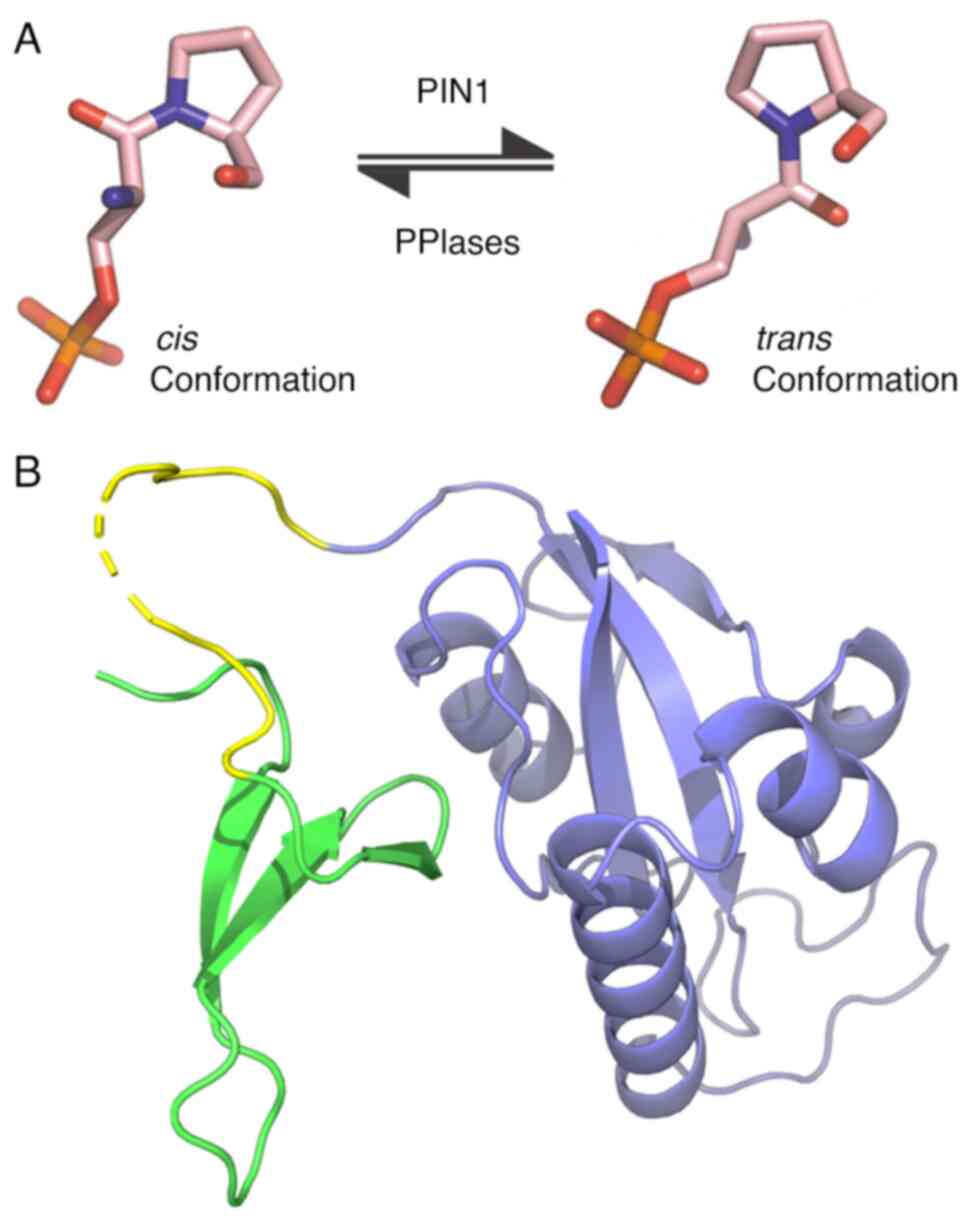
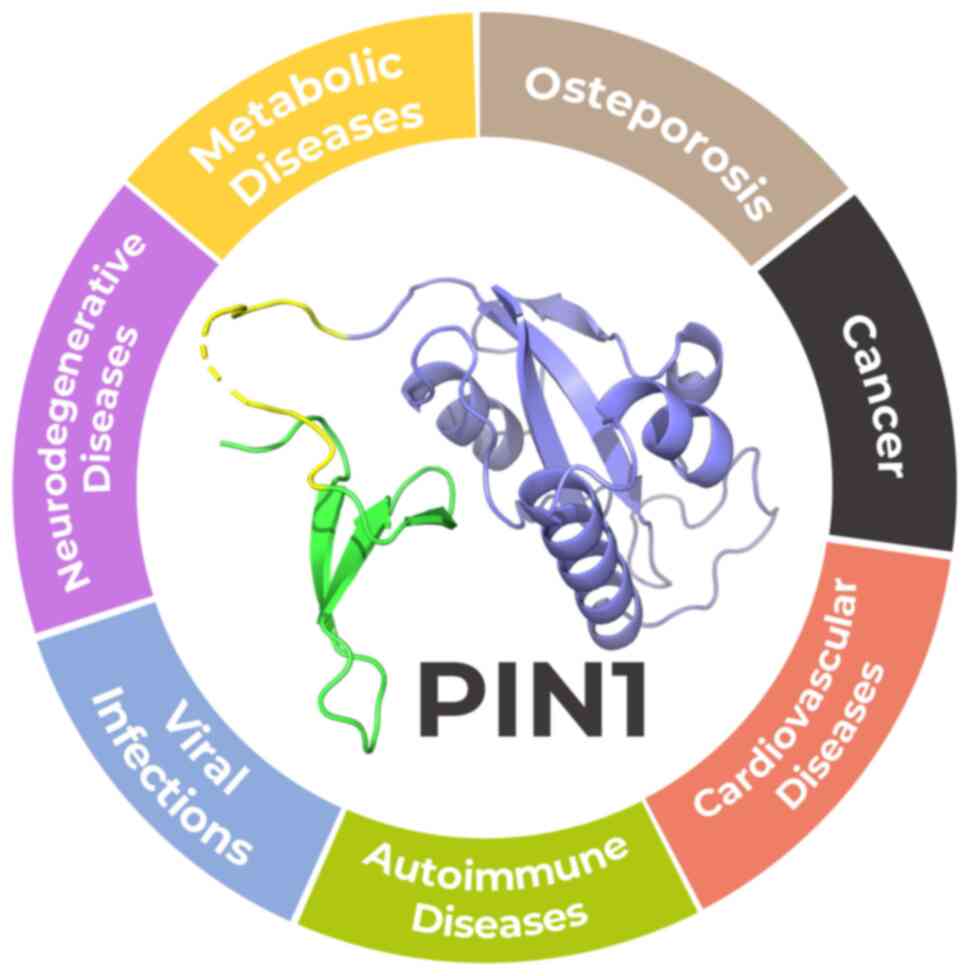
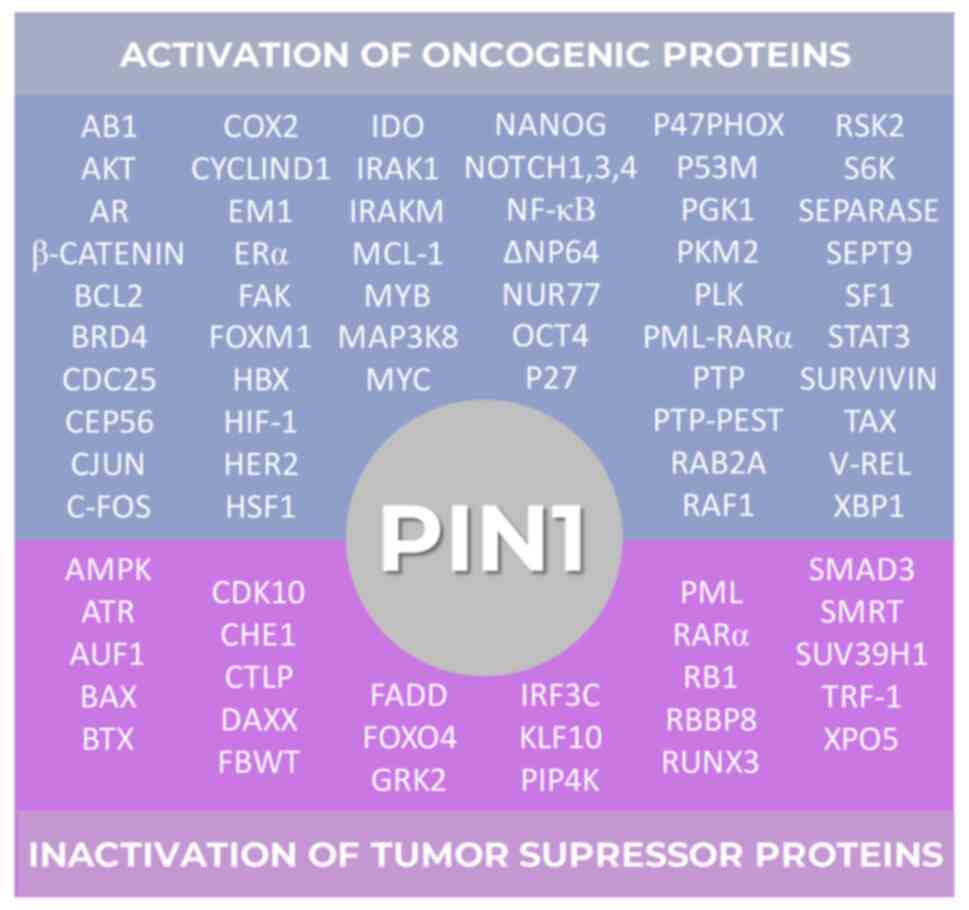
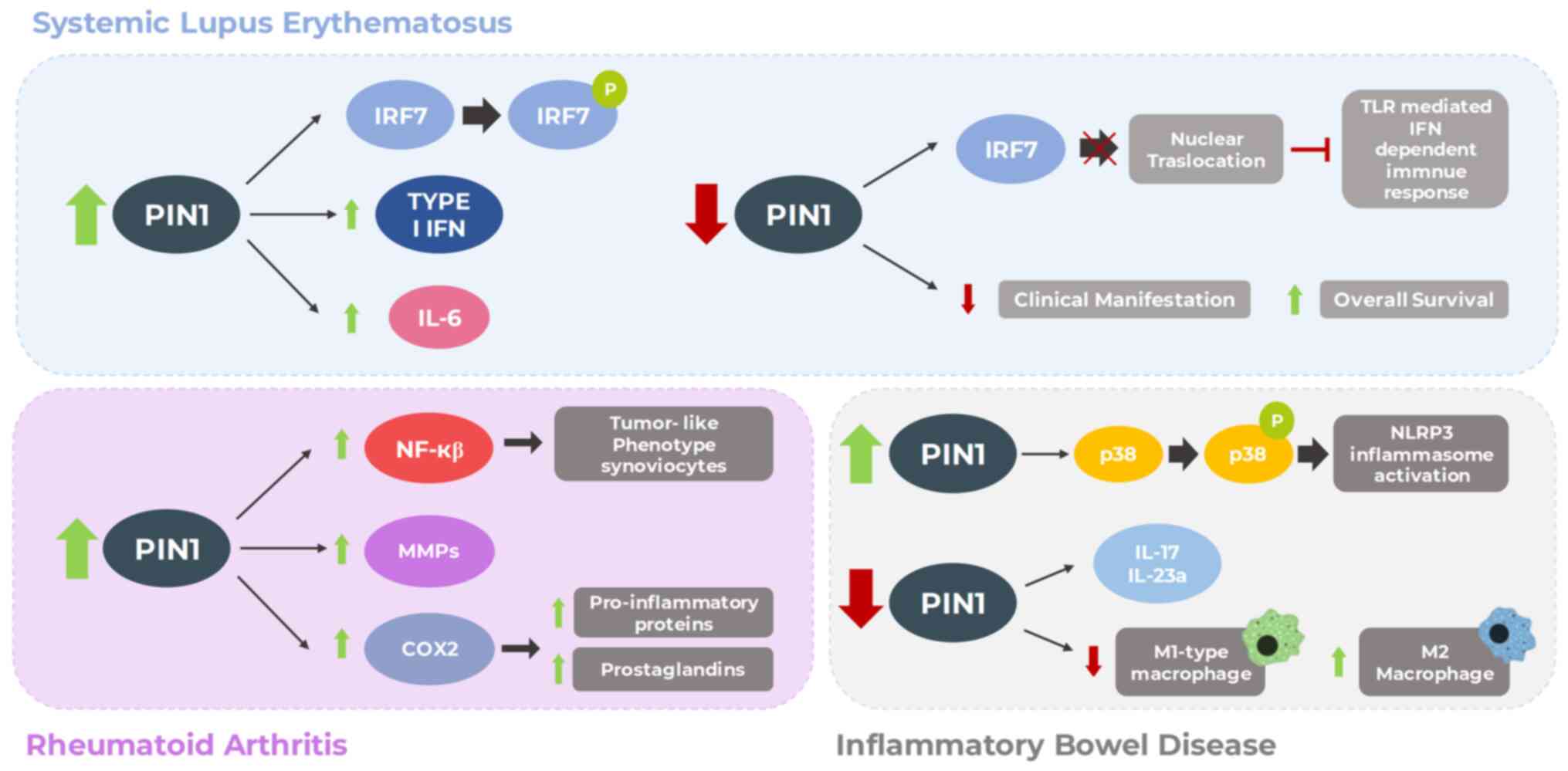
|
1
|
Liou YC, Zhou XZ and Lu KP: Prolyl
isomerase Pin1 as a molecular switch to determine the fate of
phosphoproteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 36:501–514. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Alvarez E, Northwood IC, Gonzalez FA,
Latour DA, Seth A, Abate C, Curran T and Davis RJ:
Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate
protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of
c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor
threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 266:15277–15285.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gurung D, Danielson JA, Tasnim A, Zhang
JT, Zou Y and Liu JY: Proline Isomerization: From the chemistry and
biology to therapeutic opportunities. Biology (Basel).
12(1008)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu KP, Hanes SD and Hunter T: A human
peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis.
Nature. 380:544–547. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
El Boustani M, De Stefano L, Caligiuri I,
Mouawad N, Granchi C, Canzonieri V, Tuccinardi T, Giordano A and
Rizzolio F: A Guide to PIN1 function and mutations across cancers.
Front Pharmacol. 9(1477)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rustighi A, Tiberi L, Soldano A, Napoli M,
Nuciforo P, Rosato A, Kaplan F, Capobianco A, Pece S, Di Fiore PP
and Del Sal G: The prolyl-isomerase Pin1 is a Notch1 target that
enhances Notch1 activation in cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 11:133–142.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ryo A, Liou YC, Wulf G, Nakamura M, Lee SW
and Lu KP: PIN1 is an E2F target gene essential for Neu/Ras-induced
transformation of mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol.
22:5281–5295. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
MacLachlan TK, Somasundaram K, Sgagias M,
Shifman Y, Muschel RJ, Cowan KH and El-Deiry WS: BRCA1 effects on
the cell cycle and the DNA damage response are linked to altered
gene expression. J Biol Chem. 275:2777–2785. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Luo ML, Gong C, Chen CH, Lee DY, Hu H,
Huang P, Yao Y, Guo W, Reinhardt F, Wulf G, et al: Prolyl isomerase
Pin1 acts downstream of miR200c to promote cancer stem-like cell
traits in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 74:3603–3616. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Eckerdt F, Yuan J, Saxena K, Martin B,
Kappel S, Lindenau C, Kramer A, Naumann S, Daum S, Fischer G, et
al: Polo-like kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation stabilizes Pin1 by
inhibiting its ubiquitination in human cells. J Biol Chem.
280:36575–36583. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen CH, Chang CC, Lee TH, Luo M, Huang P,
Liao PH, Wei S, Li FA, Chen RH, Zhou XZ, et al: SENP1 deSUMOylates
and regulates Pin1 protein activity and cellular function. Cancer
Res. 73:3951–3962. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hamdane M, Dourlen P, Bretteville A, Sambo
AV, Ferreira S, Ando K, Kerdraon O, Bégard S, Geay L, Lippens G, et
al: Pin1 allows for differential Tau dephosphorylation in neuronal
cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 32:155–160. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liou YC, Sun A, Ryo A, Zhou XZ, Yu ZX,
Huang HK, Uchida T, Bronson R, Bing G, Li X, et al: Role of the
prolyl isomerase Pin1 in protecting against age-dependent
neurodegeneration. Nature. 424:556–561. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fahed G, Aoun L, Bou Zerdan M, Allam S,
Bou Zerdan M, Bouferraa Y and Assi HI: Metabolic Syndrome: Updates
on pathophysiology and management in 2021. Int J Mol Sci.
23(786)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Saltiel AR: Insulin signaling in health
and disease. J Clin Invest. 131(e142241)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nakatsu Y, Mori K, Matsunaga Y, Yamamotoya
T, Ueda K, Inoue Y, Mitsuzaki-Miyoshi K, Sakoda H, Fujishiro M,
Yamaguchi S, et al: The prolyl isomerase Pin1 increases β-cell
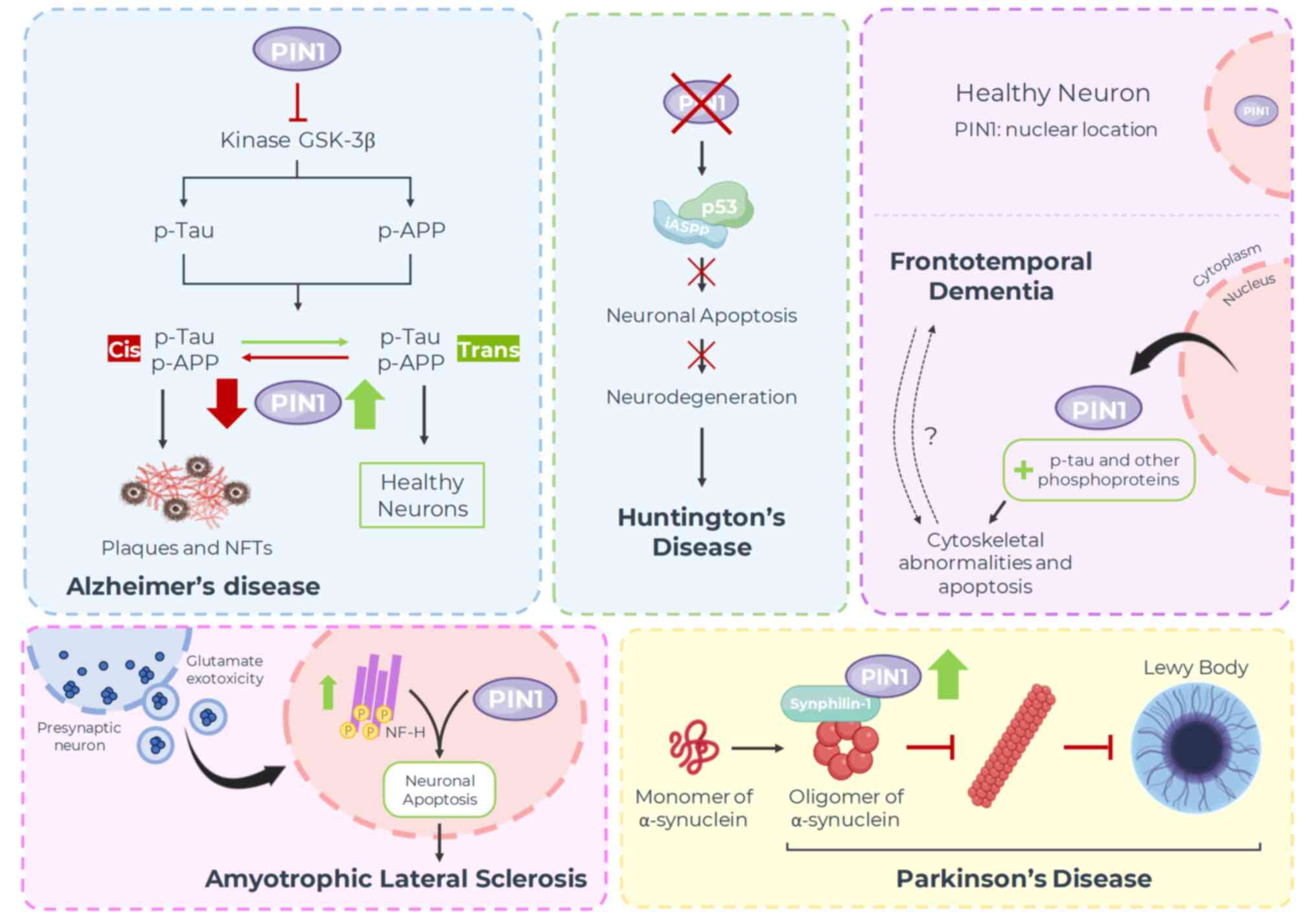
proliferation and enhances insulin secretion. J Biol Chem.
292:11886–11895. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Inoue MK, Nakatsu Y, Yamamotoya T, Hasei
S, Kanamoto M, Naitou M, Matsunaga Y, Sakoda H, Fujishiro M, Ono H,
et al: Pin1 plays essential roles in NASH development by modulating
multiple target proteins. Cells. 8(1545)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Han Y, Lee SH, Bahn M, Yeo CY and Lee KY:
Pin1 enhances adipocyte differentiation by positively regulating
the transcriptional activity of PPARγ. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
436:150–158. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nakatsu Y and Asano T: Prolyl isomerase
Pin1 impacts on metabolism in muscle and adipocytes. Yakugaku
Zasshi. 142:449–456. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Japanese).
|
|
20
|
Kanna M, Nakatsu Y, Yamamotoya T,
Kushiyama A, Fujishiro M, Sakoda H, Ono H, Arihiro K and Asano T:
Hepatic Pin1 expression, particularly in nuclei, is increased in
NASH patients in accordance with evidence of the role of Pin1 in
lipid accumulation shown in hepatoma cell lines. Int J Mol Sci.
24(8847)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Azeez TA: Osteoporosis and cardiovascular
disease: A review. Mol Biol Rep. 50:1753–1763. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu J, Yu L, Liu F, Wan L and Deng Z: The
effect of cytokines on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone
remodeling in osteoporosis: A review. Front Immunol.
14(1222129)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Islam R, Yoon WJ and Ryoo HM: Pin1, the
master orchestrator of bone cell differentiation. J Cell Physiol.
232:2339–2347. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Park KR, Kim S, Cho M, Kang SW and Yun HM:
Effects of PIN on osteoblast differentiation and matrix
mineralization through runt-related transcription factor. Int J Mol
Sci. 21(9579)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kurakula K, Hagdorn QAJ, van der Feen DE,
Vonk Noordegraaf A, Ten Dijke P, de Boer RA, Bogaard HJ, Goumans MJ
and Berger RMF: Inhibition of the prolyl isomerase Pin1 improves
endothelial function and attenuates vascular remodelling in
pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting TGF-β signalling.
Angiogenesis. 25:99–112. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shin HR, Bae HS, Kim BS, Yoon HI, Cho YD,
Kim WJ, Choi KY, Lee YS, Woo KM, Baek JH and Ryoo HM: PIN1 is a new
therapeutic target of craniosynostosis. Hum Mol Genet.
27:3827–3839. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee SH, Jeong HM, Han Y, Cheong H, Kang BY
and Lee KY: Prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates the osteogenic activity
of Osterix. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 400:32–40. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cho E, Lee JK, Lee JY, Chen Z, Ahn SH, Kim
ND, Kook MS, Min SH, Park BJ and Lee TH: BCPA {N,
N'-1,4-Butanediylbis[3-(2-chlorophenyl)acrylamide]} Inhibits
Osteoclast Differentiation through Increased Retention of
Peptidyl-Prolyl cis-trans Isomerase Never in Mitosis A-Interacting
1. Int J Mol Sci. 19(3436)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gao Y, Chen N, Fu Z and Zhang Q: Progress
of wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis. Biomolecules.
13(483)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li S, Cui Y, Li M, Zhang W, Sun X, Xin Z
and Li J: Acteoside derived from cistanche improves
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. J Invest Surg. 36(2154578)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao P, Xiao L, Peng J, Qian YQ and Huang
CC: Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
improve osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast proliferation via
MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:3962–3970.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yoshida G, Kawabata T, Takamatsu H, Saita
S, Nakamura S, Nishikawa K, Fujiwara M, Enokidani Y, Yamamuro T,
Tabata K, et al: Degradation of the NOTCH intracellular domain by
elevated autophagy in osteoblasts promotes osteoblast
differentiation and alleviates osteoporosis. Autophagy.
18:2323–2332. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vazgiourakis VM, Zervou MI, Papageorgiou
L, Chaniotis D, Spandidos DA, Vlachakis D, Eliopoulos E and
Goulielmos GN: Association of endometriosis with cardiovascular
disease: Genetic aspects (Review). Int J Mol Med.
51(29)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sarmah N, Nauli AM, Ally A and Nauli SM:
Interactions among endothelial nitric oxide synthase,
cardiovascular system, and nociception during physiological and
pathophysiological states. Molecules. 27(2835)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fagiani F, Vlachou M, Di Marino D,
Canobbio I, Romagnoli A, Racchi M, Govoni S and Lanni C: Pin1 as
molecular switch in vascular endothelium: Notes on its putative
role in age-associated vascular diseases. Cells.
10(3287)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kennard S, Ruan L, Buffett RJ, Fulton D
and Venema RC: TNFα reduces eNOS activity in endothelial cells
through serine 116 phosphorylation and Pin1 binding: Confirmation
of a direct, inhibitory interaction of Pin1 with eNOS. Vascul
Pharmacol. 81:61–68. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu M, Yu P, Jiang H, Yang X, Zhao J, Zou
Y and Ge J: TThe essential role of Pin1 via NF-κB signaling in
vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis in ApoE-/-Mice. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(644)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liang G, Wang S, Shao J, Jin YJ, Xu L, Yan
Y, Günther S, Wang L and Offermanns S: Tenascin-X mediates
Flow-induced suppression of EndMT and atherosclerosis. Circ Res.
130:1647–1659. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huminiecki L, Goldovsky L, Freilich S,
Moustakas A, Ouzounis C and Heldin CH: Emergence, development and
diversification of the TGF-beta signalling pathway within the
animal kingdom. BMC Evol Biol. 9(28)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gentile C, Muise-Helmericks RC and Drake
CJ: VEGF-mediated phosphorylation of eNOS regulates angioblast and
embryonic endothelial cell proliferation. Dev Biol. 373:163–175.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rai N, Sydykov A, Kojonazarov B, Wilhelm
J, Manaud G, Veeroju S, Ruppert C, Perros F, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann
N, et al: Targeting peptidyl-prolyl isomerase 1 in experimental
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J.
60(2101698)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim MR, Choi HS, Heo TH, Hwang SW and Kang
KW: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by
peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 in breast cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 369:547–553. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Toko H, Konstandin MH, Doroudgar S,
Ormachea L, Joyo E, Joyo AY, Din S, Gude NA, Collins B, Völkers M,
et al: Regulation of cardiac hypertrophic signaling by prolyl
isomerase Pin1. Circ Res. 112:1244–1252. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen Y, Wu YR, Yang HY, Li XZ, Jie MM, Hu
CJ, Wu YY, Yang SM and Yang YB: Prolyl isomerase Pin1: A promoter
of cancer and a target for therapy. Cell Death Dis.
9(883)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chuang HH, Zhen YY, Tsai YC, Chuang CH,
Huang MS, Hsiao M and Yang CJ: Targeting Pin1 for modulation of
cell motility and cancer therapy. Biomedicines.
9(359)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hanahan D: Hallmarks of cancer: New
dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12:31–46. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wu W, Xue X, Chen Y, Zheng N and Wang J:
Targeting prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a promising strategy to overcome
resistance to cancer therapies. Pharmacol Res.
184(106456)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Cohn GM, Liefwalker DF, Langer EM and
Sears RC: PIN1 provides dynamic control of MYC in response to
extrinsic signals. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8(224)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Nashaat S, Henen MA, El-Messery SM and
Eisa H: New benzimidazoles targeting breast cancer: Synthesis, Pin1
inhibition, 2D NMR binding, and computational studies. Molecules.
27(5245)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ueda K, Nakatsu Y, Yamamotoya T, Ono H,
Inoue Y, Inoue MK, Mizuno Y, Matsunaga Y, Kushiyama A, Sakoda H, et
al: Prolyl isomerase Pin1 binds to and stabilizes acetyl CoA
carboxylase 1 protein, thereby supporting cancer cell
proliferation. Oncotarget. 10:1637–1648. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Tan X, Zhou F, Wan J, Hang J, Chen Z, Li
B, Zhang C, Shao K, Jiang P, Shi S, et al: Pin1 expression
contributes to lung cancer: Prognosis and carcinogenesis. Cancer
Biol Ther. 9:111–119. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kim G, Bhattarai PY and Choi HS:
Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 as a
molecular target in breast cancer: A therapeutic perspective of
gynecological cancer. Arch Pharm Res. 42:128–139. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chen Y, Wu Y, Yu S, Yang H, Wang X, Zhang
Y, Zhu S, Jie M, Liu C, Li X, et al: Deficiency of microRNA-628-5p
promotes the progression of gastric cancer by upregulating PIN1.
Cell Death Dis. 11(559)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen M, Xia Y, Tan Y, Jiang G, Jin H and
Chen Y: Downregulation of microRNA-370 in esophageal squamous-cell
carcinoma is associated with cancer progression and promotes cancer
cell proliferation via upregulating PIN1. Gene. 661:68–77.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kuramochi J, Arai T, Ikeda S, Kumagai J,
Uetake H and Sugihara K: High Pin1 expression is associated with
tumor progression in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 94:155–160.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wang T, Liu Z, Shi F and Wang J: Pin1
modulates chemo-resistance by up-regulating FoxM1 and the
involvements of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cervical cancer.
Mol Cell Biochem. 413:179–187. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kim G, Bhattarai PY, Lim SC, Kim JY and
Choi HS: PIN1 facilitates ubiquitin-mediated degradation of
serine/threonine kinase 3 and promotes melanoma development via TAZ
activation. Cancer Lett. 499:164–174. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Maggio J, Cardama GA, Armando RG, Balcone
L, Sobol NT, Gomez DE and Mengual Gómez DL: Key role of PIN1 in
telomere maintenance and oncogenic behavior in a human glioblastoma
model. Oncol Rep. 49(91)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Li Q, Dong Z, Lin Y, Jia X, Li Q, Jiang H,
Wang L and Gao Y: The rs2233678 polymorphism in PIN1 promoter
region reduced cancer risk: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
8(e68148)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wulf G, Garg P, Liou YC, Iglehart D and Lu
KP: Modeling breast cancer in vivo and ex vivo reveals an essential
role of Pin1 in tumorigenesis. EMBO J. 23:3397–3407.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Takahashi K, Akiyama H, Shimazaki K,
Uchida C, Akiyama-Okunuki H, Tomita M, Fukumoto M and Uchida T:
Ablation of a peptidyl prolyl isomerase Pin1 from p53-null mice
accelerated thymic hyperplasia by increasing the level of the
intracellular form of Notch1. Oncogene. 26:3835–3845.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Girardini JE, Napoli M, Piazza S, Rustighi
A, Marotta C, Radaelli E, Capaci V, Jordan L, Quinlan P, Thompson
A, et al: A Pin1/mutant p53 axis promotes aggressiveness in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell. 20:79–91. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zucchi D, Silvagni E, Elefante E,
Signorini V, Cardelli C, Trentin F, Schilirò D, Cascarano G,
Valevich A, Bortoluzzi A and Tani C: Systemic lupus erythematosus:
One year in review 2023. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 41:997–1008.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Baek WY, Choi YS, Lee SW, Son IO, Jeon KW,
Choi SD and Suh CH: Toll-like receptor signaling inhibitory peptide
improves inflammation in animal model and human systemic lupus
erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. 22(12764)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Khoryati L, Augusto JF, Shipley E,
Contin-Bordes C, Douchet I, Mitrovic S, Truchetet ME, Lazaro E,
Duffau P, Couzi L, et al: IgE inhibits Toll-like receptor 7- and
Toll-like receptor 9-mediated expression of interferon-α by
plasmacytoid dendritic cells in patients with systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:2221–2231. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Salloum R and Niewold TB: Interferon
regulatory factors in human lupus pathogenesis. Transl Res.
157:326–331. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Tun-Kyi A, Finn G, Greenwood A, Nowak M,
Lee TH, Asara JM, Tsokos GC, Fitzgerald K, Israel E, Li X, et al:
Essential role for the prolyl isomerase Pin1 in Toll-like receptor
signaling and type I interferon-mediated immunity. Nat Immunol.
12:733–741. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wei S, Yoshida N, Finn G, Kozono S,
Nechama M, Kyttaris VC, Zhen Zhou X, Tsokos GC and Ping Lu K:
Pin1-Targeted therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 68:2503–2513. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Jacob N and Stohl W: Cytokine disturbances
in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther.
13(228)2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Ding J, Su S, You T, Xia T, Lin X, Chen Z
and Zhang L: Serum interleukin-6 level is correlated with the
disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis.
Clinics (Sao Paulo). 75(e1801)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Tackey E, Lipsky PE and Illei GG:
Rationale for interleukin-6 blockade in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Lupus. 13:339–343. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Takeno M, Gunn J, Suzuki JT, Kim NP, Kang
J, Finn TB, Vazirpour M, Martin W and Leung CJ: A novel role of
peptidyl-prolyl isomerase-1 as inducer of IL-6 expression in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J BioMedicine. 3:439–450.
2015.
|
|
74
|
Jang S, Kwon EJ and Lee JJ: Rheumatoid
arthritis: Pathogenic roles of diverse immune cells. Int J Mol Sci.
23(905)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Nagaoka A, Takizawa N, Takeuchi R, Inaba
Y, Saito I, Nagashima Y, Saito T and Aoki I: Possible involvement
of peptidylprolyl isomerase Pin1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Pathol
Int. 61:59–66. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Makarov SS: NF-kappa B in rheumatoid
arthritis: A pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and
tissue destruction. Arthritis Res. 3:200–206. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Araki Y and Mimura T: Matrix
metalloproteinase gene activation resulting from disordred
epigenetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
18(905)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Li X and Makarov SS: An essential role of
NF-kappaB in the ‘tumor-like’ phenotype of arthritic synoviocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17432–17437. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ma Y, Hong FF and Yang SL: Role of
prostaglandins in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol.
39:162–172. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Kondo N, Kuroda T and Kobayashi D:
Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int
J Mol Sci. 22(10922)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Jeong HG, Pokharel YR, Lim SC, Hwang YP,
Han EH, Yoon JH, Ahn SG, Lee KY and Kang KW: Novel role of Pin1
induction in type II collagen-mediated rheumatoid arthritis. J
Immunol. 183:6689–6697. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
M'Koma AE: Inflammatory bowel disease:
Clinical diagnosis and pharmaceutical management. Med Res Arch.
11(10)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Matsunaga Y, Hasei S, Yamamotoya T, Honda
H, Kushiyama A, Sakoda H, Fujishiro M, Ono H, Ito H, Okabe T, et
al: Pathological role of Pin1 in the development of DSS-Induced
colitis. Cells. 10(1230)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Shao BZ, Wang SL, Pan P, Yao J, Wu K, Li
ZS, Bai Y and Linghu EQ: Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome in
inflammatory bowel disease: Putting out the fire of inflammation.
Inflammation. 42:1147–1159. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Dong R, Xue Z, Fan G, Zhang N, Wang C, Li
G and Da Y: Pin1 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation by
phosphorylation of p38 MAPK pathway in septic shock. Front Immunol.
12(620238)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Dagenais A, Villalba-Guerrero C and
Olivier M: Trained immunity: A ‘new’ weapon in the fight against
infectious diseases. Front Immunol. 14(1147476)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kanna M, Nakatsu Y, Yamamotoya T, Encinas
J, Ito H, Okabe T, Asano T and Sakaguchi T: Roles of peptidyl
prolyl isomerase Pin1 in viral propagation. Front Cell Dev Biol.
10(1005325)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Stroh LJ and Krey T: Structural insights
into hepatitis C virus neutralization. Curr Opin Virol.
60(101316)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lim YS, Tran HT, Park SJ, Yim SA and Hwang
SB: Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a cellular factor required
for hepatitis C virus propagation. J Virol. 85:8777–8788.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Jeng WJ, Papatheodoridis GV and Lok ASF:
Hepatitis B. Lancet. 401:1039–1052. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Kojima Y and Ryo A: Pinning down viral
proteins: A new prototype for virus-host cell interaction. Front
Microbiol. 1(107)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Pang R, Lee TK, Poon RT, Fan ST, Wong KB,
Kwong YL and Tse E: Pin1 interacts with a specific serine-proline
motif of hepatitis B virus X-protein to enhance
hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 132:1088–1103.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Shang S, Hua F and Hu ZW: The regulation
of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic
opportunities. Oncotarget. 8:33972–33989. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Ao R, Zhang DR, Du YQ and Wang Y:
Expression and significance of Pin1, β-catenin and cyclin D1 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 10:1893–1898.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Nishi M, Miyakawa K, Matsunaga S, Khatun
H, Yamaoka Y, Watashi K, Sugiyama M, Kimura H, Wakita T and Ryo A:
Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 regulates the stability of hepatitis B virus
core protein. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8(26)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Kwon H, Kim J, Song C, Sajjad MA, Ha J,
Jung J, Park S, Shin HJ and Kim K: Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans
isomerase Pin1 interacts with hepatitis B virus core particle, but
not with HBc protein, to promote HBV replication. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 13(1195063)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Womack J and Jimenez M: Common questions
about infectious mononucleosis. Am Fam Physician. 91:372–376.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hutcheson RL, Chakravorty A and Sugden B:
Burkitt lymphomas evolve to escape dependencies on Epstein-Barr
virus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 10(606412)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Narita Y, Murata T, Ryo A, Kawashima D,
Sugimoto A, Kanda T, Kimura H and Tsurumi T: Pin1 interacts with
the Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase catalytic subunit and
regulates viral DNA replication. J Virol. 87:2120–2127.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Chang ET, Ye W, Zeng YX and Adami HO: The
evolving epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 30:1035–1047. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Xu M, Cheung CC, Chow C, Lun SW, Cheung ST
and Lo KW: Overexpression of PIN1 enhances cancer growth and
aggressiveness with cyclin D1 induction in EBV-Associated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 11(e0156833)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Yu JH, Im CY and Min SH: Function of PIN1
in cancer development and its inhibitors as cancer therapeutics.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 8(120)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Letafati A, Soheili R, Norouzi M,
Soleimani P and Mozhgani SH: Therapeutic approaches for
HTLV-1-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: A comprehensive
review. Med Oncol. 40(295)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Ernzen KJ and Panfil AR: Regulation of
HTLV-1 transformation. Biosci Rep. 42(BSR20211921)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Peloponese JM Jr, Yasunaga J, Kinjo T,
Watashi K and Jeang KT: Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerase Pin1
interacts with human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax and modulates
its activation of NF-kappaB. J Virol. 83:3238–3248. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Jeong SJ, Ryo A and Yamamoto N: The prolyl
isomerase Pin1 stabilizes the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
(HTLV-1) Tax oncoprotein and promotes malignant transformation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 381:294–299. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Mesnard JM, Barbeau B, Cesaire R and
Peloponese JM: Roles of HTLV-1 basic zip factor (HBZ) in viral
chronicity and leukemic transformation. Potential new therapeutic
approaches to prevent and treat HTLV-1-related diseases. Viruses.
7:6490–6505. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Szymonowicz KA and Chen J: Biological and
clinical aspects of HPV-related cancers. Cancer Biol Med.
17:864–878. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Fowler JR, Maani EV, Dunton CJ and Jack
BW: Cervical Cancer. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL)
ineligible companies. Disclosure: Elizabeth Maani declares no
relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Charles Dunton declares no relevant financial
relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Brian Jack
declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible
companies, 2023.
|
|
110
|
McBride AA: The papillomavirus E2
proteins. Virology. 445:57–79. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Hareza DA, Wilczynski JR and Paradowska E:
Human papillomaviruses as infectious agents in gynecological
cancers. Oncogenic properties of viral proteins. Int J Mol Sci.
23(1818)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Prabhavathy D, Vijayalakshmi R, Kanchana
MP and Karunagaran D: HHPV16 E2 enhances the expression of NF-κB
and STAT3 target genes and potentiates NF-κB activation by
inflammatory mediators. Cell Immunol. 292:70–77. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Masenga SK, Mweene BC, Luwaya E, Muchaili
L, Chona M and Kirabo A: HIV-Host Cell Interactions. Cells.
12(1351)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Sarkar S, Balakrishnan K, Chintala K,
Chintala K, Mohareer K, Luedde T, Vasudevan AAJ, Münk C and
Banerjee S: Tough Way In, Tough Way Out: The complex interplay of
host and viral factors in nucleocytoplasmic trafficking during
HIV-1 infection. Viruses. 14(2503)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Watashi K, Khan M, Yedavalli VR, Yeung ML,
Strebel K and Jeang KT: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1
replication and regulation of APOBEC3G by peptidyl prolyl isomerase
Pin1. J Virol. 82:9928–9936. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Saleh S, Lu HK, Evans V, Harisson D, Zhou
J, Jaworowski A, Sallmann G, Cheong KY, Mota TM, Tennakoon S, et
al: HIV integration and the establishment of latency in
CCL19-treated resting CD4(+) T cells require activation of NF-κB.
Retrovirology. 13(49)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Dochi T, Nakano T, Inoue M, Takamune N,
Shoji S, Sano K and Misumi S: Phosphorylation of human
immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid protein at serine 16, required
for peptidyl-prolyl isomerase-dependent uncoating, is mediated by
virion-incorporated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. J Gen
Virol. 95:1156–1166. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Rossi E, Meuser ME, Cunanan CJ and Cocklin
S: Structure, function, and interactions of the HIV-1 Capsid
Protein. Life (Basel). 11(100)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Bao Q and Zhou J: Various strategies for
developing APOBEC3G protectors to circumvent human immunodeficiency
virus type 1. Eur J Med Chem. 250(115188)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P and Shi ZL:
Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol.
19:141–154. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Yamamotoya T, Nakatsu Y, Kanna M, Hasei S,
Ohata Y, Encinas J, Ito H, Okabe T, Asano T and Sakaguchi T: Prolyl
isomerase Pin1 plays an essential role in SARS-CoV-2 proliferation,
indicating its possibility as a novel therapeutic target. Sci Rep.
11(18581)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Ino Y, Nishi M, Yamaoka Y, Miyakawa K,
Jeremiah SS, Osada M, Kimura Y and Ryo A: Phosphopeptide enrichment
using Phos-tag technology reveals functional phosphorylation of the
nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2. J Proteomics.
255(104501)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Ye H, Robak LA, Yu M, Cykowski M and
Shulman JM: Genetics and pathogenesis of Parkinson's syndrome. Annu
Rev Pathol. 18:95–121. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Hallacli E, Kayatekin C, Nazeen S, Wang
XH, Sheinkopf Z, Sathyakumar S, Sarkar S, Jiang X, Dong X, Di Maio
R, et al: The Parkinson's disease protein alpha-synuclein is a
modulator of processing bodies and mRNA stability. Cell.
185:2035–2056 e2033. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Gao V, Briano JA, Komer LE and Burre J:
Functional and Pathological Effects of α-Synuclein on Synaptic
SNARE Complexes. J Mol Biol. 435(167714)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Carvajal-Oliveros A, Dominguez-Baleon C,
Sanchez-Diaz I, Zambrano-Tipan D, Hernández-Vargas R, Campusano JM,
Narváez-Padilla V and Reynaud E: Parkinsonian phenotypes induced by
Synphilin-1 expression are differentially contributed by
serotonergic and dopaminergic circuits and suppressed by nicotine
treatment. PLoS One. 18(e0282348)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Ghosh A, Saminathan H, Kanthasamy A,
Anantharam V, Jin H, Sondarva G, Harischandra DS, Qian Z, Rana A
and Kanthasamy AG: The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 up-regulation
and proapoptotic function in dopaminergic neurons: Relevance to the
pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem. 288:21955–21971.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Ryo A, Togo T, Nakai T, Hirai A, Nishi M,
Yamaguchi A, Suzuki K, Hirayasu Y, Kobayashi H, Perrem K, et al:
Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 accumulates in lewy bodies of parkinson
disease and facilitates formation of alpha-synuclein inclusions. J
Biol Chem. 281:4117–4125. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Weller J and Budson A: Current
understanding of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and treatment.
F1000Res 7: Faculty Rev-1161, 2018.
|
|
130
|
Karran E and De Strooper B: The amyloid
hypothesis in Alzheimer disease: New insights from new
therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:306–318. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Ma C, Hong F and Yang S: Amyloidosis in
Alzheimer's Disease: Pathogeny, etiology, and related therapeutic
directions. Molecules. 27(1210)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Bianchi M and Manco M: Pin1 modulation in
physiological status and neurodegeneration. Any contribution to the
pathogenesis of type 3 diabetes? Int J Mol Sci.
19(2319)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Wang SC, Hu XM and Xiong K: The regulatory
role of Pin1 in neuronal death. Neural Regen Res. 18:74–80.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Fagiani F, Govoni S, Racchi M and Lanni C:
The Peptidyl-prolyl Isomerase Pin1 in neuronal Signaling: From
neurodevelopment to neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 58:1062–1073.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Palaiogeorgou AM, Papakonstantinou E,
Golfinopoulou R, Sigala M, Mitsis T, Papageorgiou L, Diakou I,
Pierouli K, Dragoumani K, Spandidos DA, et al: Recent approaches on
Huntington's disease (Review). Biomed Rep. 18(5)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
D'Egidio F, Castelli V, Cimini A and
d'Angelo M: Cell rearrangement and oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in
huntington's disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 12(571)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Pereira CAS, Medaglia NC, Ureshino RP,
Bincoletto C, Antonioli M, Fimia GM, Piacentini M, Pereira GJDS,
Erustes AG and Smaili SS: NAADP-Evoked Ca2+ signaling
leads to mutant huntingtin aggregation and autophagy impairment in
murine astrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 24(5593)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Sap KA, Geijtenbeek KW, Schipper-Krom S,
Guler AT and Reits EA: Ubiquitin-modifying enzymes in Huntington's
disease. Front Mol Biosci. 10(1107323)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Napoli M, Girardini JE, Piazza S and Del
Sal G: Wiring the oncogenic circuitry: Pin1 unleashes mutant p53.
Oncotarget. 2:654–656. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Steger M, Murina O, Hühn D, Ferretti LP,
Walser R, Hänggi K, Lafranchi L, Neugebauer C, Paliwal S, Janscak
P, et al: Prolyl isomerase PIN1 regulates DNA double-strand break
repair by counteracting DNA end resection. Mol Cell. 50:333–343.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Ulugut H and Pijnenburg YAL:
Frontotemporal dementia: Past, present, and future. Alzheimers
Dement. 19:5253–5263. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Thorpe JR, Mosaheb S, Hashemzadeh-Bonehi
L, Cairns NJ, Kay JE, Morley SJ and Rulten SL: Shortfalls in the
peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase protein Pin1 in neurons are
associated with frontotemporal dementias. Neurobiol Dis.
17:237–249. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Cataldo AM, Peterhoff CM, Troncoso JC,
Gomez-Isla T, Hyman BT and Nixon RA: Endocytic pathway
abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic
Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome: Differential effects of APOE
genotype and presenilin mutations. Am J Pathol. 157:277–286.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Husseman JW, Nochlin D and Vincent I:
Mitotic activation: A convergent mechanism for a cohort of
neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging. 21:815–828.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Mead RJ, Shan N, Reiser HJ, Marshall F and
Shaw PJ: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A neurodegenerative
disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 22:185–212. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Iridoy MO, Zubiri I, Zelaya MV, Martinez
L, Ausín K, Lachen-Montes M, Santamaría E, Fernandez-Irigoyen J and
Jericó I: Neuroanatomical quantitative proteomics reveals common
pathogenic biological routes between amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Int J Mol Sci.
20(4)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Perrot R and Eyer J: Neuronal intermediate
filaments and neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res Bull.
80:282–295. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Kesavapany S, Patel V, Zheng YL, Pareek
TK, Bjelogrlic M, Albers W, Amin N, Jaffe H, Gutkind JS, Strong MJ,
et al: Inhibition of Pin1 reduces glutamate-induced perikaryal
accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilament-H in neurons. Mol Biol
Cell. 18:3645–3655. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Chao SH, Greenleaf AL and Price DH:
Juglone, an inhibitor of the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1, also
directly blocks transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:767–773.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Xi L, Wang Y, He Q, Zhang Q and Du L:
Interaction between Pin1 and its natural product inhibitor
epigallocatechin-3-gallate by spectroscopy and molecular dynamics
simulations. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 169:134–143.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Bayer E, Thutewohl M, Christner C, Tradler
T, Osterkamp F, Waldmann H and Bayer P: Identification of hPin1
inhibitors that induce apoptosis in a mammalian Ras transformed
cell line. Chem Commun (Camb). 516–518. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Jiang B and Pei D: A selective,
cell-permeable nonphosphorylated bicyclic peptidyl inhibitor
against Peptidyl-Prolyl isomerase Pin1. J Med Chem. 58:6306–6312.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
He S, Li L, Jin R and Lu X: Biological
function of Pin1 in vivo and its inhibitors for preclinical study:
Early development, current strategies, and future directions. J Med
Chem. 66:9251–9277. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Guo C, Hou X, Dong L, Dagostino E,
Greasley S, Ferre R, Marakovits J, Johnson MC, Matthews D,
Mroczkowski B, et al: Structure-based design of novel human Pin1
inhibitors (I). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:5613–5616. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Russo Spena C, De Stefano L, Poli G,
Granchi C, El Boustani M, Ecca F, Grassi G, Grassi M, Canzonieri V,
Giordano A, et al: Virtual screening identifies a PIN1 inhibitor
with possible antiovarian cancer effects. J Cell Physiol.
234:15708–15716. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Campaner E, Rustighi A, Zannini A,
Cristiani A, Piazza S, Ciani Y, Kalid O, Golan G, Baloglu E,
Shacham S, et al: A covalent PIN1 inhibitor selectively targets
cancer cells by a dual mechanism of action. Nat Commun.
8(15772)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Liu L, Zhu R, Li J, Pei Y, Wang S, Xu P,
Wang M, Wen Y, Zhang H, Du D, et al: Computational and
structure-based development of high potent cell-active covalent
inhibitor targeting the Peptidyl-Prolyl isomerase
NIMA-Interacting-1 (Pin1). J Med Chem. 65:2174–2190.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Born A, Henen MA and Vogeli B: Activity
and Affinity of Pin1 Variants. Molecules. 25:2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Liou YC, Noel JP and Lu
KP: Critical role of WW domain phosphorylation in regulating
phosphoserine binding activity and Pin1 function. J Biol Chem.
277:2381–2384. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Verdecia MA, Bowman ME, Lu KP, Hunter T
and Noel JP: Structural basis for phosphoserine-proline recognition
by group IV WW domains. Nat Struct Biol. 7:639–643. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Wang JZ, Xi L, Lin T, Wang Y, Zhu GF and
Du LF: The structural and functional role of the three tryptophan
residues in Pin1. J Photochem Photobiol B. 146:58–67.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Li K, Li L, Wang S, Li X, Ma T, Liu D,
Jing Y and Zhao L: Design and synthesis of novel 2-substituted
11-keto-boswellic acid heterocyclic derivatives as anti-prostate
cancer agents with Pin1 inhibition ability. Eur J Med Chem.
126:910–919. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Maggio J, Cabrera M, Armando R, Chinestrad
P, Pifano M, Menna PL, Gomez DE and Gómez DLM: Rational design of
PIN1 inhibitors for cancer treatment based on conformational
diversity analysis and docking based virtual screening. J Biomol
Struct Dyn. 40:5858–5867. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|