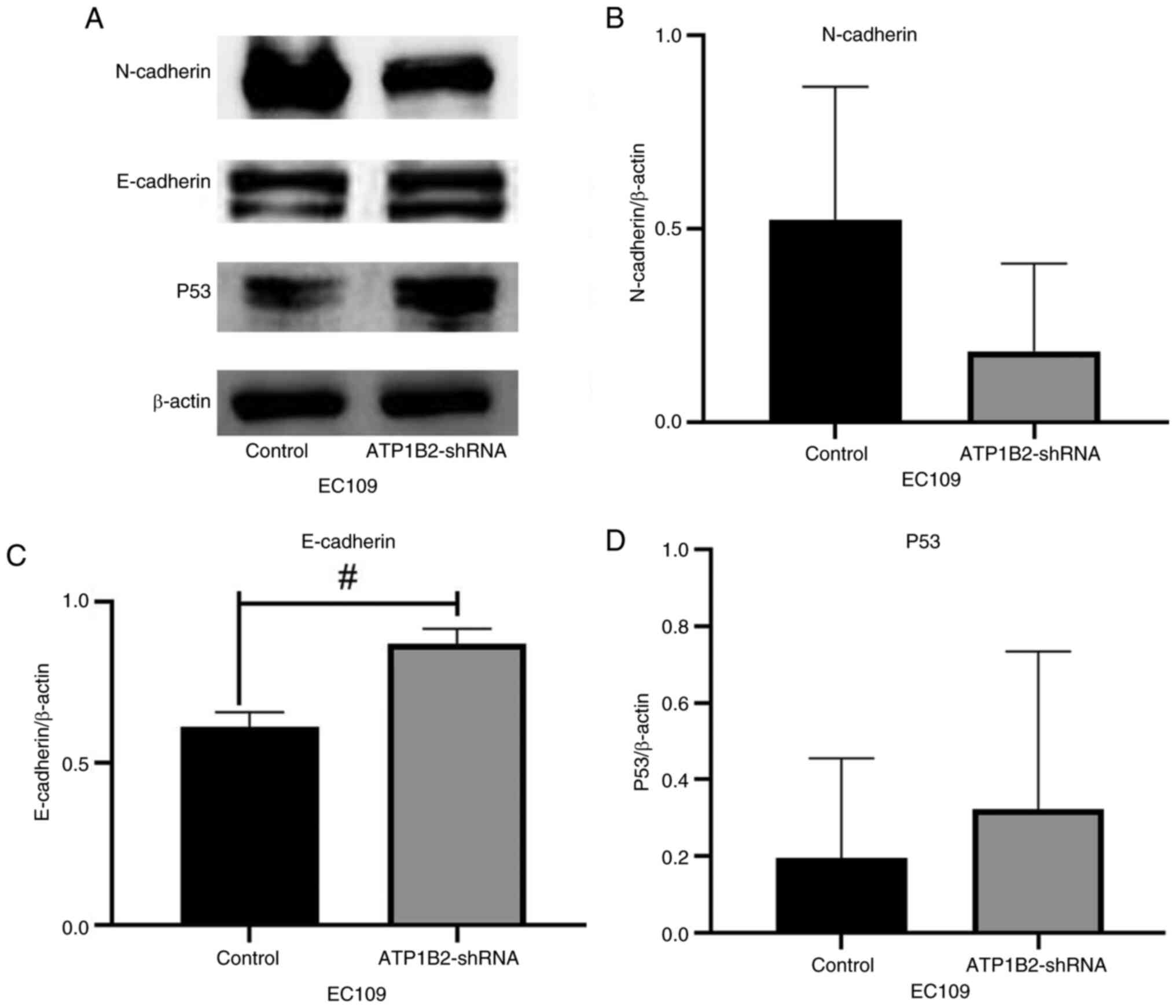
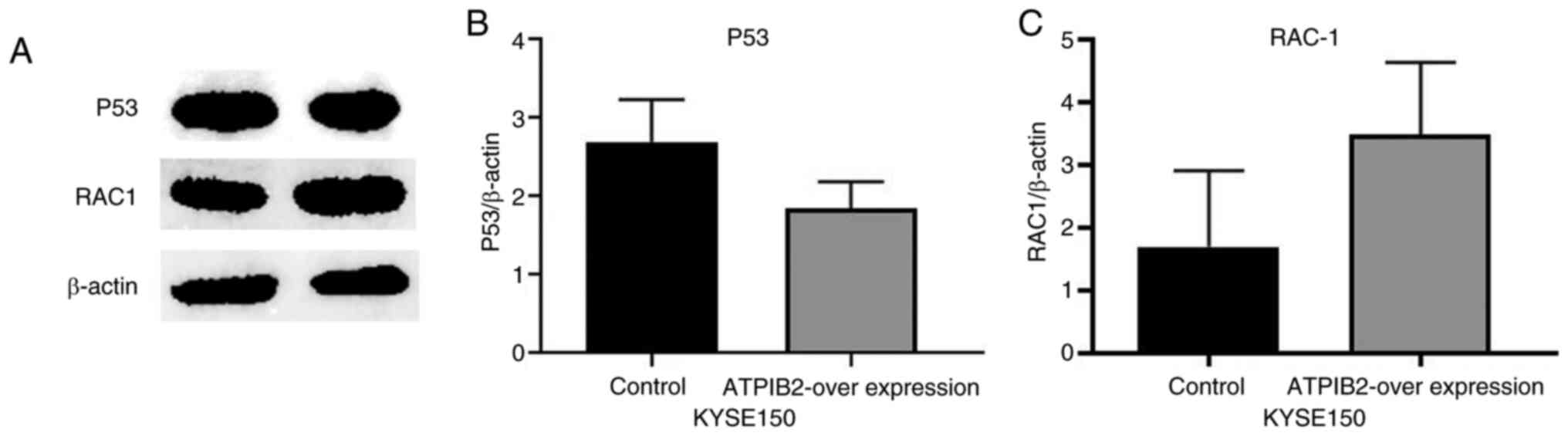
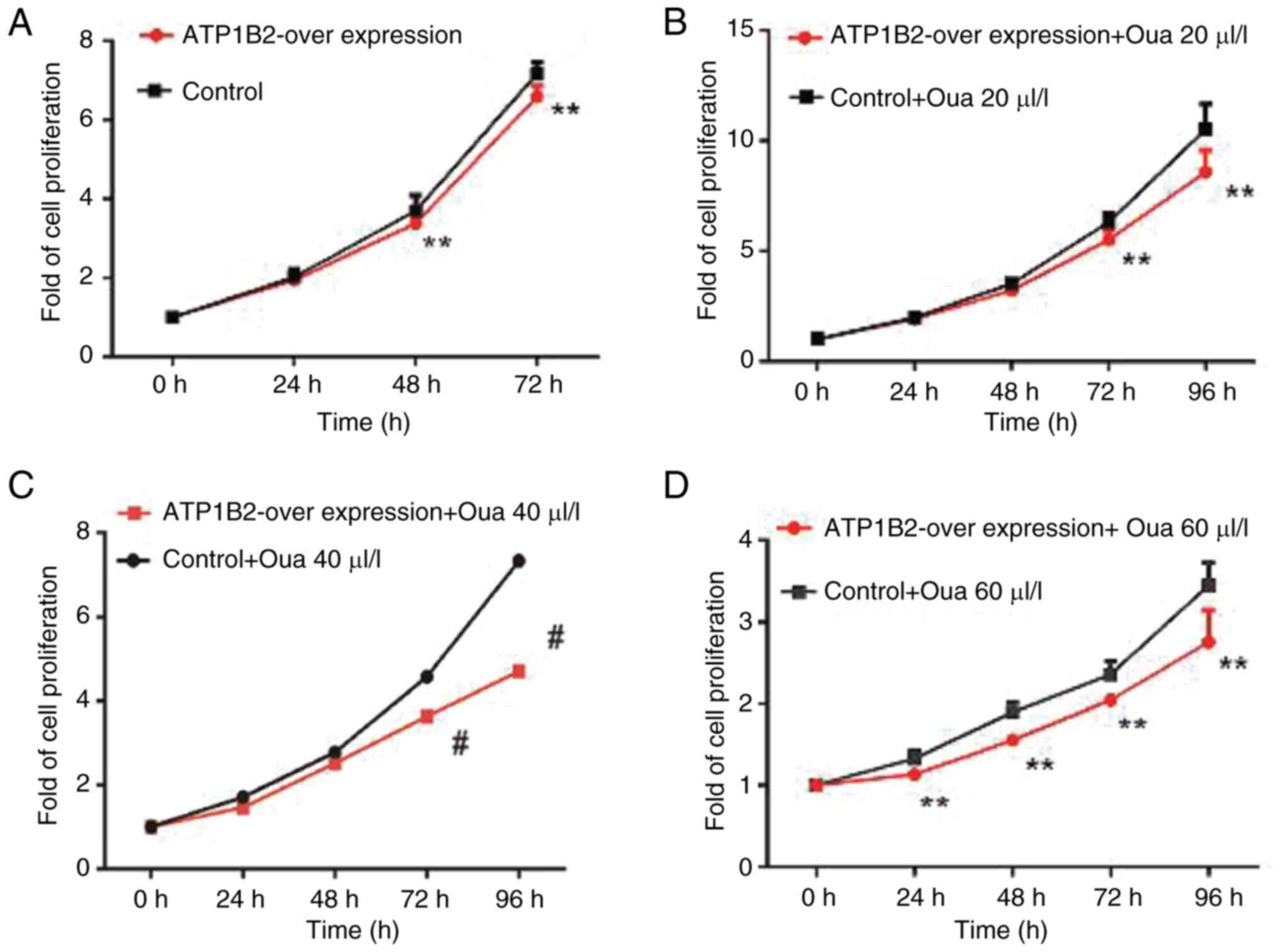
|
1
|
Chen L, Jiang P, Li J, Xie Z, Xu Y, Qu W,
Feng F and Liu W: Periplocin promotes wound healing through the
activation of Src/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways mediated by
Na/K-ATPase. Phytomedicine. 57:72–83. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Felippe Goncalves-De-Albuquerque C,
Ribeiro Silva A, Ignacio Da Silva C, Caire Castro-Faria-Neto H and
Burth P: Na/K pump and beyond: Na/K-ATPase as a modulator of
apoptosis and autophagy. Molecules. 22:5782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bejček J, Spiwok V, Kmoníčková E and
Rimpelová S: Na+/K+-ATPase revisited: On its mechanism of action,
role in cancer, and activity modulation. Molecules. 26:19052021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hilbers F, Kopec W, Isaksen TJ, Holm TH,
Lykke-Hartmann K, Nissen P, Khandelia H and Poulsen H: Tuning of
the Na,K-ATPase by the beta subunit. Sci Rep. 6:204422016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rotoli D, Cejas MM, Maeso MD,
Pérez-Rodríguez ND, Morales M, Ávila J, Mobasheri A and
Martín-Vasallo P: The Na, K-ATPase β-subunit isoforms expression in
glioblastoma multiforme: Moonlighting roles. Int J Mol Sci.
18:23692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Banerjee M, Cui X, Li Z, Yu H, Cai L, Jia
X, He D, Wang C, Gao T and Xie Z: Na/K-ATPase Y260
Phosphorylation-mediated src regulation in control of aerobic
glycolysis and tumor growth. Sci Rep. 8:123222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Busonero C, Leone S, Bianchi F, Maspero E,
Fiocchetti M, Palumbo O, Cipolletti M, Bartoloni S and Acconcia F:
Ouabain and digoxin activate the proteasome and the degradation of
the ERα in cells modeling primary and metastatic breast cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 12:38402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du J, Jiang L, Chen F, Hu H and Zhou M:
Cardiac glycoside ouabain exerts anticancer activity via
downregulation of STAT3. Front Oncol. 11:6843162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Wu C, Qin Y, Liu S and Zhang R:
Multi-angle investigation of the fractal characteristics of
nanoscale pores in the lower cambrian niutitang shale and their
implications for CH4 adsorption. J Nanosci Nanotechnol.
21:156–167. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li S, Dai Z, Yang D, Li W, Dai H, Sun B,
Liu X, Xie X, Xu R and Zhao X: Targeting β2 subunit of
Na+/K+-ATPase induces glioblastoma cell apoptosis through elevation
of intracellular Ca2. Am J Cancer Res. 9:1293–1308. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J: Digestive cancer incidence and
mortality among young adults worldwide in 2020: A population-based
study. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 14:278–294. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu SG, Zhang WW, Sun JY, Li FY, Lin Q and
He ZY: Patterns of distant metastasis between histological types in
esophageal cancer. Front Oncol. 8:3022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu C, Wang Z, Song X, Feng XS, Abnet CC,
He J, Hu N, Zuo XB, Tan W, Zhan Q, et al: Joint analysis of three
genome-wide association studies of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat Genet. 46:1001–1006. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singhi AD, Wood LD, Parks E, Torbenson MS,
Felsenstein M, Hruban RH, Nikiforova MN, Wald AI, Kaya C, Nikiforov
YE, et al: Recurrent rearrangements in PRKACA and PRKACB in
intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasms of the pancreas and bile
duct. Gastroenterology. 158:573–582.e2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang M, James AD, Suman R, Kasprowicz R,
Nelson M, O'Toole PJ and Brackenbury WJ: Voltage-dependent
activation of Rac1 by Nav 1.5 channels promotes cell migration. J
Cell Physiol. 235:3950–3972. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leslie TK, James AD, Zaccagna F, Grist JT,
Deen S, Kennerley A, Riemer F, Kaggie JD, Gallagher FA, Gilbert FJ
and Brackenbury WJ: Sodium homeostasis in the tumour
microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1872:1883042019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Capatina AL, Lagos D and Brackenbury WJ:
Targeting ion channels for cancer treatment: Current progress and
future challenges. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 183:1–43. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shandell MA, Capatina AL, Lawrence SM,
Brackenbury WJ and Lagos D: Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase by
cardiac glycosides suppresses expression of the IDO1 immune
checkpoint in cancer cells by reducing STAT1 activation. J Biol
Chem. 298:1017072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pelin M, Stocco G, Florio C, Sosa S and
Tubaro A: In vitro cell sensitivity to palytoxin correlates with
high gene expression of the Na+/K+-ATPase β2 subunit isoform. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:58332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu YW, Peng YH, Chen B, Wu ZY, Wu JY, Shen
JH, Zheng CP, Wang SH, Guo HP, Li EM and Xu LY: Autoantibodies as
potential biomarkers for the early detection of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 109:36–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ardalan Khales S, Abbaszadegan MR, Majd A
and Forghanifard MM: TWIST1 upregulates matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP) genes family in esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Gene
Expr Patterns. 37:1191272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao L, Zhong X, Huang G, Ma Q, Xu L, Xiao
H and Guo X: Investigation on the potential correlation between
TP53 and esophageal cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7303372021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang N, Shi J, Shi X, Chen W and Liu J:
Mutational characterization and potential prognostic biomarkers of
Chinese patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
OncoTargets Ther. 13:12797–12809. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dey B, Raphael V, Khonglah Y and Lynrah
KG: Immunohistochemical analysis of P53 and PRB in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Diagn Res. 8:FC01–FC03.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Yan G, Zhang Y, Jia X and Bu P:
Long non-coding RNA MEG3 suppresses migration and invasion of
thyroid carcinoma by targeting of Rac1. Neoplasma. 62:541–549.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim HJ, Ryu KJ, Kim M, Kim T, Kim SH, Han
H, Kim H, Hong KS, Song CY, Choi Y, et al: RhoGDI2-mediated Rac1
recruitment to filamin a enhances Rac1 activity and promotes
invasive abilities of gastric cancer cells. Cancers (Basel).
14:2552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Q, Luo GY, Li Y, Shan HB, Wang HY and
Xu GL: Expression of Rac-1 related to tumor depth, lymph node
metastasis and patient prognosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:6892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L, Feng R, Xu Q, Zhang F, Liu T, Cao J
and Fei S: Expression of the β3 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase is
increased in gastric cancer and regulates gastric cancer cell
progression and prognosis via the PI3/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
8:84285–84299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun MZ, Kim JM, Oh MC, Safaee M, Kaur G,
Clark AJ, Bloch O, Ivan ME, Kaur R, Oh T, et al: Na+/K+-ATPase
β2-subunit (AMOG) expression abrogates invasion of
glioblastoma-derived brain tumor-initiating cells. Neuro Oncol.
15:1518–1531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun R, Xie HY, Qian JX, Huang YN, Yang F,
Zhang FL, Shao ZM and Li DQ: FBXO22 possesses both protumorigenic
and antimetastatic roles in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res.
78:5274–5286. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng Z, Geng H, Cheng Y, Dong N, Ning F,
Yu Z, Jian J and Chen S: Effects of MiR-210 on proliferation,
apoptosis and invasion abilities of esophageal cancer cells. J
BUON. 23:814–819. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Srovnal J,
Zemanova M, Harustiak T, Ehrmann J, Hajduch M, Sachlova M, Svoboda
M and Slaby O: MiR-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in
adenocarcinoma and an oncogene in squamous cell carcinoma of
esophagus. Tumour Biol. 37:8007–8018. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Botelho AFM, Pierezan F, Soto-Blanco B and
Melo MM: A review of cardiac glycosides: Structure, toxicokinetics,
clinical signs, diagnosis and antineoplastic potential. Toxicon.
158:63–68. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tverskoi AM, Poluektov YM, Klimanova EA,
Mitkevich VA, Makarov AA, Orlov SN, Petrushanko IY and Lopina OD:
Depth of the steroid core location determines the mode of
Na,K-ATPase inhibition by cardiotonic steroids. Int J Mol Sci.
22:132682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rupaimoole R, Yoon B, Zhang WC, Adams BD
and Slack FJ: A High-throughput small molecule screen identifies
ouabain as synergistic with miR-34a in killing lung cancer cells.
iScience. 23:1008782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chang YM, Shih YL, Chen CP, Liu KL, Lee
MH, Lee MZ, Hou HT, Huang HC, Lu HF, Peng SF, et al: Ouabain
induces apoptotic cell death in human prostate DU 145 cancer cells
through DNA damage and TRAIL pathways. Environ Toxicol.
34:1329–1339. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Klimanova EA, Fedorov DA, Sidorenko SV,
Abramicheva PA, Lopina OD and Orlov SN: Ouabain and
marinobufagenin: Physiological effects on human epithelial and
endothelial cells. Biochemistry (Mosc). 85:507–515. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Akimova OA, Tverskoi AM, Smolyaninova LV,
Mongin AA, Lopina OD, La J, Dulin NO and Orlov SN: Critical role of
the α1-Na(+), K(+)-ATPase subunit in insensitivity of rodent cells
to cytotoxic action of ouabain. Apoptosis. 20:1200–1110. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Petrič M, Vidović A, Dolinar K, Miš K,
Chibalin AV and Pirkmajer S: Phosphorylation of Na+,K+-ATPase at
Tyr10 of the α1-Subunit is suppressed by AMPK and enhanced by
ouabain in cultured kidney cells. J Membr Biol. 254:531–548. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang JL, Yang MD, Chen JC, Lu KW, Huang
YP, Peng SF, Chueh FS, Liu KC, Lin TS, Chen PY and Chen WJ: Ouabain
induces DNA damage in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells and alters
the expression of DNA damage and DNA Repair-associated proteins. In
Vivo. 35:2687–2696. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|