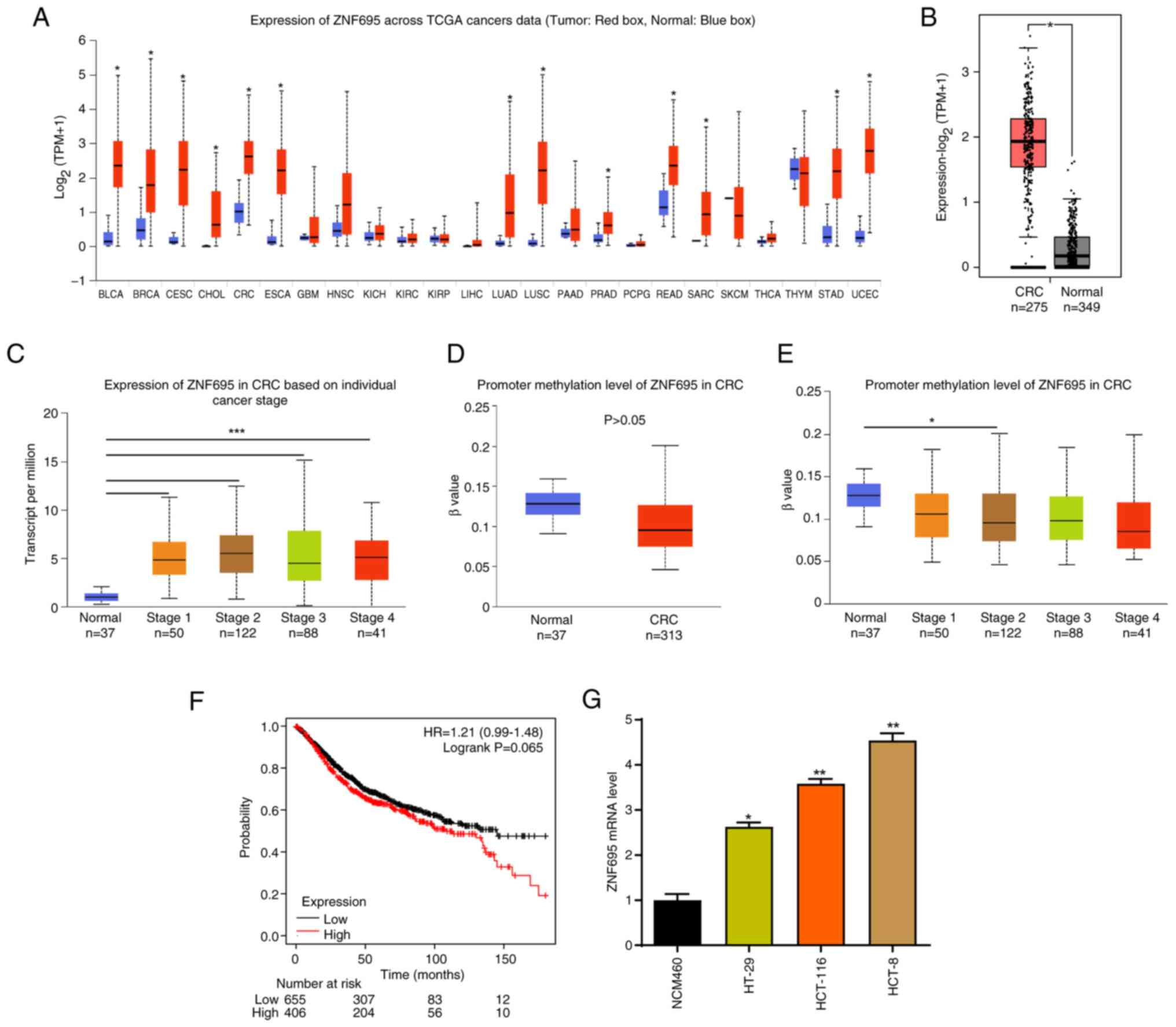
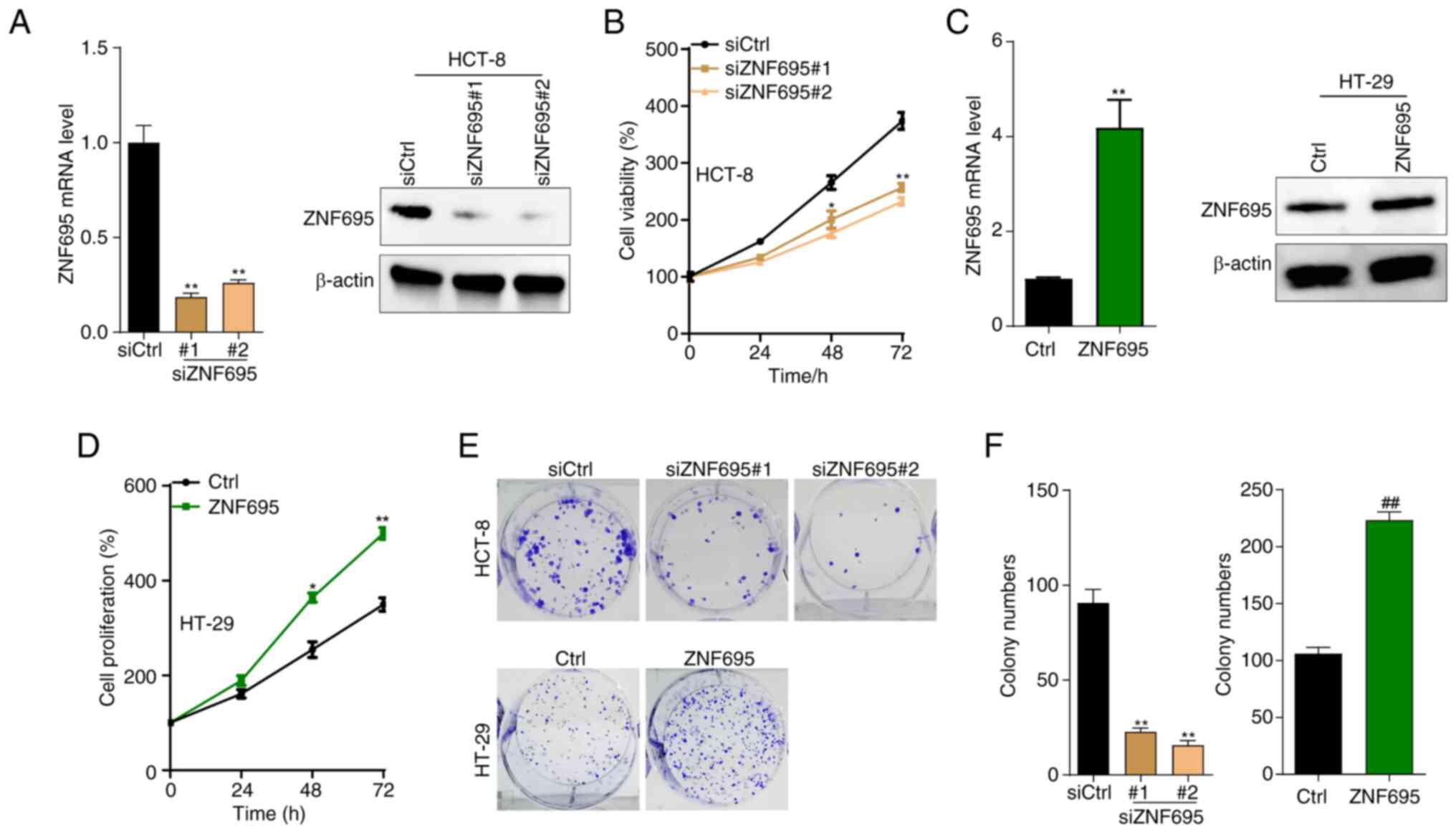
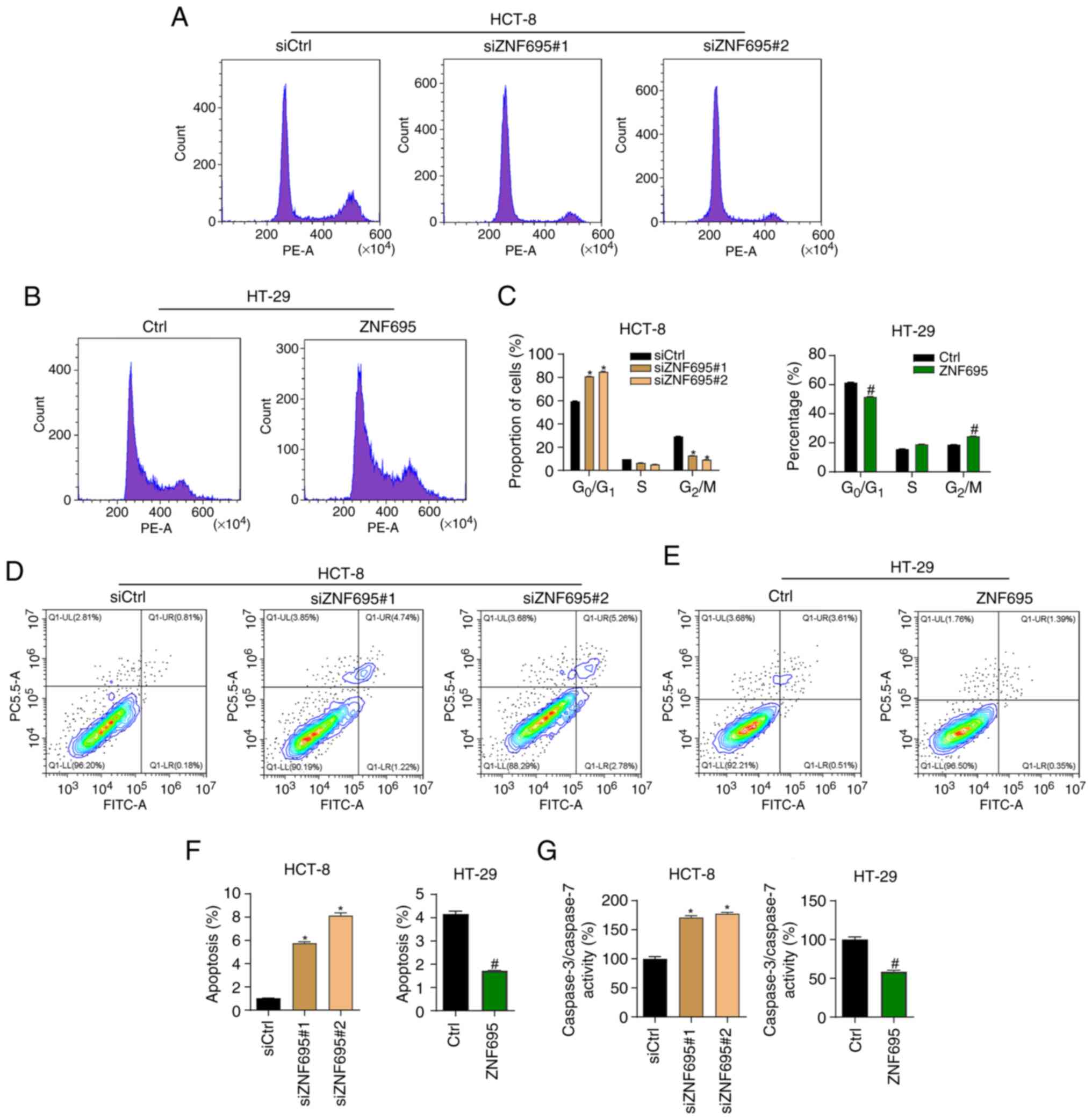
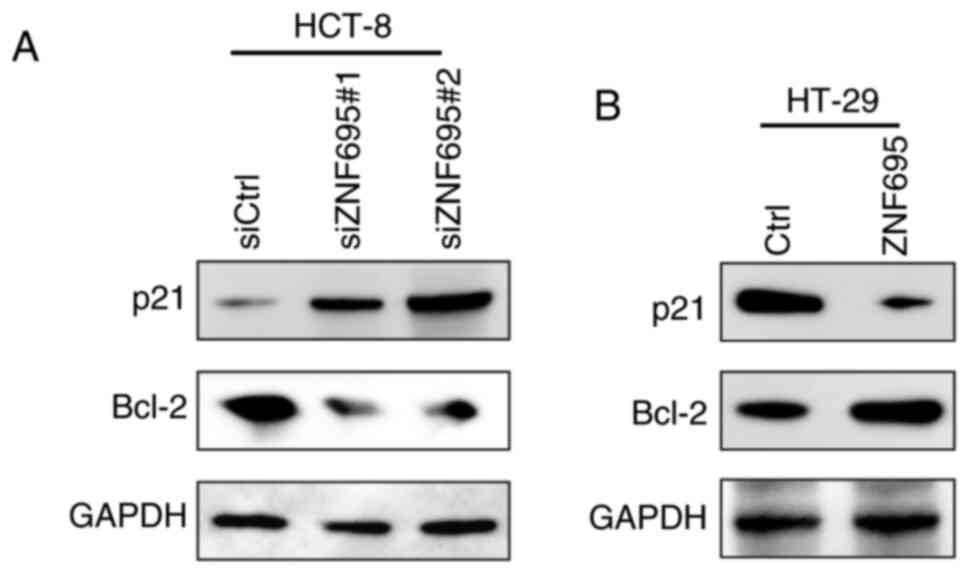
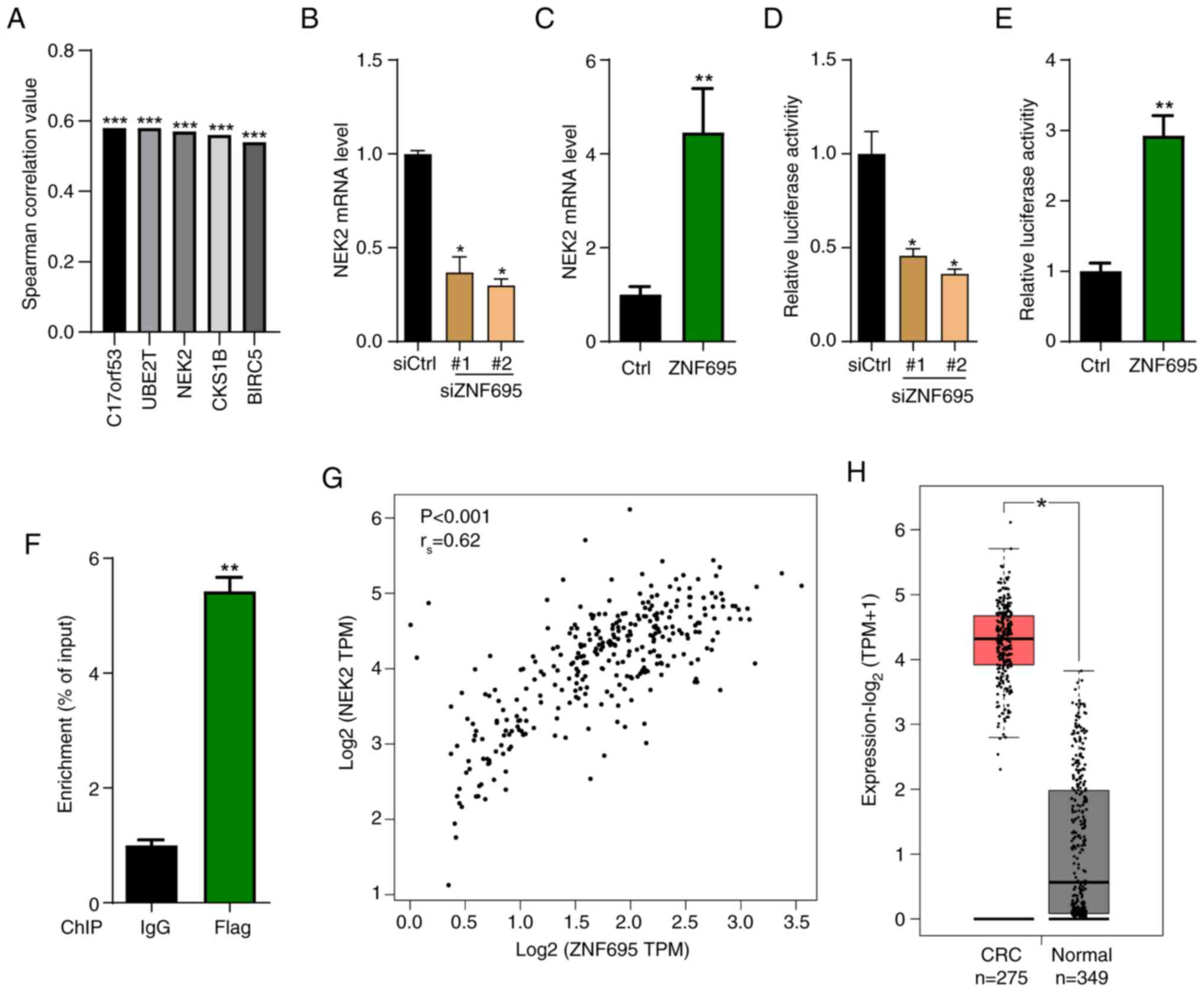
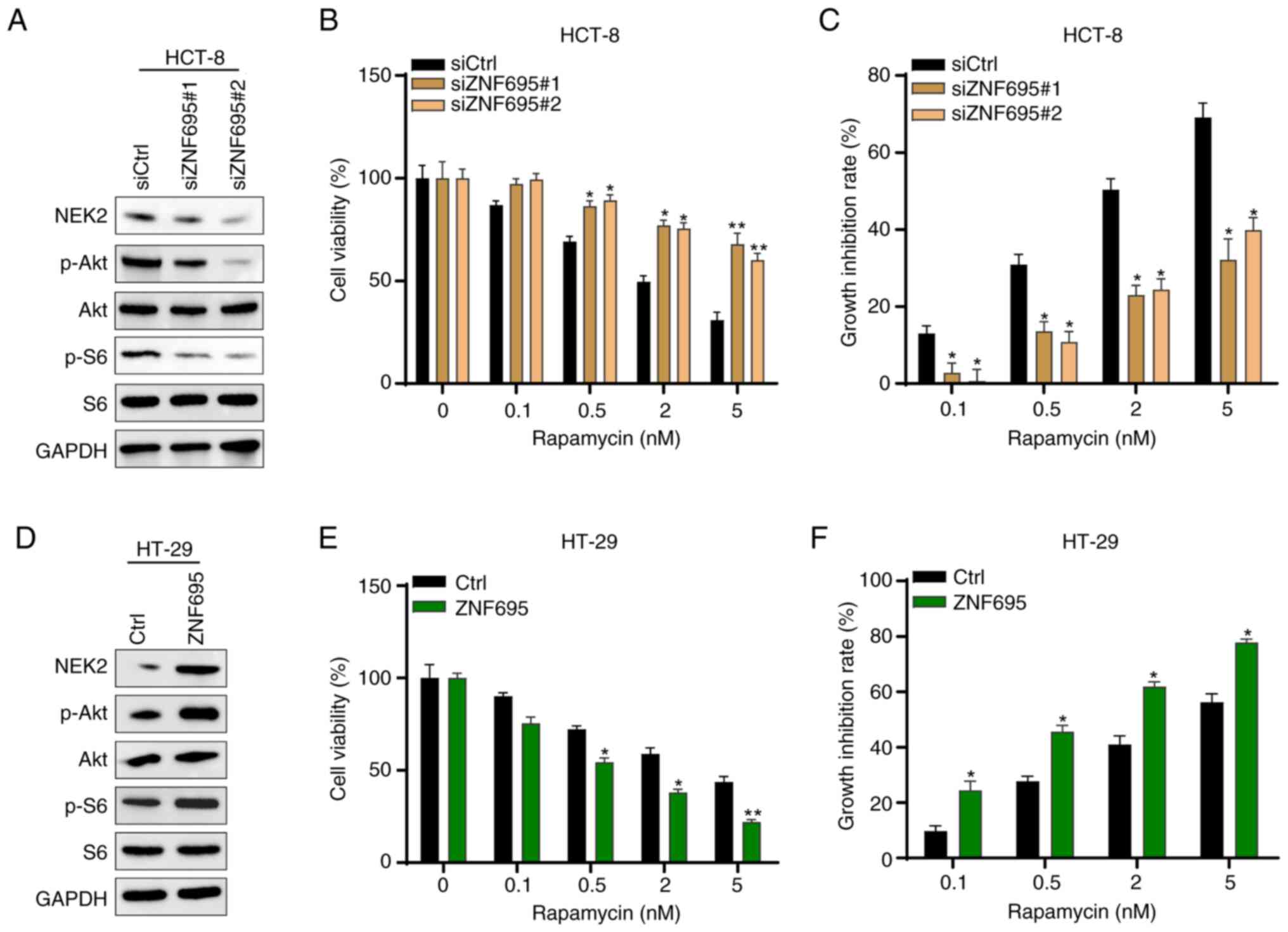
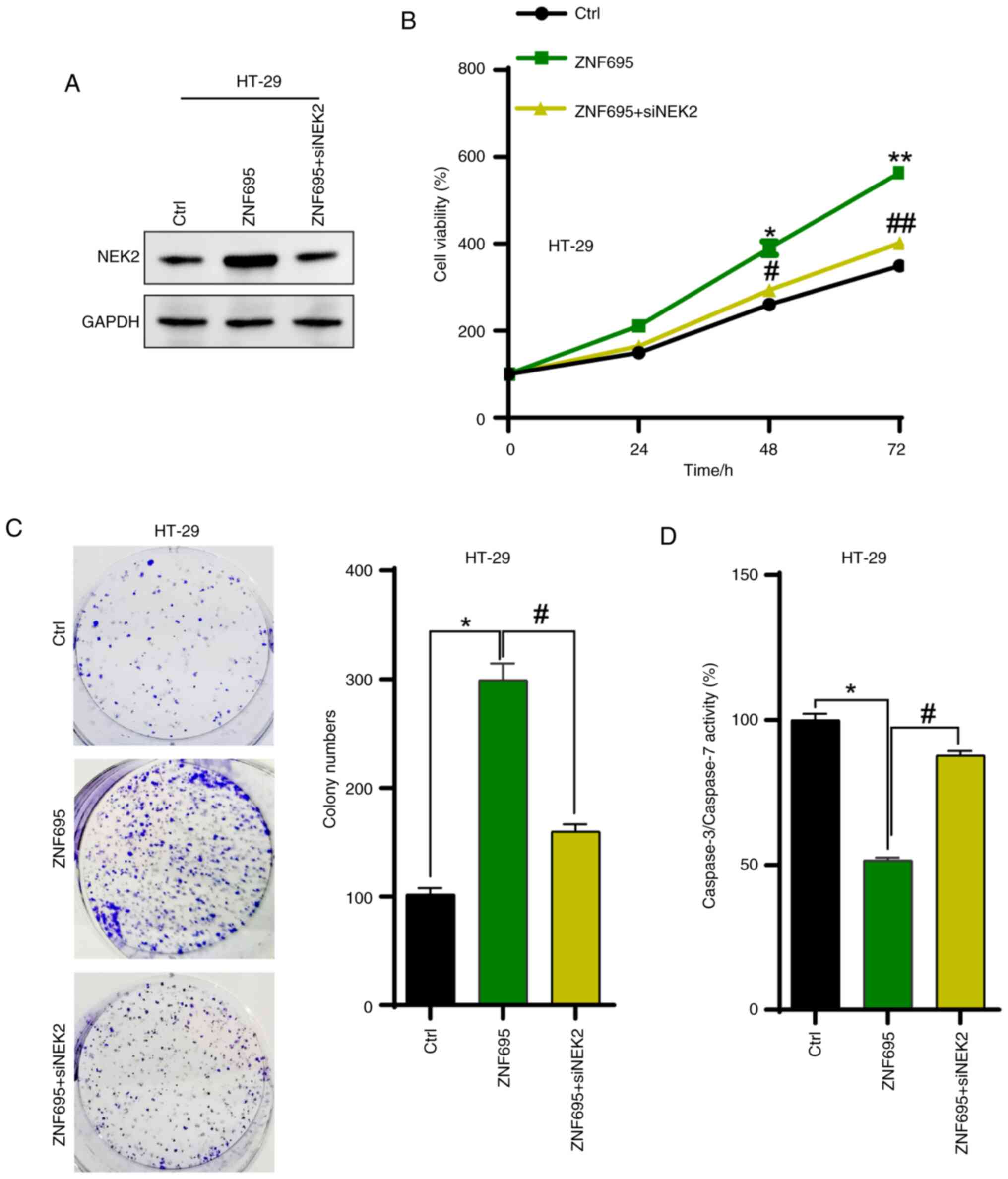
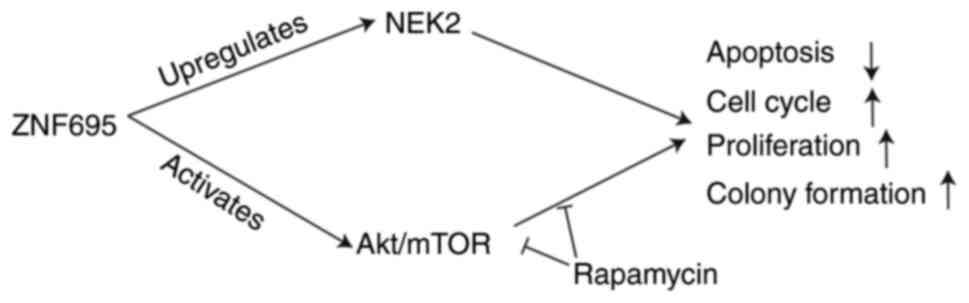
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S,
Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N and Chen W: Cancer statistics in China
and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin
Med J (Engl). 135:584–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li N, Lu B, Luo C, Cai J, Lu M, Zhang Y,
Chen H and Dai M: Incidence, mortality, survival, risk factor and
screening of colorectal cancer: A comparison among China, Europe,
and northern America. Cancer Lett. 522:255–268. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Housini M, Dariya B, Ahmed N, Stevens A,
Fiadjoe H, Nagaraju GP and Basha R: Colorectal cancer: Genetic
alterations, novel biomarkers, current therapeutic strategies and
clinical trials. Gene. 892:1478572024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shin AE, Giancotti FG and Rustgi AK:
Metastatic colorectal cancer: Mechanisms and emerging therapeutics.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 44:222–236. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shinji S, Yamada T, Matsuda A, Sonoda H,
Ohta R, Iwai T, Takeda K, Yonaga K, Masuda Y and Yoshida H: Recent
advances in the treatment of colorectal cancer: A review. J Nippon
Med Sch. 89:246–254. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abedizadeh R, Majidi F, Khorasani HR,
Abedi H and Sabour D: Colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review of
carcinogenesis, diagnosis, and novel strategies for classified
treatments. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 43:729–753. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ionescu VA, Gheorghe G, Bacalbasa N,
Chiotoroiu AL and Diaconu C: Colorectal cancer: From risk factors
to oncogenesis. Medicina (Kaunas). 59:16462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu H, Liu L, Li W, Zou D, Yu J, Wang L and
Wong CC: Transcription factors in colorectal cancer: Molecular
mechanism and therapeutic implications. Oncogene. 40:1555–1569.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jen J and Wang YC: Zinc finger proteins in
cancer progression. J Biomed Sci. 23:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cassandri M, Smirnov A, Novelli F, Pitolli
C, Agostini M, Malewicz M, Melino G and Raschellà G: Zinc-finger
proteins in health and disease. Cell Death Discov. 3:170712017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Krishna SS, Majumdar I and Grishin NV:
Structural classification of zinc fingers: Survey and summary.
Nucleic Acids Res. 31:532–550. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huntley S, Baggott DM, Hamilton AT,
Tran-Gyamfi M, Yang S, Kim J, Gordon L, Branscomb E and Stubbs L: A
comprehensive catalog of human KRAB-associated zinc finger genes:
Insights into the evolutionary history of a large family of
transcriptional repressors. Genome Res. 16:669–677. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ecco G, Imbeault M and Trono D: KRAB zinc
finger proteins. Development. 144:2719–2729. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao J, Wen D, Zhang S, Jiang H and Di X:
The role of zinc finger proteins in malignant tumors. FASEB J.
37:e231572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding X, Wan A, Qi X, Jiang K, Liu Z and
Chen B: ZNF695, A potential prognostic biomarker, correlates with
im mune infiltrates in cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endoce
rvical adenocarcinoma: Bioinformatic analysis and experimental
verification. Curr Gene Ther. 24:441–452. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li C, Kuang L, Zhu B, Chen J, Wang X and
Huang X: Identification of prognostic risk factors of acute
lymphoblastic leukemia based on mRNA expression profiling.
Neoplasma. 64:494–501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ke ZB, You Q, Chen JY, Sun JB, Xue YT,
Zhuang RB, Zheng QS, Chen YH, Wei Y, Sun XL, et al: A radiation
resistance related index for biochemical recurrence and tumor
immune environment in prostate cancer patients. Comput Biol Med.
146:1057112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia J, Zhao H, Edmondson JL, Koss B and
Zhan F: Role of NEK2 in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Trends
Mol Med. 31:79–93. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi BK, Dayaram T, Parikh N, Wilkins AD,
Nagarajan M, Novikov IB, Bachman BJ, Jung SY, Haas PJ, Labrie JL,
et al: Literature-based automated discovery of tumor suppressor p53
phosphorylation and inhibition by NEK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:10666–10671. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ersahin T, Tuncbag N and Cetin-Atalay R:
The PI3K/AKT/mTOR interactive pathway. Mol Biosyst. 11:1946–1954.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fleming-de-Moraes CD, Rocha MR, Tessmann
JW, de Araujo WM and Morgado-Diaz JA: Crosstalk between PI3K/Akt
and Wnt/β-catenin pathways promote colorectal cancer progression
regardless of mutational status. Cancer Biol Ther. 23:1–13. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu L, Wei J and Liu P: Attacking the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment
in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 85:69–94. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leiphrakpam PD and Are C: PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway as a target for colorectal cancer treatment. Int
J Mol Sci. 25:31782024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla
PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne
U, et al: UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis
platform. Neoplasia. 25:18–27. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Győrffy B: Integrated analysis of public
datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated
genes in solid tumors. Innovation (Camb). 5:1006252024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Wang Y, Hou S, Chi X, Ding D, Xue
M, Zhang M, Wang J, Shuai J, Sun H, et al: Overexpression of ZNF169
promotes the growth and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells
via the upregulation of ANKZF1. Oncol Rep. 51:822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tompkins WA, Watrach AM, Schmale JD,
Schultz RM and Harris JA: Cultural and antigenic properties of
newly established cell strains derived from adenocarcinomas of the
human colon and rectum. J Natl Cancer Inst. 52:1101–1110. 1974.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhattacharya A, Tóth K, Sen A, Seshadri M,
Cao S, Durrani FA, Faber E, Repasky EA and Rustum YM: Inhibition of
colon cancer growth by methylselenocysteine-induced angiogenic
chemomodulation is influenced by histologic characteristics of the
tumor. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 8:155–162. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang X, Zhang G, Tang T, Gao X and Liang
T: One shoot, three birds: Targeting NEK2 orchestrates
chemoradiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy in cancer
treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1877:1886962022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cui F, Chen Y, Wu X and Zhao W:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miR-486-5p inhibit
glycolysis and cell stemness in colorectal cancer by targeting
NEK2. BMC Cancer. 24:13562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ko MJ, Seo YR, Seo D, Park SY, Seo JH,
Jeon EH, Kim SW, Park KU, Koo DB, Kim S, et al: RPL17 promotes
colorectal cancer proliferation and stemness through ERK and
NEK2/β-catenin signaling pathways. J Cancer. 13:2570–2583. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stefani C, Miricescu D, Stanescu-Spinu II,
Nica RI, Greabu M, Totan AR and Jinga M: Growth factors,
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer
pathogenesis: Where are we now? Int J Mol Sci. 22:102602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ye Q, Liu J and Xie K: Zinc finger
proteins and regulation of the hallmarks of cancer. Histol
Histopathol. 34:1097–1109. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De la Rosa R, Villegas-Ruíz V,
Caballero-Palacios MC, Pérez-López EI, Murata C, Zapata-Tarres M,
Cárdenas-Cardos R, Paredes-Aguilera R, Rivera-Luna R and
Juárez-Méndez S: Expression of ZNF695 transcript variants in
childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes (Basel).
10:7162019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li R, Campos J and Iida J: A gene
regulatory program in human breast cancer. Genetics. 201:1341–1348.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roberts MS, Sahni JM, Schrock MS, Piemonte
KM, Weber-Bonk KL, Seachrist DD, Avril S, Anstine LJ, Singh S,
Sizemore ST, et al: LIN9 and NEK2 are core regulators of mitotic
fidelity that can be therapeutically targeted to overcome taxane
resistance. Cancer Res. 80:1693–1706. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Boulay G, Awad ME, Riggi N, Archer TC,
Iyer S, Boonseng WE, Rossetti NE, Naigles B, Rengarajan S, Volorio
A, et al: OTX2 activity at distal regulatory elements shapes the
chromatin landscape of group 3 medulloblastoma. Cancer Discov.
7:288–301. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng X, Guo J, An G, Wu Y, Liu Z, Meng B,
He N, Zhao X, Chen S, Zhu Y, et al: Genetic aberrations and
interaction of NEK2 and TP53 accelerate aggressiveness of multiple
myeloma. Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e21044912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Deng L, Sun J, Chen X, Liu L and Wu D:
Nek2 augments sorafenib resistance by regulating the ubiquitination
and localization of β-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 38:3162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nabilsi NH, Ryder DJ, Peraza-Penton AC,
Poudyal R, Loose DS and Kladde MP: Local depletion of DNA
methylation identifies a repressive p53 regulatory region in the
NEK2 promoter. J Biol Chem. 288:35940–35951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ji YY, Meng M and Miao Y: lncRNA SNHG1
Promotes progression of cervical cancer through miR-195/NEK2 axis.
Cancer Manag Res. 12:11423–11433. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xia B, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Wang Y, Zhao Y and
Wang J: Circular RNA circTNPO3 regulates paclitaxel resistance of
ovarian cancer cells by miR-1299/NEK2 signaling pathway. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 21:780–791. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fang Y and Zhang X: Targeting NEK2 as a
promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment. Cell Cycle.
15:895–907. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Naro C, Barbagallo F, Chieffi P, Bourgeois
CF, Paronetto MP and Sette C: The centrosomal kinase NEK2 is a
novel splicing factor kinase involved in cell survival. Nucleic
Acids Res. 42:3218–3227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhou W, Yang Y, Xia J, Wang H, Salama ME,
Xiong W, Xu H, Shetty S, Chen T, Zeng Z, et al: NEK2 induces drug
resistance mainly through activation of efflux drug pumps and is
associated with poor prognosis in myeloma and other cancers. Cancer
Cell. 23:48–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Neal CP, Fry AM, Moreman C, McGregor A,
Garcea G, Berry DP and Manson MM: Overexpression of the Nek2 kinase
in colorectal cancer correlates with beta-catenin relocalization
and shortened cancer-specific survival. J Surg Oncol. 110:828–838.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lim J, Hwang YS, Kim JT, Yoon HR, Park HM,
Han J, Kwon T, Lee KH, Cho HJ and Lee HG: NEK2 phosphorylates
RhoGDI1 to promote cell proliferation, migration and invasion
through the activation of RhoA and Rac1 in colon cancer cells.
Cells. 13:20722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Takahashi Y, Iwaya T, Sawada G, Kurashige
J, Matsumura T, Uchi R, Ueo H, Takano Y, Eguchi H, Sudo T, et al:
Up-regulation of NEK2 by microRNA-128 methylation is associated
with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
21:205–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yi YW, You KS, Park JS, Lee SG and Seong
YS: Ribosomal protein S6: A potential therapeutic target against
cancer? Int J Mol Sci. 23:482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Grasso S, Tristante E, Saceda M, Carbonell
P, Mayor-López L, Carballo-Santana M, Carrasco-García E,
Rocamora-Reverte L, García-Morales P, Carballo F, et al: Resistance
to Selumetinib (AZD6244) in colorectal cancer cell lines is
mediated by p70S6K and RPS6 activation. Neoplasia. 16:845–860.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wan H, Xu L, Zhang H, Wu F, Zeng W and Li
T: High expression of NEK2 promotes gastric cancer progression via
activating AKT signaling. J Physiol Biochem. 77:25–34. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chang YY, Yen CJ, Chan SH, Chou YW, Lee
YP, Bao CY, Huang CJ and Huang W: NEK2 promotes hepatoma metastasis
and serves as biomarker for high recurrence risk after hepatic
resection. Ann Hepatol. 17:843–856. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|