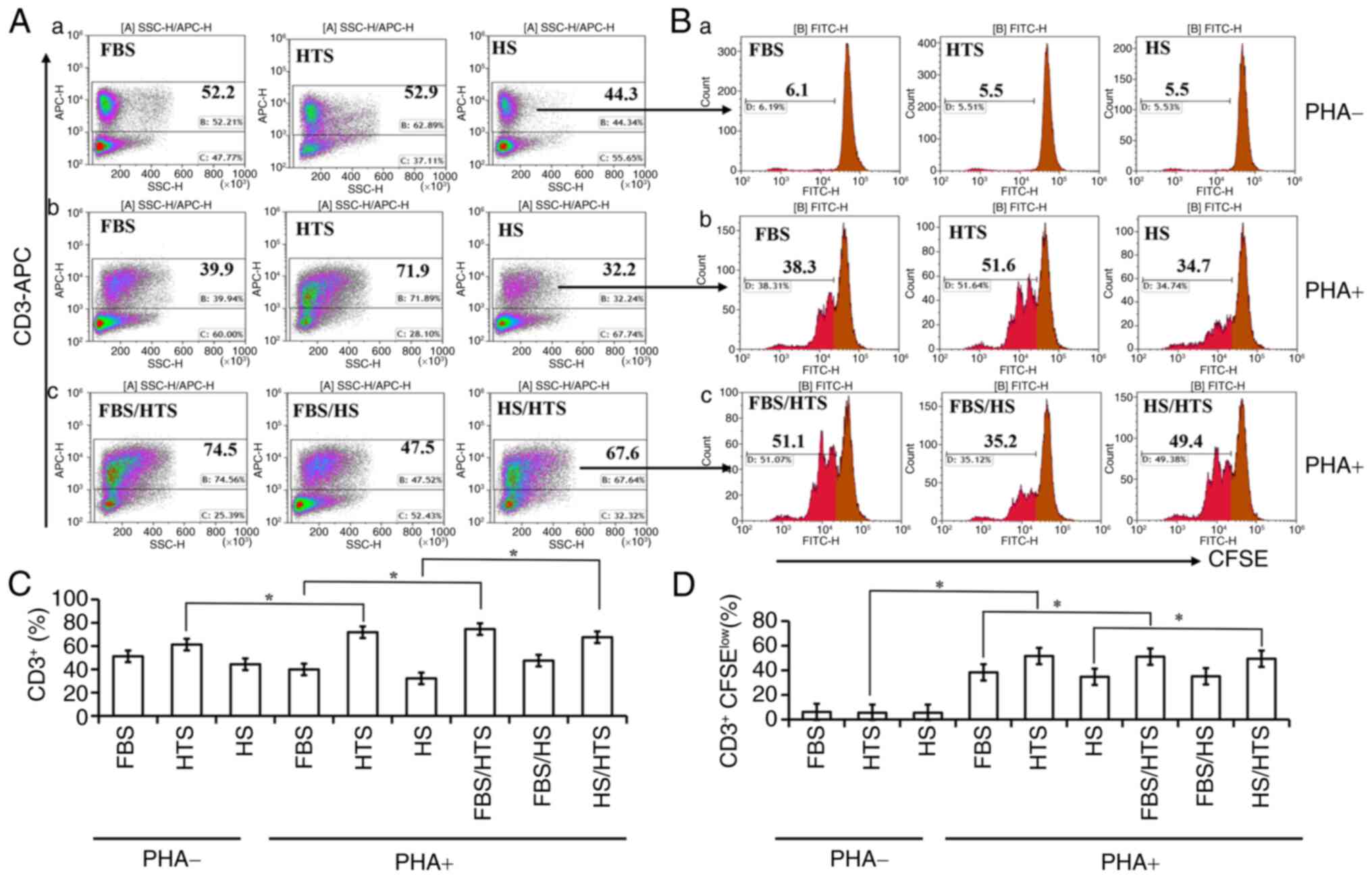
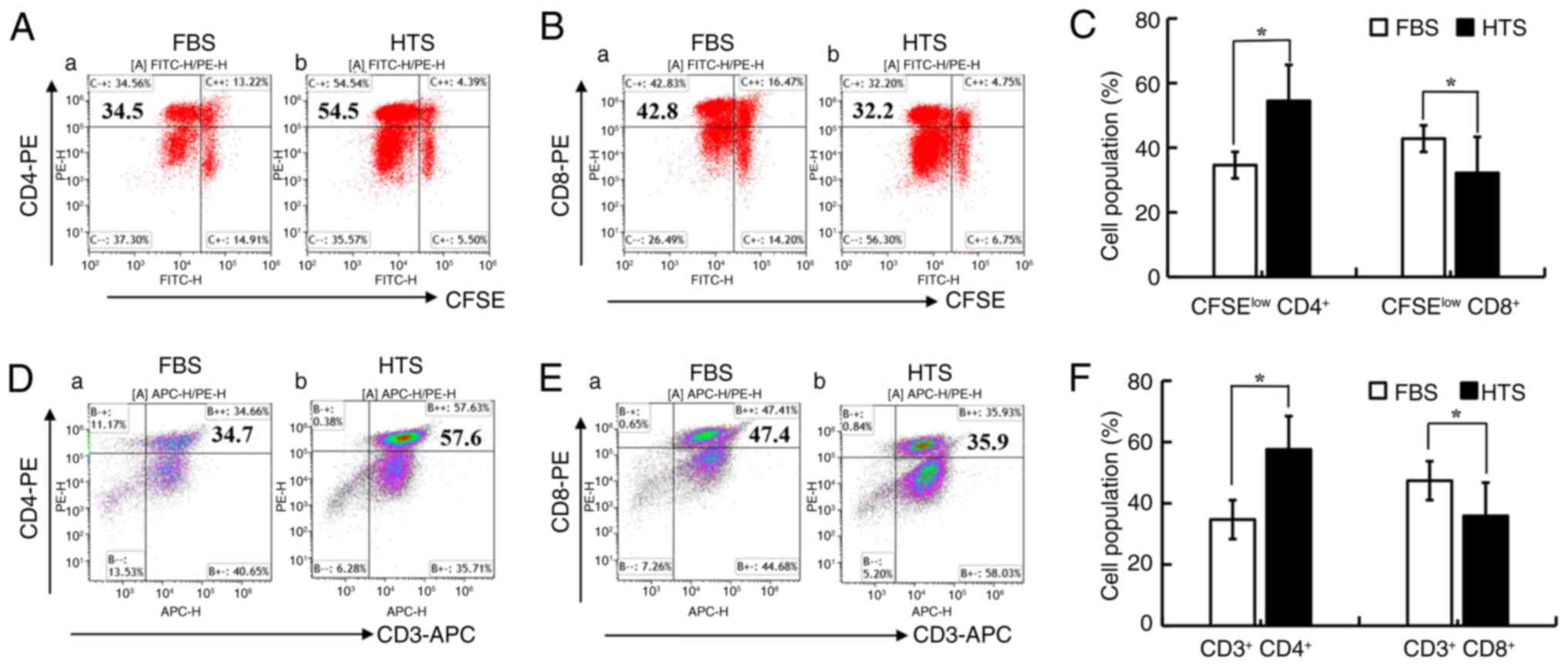
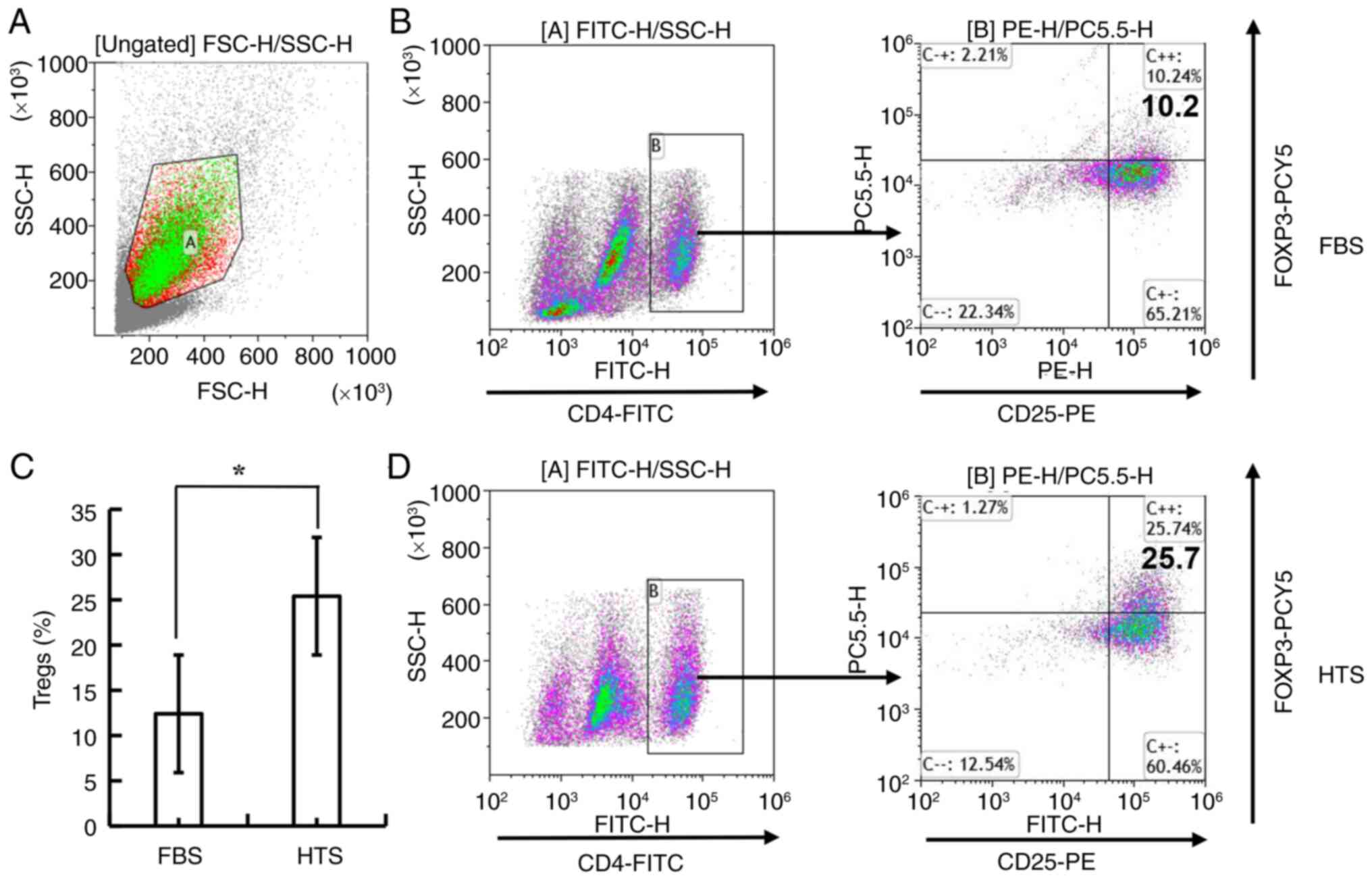
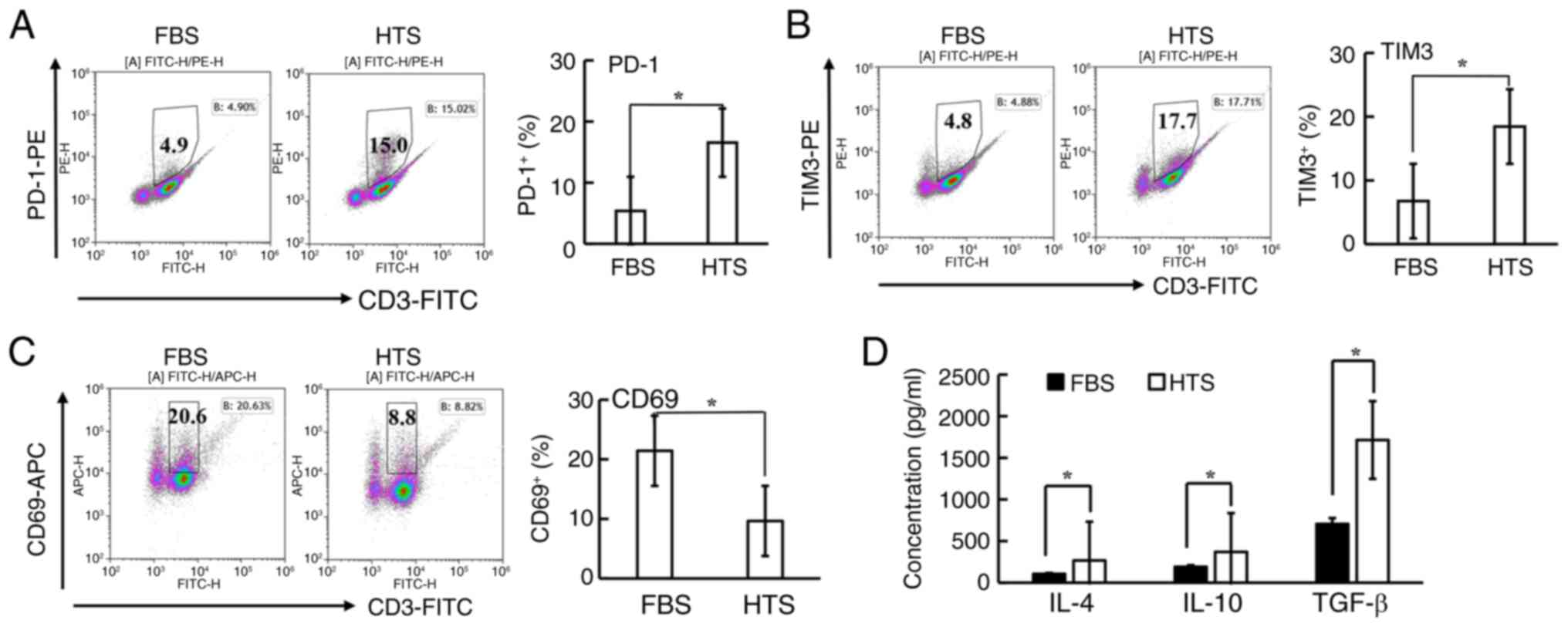
|
1
|
Satgunaseelan L, Allanson BM, Asher R,
Reddy R, Low HTH, Veness M, Gopal Iyer N, Smee RI, Palme CE, Gupta
R and Clark JR: The incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the
oral tongue is rising in young non-smoking women: An international
multi-institutional analysis. Oral Oncol. 110:1048752020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Satgunaseelan L, Strbenac D, Willet C,
Chew T, Sadsad R, Wykes J, Low TH, Cooper WA, Lee CS, Palme CE, et
al: Whole genome duplication in oral squamous cell carcinoma in
patients younger than 50 years: Implications for prognosis and
adverse clinicopathological factors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
61:561–571. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang Z, Liang X, Fu Y, Liu Y, Zheng L, Liu
F, Li T, Yin X, Qiao X and Xu X: Identification of AUNIP as a
candidate diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for oral squamous
cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 47:44–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manzano-Moreno FJ, Costela-Ruiz VJ,
Garcia-Recio E, Olmedo-Gaya MV, Ruiz C and Reyes-Botella C: Role of
salivary MicroRNA and cytokines in the diagnosis and prognosis of
oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 22:122152021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bai G, Wei N, Li F, Zhao P, Meng Z, Zou B,
Liu Y, Xu K, Li K, Yao C and Yang P: Function and transcriptional
regulation of TCTN1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
47:262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gu W, Kim M, Wang L, Yang Z, Nakajima T
and Tsushima Y: Multi-omics analysis of ferroptosis regulation
patterns and characterization of tumor microenvironment in patients
with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 17:3476–3492.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vitório JG, Duarte-Andrade FF, Dos Santos
Fontes Pereira T, Fonseca FP, Amorim LSD, Martins-Chaves RR, Gomes
CC, Canuto GAB and Gomez RS: Metabolic landscape of oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Metabolomics. 16:1052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang M and Li B: STAT3 and its targeting
inhibitors in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cells. 11:31312022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chai AWY, Lim KP and Cheong SC:
Translational genomics and recent advances in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 61:71–83. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kavarthapu A and Gurumoorthy K: Linking
chronic periodontitis and oral cancer: A review. Oral Oncology.
121:1053752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reynolds BA, Oli MW and Oli MK:
Eco-oncology: Applying ecological principles to understand and
manage cancer. Ecol Evol. 10:8538–8553. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anderson ARA and Maini PK: Mathematical
oncology. Bull Math Biol. 80:945–953. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adler FR and Gordon DM: Cancer ecology and
evolution: Positive interactions and system vulnerability. Curr
Opin Syst Biol. 17:1–7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seliger B, Massa C, Yang B, Bethmann D,
Kappler M, Eckert AW and Wickenhauser C: Immune escape mechanisms
and their clinical relevance in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:70322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pansy K, Uhl B, Krstic J, Szmyra M,
Fechter K, Santiso A, Thuminger L, Greinix H, Kargl J, Prochazka K,
et al: Immune regulatory processes of the tumor microenvironment
under malignant conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 22:133112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Donnell JS, Teng MWL and Smyth MJ:
Cancer immunoediting and resistance to T cell-based immunotherapy.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:151–167. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Iorgulescu JB, Braun D, Oliveira G, Keskin
DB and Wu CJ: Acquired mechanisms of immune escape in cancer
following immunotherapy. Genome Med. 10:872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eichmuller SB, Osen W, Mandelboim O and
Seliger B: Immune modulatory microRNAs involved in tumor attack and
tumor immune escape. J Natl Cancer Inst. 109:1092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee J, Han Y, Wang W, Jo H, Kim H, Kim S,
Yang KM, Kim SJ, Dhanasekaran DN and Song YS: Phytochemicals in
cancer immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Biomolecules.
11:11072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amaya-Uribe L, Rojas M, Azizi G, Anaya JM
and Gershwin ME: Primary immunodeficiency and autoimmunity: A
comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 99:52–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chi H, Zhao S, Yang J, Gao X, Peng G,
Zhang J, Xie X, Song G, Xu K, Xia Z, et al: T-cell exhaustion
signatures characterize the immune landscape and predict HCC
prognosis via integrating single-cell RNA-seq and bulk
RNA-sequencing. Front Immunol. 14:11370252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mao J, Li J, Chen J, Wen Q, Cao M, Zhang
F, Li B, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Zhang J and Shen J: CXCL10 and
Nrf2-upregulated mesenchymal stem cells reinvigorate T lymphocytes
for combating glioblastoma. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0074812023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu YH, Lin PY, Yang JH, Kuo YS and Wu YC:
Serum levels and positive rates of tumor biomarkers in oral
precancer patients. J Formos Med Assoc. 120:1324–1331. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abramson VG and Mayer IA: Clinical utility
of serum tumor markers and circulating tumor cell assays in the
treatment of breast cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 12:403–411.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Almangush A, Heikkinen I, Mäkitie AA,
Coletta RD, Läärä E, Leivo I and Salo T: Prognostic biomarkers for
oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 117:856–866. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Graham R, Gazinska P, Zhang B, Khiabany A,
Sinha S, Alaguthurai T, Flores-Borja F, Vicencio J, Beuron F,
Roxanis I, et al: Serum-derived extracellular vesicles from breast
cancer patients contribute to differential regulation of
T-cell-mediated immune-escape mechanisms in breast cancer subtypes.
Front Immunol. 14:12042242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oyeyemi BF, Kaur US, Paramraj A,
Chintamani, Tandon R, Kumar A and Bhavesh NS: Microbiome analysis
of saliva from oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patients and
tobacco abusers with potential biomarkers for oral cancer
screening. Heliyon. 9:e217732023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lauwerends LJ, Zweedijk BE, Galema HA,
Neijenhuis LKA, Dekker-Ensink NG, Baatenburg de Jong RJ, Verhoef C,
Bhairosingh SS, Kuppen PJK, Vahrmeijer AL, et al: Tumour marker
expression in head and neck malignancies to identify potential
targets for intraoperative molecular Near-infrared imaging. Mol
Diagn Ther. 28:811–820. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK and Gershenwald JE: AJCC Cancer Staging
Manual. (8th edition). Springer; Heidelberg: 2017
|
|
31
|
Fyhrquist N, Ruokolainen L, Suomalainen A,
Lehtimäki S, Veckman V, Vendelin J, Karisola P, Lehto M, Savinko T,
Jarva H, et al: Acinetobacter species in the skin microbiota
protect against allergic sensitization and inflammation. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 134:1301–1309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tebbi CK, Badiga A, Sahakian E, Powers JJ,
Achille AN, Patel S and Migone F: Exposure to a mycovirus
containing Aspergillus Flavus reproduces acute lymphoblastic
leukemia cell surface and genetic markers in cells from patients in
remission and not controls. Cancer Treat Res Commun.
26:1002792021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang P, Su DM, Liang M and Fu J:
Chemopreventive agents induce programmed death-1-ligand 1 (PD-L1)
surface expression in breast cancer cells and promote
PD-L1-mediated T cell apoptosis. Mol Immunol. 45:1470–1476. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moreno Ayala MA, Campbell TF, Zhang C,
Dahan N, Bockman A, Prakash V, Feng L, Sher T and DuPage M: CXCR3
expression in regulatory T cells drives interactions with type I
dendritic cells in tumors to restrict CD8+ T cell
antitumor immunity. Immunity. 56:1613–1630. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Obradovic A, Ager C, Turunen M, Nirschl T,
Khosravi-Maharlooei M, Iuga A, Jackson CM, Yegnasubramanian S,
Tomassoni L, Fernandez EC, et al: Systematic elucidation and
pharmacological targeting of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cell
master regulators. Cancer Cell. 41:933–949. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang P, Zhou X, Zheng M, Yu Y, Jin G and
Zhang S: Regulatory T cells are associated with the tumor immune
microenvironment and immunotherapy response in triple-negative
breast cancer. Front Immunol. 14:12635372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sasahira T and Kirita T: Hallmarks of
Cancer-related newly prognostic factors of oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 19:24132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao XT, Zhu Y, Zhou JF, Gao YJ and Liu
FZ: Development of a novel 7 immune-related genes prognostic model
for oral cancer: A study based on TCGA database. Oral Oncol.
112:1050882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim JW, Park Y, Roh JL, Cho KJ, Choi SH,
Nam SY and Kim SY: Prognostic value of glucosylceramide synthase
and P-glycoprotein expression in oral cavity cancer. Int J Clin
Oncol. 21:883–889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ni YH, Ding L, Hu QG and Hua ZC: Potential
biomarkers for oral squamous cell carcinoma: proteomics discovery
and clinical validation. Proteomics Clin Appl. 9:86–97. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pio R, Ajona D, Ortiz-Espinosa S,
Mantovani A and Lambris JD: Complementing the Cancer-immunity
cycle. Front Immunol. 10:7742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, van der
Bruggen P and Boon T: Tumour antigens recognized by T lymphocytes:
At the core of cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:135–146.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Somarribas Patterson LF and Vardhana SA:
Metabolic regulation of the cancer-immunity cycle. Trends Immunol.
42:975–993. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Elements of cancer
immunity and the Cancer-immune set point. Nature. 541:321–330.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen DS and Mellman I: Oncology meets
immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. 39:1–10. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Casey M and Nakamura K: The
Cancer-immunity cycle in multiple myeloma. Immunotargets Ther.
10:247–260. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Boyle ST, Johan MZ and Samuel MS:
Tumour-directed microenvironment remodelling at a glance. J Cell
Sci. 133:jcs2477832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Ge J,
Xiang B, Wu X, Ma J, Zhou M, Li X, et al: Role of the tumor
microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Molr
Cancer. 18:102019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Paiva JA and Pereira JM: Biomarkers of
fungal lung infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 32:136–142. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yao Y, Wang X, Guan J, Xie C, Zhang H,
Yang J, Luo Y, Chen L, Zhao M, Huo B, et al: Metabolomic
differentiation of benign vs malignant pulmonary nodules with high
specificity via high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis of
patient sera. Nat Commun. 14:23392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Groom JR: Regulators of T-cell fate:
Integration of cell migration, differentiation and function.
Immunol Rev. 289:101–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shi Y, Ren X, Cao S, Chen X, Yuan B,
Brasil da Costa FH, Rodriguez Rosario AE, Corona A, Michikawa C,
Veeramachaneni R, et al: TP53 gain-of-function mutation modulates
the immunosuppressive microenvironment in non-HPV-associated oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 11:e0066662023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li H, Liu Y, Zhou S, Zhou Q and Yang X:
Systematic evaluation of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism associated with
onset and progression of oral potentially malignant disorders. BMC
Oral Health. 23:6592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lewis DA and Ly T: Cell cycle entry
control in naïve and memory CD8+ T cells. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7274412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Damo M and Joshi NS: Treg cell IL-10 and
IL-35 exhaust CD8+ T cells in tumors. Nat Immunol. 20:674–675.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kamimaki C, Kobayashi N, Hirata M,
Somekawa K, Fukuda N, Kubo S, Katakura S, Teranishi S, Watanabe K,
Horita N, et al: T-cell response to phytohemagglutinin in the
interferon-γ release assay as a potential biomarker for the
response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small
cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 12:1726–1734. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Vivekanandan MM, Adankwah E, Aniagyei W,
Acheampong I, Minadzi D, Yeboah A, Arthur JF, Lamptey M, Abass MK,
Kumbel F, et al: Impaired T-cell response to phytohemagglutinin
(PHA) in tuberculosis patients is associated with high IL-6 plasma
levels and normalizes early during anti-mycobacterial treatment.
Infection. 51:1013–1023. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Trickett A and Kwan YL: T cell stimulation
and expansion using anti-CD3/CD28 beads. J Immunol Methods.
275:251–255. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kay JE: Mechanisms of T lymphocyte
activation. Immunol Lett. 29:51–54. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Brummelman J, Pilipow K and Lugli E: The
single-cell phenotypic identity of human CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. Int
Rev Cell Mol Biol. 341:63–124. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Farhood B, Najafi M and Mortezaee K: CD8+
cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: A review. J Cell
Physiol. 234:8509–8521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kogo H, Shimizu M, Negishi Y, Uchida E and
Takahashi H: Suppression of murine tumour growth through CD8+
cytotoxic T lymphocytes via activated DEC-205+ dendritic cells by
sequential administration of α-galactosylceramide in vivo.
Immunology. 151:324–339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mittrucker HW, Visekruna A and Huber M:
Heterogeneity in the differentiation and function of CD8+ T cells.
Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 62:449–458. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Raeber ME, Zurbuchen Y, Impellizzieri D
and Boyman O: The role of cytokines in T-cell memory in health and
disease. Immunol Rev. 283:176–193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hermans D, Gautam S, Garcia-Canaveras JC,
Gromer D, Mitra S, Spolski R, Li P, Christensen S, Nguyen R, Lin
JX, et al: Lactate dehydrogenase inhibition synergizes with IL-21
to promote CD8+ T cell stemness and antitumor immunity. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 117:6047–6055. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yu N and Li X, Song W, Li D, Yu D, Zeng X,
Li M, Leng X and Li X: CD4(+)CD25 (+)CD127 (low/-) T cells: A more
specific Treg population in human peripheral blood. Inflammation.
35:1773–1780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li C, Jiang P, Wei S, Xu X and Wang J:
Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: New mechanisms,
potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer.
19:1162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shen LS, Wang J, Shen DF, Yuan XL, Dong P,
Li MX, Xue J, Zhang FM, Ge HL and Xu D: CD4(+)CD25(+)CD127(low/-)
regulatory T cells express Foxp3 and suppress effector T cell
proliferation and contribute to gastric cancers progression.
Clinical Immunology. 131:109–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu C, Chikina M, Deshpande R, Menk AV,
Wang T, Tabib T, Brunazzi EA, Vignali KM, Sun M, Stolz DB, et al:
Treg Cells promote the SREBP1-dependent metabolic fitness of
Tumor-promoting macrophages via repression of CD8+ T Cell-derived
Interferon-γ. Immunity. 51:381–397.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Churov AV, Mamashov KY and Novitskaia AV:
Homeostasis and the functional roles of CD4+ Treg cells in aging.
Immunol Lett. 226:83–89. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 133:775–787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lu J, Li P, Du X, Liu Y, Zhang B and Qi F:
Regulatory T cells induce transplant immune tolerance. Transpl
Immunol. 67:1014112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Liu C, Workman CJ and Vignali DA:
Targeting regulatory T cells in tumors. FEBS J. 283:2731–2748.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sakaguchi S, Mikami N, Wing JB, Tanaka A,
Ichiyama K and Ohkura N: Regulatory T cells and human disease. Annu
Rev Immunol. 38:541–566. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tanaka A and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 27:109–118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Xie W, Medeiros LJ, Li S, Yin CC, Khoury
JD and Xu J: PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway and its blockade in patients with
classic hodgkin lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Large-cell lymphomas. Curr
Hematol Malig Rep. 15:372–381. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
McLane LM, Abdel-Hakeem MS and Wherry EJ:
CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer.
Annu Rev Immunol. 37:457–495. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chow A, Perica K, Klebanoff CA and Wolchok
JD: Clinical implications of T cell exhaustion for cancer
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:775–790. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zarour HM: Reversing T-cell dysfunction
and exhaustion in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:1856–1864. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wherry EJ and Kurachi M: Molecular and
cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol.
15:486–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Pauken KE and Wherry EJ: Overcoming T cell
exhaustion in infection and cancer. Trends Immunol. 36:265–276.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Busso-Lopes AF, Neves LX, Câmara GA,
Granato DC, Pretti MAM, Heberle H, Patroni FMS, Sá J, Yokoo S,
Rivera C, et al: Connecting multiple microenvironment proteomes
uncovers the biology in head and neck cancer. Nat Commun.
13:67252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lisa Cheng YS, Jordan L, Gorugantula LM,
Schneiderman E, Chen HS and Rees T: Salivary interleukin-6 and −8
in patients with oral cancer and patients with chronic oral
inflammatory diseases. J Periodontol. 85:956–965. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
AlAli AM, Walsh T and Maranzano M: CYFRA
21-1 and MMP-9 as salivary biomarkers for the detection of oral
squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review of diagnostic test
accuracy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 49:973–983. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Vollrath JT, Schindler CR, Herrmann E,
Verboket RD, Henrich D, Marzi I and Störmann P: Evaluation of Cyfra
21-1, Angiopoetin-2, Pentraxin-3, srage, IL-6, and IL-10 in
polytraumatized patients with concomitant thoracic trauma-helpful
markers to predict pneumonia? Shock. 60:392–399. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|