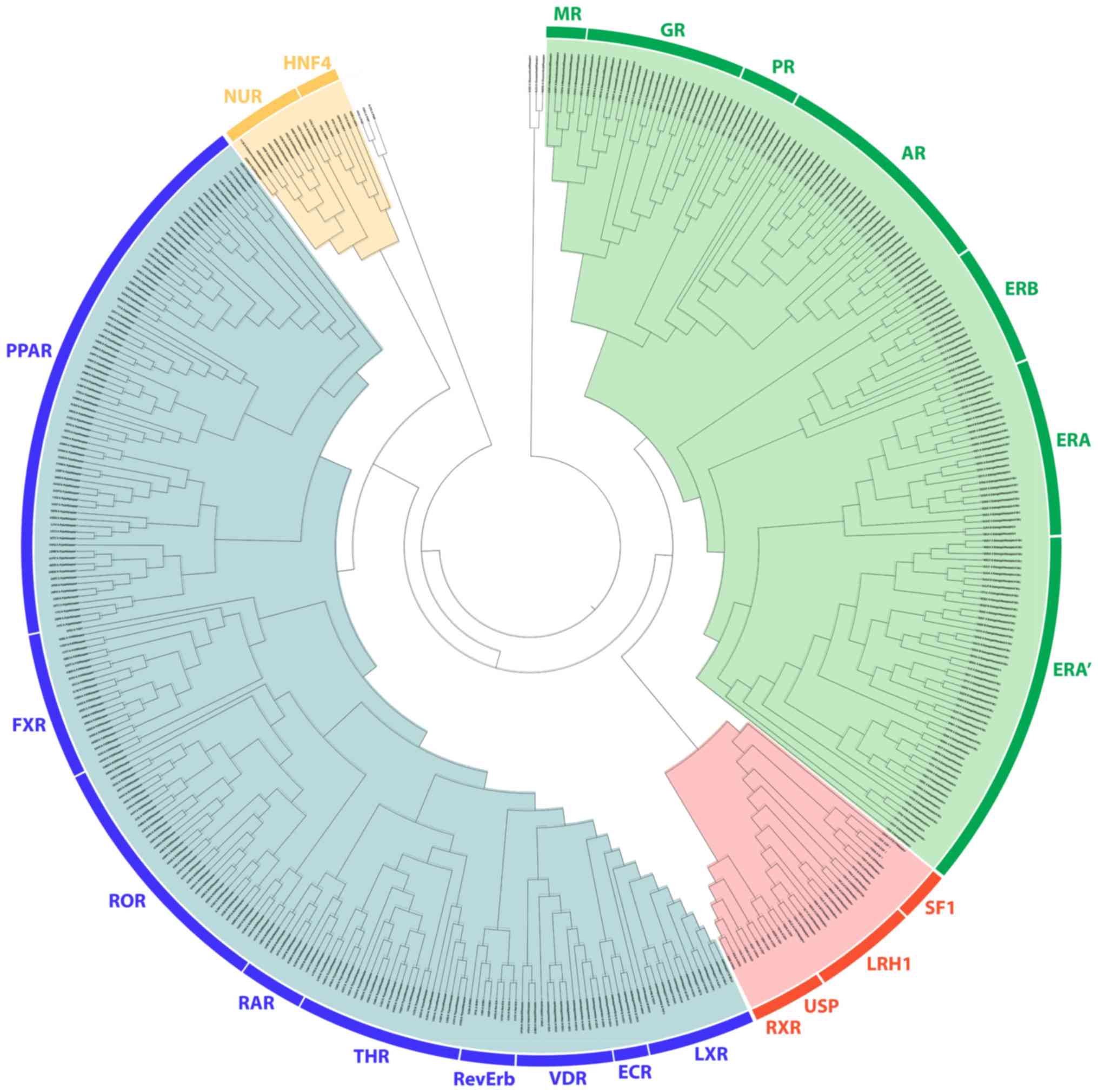
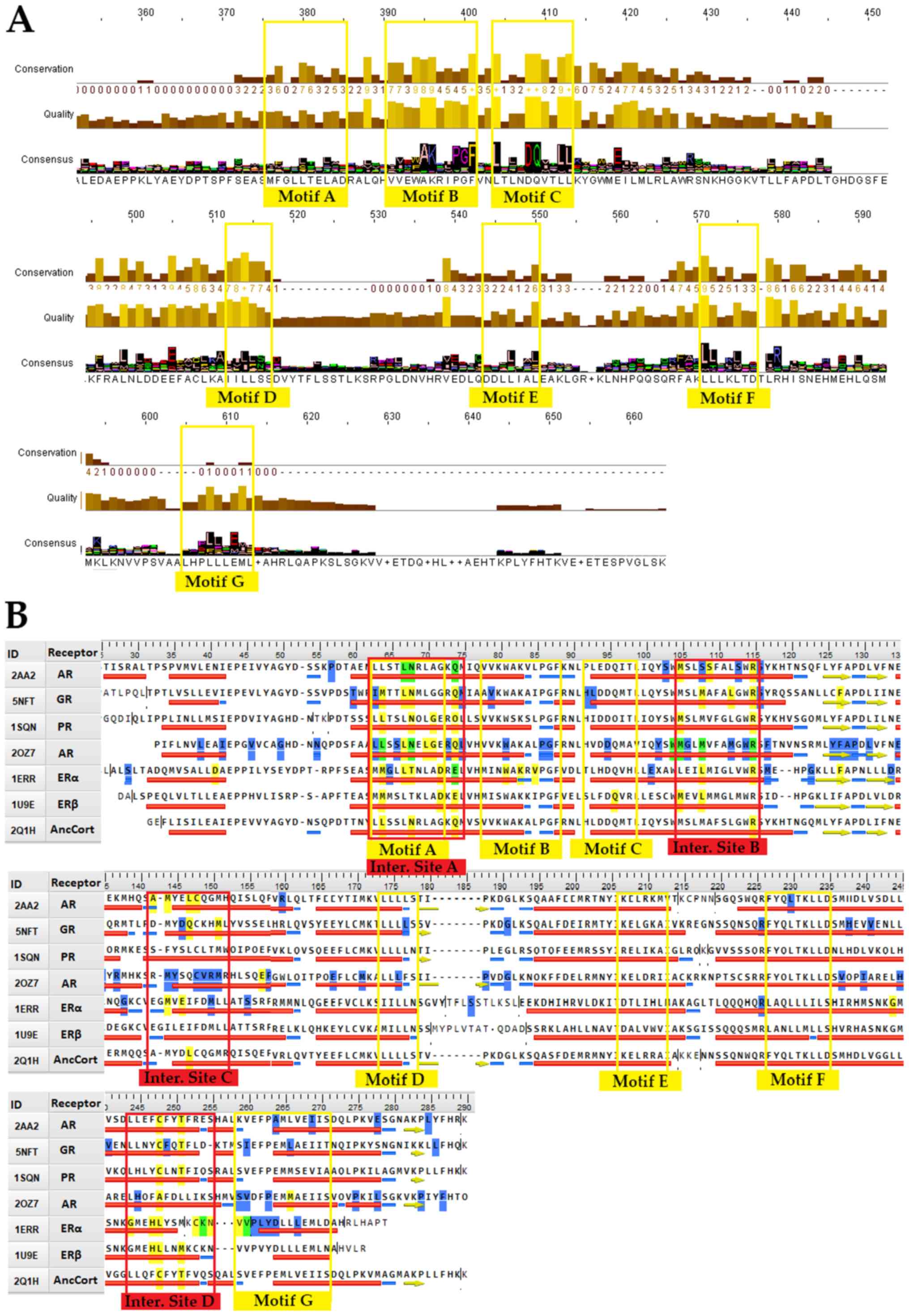
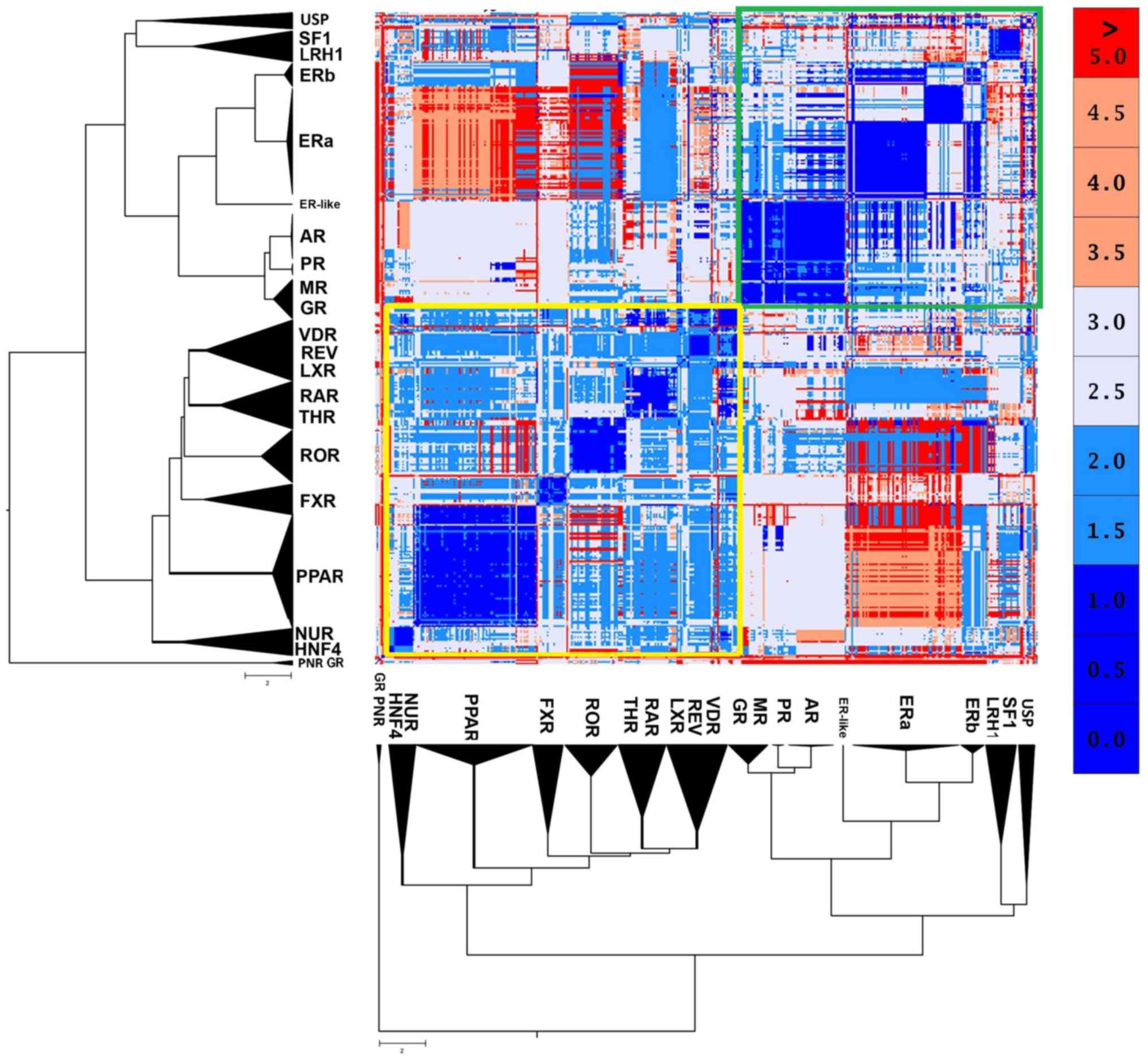
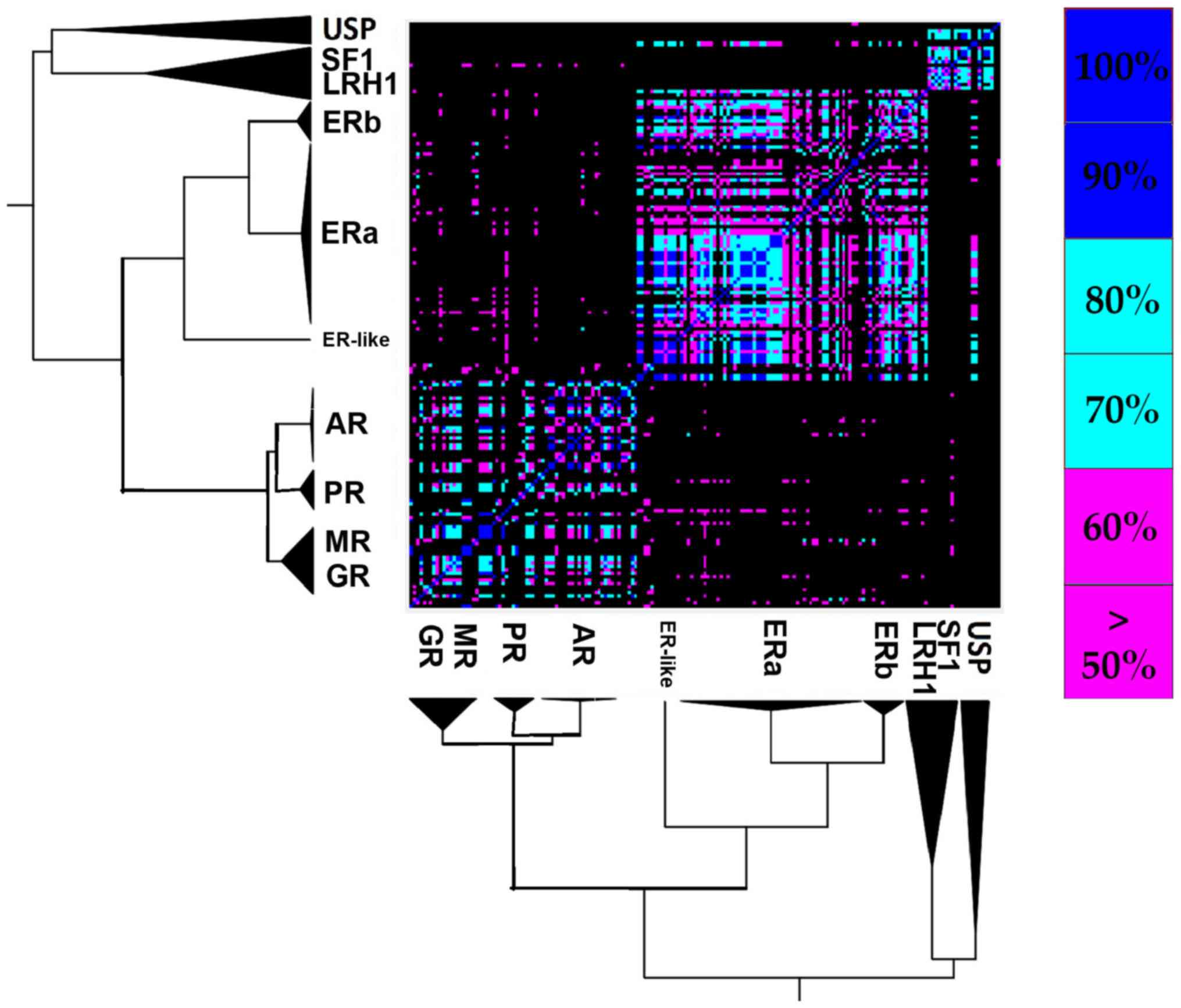
|
1
|
Robinson-Rechavi M, Escriva Garcia H and
Laudet V: The nuclear receptor superfamily. J Cell Sci.
116:585–586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chrousos GP: The glucocorticoid receptor
gene, longevity, and the complex disorders of Western societies. Am
J Med. 117:204–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bereshchenko O, Migliorati G, Bruscoli S
and Riccardi C: Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: A Novel
Anti-inflammatory Molecule. Front Pharmacol. 10(308)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hollenberg SM, Weinberger C, Ong ES,
Cerelli G, Oro A, Lebo R, Thompson EB, Rosenfeld MG and Evans RM:
Primary structure and expression of a functional human
glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 318:635–641. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nicolaides NC, Galata Z, Kino T, Chrousos
GP and Charmandari E: The human glucocorticoid receptor: Molecular
basis of biologic function. Steroids. 75:1–12. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kadmiel M and Cidlowski JA: Glucocorticoid
receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
34:518–530. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bledsoe RK, Montana VG, Stanley TB, Delves
CJ, Apolito CJ, McKee DD, Consler TG, Parks DJ, Stewart EL, Willson
TM, et al: Crystal structure of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand
binding domain reveals a novel mode of receptor dimerization and
coactivator recognition. Cell. 110:93–105. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang P, Chandra V and Rastinejad F:
Structural overview of the nuclear receptor superfamily: Insights
into physiology and therapeutics. Annu Rev Physiol. 72:247–272.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Evans RM and Mangelsdorf DJ: Nuclear
Receptors, RXR, and the Big Bang. Cell. 157:255–266.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lim HW, Uhlenhaut NH, Rauch A, Weiner J,
Hübner S, Hübner N, Won KJ, Lazar MA, Tuckermann J and Steger DJ:
Genomic redistribution of GR monomers and dimers mediates
transcriptional response to exogenous glucocorticoid in vivo.
Genome Res. 25:836–844. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Holzer G, Markov GV and Laudet V:
Evolution of Nuclear Receptors and Ligand Signaling: Toward a Soft
Key-Lock Model? Curr Top Dev Biol. 125:1–38. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Klinge CM: Steroid Hormone Receptors and
Signal Transduction Processes. In: Principles of Endocrinology and
Hormone Action. Belfiore A and LeRoith D (eds). Springer
International Publishing, Cham, pp187-232, 2018.
|
|
13
|
Bertrand S, Brunet FG, Escriva H,
Parmentier G, Laudet V and Robinson-Rechavi M: Evolutionary
genomics of nuclear receptors: From twenty-five ancestral genes to
derived endocrine systems. Mol Biol Evol. 21:1923–1937.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Markov GV and Laudet V: Origin and
evolution of the ligand-binding ability of nuclear receptors. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 334:21–30. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland
G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN and Bourne PE: The Protein
Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:235–242. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sobie EA: An introduction to MATLAB. Sci
Signal. 4(tr7)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Papageorgiou L, Loukatou S, Sofia K,
Maroulis D and Vlachakis D: An updated evolutionary study of
Flaviviridae NS3 helicase and NS5 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
reveals novel invariable motifs as potential pharmacological
targets. Mol Biosyst. 12:2080–2093. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pearson WR: Selecting the Right
Similarity-Scoring Matrix. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics.
43:3.5.1–3.5.9. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM,
Clamp M and Barton GJ: Jalview Version 2 - a multiple sequence
alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics.
25:1189–1191. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Vilar S, Cozza G and Moro S: Medicinal
chemistry and the molecular operating environment (MOE):
Application of QSAR and molecular docking to drug discovery. Curr
Top Med Chem. 8:1555–1572. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kufareva I and Abagyan R: Methods of
protein structure comparison. Methods Mol Biol. 857:231–257.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aertgeerts K, Skene R, Yano J, Sang BC,
Zou H, Snell G, Jennings A, Iwamoto K, Habuka N, Hirokawa A, et al:
Structural analysis of the mechanism of inhibition and allosteric
activation of the kinase domain of HER2 protein. J Biol Chem.
286:18756–18765. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Papageorgiou L, Loukatou S, Koumandou VL,
Makałowski W, Megalooikonomou V, Vlachakis D and Kossida S:
Structural models for the design of novel antiviral agents against
Greek Goat Encephalitis. PeerJ. 2(e664)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Papageorgiou L, Megalooikonomou V and
Vlachakis D: Genetic and structural study of DNA-directed RNA
polymerase II of Trypanosoma brucei, towards the designing of novel
antiparasitic agents. PeerJ. 5(e3061)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Michener CD and Sokal RR: A quantitative
approach to a problem in classification. Evolution. 11:130–162.
1957. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sneath PHA and Sokal RR: Unweighted pair
group method with arithmetic mean. In: Numerical Taxonomy. W.H.
Freeman, San Francisco, CA, pp230-234, 1973.
|
|
27
|
Pavlopoulos GA, Soldatos TG, Barbosa-Silva
A and Schneider R: A reference guide for tree analysis and
visualization. BioData Min. 3(1)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lu J, Xu G, Zhang S and Lu B: An effective
sequence-alignment-free superpositioning of pairwise or multiple
structures with missing data. Algorithms Mol Biol.
11(18)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Leaché AD, Wagner P, Linkem CW, Böhme W,
Papenfuss TJ, Chong RA, Lavin BR, Bauer AM, Nielsen SV, Greenbaum
E, et al: A hybrid phylogenetic-phylogenomic approach for species
tree estimation in African Agama lizards with applications to
biogeography, character evolution, and diversification. Mol
Phylogenet Evol. 79:215–230. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fouquier J, Rideout JR, Bolyen E, Chase J,
Shiffer A, McDonald D, Knight R, Caporaso JG and Kelley ST:
Ghost-tree: Creating hybrid-gene phylogenetic trees for diversity
analyses. Microbiome. 4(11)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Stecher G, Liu L, Sanderford M, Peterson
D, Tamura K and Kumar S: MEGA-MD: Molecular evolutionary genetics
analysis software with mutational diagnosis of amino acid
variation. Bioinformatics. 30:1305–1307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mellor CL, Marchese Robinson RL, Benigni
R, Ebbrell D, Enoch SJ, Firman JW, Madden JC, Pawar G, Yang C and
Cronin MTD: Molecular fingerprint-derived similarity measures for
toxicological read-across: Recommendations for optimal use. Regul
Toxicol Pharmacol. 101:121–134. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rácz A, Bajusz D and Héberger K: Life
beyond the Tanimoto coefficient: Similarity measures for
interaction fingerprints. J Cheminform. 10(48)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bajusz D, Rácz A and Héberger K: Why is
Tanimoto index an appropriate choice for fingerprint-based
similarity calculations? J Cheminform. 7(20)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ferraz-de-Souza B, Lin L and Achermann JC:
Steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) and human disease. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 336:198–205. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fayard E, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K:
LRH-1: An orphan nuclear receptor involved in development,
metabolism and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 14:250–260.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hall BL and Thummel CS: The RXR homolog
ultraspiracle is an essential component of the Drosophila
ecdysone receptor. Development. 125:4709–4717. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hill RJ, Billas IM, Bonneton F, Graham LD
and Lawrence MC: Ecdysone receptors: From the Ashburner model to
structural biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 58:251–271. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Laffitte BA, Kast HR, Nguyen CM, Zavacki
AM, Moore DD and Edwards PA: Identification of the DNA binding
specificity and potential target genes for the farnesoid
X-activated receptor. J Biol Chem. 275:10638–10647. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Greschik H, Flaig R and Moras D:
Ligand/cofactor complexes of nuclear receptor ligand-binding
domains. https://www.academia.edu/18571843/Ligand_cofactor_complexes_of_nuclear_receptor_ligand-binding_domains.
|
|
41
|
Marchler-Bauer A, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales
NR, Lu S, Chitsaz F, Geer LY, Geer RC, He J, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI,
et al: CDD: NCBI's conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D222–D226. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nicolaides NC, Roberts ML, Kino T,
Braatvedt G, Hurt DE, Katsantoni E, Sertedaki A, Chrousos GP and
Charmandari E: A novel point mutation of the human glucocorticoid
receptor gene causes primary generalized glucocorticoid resistance
through impaired interaction with the LXXLL motif of the p160
coactivators: Dissociation of the transactivating and
transreppressive activities. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:E902–E907.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jääskeläinen J, Mongan NP, Harland S and
Hughes IA: Five novel androgen receptor gene mutations associated
with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome. Hum Mutat.
27(291)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vitellius G, Fagart J, Delemer B, Amazit
L, Ramos N, Bouligand J, Le Billan F, Castinetti F, Guiochon-Mantel
A, Trabado S, et al: Three Novel Heterozygous Point Mutations of
NR3C1 Causing Glucocorticoid Resistance. Hum Mutat. 37:794–803.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Harrod A, Fulton J, Nguyen VTM, et al:
Genomic modelling of the ESR1 Y537S mutation for evaluating
function and new therapeutic approaches for metastatic breast
cancer. Oncogene. 36:2286–2296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Achermann JC, Schwabe J, Fairall L and
Chatterjee K: Genetic disorders of nuclear receptors. J Clin
Invest. 127:1181–1192. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ai N, Krasowski MD, Welsh WJ and Ekins S:
Understanding nuclear receptors using computational methods. Drug
Discov Today. 14:486–494. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Matias PM, Carrondo MA, Coelho R, Thomaz
M, Zhao XY, Wegg A, Crusius K, Egner U and Donner P: Structural
basis for the glucocorticoid response in a mutant human androgen
receptor (AR(ccr)) derived from an androgen-independent prostate
cancer. J Med Chem. 45:1439–1446. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Puyang X, Furman C, Zheng GZ, Wu ZJ, Banka
D, Aithal K, Agoulnik S, Bolduc DM, Buonamici S, Caleb B, et al:
Discovery of Selective Estrogen Receptor Covalent Antagonists for
the Treatment of ERαWT and ERαMUT Breast
Cancer. Cancer Discov. 8:1176–1193. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Nettles KW, Bruning JB, Gil G, O'Neill EE,
Nowak J, Guo Y, Kim Y, DeSombre ER, Dilis R, Hanson RN, et al:
Structural plasticity in the oestrogen receptor ligand-binding
domain. EMBO Rep. 8:563–568. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Siltberg-Liberles J, Grahnen JA and
Liberles DA: The evolution of protein structures and structural
ensembles under functional constraint. Genes (Basel). 2:748–762.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wurtz JM, Bourguet W, Renaud JP, Vivat V,
Chambon P, Moras D and Gronemeyer H: A canonical structure for the
ligand-binding domain of nuclear receptors. Nat Struct Biol.
3:87–94. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kandil S, Biondaro S, Vlachakis D, Cummins
AC, Coluccia A, Berry C, Leyssen P, Neyts J and Brancale A:
Discovery of a novel HCV helicase inhibitor by a de novo drug
design approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:2935–2937.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|