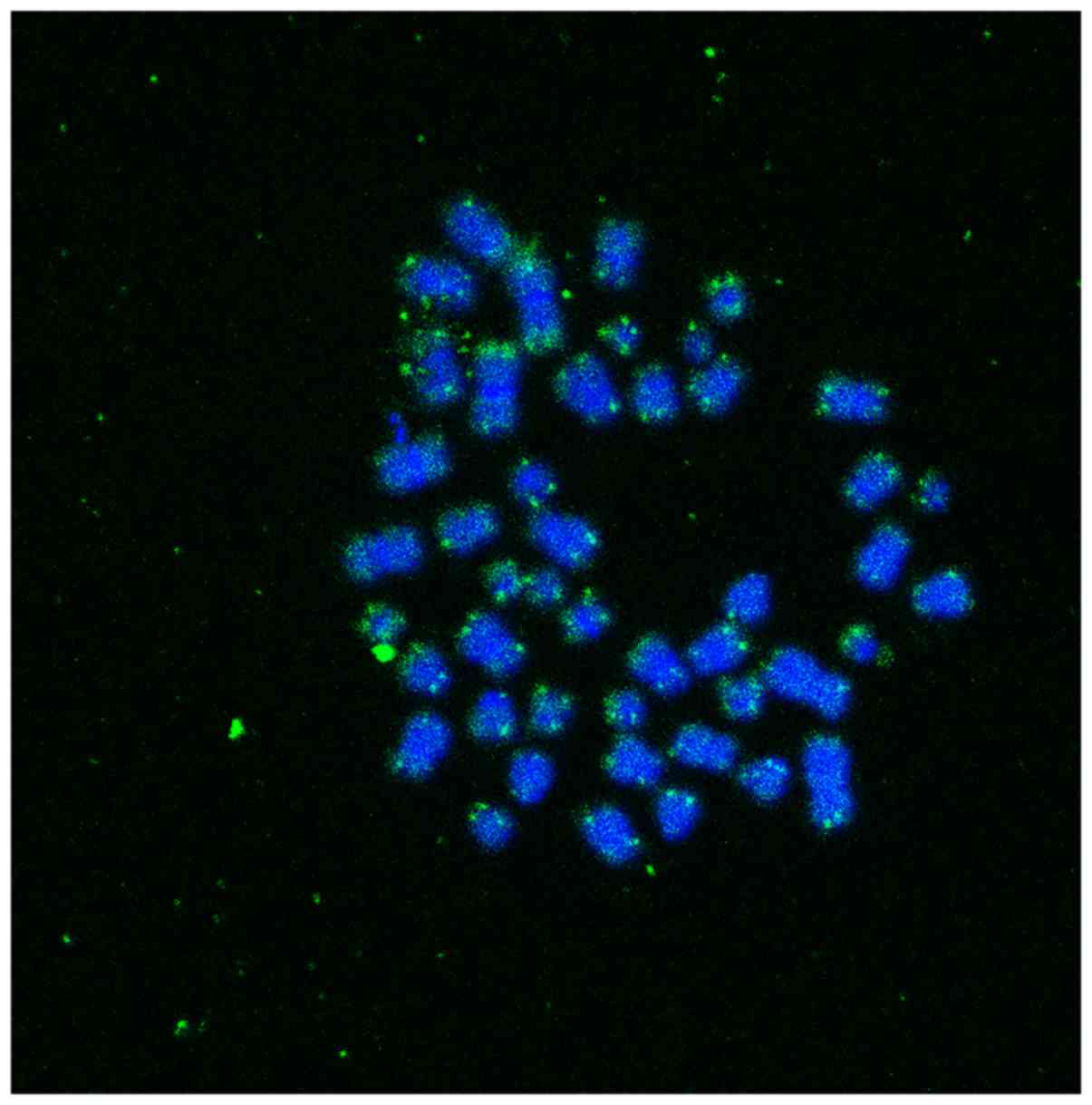
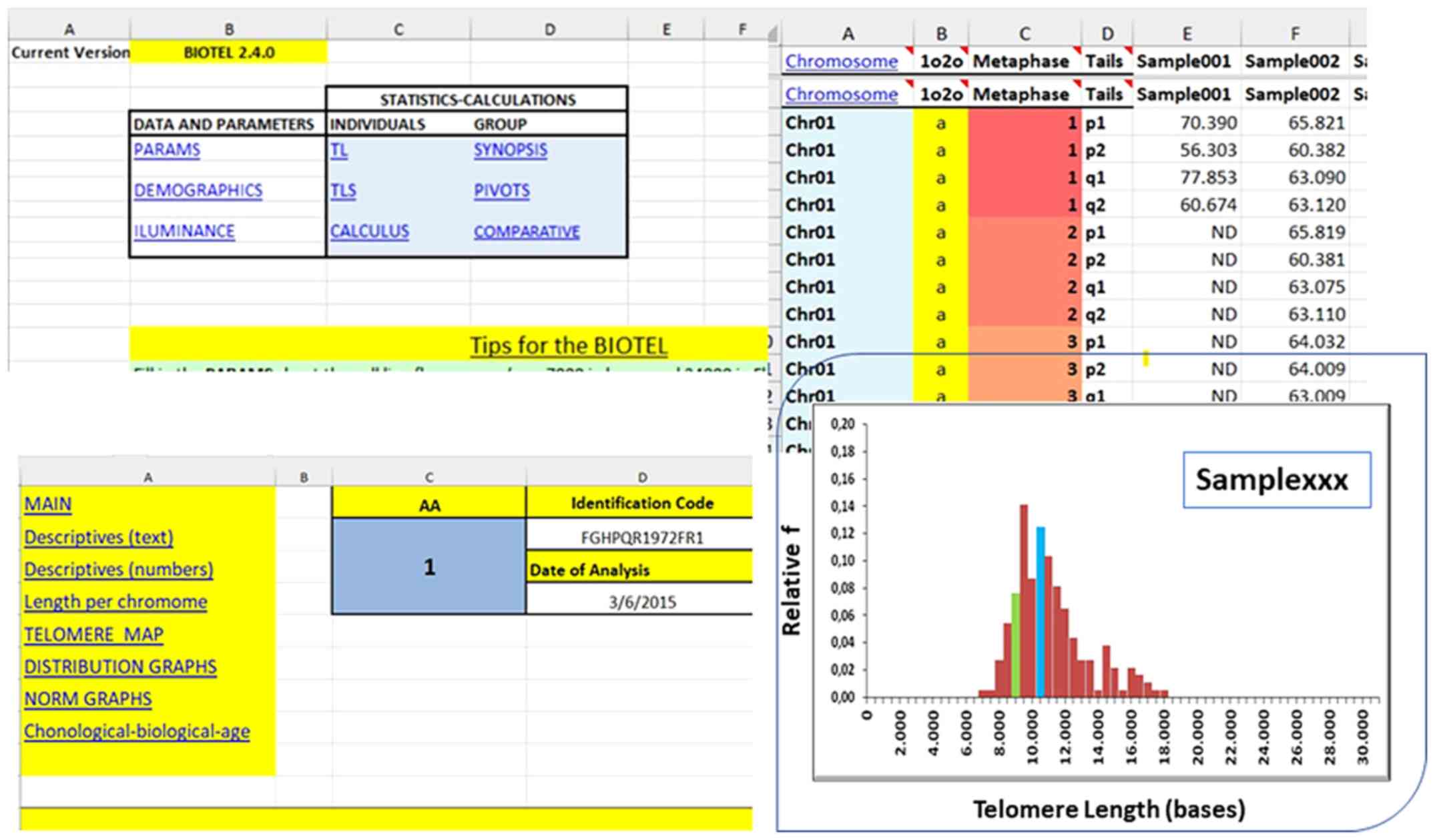
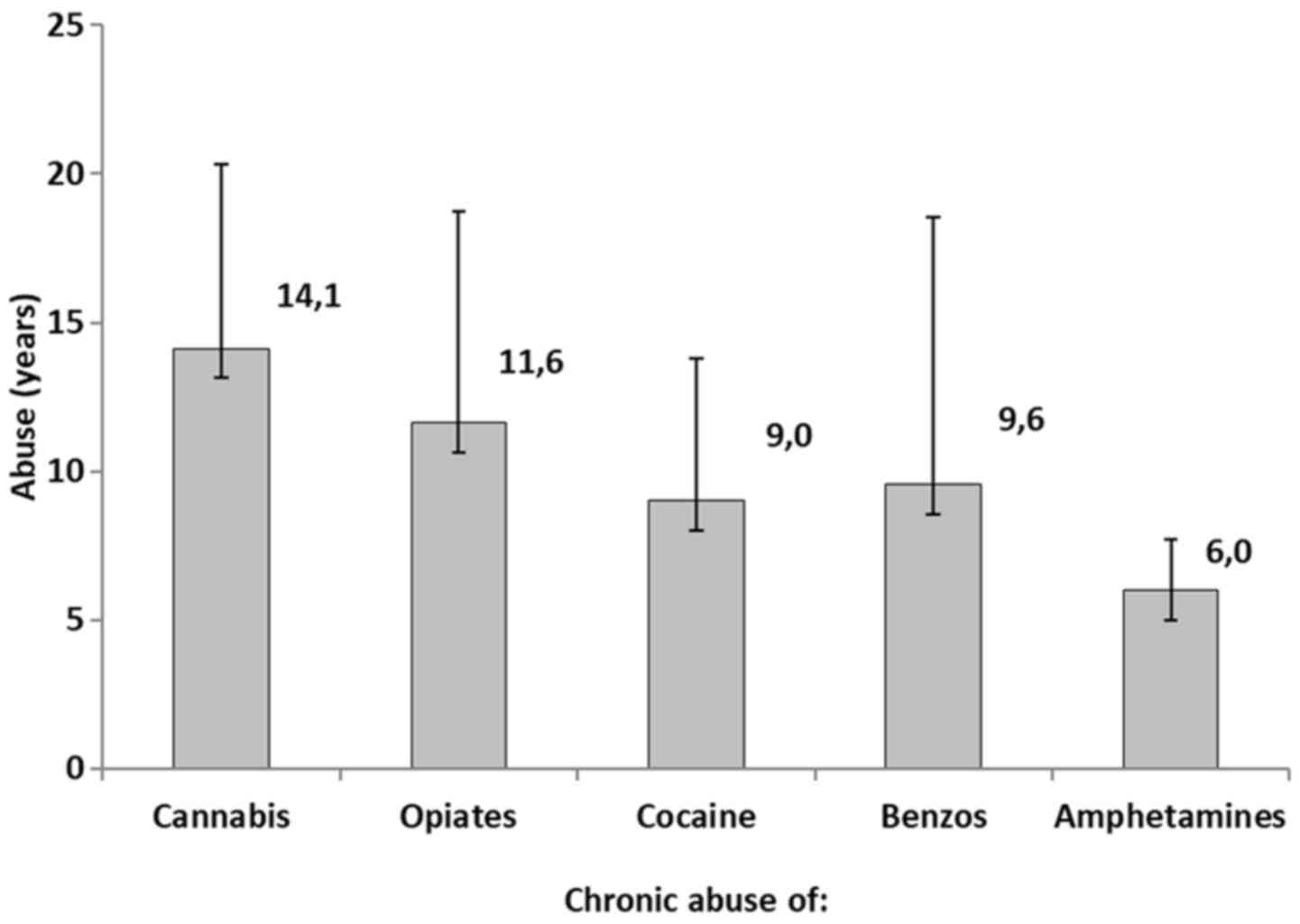
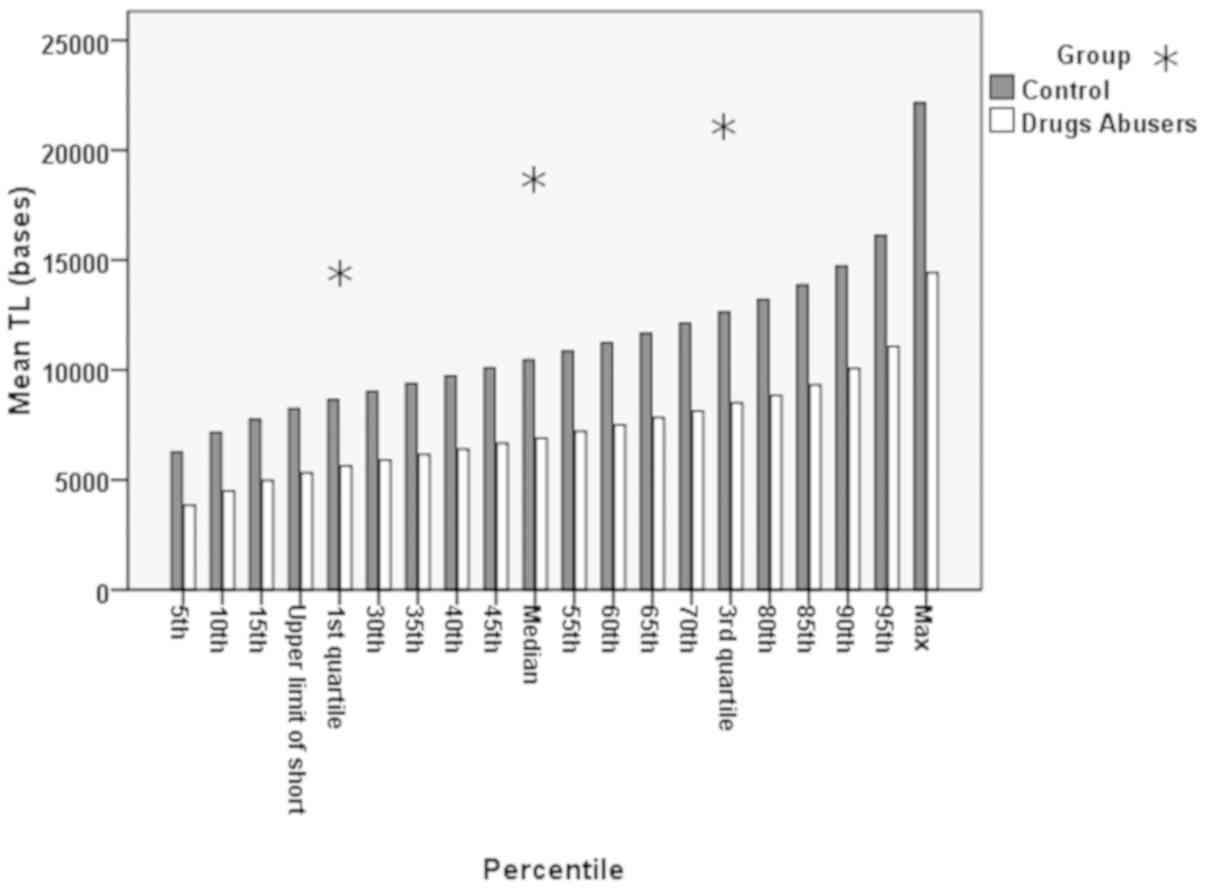
|
1
|
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and
Drug Addiction (EMCDDA): http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/data/stats2017_en.
Accessed January 23,2019.
|
|
2
|
Tzatzarakis MN, Vakonaki E, Kovatsi L,
Belivanis S, Mantsi M, Alegakis A, Liesivuori J and Tsatsakis AM:
Determination of buprenorphine, norbuprenorphine and naloxone in
fingernail clippings and urine of patients under opioid
substitution therapy. J Anal Toxicol. 39:313–320. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Diaper AM, Law FD and Melichar JK:
Pharmacological strategies for detoxification. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
77:302–314. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence:
Thirty-eighth report. In: WHO Technical Report Series. WHO,
Switzerland. 2017.
|
|
5
|
Nestoros JN, Vakonaki E, Tzatzarakis MN,
Alegakis A, Skondras MD and Tsatsakis AM: Long lasting effects of
chronic heavy cannabis abuse. Am J Addict. 26:335–342.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cheng GL, Zeng H, Leung MK, Zhang HJ, Lau
BW, Liu YP, Liu GX, Sham PC, Chan CC, So KF, et al: Heroin abuse
accelerates biological aging: A novel insight from telomerase and
brain imaging interaction. Transl Psychiatry.
3(e260)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ersche KD, Jones PS, Williams GB, Robbins
TW and Bullmore ET: Cocaine dependence: A fast-track for brain
ageing? Mol Psychiatry. 18:134–135. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bachi K, Sierra S, Volkow ND, Goldstein RZ
and Alia-Klein N: Is biological aging accelerated in drug
addiction? Curr Opin Behav Sci. 13:34–39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Vakonaki E, Tsiminikaki K, Plaitis S,
Fragkiadaki P, Tsoukalas D, Katsikantami I, Vaki G, Tzatzarakis MN,
Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM: Common mental disorders and
association with telomere length. Biomed Rep. 8:111–116.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Blackburn EH: Switching and signaling at
the telomere. Cell. 106:661–673. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
de Lange T: Shelterin: The protein complex
that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev.
19:2100–2110. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chan SW and Blackburn EH: New ways not to
make ends meet: Telomerase, DNA damage proteins and
heterochromatin. Oncogene. 21:553–563. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Harley CB, Futcher AB and Greider CW:
Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature.
345:458–460. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Calado RT and Young NS: Telomere diseases.
N Engl J Med. 361:2353–2365. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Starkweather AR, Alhaeeri AA, Montpetit A,
Brumelle J, Filler K, Montpetit M, Mohanraj L, Lyon DE and
Jackson-Cook CK: An integrative review of factors associated with
telomere length and implications for biobehavioral research. Nurs
Res. 63:36–50. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
McIlrath J, Bouffler SD, Samper E,
Cuthbert A, Wojcik A, Szumiel I, Bryant PE, Riches AC, Thompson A,
Blasco MA, et al: Telomere length abnormalities in mammalian
radiosensitive cells. Cancer Res. 61:912–915. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Armanios M, Alder JK, Parry EM, Karim B,
Strong MA and Greider CW: Short telomeres are sufficient to cause
the degenerative defects associated with aging. Am J Hum Genet.
85:823–832. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Blasco MA: Telomere length, stem cells and
aging. Nat Chem Biol. 3:640–649. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hao LY, Armanios M, Strong MA, Karim B,
Feldser DM, Huso D and Greider CW: Short telomeres, even in the
presence of telomerase, limit tissue renewal capacity. Cell.
123:1121–1131. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hemann MT, Strong MA, Hao LY and Greider
CW: The shortest telomere, not average telomere length, is critical
for cell viability and chromosome stability. Cell. 107:67–77.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rajaraman S, Choi J, Cheung P, Beaudry V,
Moore H and Artandi SE: Telomere uncapping in progenitor cells with
critical telomere shortening is coupled to S-phase progression in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:17747–17752. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Samper E, Flores JM and Blasco MA:
Restoration of telomerase activity rescues chromosomal instability
and premature aging in Terc-/- mice with short telomeres. EMBO Rep.
2:800–807. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang Z, Ye J, Li C, Zhou D, Shen Q, Wu J,
Cao L, Wang T, Cui D, He S, et al: Drug addiction is associated
with leukocyte telomere length. Sci Rep. 3(1542)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Willeit P, Willeit J, Brandstätter A,
Ehrlenbach S, Mayr A, Gasperi A, Weger S, Oberhollenzer F, Reindl
M, Kronenberg F, et al: Cellular aging reflected by leukocyte
telomere length predicts advanced atherosclerosis and
cardiovascular disease risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:1649–1656. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Demissie S, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Cupples
LA, Gardner JP, Herbert A, Kimura M, Larson MG, Meigs JB, Keaney
JF, et al: Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, hypertension, and
leukocyte telomere length in men from the Framingham Heart Study.
Aging Cell. 5:325–330. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fitzpatrick AL, Kronmal RA, Gardner JP,
Psaty BM, Jenny NS, Tracy RP, Walston J, Kimura M and Aviv A:
Leukocyte telomere length and cardiovascular disease in the
cardiovascular health study. Am J Epidemiol. 165:14–21.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Jorsal A, Lajer M,
Nzietchueng R, Benetos A, Rossing P and Parving HH: Telomere length
predicts all-cause mortality in patients with type 1 diabetes.
Diabetologia. 53:45–48. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Olivieri F, Lorenzi M, Antonicelli R,
Testa R, Sirolla C, Cardelli M, Mariotti S, Marchegiani F, Marra M,
Spazzafumo L, et al: Leukocyte telomere shortening in elderly
Type2DM patients with previous myocardial infarction.
Atherosclerosis. 206:588–593. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lin TT, Norris K, Heppel NH, Pratt G,
Allan JM, Allsup DJ, Bailey J, Cawkwell L, Hills R, Grimstead JW,
et al: Telomere dysfunction accurately predicts clinical outcome in
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, even in patients with early stage
disease. Br J Haematol. 167:214–223. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gancarcíková M, Zemanová Z, Brezinová J,
Berková A, Vcelíková S, Smigová J and Michalová K: The role of
telomeres and telomerase complex in haematological neoplasia: The
length of telomeres as a marker of carcinogenesis and prognosis of
disease. Prague Med Rep. 111:91–105. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nzietchueng R, Elfarra M, Nloga J, Labat
C, Carteaux JP, Maureira P, Lacolley P, Villemot JP and Benetos A:
Telomere length in vascular tissues from patients with
atherosclerotic disease. J Nutr Health Aging. 15:153–156.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saliques S, Zeller M, Lorin J, Lorgis L,
Teyssier JR, Cottin Y, Rochette L and Vergely C: Telomere length
and cardiovascular disease. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 103:454–459.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ma D, Zhu W, Hu S, Yu X and Yang Y:
Association between oxidative stress and telomere length in type 1
and type 2 diabetic patients. J Endocrinol Invest. 36:1032–1037.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Testa R, Olivieri F, Sirolla C, Spazzafumo
L, Rippo MR, Marra M, Bonfigli AR, Ceriello A, Antonicelli R,
Franceschi C, et al: Leukocyte telomere length is associated with
complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med.
28:1388–1394. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yan J, Yang Y, Chen C, Peng J, Ding H and
Wen Wang D: Short leukocyte telomere length is associated with
aortic dissection. Intern Med. 50:2871–2875. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wikgren M, Maripuu M, Karlsson T,
Nordfjäll K, Bergdahl J, Hultdin J, Del-Favero J, Roos G, Nilsson
LG, Adolfsson R and Norrback KF: Short telomeres in depression and
the general population are associated with a hypocortisolemic
state. Biol Psychiatry. 71:294–300. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wolkowitz OM, Jeste DV, Martin AS, Lin J,
Daly RE, Reuter C and Kraemer H: Leukocyte telomere length: Effects
of schizophrenia, age, and gender. J Psychiatr Res. 85:42–48.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Garcia-Rizo C, Fernandez-Egea E, Miller
BJ, Oliveira C, Justicia A, Griffith JK, Heaphy CM, Bernardo M and
Kirkpatrick B: Abnormal glucose tolerance, white blood cell count,
and telomere length in newly diagnosed, antidepressant-naïve
patients with depression. Brain Behav Immun. 28:49–53.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fernandez-Egea E, Bernardo M, Heaphy CM,
Griffith JK, Parellada E, Esmatjes E, Conget I, Nguyen L, George V,
Stöppler H, et al: Telomere length and pulse pressure in newly
diagnosed, antipsychotic-naive patients with nonaffective
psychosis. Schizophr Bull. 35:437–442. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Karabatsiakis A, Kolassa IT, Kolassa S,
Rudolph KL and Dietrich DE: Telomere shortening in leukocyte
subpopulations in depression. BMC Psychiatry.
14(192)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Boks MP, van Mierlo HC, Rutten BP,
Radstake TR, De Witte L, Geuze E, Horvath S, Schalkwyk LC, Vinkers
CH, Broen JC, et al: Longitudinal changes of telomere length and
epigenetic age related to traumatic stress and post-traumatic
stress disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 51:506–512.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ramin C, Wang W, Prescott J, Rosner B,
Simon NM, De Vivo I and Okereke OI: A prospective study of
leukocyte telomere length and risk of phobic anxiety among women.
Psychiatry Res. 230:545–552. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Okereke OI, Prescott J, Wong JY, Han J,
Rexrode KM and De Vivo I: High phobic anxiety is related to lower
leukocyte telomere length in women. PLoS One.
7(e40516)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hartmann N, Boehner M, Groenen F and Kalb
R: Telomere length of patients with major depression is shortened
but independent from therapy and severity of the disease. Depress
Anxiety. 27:1111–1116. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Simon NM, Walton ZE, Bui E, Prescott J,
Hoge E, Keshaviah A, Schwarz N, Dryman T, Ojserkis RA, Kovachy B,
et al: Telomere length and telomerase in a well-characterized
sample of individuals with major depressive disorder compared to
controls. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 58:9–22. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Czepielewski LS, Massuda R, Panizzutti B,
da Rosa ED, de Lucena D, Macêdo D, Grun LK, Barbé-Tuana FM and Gama
CS: Telomere length in subjects with schizophrenia, their
unaffected siblings and healthy controls: Evidence of accelerated
aging. Schizophr Res. 174:39–42. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Needham BL, Mezuk B, Bareis N, Lin J,
Blackburn EH and Epel ES: Depression, anxiety and telomere length
in young adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey. Mol Psychiatry. 20:520–528. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Imam T, Jitratkosol MH, Soudeyns H, Sattha
B, Gadawski I, Maan E, Forbes JC, Alimenti A, Lapointe N, Lamarre
V, et al: CIHR Emerging Team Grant on HIV Therapy and Aging: CARMA:
Leukocyte telomere length in HIV-infected pregnant women treated
with antiretroviral drugs during pregnancy and their uninfected
infants. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 60:495–502. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Epel ES, Blackburn EH, Lin J, Dhabhar FS,
Adler NE, Morrow JD and Cawthon RM: Accelerated telomere shortening
in response to life stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:17312–17315. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wolkowitz OM, Epel ES, Reus VI and Mellon
SH: Depression gets old fast: Do stress and depression accelerate
cell aging? Depress Anxiety. 27:327–338. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Furumoto K, Inoue E, Nagao N, Hiyama E and
Miwa N: Age-dependent telomere shortening is slowed down by
enrichment of intracellular vitamin C via suppression of oxidative
stress. Life Sci. 63:935–948. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|