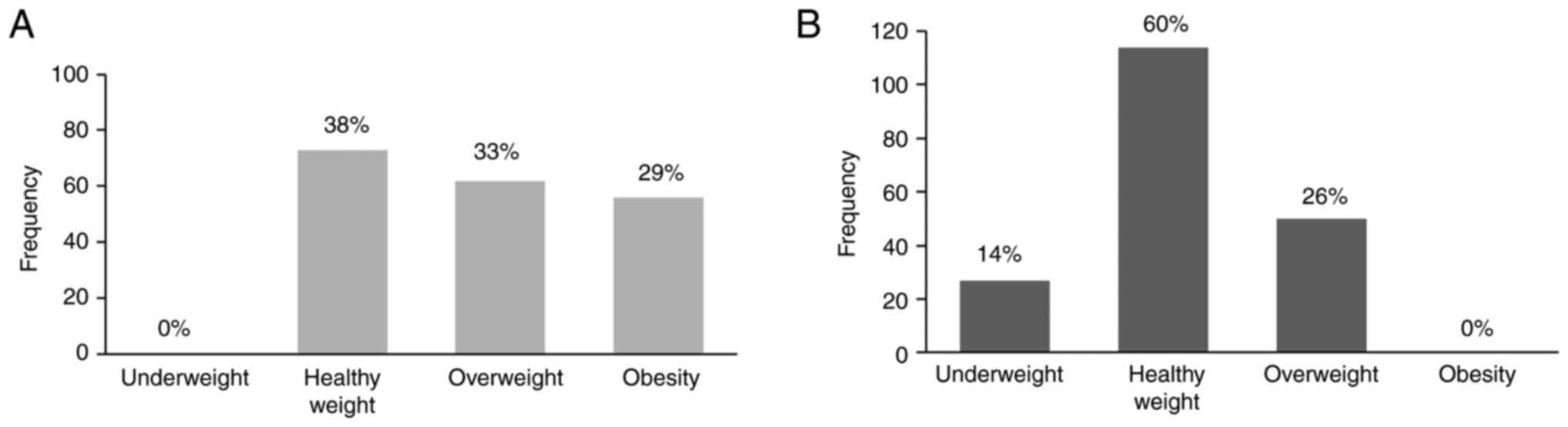
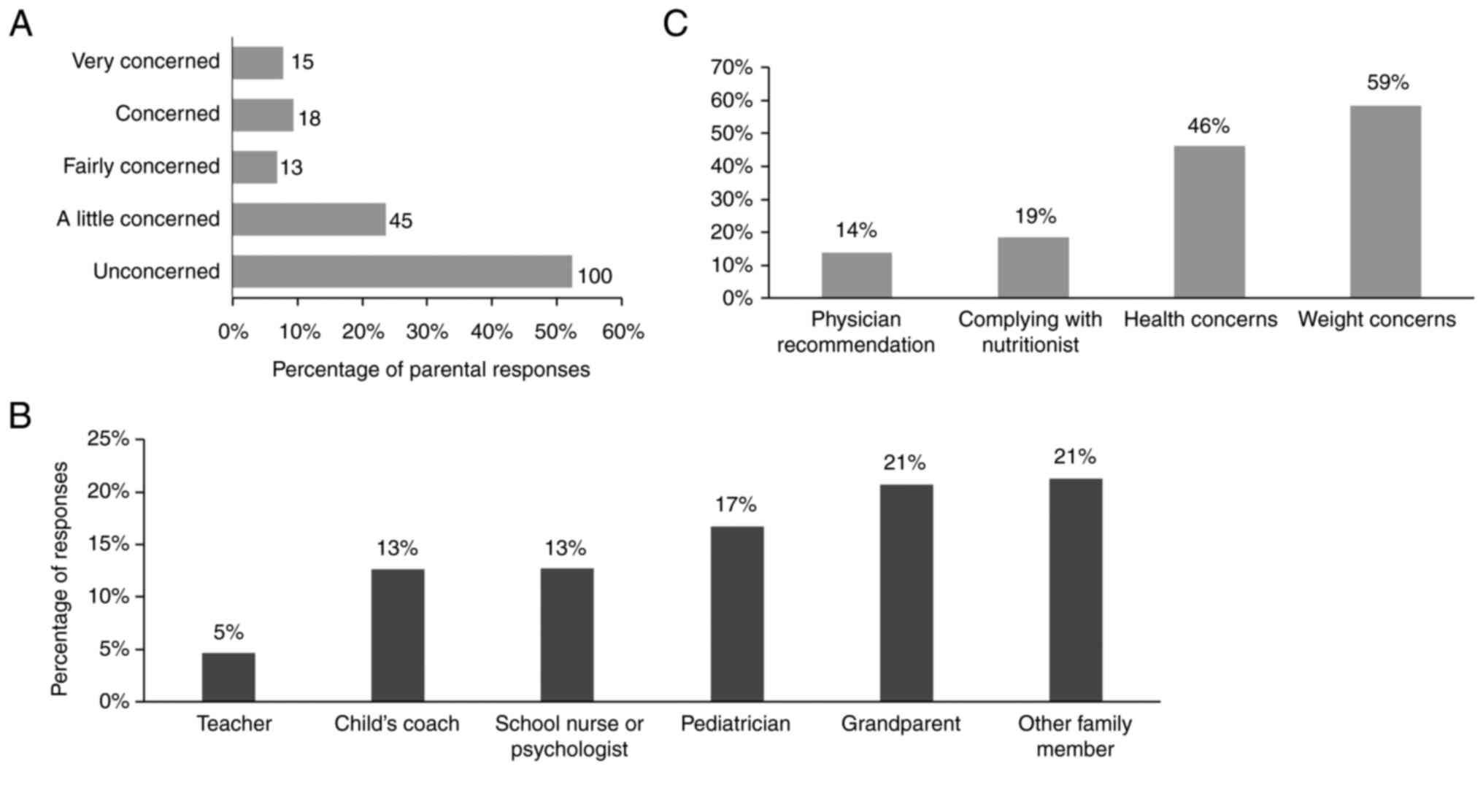
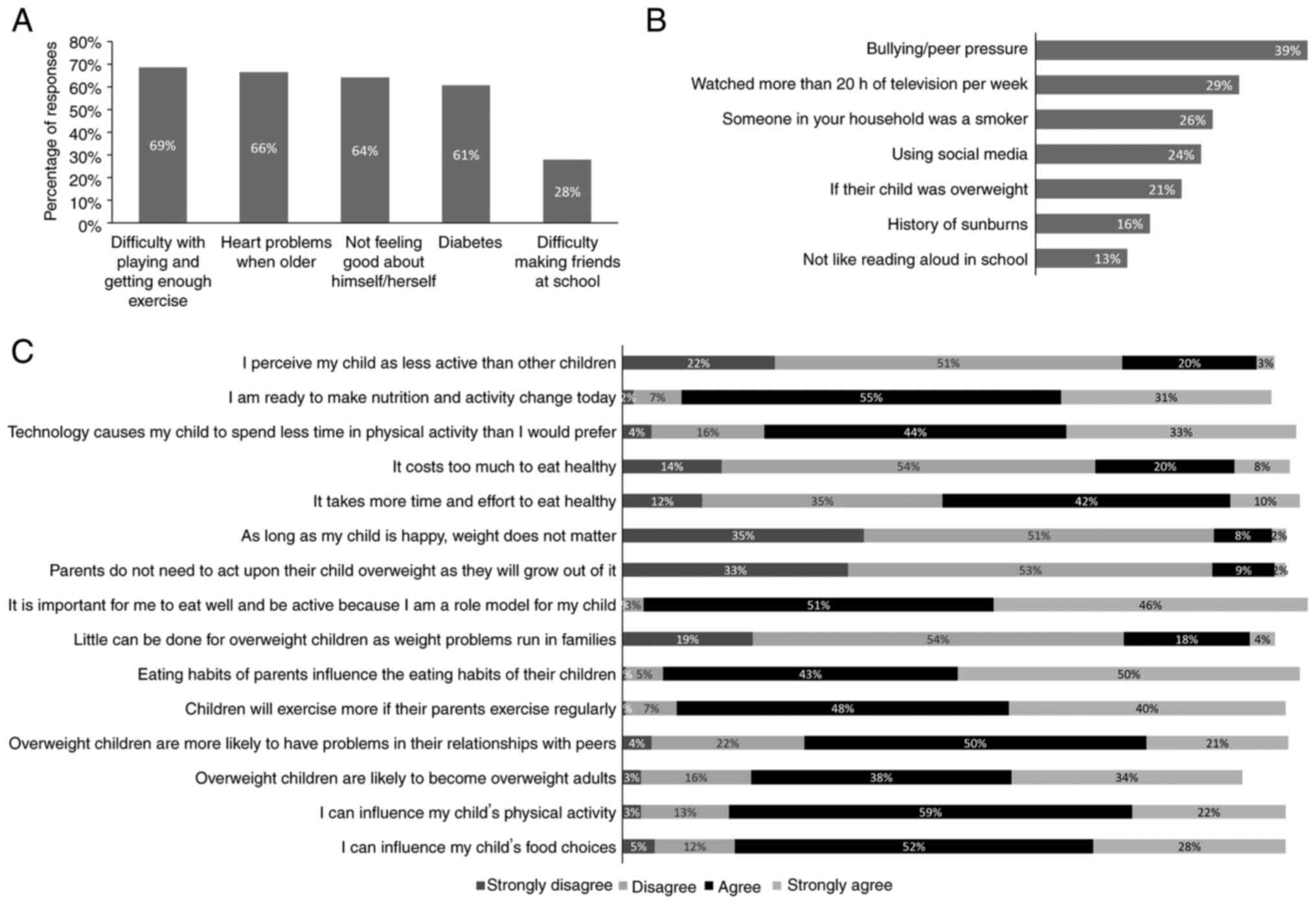
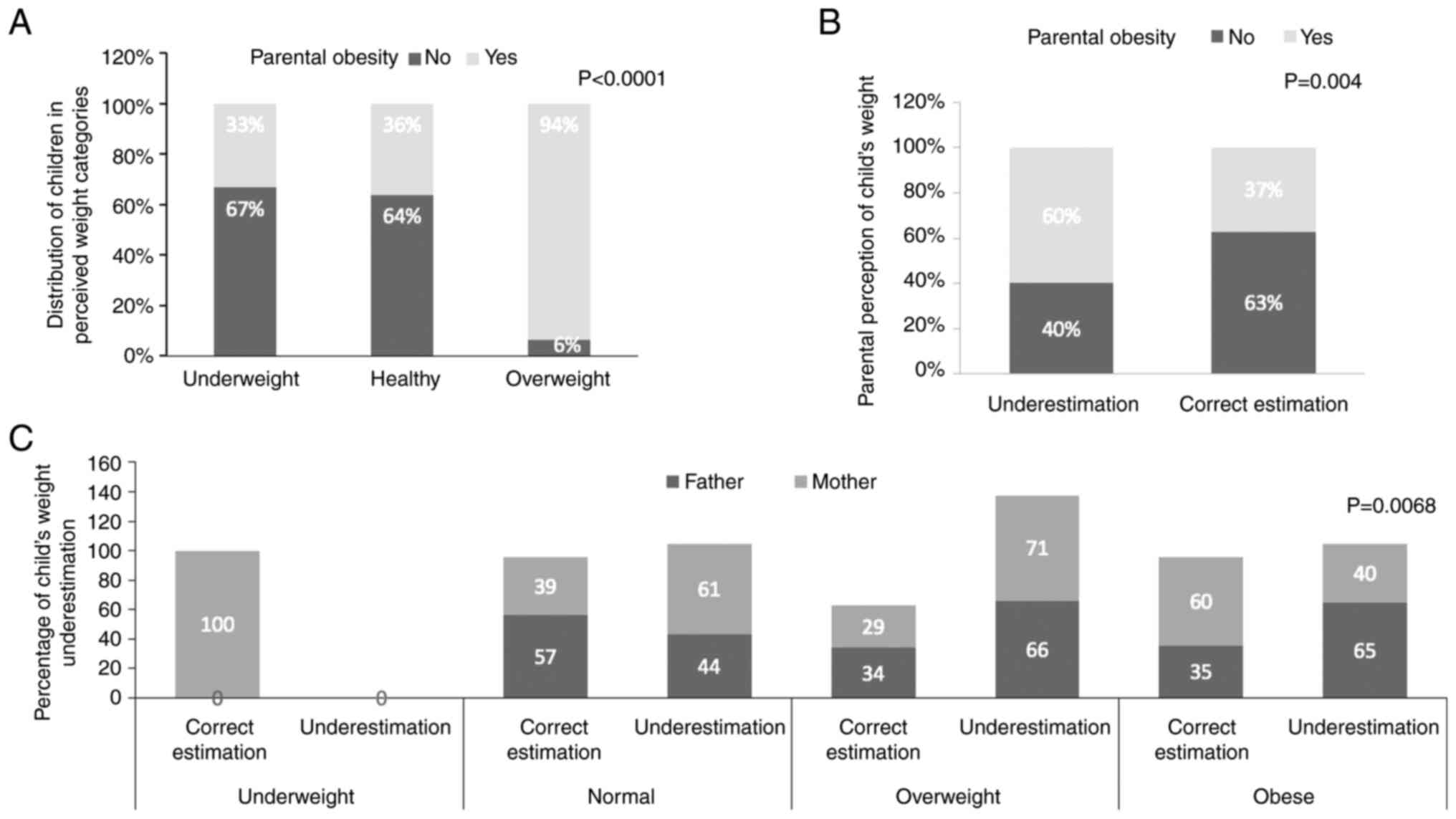
|
1
|
Lee JS, Jin MH and Lee HJ: Global
relationship between parent and child obesity: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Pediatr. 65:35–46. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mead E, Brown T, Rees K, Azevedo LB,
Whittaker V, Jones D, Olajide J, Mainardi GM, Corpeleijn E,
O'Malley C, et al: Diet, physical activity and behavioural
interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children
from the age of 6 to 11 years. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
6(CD012651)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Report of
the commission on ending childhood obesity. In: Ending Childhood
Obesity. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
|
|
4
|
de Onis M, Blössner M and Borghi E: Global
prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool
children. Am J Clin Nutr. 92:1257–1264. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mallat S, Geagea A, Jurjus R, Rizkallah A,
Oueidat D, Matar M, Tawilah J, Berbari A and Jurjus A: Obesity in
Lebanon: A national problem. World J Cardiovasc Dis. 6:166–174.
2016.
|
|
6
|
World Health Organization (WHO): Obesity
and overweight factsheet. World Health Organization, Geneva,
Switzerland, 2021. Accessed Febr 25, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
|
|
7
|
Moussa H, Salameh P, Barakat S, Farfour I,
Dana R and Abou Merhi B: Parents perception of childhood overweight
and obesity and their attitude toward behaviour and lifestyle
changes: A 2020 study on a lebanese population. Clin Pediatr.
6(171)2021.
|
|
8
|
Sibai AM, Hwalla N, Adra N and Rahal B:
Prevalence and covariates of obesity in Lebanon: Findings from the
first epidemiological study. Obes Res. 11:1353–1361.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nasreddine L, Naja F, Akl C, Chamieh MC,
Karam S, Sibai AM and Hwalla N: Dietary, lifestyle and
socio-economic correlates of overweight, obesity and central
adiposity in Lebanese children and adolescents. Nutrients.
6:1038–1062. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Skinner AC and Skelton JA: Prevalence and
trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United
States, 1999-2012. JAMA Pediatr. 168:561–566. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wright DR, Lozano P, Dawson-Hahn E,
Christakis DA, Haaland WL and Basu A: Parental predictions and
perceptions regarding long-term childhood obesity-related health
risks. Acad Pediatr. 16:475–481. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Doolen J, Alpert PT and Miller SK:
Parental disconnect between perceived and actual weight status of
children: A metasynthesis of the current research. J Am Acad Nurse
Pract. 21:160–166. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lobstein T, Baur L and Uauy R: IASO
International Obesity TaskForce. Obesity in children and young
people: A crisis in public health. Obes Rev. 5 (Suppl 1):S4–S104.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Musaiger AO: Overweight and obesity in the
Eastern Mediterranean Region: can we control it? East Mediterr
Health J. 10:789–793. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ashraf H, Shamsi NI and Ashraf R: Parental
perception and childhood obesity: Contributors to incorrect
perception. J Pak Med Assoc. 67:214–219. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pocock M, Trivedi D, Wills W, Bunn F and
Magnusson J: Parental perceptions regarding healthy behaviours for
preventing overweight and obesity in young children: A systematic
review of qualitative studies. Obes Rev. 11:338–353.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Black JA, Park M, Gregson J, Falconer CL,
White B, Kessel AS, Saxena S, Viner RM and Kinra S: Child obesity
cut-offs as derived from parental perceptions: Cross-sectional
questionnaire. Br J Gen Pract. 65:e234–e239. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Carnell S, Edwards C, Croker H, Boniface D
and Wardle J: Parental perceptions of overweight in 3-5 y olds. Int
J Obes (Lond). 29:353–355. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He M and Evans A: Are parents aware that
their children are overweight or obese? Do they care? Can Fam
Physician. 53:1493–1499. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rietmeijer-Mentink M, Paulis WD, van
Middelkoop M, Bindels PJ and van der Wouden JC: Difference between
parental perception and actual weight status of children: A
systematic review. Matern Child Nutr. 9:3–22. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Baughcum AE, Chamberlin LA, Deeks CM,
Powers SW and Whitaker RC: Maternal perceptions of overweight
preschool children. Pediatrics. 106:1380–1386. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Eckstein KC, Mikhail LM, Ariza AJ, Thomson
JS, Millard SC and Binns HJ: Pediatric Practice Research Group.
Parents' perceptions of their child's weight and health.
Pediatrics. 117:681–690. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Myers S and Vargas Z: Parental perceptions
of the preschool obese child. Pediatr Nurs. 26:23–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sylvetsky-Meni AC, Gillepsie SE, Hardy T
and Welsh JA: The impact of parents' categorization of their own
weight and their child's weight on healthy lifestyle promoting
beliefs and practices. J Obes. 2015(307381)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
White DA, Rofey DL, Kriska AM, Venditti
EM, Barone Gibbs B, Gallagher JD and Jakicic JM: The impact of
expressing concern for a child's weight on the parents' perception
of child weight and the parents concern for future weight problems.
J Child Obes. 1(23)2016.
|
|
26
|
World Health Organization (WHO): A healthy
lifestyle-WHO recommendations. World Health Organization, Geneva,
Switzerland, 2010. https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/a-healthy-lifestyle-who-recommendations.
Accessed February 15, 2023.
|
|
27
|
de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A,
Nishida C and Siekmann J: Development of a WHO growth reference for
school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ.
85:660–667. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rodrigues D, Machado-Rodrigues AM and
Padez C: Parental misperception of their child's weight status and
how weight underestimation is associated with childhood obesity. Am
J Hum Biol. 32(e23393)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Karmali S, Battram DS, Burke SM, Cramp A,
Johnson AM, Mantler T, Morrow D, Ng V, Pearson ES, Petrella RJ, et
al: Perspectives and impact of a parent-child intervention on
dietary intake and physical activity behaviours, parental
motivation, and parental body composition: A randomized controlled
trial. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 17(6822)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Peyer KL, Welk G, Bailey-Davis L, Yang S
and Kim JK: Factors associated with parent concern for child weight
and parenting behaviors. Child Obes. 11:269–274. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jain A, Sherman SN, Chamberlin LA, Carter
Y, Powers SW and Whitaker RC: Why don't low-income mothers worry
about their preschoolers being overweight? Pediatrics.
107:1138–1146. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Taylor RW, Williams SM, Dawson AM, Haszard
JJ and Brown DA: Parental motivation to change body weight in young
overweight children. Public Health Nutr. 18:1807–1814.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang J, Rosenqvist U, Wang H, Greiner T,
Lian G and Sarkadi A: Influence of grandparents on eating behaviors
of young children in Chinese three-generation families. Appetite.
48:377–383. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lau JD, Au LY, Chao E, Elbaar L and Tse R:
The association of grandparent care with childhood overweight and
obesity in Chinese American families. Child Obes. 15:14–20.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Farrow C: A comparison between the feeding
practices of parents and grandparents. Eat Behav. 15:339–342.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lindberg L, Ek A, Nyman J, Marcus C,
Ulijaszek S and Nowicka P: Low grandparental social support
combined with low parental socioeconomic status is closely
associated with obesity in preschool-aged children: A pilot study.
Pediatr Obes. 11:313–316. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Etelson D, Brand DA, Patrick PA and
Shirali A: Childhood obesity: Do parents recognize this health
risk? Obes Res. 11:1362–1368. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Golan M and Crow S: Parents are key
players in the prevention and treatment of weight-related problems.
Nutr Rev. 62:39–50. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wolfenden L, Bell C, Wiggers J, Butler M,
James E and Chipperfield K: Engaging parents in child obesity
prevention: Support preferences of parents. J Paediatr Child
Health. 48:E4–E6. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Colley RC, Garriguet D, Janssen I, Craig
CL, Clarke J and Tremblay MS: Physical activity of Canadian adults:
Accelerometer results from the 2007 to 2009 Canadian health
measures survey. Health Rep. 22:7–14. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lindsay AC, Sussner KM, Kim J and
Gortmaker S: The role of parents in preventing childhood obesity.
Future Child. 16:169–186. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ash T, Agaronov A, Young TL,
Aftosmes-Tobio A and Davison KK: Family-based childhood obesity
prevention interventions: A systematic review and quantitative
content analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 14(113)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|