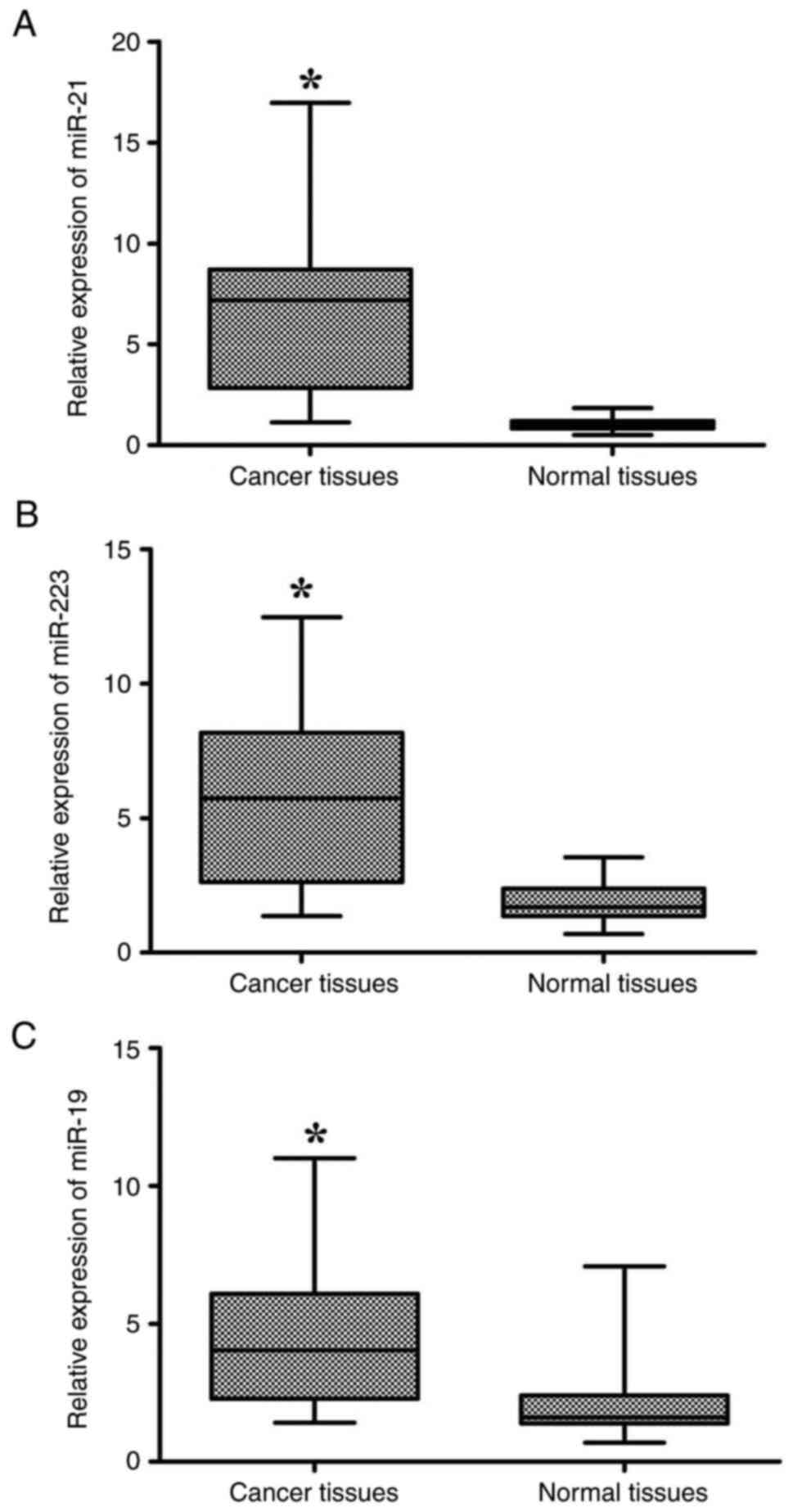
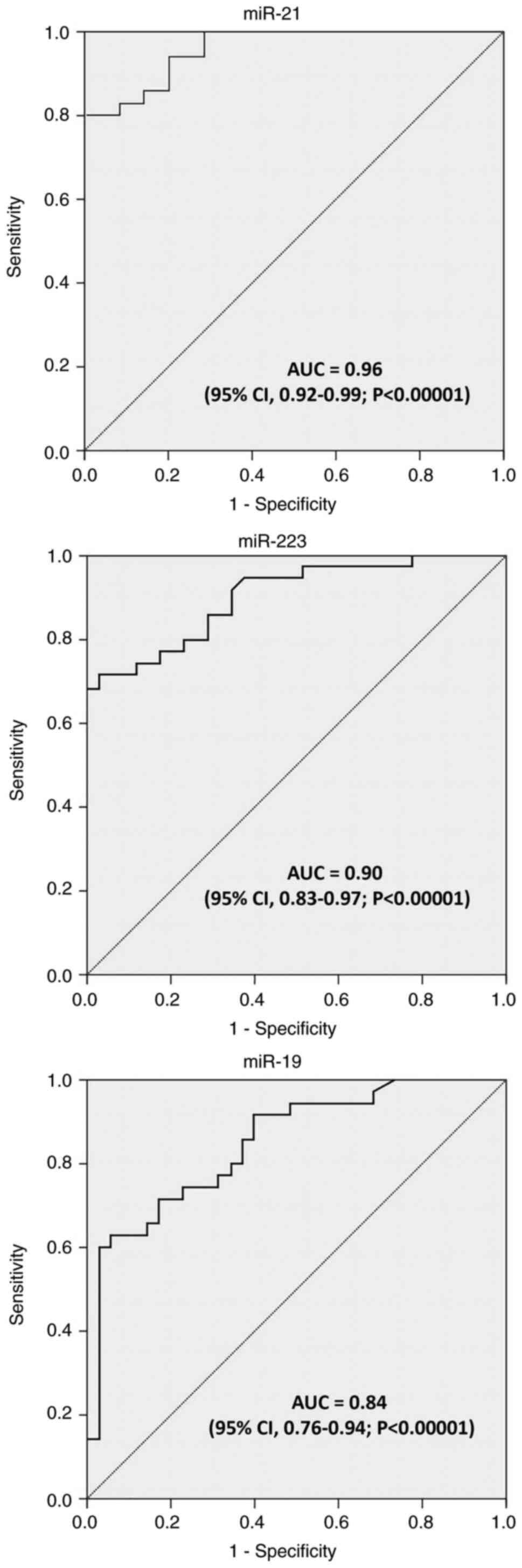
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Konturek PC, Konturek SJ and Brzozowski T:
Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancerogenesis. J
Physiol Pharmacol. 60:3–21. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson MP and Kurzrock R: Epstein-Barr
virus and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:803–821. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fuccio L, Eusebi LH and Bazzoli F: Gastric
cancer, Helicobacter pylori infection and other risk
factors. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2:342–347. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of microRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1723)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, Sabir DK,
Taheri M and Ghafouri-Fard S: MicroRNA: A signature for cancer
progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 138(111528)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Arif KMT, Elliott EK, Haupt LM and
Griffiths LR: Regulatory mechanisms of epigenetic miRNA
relationships in human cancer and potential as therapeutic targets.
Cancers (Basel). 12(2922)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5'UTR as in the 3'UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T,
Stark A, Bork P and Izaurralde E: mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping
complexes. Genes Dev. 20:1885–1898. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C and Zardo G:
MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear
functions. Int J Mol Sci. 17(1712)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gregory RI and Shiekhattar R: MicroRNA
biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 65:3509–3512. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH,
Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, Iliopoulos D, Pilozzi E, Liu CG, Negrini
M, et al: E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell.
13:272–286. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M and
Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D155–D162. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yuan C, Zhang Y, Tu W and Guo Y:
Integrated miRNA profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal
upregulated miRNAs in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 18:1979–1988.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Irmak-Yazicioglu MB: Mechanisms of
microRNA deregulation and microRNA targets in gastric cancer. Oncol
Res Treatment. 39:136–139. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu L, Zhao Y, Fan G, Shuai T, Li B and Li
Y: Helicobacter pylori infection enhances heparanase leading
to cell proliferation via mitogen-activated protein kinase
signalling in human gastric cancer cells. Mol Med Rep.
18:5733–5741. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ding N, Zou Z, Sha H, Su S, Qian H, Meng
F, Chen F, Du S, Zhou S, Chen H, et al: iRGD synergizes with PD-1
knockout immunotherapy by enhancing lymphocyte infiltration in
gastric cancer. Nat Commun. 10(1336)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Prinz C, Mese K and Weber D: MicroRNA
Changes in gastric carcinogenesis: Differential dysregulation
during Helicobacter pylori and EBV Infection. Genes.
12(597)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Săsăran MO, Meliț LE and Dobru ED:
Microrna modulation of host immune response and inflammation
triggered by Helicobacter pylori. Int J Mol Sci.
22(1406)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Iizasa H, Kim H, Kartika AV, Kanehiro Y
and Yoshiyama H: Role of viral and host microRNAs in immune
regulation of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases. Front
Immunol. 11(367)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lu JJ, Perng CL, Shyu RY, Chen CH, Lou Q,
Chong SK and Lee CH: Comparison of five PCR methods for detection
of Helicobacter pylori DNA in gastric tissues. J Clin
Microbiol. 37:772–774. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ortiz-Princz D, Guariglia-Oropeza V, Avila
M, Correnti M, Perrone M, Gutierrez B, Torres J, Megraud F and
Cavazza ME: Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA genotypes in
Cuban and Venezuelan populations. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz.
105:331–335. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu H, Zhu C, Li F, Xu W, Tao D and Feng X:
Putative periodontopathic bacteria and herpesviruses in pregnant
women: A case-control study. Sci Rep. 6(27796)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ebert MP and Röcken C: Molecular screening
of gastric cancer by proteome analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 18:847–853. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu X, Cai H and Wang Y: Prognostic
significance of tumour markers in Chinese patients with gastric
cancer. ANZ J Surg. 84:448–453. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang D, Fan Z, Liu F and Zuo J: Hsa-miR-21
and Hsa-miR-29 in tissue as potential diagnostic and prognostic
biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 37:1454–1462.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Emami SS, Nekouian R, Akbari A, Faraji A,
Abbasi V and Agah S: Evaluation of circulating miR-21 and miR-222
as diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Ther.
15:115–119. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu
W, Xiao S and Lu H: miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer
pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest. 88:1358–1366.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Du YY, Dai DQ and Yang Z: Role of RECK
methylation in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. World
J Gastroenterol. 16:904–908. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao H, Wang Y, Yang L, Jiang R and Li W:
MiR-25 promotes gastric cancer cells growth and motility by
targeting RECK. Mol Cell Biochem. 385:207–213. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li J, Guo Y, Liang X, Sun M, Wang G, De W
and Wu W: MicroRNA-223 functions as an oncogene in human gastric
cancer by targeting FBXW7/hCdc4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:763–774. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qin S, Ai F, Ji WF, Rao W, Zhang HC and
Yao WJ: miR-19a promotes cell growth and tumorigenesis through
targeting SOCS1 in gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:835–840. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chang H, Kim N, Park JH, Nam RH, Choi YJ,
Lee HS, Yoon H, Shin CM, Park YS, Kim JM and Lee DH: Different
microRNA expression levels in gastric cancer depending on
Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut Liver. 9:188–196.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Riley KJ, Rabinowitz GS, Yario TA, Luna
JM, Darnell RB and Steitz JA: EBV and human microRNAs co-target
oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency. EMBO
J. 31:2207–2221. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zheng Q, Chen C, Guan H, Kang W and Yu C:
Prognostic role of microRNAs in human gastrointestinal cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 8:46611–46623.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Sun X, Zhang K and Li D: Prognostic
potential of miR-21-3p in gastric cancer. J BUON. 25:2678–2682.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|