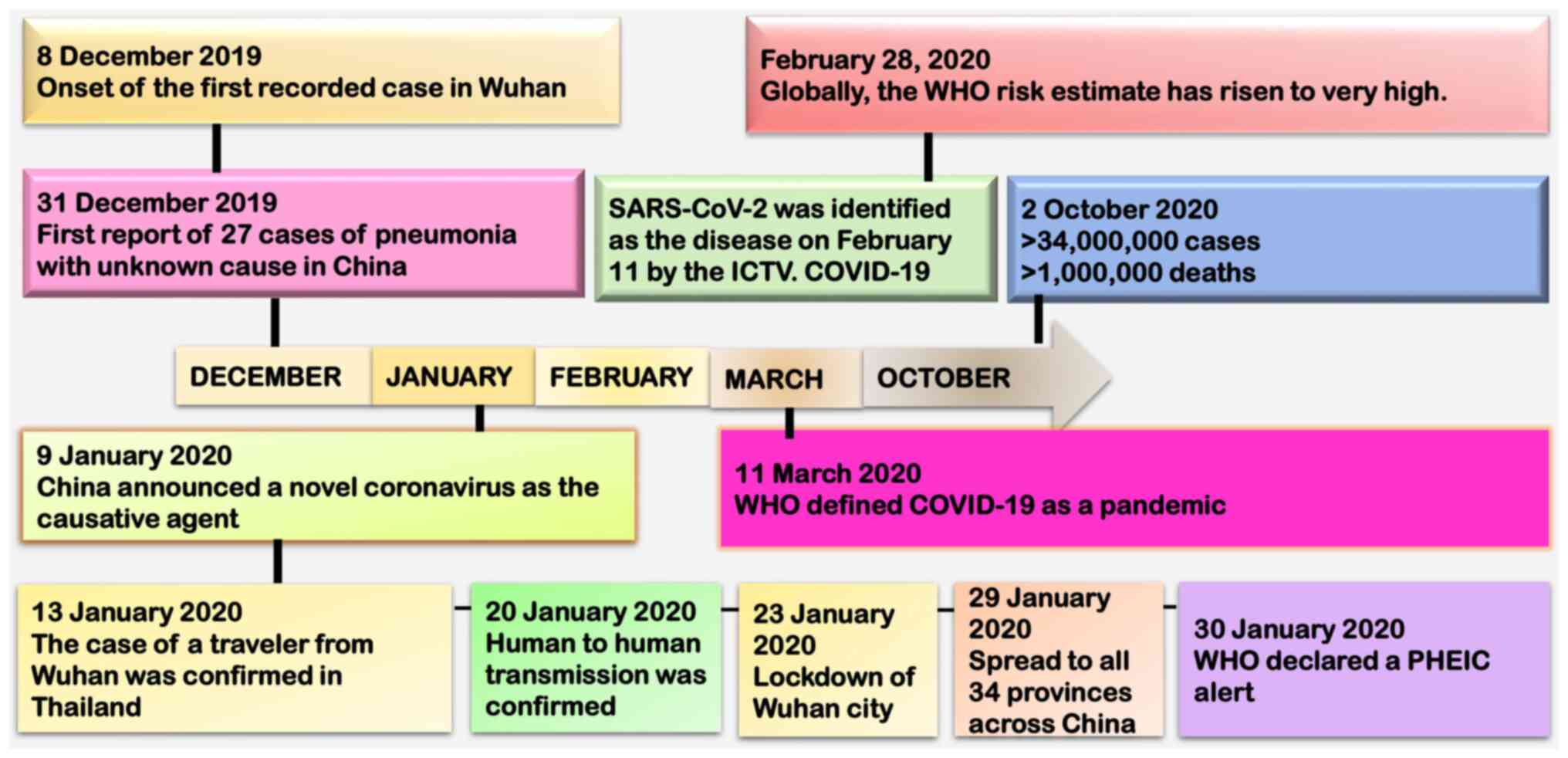
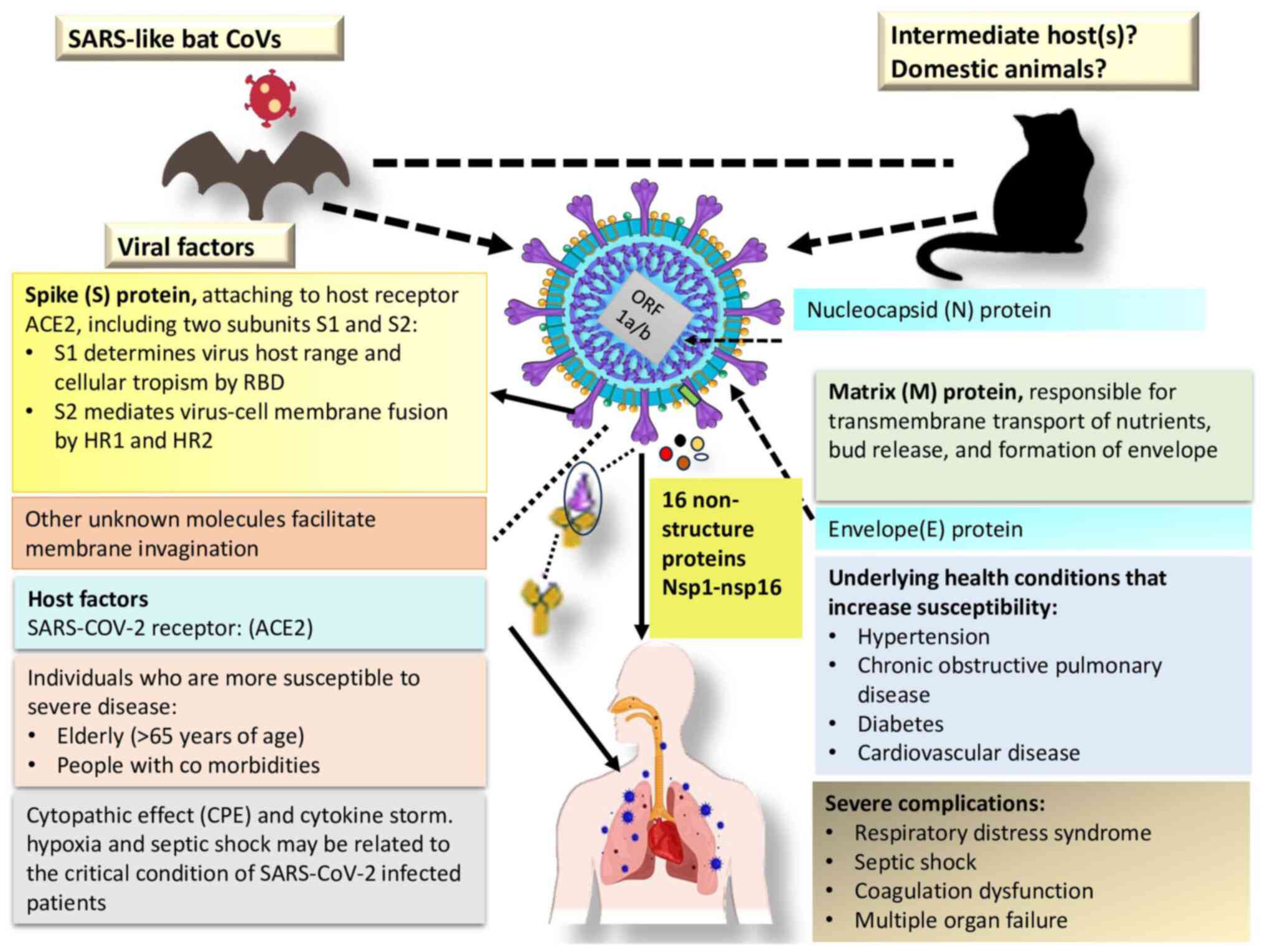
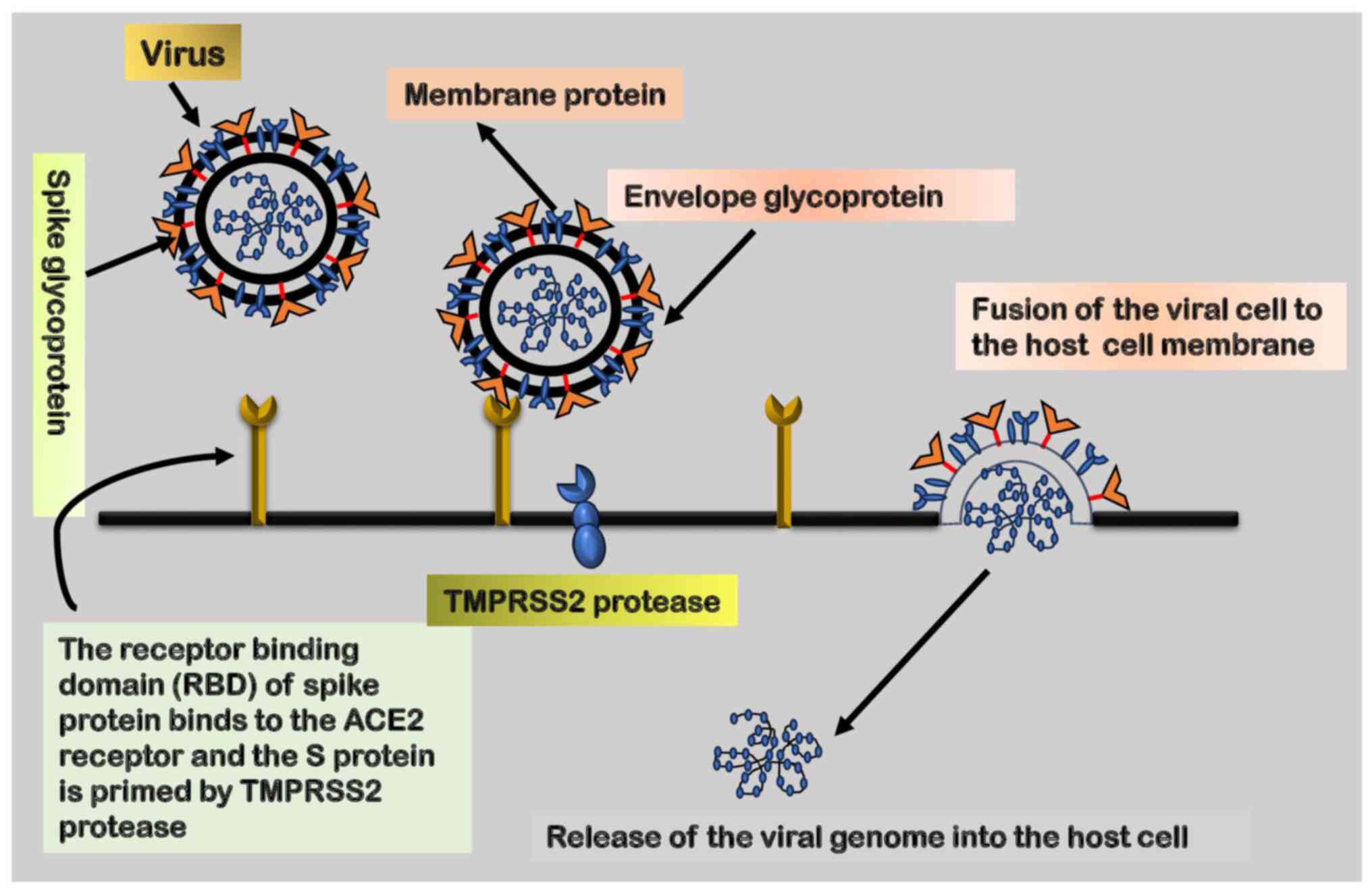
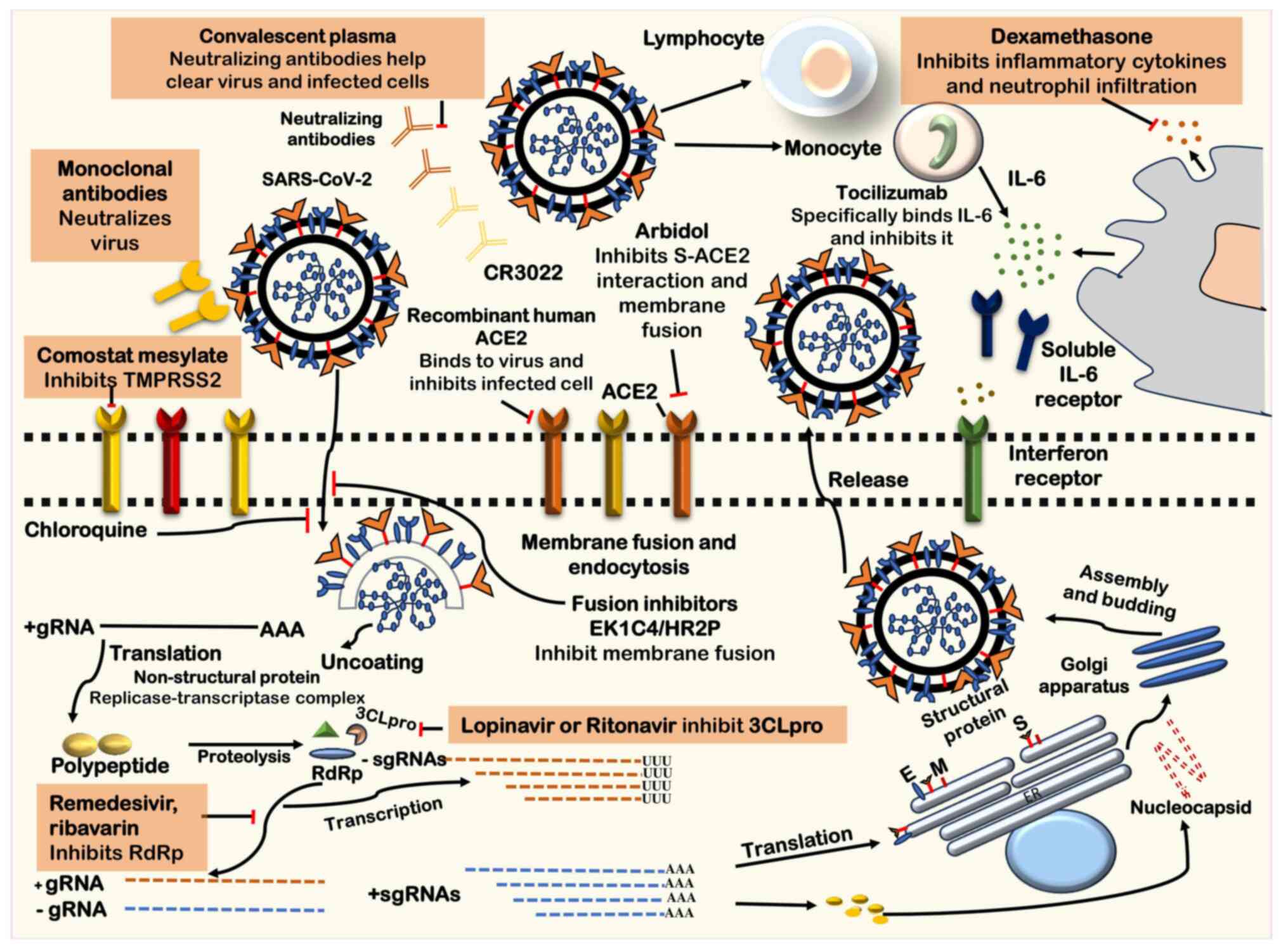
|
1
|
Cheval S, Adamescu CM, Georgiadis T,
Herrnegger M, Piticar A and Legates DR: Observed and potential
impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the environment. Int J Environ
Res Public Health. 17(4140)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Woolhouse ME, Adair K and Brierley L: RNA
viruses: A case study of the biology of emerging infectious
diseases. Microbiol Spectr.
1(10.1128/microbiolspec.OH-0001-2012)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Markov PV, Ghafari M, Beer M, Lythgoe K,
Simmonds P, Stilianakis NI and Katzourakis A: The evolution of
SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 21:361–379. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chakraborty C, Chatterjee S, Bhattacharya
M, Chopra H, Bhattacharya P, Islam MA and Dhama K: The D614G
mutation helps to increase the transmissibility and reduce the
virulence of SARS-CoV-2 variants through natural selection. Int J
Surg. 109:171–174. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lythgoe KA, Hall M, Ferretti L, de Cesare
M, MacIntyre-Cockett G, Trebes A, Andersson M, Otecko N, Wise EL,
Moore N, et al: SARS-CoV-2 within-host diversity and transmission.
Science. 372(eabg0821)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wacharapluesadee S, Tan CW, Maneeorn P,
Duengkae P, Zhu F, Joyjinda Y, Kaewpom T, Chia WN, Ampoot W, Lim
BL, et al: Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 related coronaviruses
circulating in bats and pangolins in Southeast Asia. Nat Commun.
12(972)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
She J, Jiang J, Ye L, Hu L, Bai C and Song
Y: 2019 novel coronavirus of pneumonia in Wuhan, China: Emerging
attack and management strategies. Clin Transl Med.
9(19)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P and Shi ZL:
Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol.
19:141–154. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Worobey M, Levy JI, Malpica Serrano L,
Crits-Christoph A, Pekar JE, Goldstein SA, Rasmussen AL, Kraemer
MUG, Newman C, Koopmans MPG, et al: The huanan seafood wholesale
market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Science. 377:951–959. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Reis J, Le Faou A, Buguet A, Sandner G and
Spencer P: Covid-19: Early cases and disease spread. Ann Glob
Health. 88(83)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: A novel coronavirus from
patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–733.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gralinski LE and Menachery VD: Return of
the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses. 12(135)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Eurosurveillance Editorial Team. Note from
the editors: World Health Organization declares novel coronavirus
(2019-nCoV) sixth public health emergency of international concern.
Euro Surveill. 25(200131e)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Coronaviridae Study Group of the
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species severe
acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying
2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat Microbiol. 5:536–544.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zanin M, Xiao C, Liang T, Ling S, Zhao F,
Huang Z, Lin F, Lin X, Jiang Z and Wong SS: The public health
response to the COVID-19 outbreak in mainland China: A narrative
review. J Thorac Dis. 12:4434–4449. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Deng SQ and Peng HJ: Characteristics of
and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019
outbreak in China. J Clin Med. 9(575)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
World Health Organization: Coronavirus
disease 2019 (COVID-19). Situation report-51, 2020. Available at:
https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200311-sitrep-51-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=1ba62e57_10.
|
|
18
|
Deslandes A, Berti V, Tandjaoui-Lambotte
Y, Alloui C, Carbonnelle E, Zahar JR, Brichler S and Cohen Y:
SARS-CoV-2 was already spreading in France in late December 2019.
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 55(106006)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pal M, Berhanu G, Desalegn C and Kandi V:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An
update. Cureus. 12(e7423)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH,
Holbrook MG, Gamble A, Williamson BN, Tamin A, Harcourt JL,
Thornburg NJ, Gerber SI, et al: Aerosol and surface stability of
SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med.
382:1564–1567. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aboubakr HA, Sharafeldin TA and Goyal SM:
Stability of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses in the environment
and on common touch surfaces and the influence of climatic
conditions: A review. Transbound Emerg Dis. 68:296–312.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kasloff SB, Leung A, Strong JE, Funk D and
Cutts T: Stability of SARS-CoV-2 on critical personal protective
equipment. Sci Rep. 11(984)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lauer SA, Grantz KH, Bi Q, Jones FK, Zheng
Q, Meredith HR, Azman AS, Reich NG and Lessler J: The incubation
period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly
reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application. Ann Intern
Med. 172:577–582. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu Y, Kang L, Guo Z, Liu J, Liu M and
Liang W: Incubation period of COVID-19 caused by unique SARS-CoV-2
strains: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open.
5(e2228008)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huang SW and Wang SF: SARS-CoV-2 entry
related viral and host genetic variations: Implications on COVID-19
severity, immune escape, and infectivity. Int J Mol Sci.
22(3060)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Men K, Li Y, Wang X, Zhang G, Hu J, Gao Y,
Han A, Liu W and Han H: Estimate the incubation period of
coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). Comput Biol Med.
158(106794)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Batra A, Clark JR, Kang AK, Ali S, Patel
TR, Shlobin NA, Hoffman SC, Lim PH, Orban ZS, Visvabharathy L, et
al: Persistent viral RNA shedding of SARS-CoV-2 is associated with
delirium incidence and six-month mortality in hospitalized COVID-19
patients. Geroscience. 44:1241–1254. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Boni MF, Lemey P, Jiang X, Lam TT, Perry
BW, Castoe TA, Rambaut A and Robertson DL: Evolutionary origins of
the SARS-CoV-2 sarbecovirus lineage responsible for the COVID-19
pandemic. Nat Microbiol. 5:1408–1417. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen YM, Wang W, Song
ZG, Hu Y, Tao ZW, Tian JH, Pei YY, et al: A new coronavirus
associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature.
579:265–269. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He B, Zhang Y, Xu L, Yang W, Yang F, Feng
Y, Xia L, Zhou J, Zhen W, Feng Y, et al: Identification of diverse
alphacoronaviruses and genomic characterization of a novel severe
acute respiratory syndrome-like coronavirus from bats in China. J
Virol. 88:7070–7082. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zheng J: SARS-CoV-2: An emerging
coronavirus that causes a global threat. Int J Biol Sci.
16:1678–1685. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Temmam S, Vongphayloth K, Baquero E,
Munier S, Bonomi M, Regnault B, Douangboubpha B, Karami Y, Chrétien
D, Sanamxay D, et al: Author Correction: Bat coronaviruses related
to SARS-CoV-2 and infectious for human cells. Nature.
607(E19)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou H, Chen X, Hu T, Li J, Song H, Liu Y,
Wang P, Liu D, Yang J, Holmes EC, et al: A novel bat coronavirus
closely related to SARS-CoV-2 contains natural insertions at the
S1/S2 cleavage site of the spike protein. Curr Biol.
30:2196–2203.e3. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou H, Ji J, Chen X, Bi Y, Li J, Wang Q,
Hu T, Song H, Zhao R, Chen Y, et al: Identification of novel bat
coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2
and related viruses. Cell. 184:4380–4391. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou H, Fan S,
Zhang Q, Shi X, Wang Q, Zhang L and Wang X: Structure of the
SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2
receptor. Nature. 581:215–220. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Li X, Li T, Zhang S, Wang L, Wu X
and Liu J: The genetic sequence, origin, and diagnosis of
SARS-CoV-2. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 39:1629–1635.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nie J, Li Q, Zhang L, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Li
T, Wu J, Liu S, Zhang M, Zhao C, et al: Functional comparison of
SARS-CoV-2 with closely related pangolin and bat coronaviruses.
Cell Discov. 7(21)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yi C, Sun X, Ye J, Ding L, Liu M, Yang Z,
Lu X, Zhang Y, Ma L, Gu W, et al: Key residues of the receptor
binding motif in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 that interact with
ACE2 and neutralizing antibodies. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:621–630.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang S, Qiao S, Yu J, Zeng J, Shan S,
Tian L, Lan J, Zhang L and Wang X: Bat and pangolin coronavirus
spike glycoprotein structures provide insights into SARS-CoV-2
evolution. Nat Commun. 12(1607)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sharun K, Dhama K, Pawde AM, Gortázar C,
Tiwari R, Bonilla-Aldana DK, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, de la Fuente J,
Michalak I and Attia YA: SARS-CoV-2 in animals: Potential for
unknown reservoir hosts and public health implications. Vet Q.
41:181–201. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dhama K, Khan S, Tiwari R, Sircar S, Bhat
S, Malik YS, Singh KP, Chaicumpa W, Bonilla-Aldana DK and
Rodriguez-Morales AJ: Coronavirus disease 2019-COVID-19. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 33:e00028–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
De Wit E, Van Doremalen N, Falzarano D and
Munster VJ: SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging
coronaviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol. 14:523–534. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cui J, Li F and Shi ZL: Origin and
evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol.
17:181–192. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS and Li
F: Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An
analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS
coronavirus. J Virol. 94:e00127–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Banerjee A, Doxey AC, Mossman K and Irving
AT: Unraveling the zoonotic origin and transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
Trends Ecol Evol. 36:180–184. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Focosi D and Maggi F: Recombination in
coronaviruses, with a focus on SARS-CoV-2. Viruses.
14(1239)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C,
Huang B, Liu R, He X, Shuai L, Sun Z, et al: Susceptibility of
ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to
SARS-coronavirus 2. Science. 368:1016–1020. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Oreshkova N, Molenaar RJ, Vreman S,
Harders F, Oude Munnink BB, Hakze-van der Honing RW, Gerhards N,
Tolsma P, Bouwstra R, Sikkema RS, et al: SARS-CoV-2 infection in
farmed minks, the Netherlands, April and May 2020. Euro Surveill.
25(2001005)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sit TH, Brackman CJ, Ip SM, Tam KWS, Law
PYT, To EMW, Yu VYT, Sims LD, Tsang DNC, Chu DKW, et al: Canine
SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature. 586:776–778. 2020.
|
|
50
|
Zhang Q, Zhang H, Gao J, Huang K, Yang Y,
Hui X, He X, Li C, Gong W, Zhang Y, et al: A serological survey of
SARS-CoV-2 in cats in Wuhan. Emerg Microbes Infect. 9:2013–2019.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Fehr AR and Perlman S: Coronaviruses: An
overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol.
1282:1–23. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Mohan SV, Hemalatha M, Kopperi H, Ranjith
I and Kumar AK: SARS-CoV-2 in environmental perspective:
Occurrence, persistence, surveillance, inactivation and challenges.
Chem Eng J. 405(126893)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu DX, Liang JQ and Fung TS: Human
coronavirus-229E, -OC43, -NL63, and -HKU1 (Coronaviridae).
Encyclopedia Virol. (428)2021.
|
|
54
|
Wen C, Sun L, Zhao MC, Duan SX, Wang L and
Cui XW: Clinical study of human coronavirus NL63, OC43, 229E, HKU1
infections in hospitalized children from 2015 to 2020. Infect Drug
Resist. 15:1093–1101. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Rastogi M, Pandey N, Shukla A and Singh
SK: SARS coronavirus 2: From genome to infectome. Respir Res.
21:318. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhu Z, Lian X, Su X, Wu W, Marraro GA and
Zeng Y: From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: A brief summary and
comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three
highly pathogenic human coronaviruses. Respir Res.
21(224)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bourgonje AR, Abdulle AE, Timens W,
Hillebrands JL, Navis GJ, Gordijn SJ, Bolling MC, Dijkstra G, Voors
AA, Osterhaus AD, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2),
SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19). J Pathol. 251:228–248. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q,
Zhong JC, Turner AJ, Raizada MK, Grant MB and Oudit GY:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator
of the renin-angiotensin system: Celebrating the 20th anniversary
of the discovery of ACE2. Circ Res. 126:1456–1474. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Petrosillo N, Viceconte G, Ergonul O,
Ippolito G and Petersen E: COVID-19, SARS and MERS: Are they
closely related? Clin Microbiol Infect. 26:729–734. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Xiao J, Fang M, Chen Q and He B: SARS,
MERS and COVID-19 among healthcare workers: A narrative review. J
Infect Public Health. 13:843–848. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Bharati S, Podder P, Mondal MR, Podder P
and Kose U: A review on epidemiology, genomic characteristics,
spread, and treatments of COVID-19. Data Sci COVID-19. 487–505.
2022.
|
|
62
|
Harvey WT, Carabelli AM, Jackson B, Gupta
RK, Thomson EC, Harrison EM, Ludden C, Reeve R and Rambaut A:
COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) Consortium et al. SARS-CoV-2
variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat Rev Microbiol.
19:409–424. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Marjanovic S, Romanelli RJ, Ali GC, Leach
B, Bonsu M, Rodriguez-Rincon D and Ling T: COVID-19 Genomics UK
(COG-UK) Consortium: Final Report. Rand Health Q.
9(24)2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Khetran SR and Mustafa R: Mutations of
SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins in the alpha, beta, gamma, and delta
variants: Bioinformatics analysis. JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol.
4(e43906)2023.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
European Centre for Disease Prevention and
Control: Threat Assessment Brief: Rapid increase of a SARS-CoV-2
variant with multiple spike protein mutations observed in the
United Kingdom. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/SARS-CoV-2-variant-multiple-spike-protein-mutations-United-Kingdom.pdf.
|
|
66
|
Mahmoud IS, Jarrar YB, Alshaer W and
Ismail S: SARS-CoV-2 entry in host cells-multiple targets for
treatment and prevention. Biochimie. 175:93–98. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Xie Y, Karki CB, Du D, Li H, Wang J,
Sobitan A, Teng S, Tang Q and Li L: Spike proteins of SARS-CoV and
SARS-CoV-2 utilize different mechanisms to bind with human ACE2.
Front Mol Biosci. 7(591873)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zamorano Cuervo N and Grandvaux N: ACE2:
Evidence of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications
in comorbidities. Elife. 9(e61390)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wu J, Deng W, Li S and Yang X: Advances in
research on ACE2 as a receptor for 2019-CoV. Cell Mol Life Sci.
78:531–544. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Alipoor SD and Mirsaeidi M: SARS-CoV-2
cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor. Mol Biol Rep. 49:10715–10727.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Guo H, Li A, Dong TY, Si HR, Hu B, Li B,
Zhu Y, Shi ZL and Letko M: Isolation of ACE2-dependent and
-independent sarbecoviruses from Chinese horseshoe bats. J Virol.
97(e0039523)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Shereen MA, Khan S, Kazmi A, Bashir N and
Siddique R: COVID-19 infection: Emergence, transmission, and
characteristics of human coronaviruses. J Adv Res. 24:91–98.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Najafi N, Davoudi A, Izadyar H, Alishahi
A, Mokhtariani A, Soleimanpourian B, Tabarrayi M, Moosazadeh M,
Daftarian Z and Ahangarkani F: The effect of ACE inhibitors and
ARBs on outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Ir J Med
Sci. 192:1517–1523. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Liu K, Tan S, Niu S, Wang J, Wu L, Sun H,
Zhang Y, Pan X, Qu X, Du P, et al: Cross-species recognition of
SARS-CoV-2 to bat ACE2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118(e2020216118)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wettstein L, Kirchhoff F and Münch J: The
Transmembrane Protease TMPRSS2 as a Therapeutic Target for COVID-19
Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 23(1351)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Guang C, Phillips RD, Jiang B and Milani
F: Three key proteases-angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE), ACE2
and renin-within and beyond the renin-angiotensin system. Arch
Cardiovasc Dis. 105:373–385. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Kucukoglu K, Faydalı N and Bul D: What are
the drugs having potential against COVID-19? Med Chem Res.
29:1935–1955. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Lee JS, Goldstein JM, Moon JL, Herzegh O,
Bagarozzi DA Jr, Oberste MS, Hughes H, Bedi K, Gerard D, Cameron B,
et al: Analysis of the initial lot of the CDC 2019-novel
coronavirus (2019-nCoV) real-time RT-PCR diagnostic panel. PLoS
One. 16(e0260487)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Sheikhzadeh E, Eissa S, Ismail A and
Zourob M: Diagnostic techniques for COVID-19 and new developments.
Talanta. 220(121392)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Udugama B, Kadhiresan P, Kozlowski HN,
Malekjahani A, Osborne M, Li VYC, Chen H, Mubareka S, Gubbay JB and
Chan WCW: Diagnosing COVID-19: The disease and tools for detection.
ACS Nano. 14:3822–3535. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Xie X, Zhong Z, Zhao W, Zheng C, Wang F
and Liu J: Chest CT for typical coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
pneumonia: Relationship to negative RT-PCR testing. Radiology.
296:E41–E45. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Kanne JP: Chest CT findings in 2019 novel
coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections from Wuhan, China: Key points
for the radiologist. Radiology. 295:16–17. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Machado BA, Hodel KV, Barbosa-Junior VG,
Soares MB and Badaro R: The main molecular and serological methods
for diagnosing COVID-19: An overview based on the literature.
Viruses. 13(40)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Liu YX, Zhou YH, Jiang CH, Liu J and Chen
DQ: Prevention, treatment and potential mechanism of herbal
medicine for Corona viruses: A review. Bioengineered. 13:5480–5508.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Shuster A, Pechalrieu D, Jackson CB, Abegg
D, Choe H and Adibekian A: Clinical antiviral drug arbidol inhibits
infection by SARS-CoV-2 and variants through direct binding to the
spike protein. ACS Chem Biol. 16:2845–2851. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kang CK, Seong MW, Choi SJ, Kim TS, Choe
PG, Song SH, Kim NJ, Park WB and Oh MD: In vitro activity of
lopinavir/ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine against severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 at concentrations achievable by
usual doses. Korean J Intern Med. 35(728)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
RECOVERY Collaborative Group.
Lopinavir-ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19
(RECOVERY): A randomized, controlled, open-label, platform trial.
Lancet. 396:1345–1352. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Nutho B, Mahalapbutr P, Hengphasatporn K,
Pattaranggoon NC, Simanon N, Shigeta Y, Hannongbua S and
Rungrotmongkol T: Why are lopinavir and ritonavir effective against
the newly emerged coronavirus 2019? Atomistic insights into the
inhibitory mechanisms. Biochemistry. 59:1769–1779. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lian N, Xie H, Lin S, Huang J, Zhao J and
Lin Q: Umifenovir treatment is not associated with improved
outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective
study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 26:917–921. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Li Y, Xie Z, Lin W, Cai W, Wen C, Guan Y,
Mo X, Wang J, Wang Y, Peng P, et al: Efficacy and safety of
lopinavir/ritonavir or arbidol in adult patients with mild/moderate
COVID-19: An exploratory randomized controlled trial. Med.
1:105–113. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Djomkam ALZ, Olwal CO, Sala TB and Paemka
L: Commentary: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Front
Oncol. 10(1448)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Li K, Meyerholz DK, Bartlett JA and McCray
PB Jr: The TMPRSS2 inhibitor nafamostat reduces SARS-CoV-2
pulmonary infection in mouse models of COVID-19. mBio.
12(e0097021)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Chitsike L and Duerksen-Hughes P: Keep
out! SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors: Their role and utility as
COVID-19 therapeutics. Virol J. 18(154)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Hoffmann M, Hofmann-Winkler H, Smith JC,
Krüger N, Arora P, Sørensen LK, Søgaard OS, Hasselstrøm JB, Winkler
M, Hempel T, et al: Camostat mesylate inhibits SARS-CoV-2
activation by TMPRSS2-related proteases and its metabolite GBPA
exerts antiviral activity. EBioMedicine. 65(103255)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Tang W, Cao Z, Han M, Wang Z, Chen J, Sun
W, Wu Y, Xiao W, Liu S, Chen E, et al: Hydroxychloroquine in
patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019:
Open label, randomised controlled trial. BMJ.
369(m1849)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, Hoang VT,
Meddeb L, Mailhe M, Doudier B, Courjon J, Giordanengo V, Vieira VE,
et al: Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of
COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial.
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 56(105949)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Manivannan E, Karthikeyan C, Moorthy NSHN
and Chaturvedi SC: The rise and fall of
Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine as compassionate therapy of
COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 12(584940)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Kumar S, Dutta D, Ravichandiran V and
Sukla S: Monoclonal antibodies: A remedial approach to prevent
SARS-CoV-2 infection. 3 Biotech. 12(227)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Javalkote VS, Kancharla N, Bhadra B,
Shukla M, Soni B, Sapre A, Goodin M, Bandyopadhyay A and Dasgupta
S: CRISPR-based assays for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2. Methods.
203:594–603. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Joung J, Ladha A, Saito M, Segel M,
Bruneau R, Huang MW, Kim NG, Yu X, Li J, Walker BD, et al:
Point-of-care testing for COVID-19 using SHERLOCK diagnostics.
medRxiv [Preprint]: May 8, 2020 doi:
10.1101/2020.05.04.20091231.
|
|
102
|
Yang SM, Lv S, Zhang W and Cui Y:
Microfluidic point-of-care (POC) devices in early diagnosis: A
review of opportunities and challenges. Sensors (Basel).
22(1620)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Rizvi ZA, Babele P, Madan U, Sadhu S,
Tripathy MR, Goswami S, Mani S, Dikshit M and Awasthi A:
Pharmacological potential of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal
and Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers on the experimental
models of COVID-19, T cell differentiation, and neutrophil
functions. Front Immunol. 14(1138215)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Amponsah SK, Tagoe B, Adams I and Bugyei
KA: Efficacy and safety profile of corticosteroids and
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in COVID-19 management: A
narrative review. Front Pharmacol. 13(1063246)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Falk JA, Minai OA and Mosenifar Z: Inhaled
and systemic corticosteroids in chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 5:506–512. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Kushner P, McCarberg BH, Grange L, Kolosov
A, Haveric AL, Zucal V, Petruschke R and Bissonnette S: The use of
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in COVID-19. NPJ
Prim Care Respir Med. 32(35)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Robb CT, Goepp M, Rossi AG and Yao C:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins, and
COVID-19. Br J Pharmacol. 177:4899–4920. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Sokolowska M, Rovati GE, Diamant Z,
Untersmayr E, Schwarze J, Lukasik Z, Sava F, Angelina A, Palomares
O, Akdis CA, et al: Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs and other eicosanoid pathway modifiers on antiviral and
allergic responses: EAACI task force on eicosanoids consensus
report in times of COVID-19. Allergy. 77:2337–2354. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Kanchanasurakit S, Arsu A, Siriplabpla W,
Duangjai A and Saokaew S: Acetaminophen use and risk of renal
impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Res Clin
Pract. 39(81)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
De Spiegeleer A, Bronselaer A, Teo JT,
Byttebier G, De Tré G, Belmans L, Dobson R, Wynendaele E, Van De
Wiele C, Vandaele F, et al: The effects of ARBs, ACEis, and statins
on clinical outcomes of COVID-19 infection among nursing home
residents. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 21:909–914.e2. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Geng S, Mei Q, Zhu C, Yang T, Yang Y, Fang
X and Pan A: High flow nasal cannula is a good treatment option for
COVID-19. Heart Lung. 49:444–445. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Lockhart SL, Duggan LV, Wax RS, Saad S and
Grocott HP: Personal protective equipment (PPE) for both
anesthesiologists and other airway managers: Principles and
practice during the COVID-19 pandemic. Can J Anaesth. 67:1005–1015.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Gilardi KVK and Mazet JAK: The United
States Agency for international development emerging pandemic
threats PREDICT project-global detection of emerging wildlife viral
zoonoses. Fowler's Zoo Wild Animal Med Curr Ther. 9:110–116.
2019.
|
|
114
|
Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Bhattacharya M,
Agoramoorthy G and Lee SS: The drug repurposing for COVID-19
clinical trials provide very effective therapeutic combinations:
Lessons learned from major clinical studies. Front Pharmacol.
12(704205)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Okuyama R: mRNA and adenoviral vector
vaccine platforms utilized in COVID-19 vaccines: Technologies,
ecosystem, and future directions. Vaccines (Basel).
11(1737)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Wang N, Chen M and Wang T: Liposomes used
as a vaccine Adjuvant-delivery system: From basics to clinical
immunization. J Control Release. 303:130–150. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Tretiakova DS and Vodovozova EL: Liposomes
as adjuvants and vaccine delivery systems. Biochem (Mosc) Suppl Ser
A Membr Cell Biol. 16:1–20. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Petkar KC, Patil SM, Chavhan SS, Kaneko K,
Sawant KK, Kunda NK and Saleem IY: An overview of Nanocarrier-based
adjuvants for vaccine delivery. Pharmaceutics.
13(455)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Karunakaran B, Gupta R, Patel P, Salave S,
Sharma A, Desai D, Benival D and Kommineni N: Emerging trends in
lipid-based vaccine delivery: A special focus on developmental
strategies, fabrication methods, and applications. Vaccines
(Basel). 11(661)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Ali H, Akbar M, Iqbal B, Ali F, Sharma NK,
Kumar N, Najmi A, Albratty M, Alhazmi HA, Madkhali OA, et al:
Virosome: An engineered virus for vaccine delivery. Saudi Pharm J.
31:752–764. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Nakanishi T, Hayashi A, Kunisawa J,
Tsutsumi Y, Tanaka K, Yashiro-Ohtani Y, Nakanishi M, Fujiwara H,
Hamaoka T and Mayumi T: Fusogenic liposomes efficiently deliver
exogenous antigen through the cytoplasm into the MHC class I
processing pathway. Eur J Immunol. 30:1740–1747. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Marchese AM, Zhou X, Kinol J, Underwood E,
Woo W, McGarry A, Beyhaghi H, Áñez G, Toback S and Dunkle LM:
NVX-CoV2373 vaccine efficacy against hospitalization: A post hoc
analysis of the PREVENT-19 phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled
trial. Vaccine. 41:3461–3466. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Frederiksen LSF, Zhang Y, Foged C and
Thakur A: The long road toward COVID-19 herd immunity: Vaccine
platform technologies and mass immunization strategies. Front
Immunol. 11(1817)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Sanders B, Koldijk M and Schuitemaker H:
Inactivated viral vaccines. Vaccine Analysis: Strategies Principles
Control: 45-80, 2014 doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-45024-6_2.
|
|
125
|
Wang C, Chen LY, Lu QB and Cui F:
Vaccination with the inactivated vaccine (Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV)
ensures protection against SARS-CoV-2 related disease. Vaccines
(Basel). 10(920)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Hu L, Sun J, Wang Y, Tan D, Cao Z, Gao L,
Guan Y, Jia X and Mao J: A review of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine
development in China: Focusing on safety and efficacy in special
populations. Vaccines (Basel). 11(1045)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Soysal A, Gönüllü E, Karabayır N, Alan S,
Atıcı S, Yıldız İ, Engin H, Çivilibal M and Karaböcüoğlu M:
Comparison of immunogenicity and reactogenicity of inactivated
SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in previously SARS-CoV-2 infected
and uninfected health care workers. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
17:3876–3880. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Pagliusi S, Jarrett S, Hayman B, Kreysa U,
Prasad SD, Reers M, Hong Thai P, Wu K, Zhang YT, Baek YO, et al:
Emerging manufacturers engagements in the COVID-19 vaccine
research, development and supply. Vaccine. 38:5418–5423.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Thanh Le T, Andreadakis Z, Kumar A, Gómez
Román R, Tollefsen S, Saville M and Mayhew S: The COVID-19 vaccine
development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:305–306.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Chaplin DD: Overview of the immune
response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125 (2 Suppl 2):S3–S23.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Chavda VP, Bezbaruah R, Valu D, Patel B,
Kumar A, Prasad S, Kakoti BB, Kaushik A and Jesawadawala M:
Adenoviral vector-based vaccine platform for COVID-19: Current
status. Vaccines (Basel). 11(432)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Elkashif A, Alhashimi M, Sayedahmed EE,
Sambhara S and Mittal SK: Adenoviral vector-based platforms for
developing effective vaccines to combat respiratory viral
infections. Clin Transl Immunology. 10(e1345)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Zhu FC, Guan XH, Li YH, Huang JY, Jiang T,
Hou LH, Li JX, Yang BF, Wang L, Wang WJ, et al: Immunogenicity and
safety of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine
in healthy adults aged 18 years or older: A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet.
396:479–488. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Joe CCD, Jiang J, Linke T, Li Y, Fedosyuk
S, Gupta G, Berg A, Segireddy RR, Mainwaring D, Joshi A, et al:
Manufacturing a chimpanzee adenovirus-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine
to meet global needs. Biotechnol Bioeng. 119:48–58. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Asano M, Okada H, Itoh Y, Hirata H,
Ishikawa K, Yoshida E, Matsui A, Kelly EJ, Shoemaker K, Olsson U
and Vekemans J: Immunogenicity and safety of AZD1222 (ChAdOx1
nCoV-19) against SARS-CoV-2 in Japan: A double-blind, randomized
controlled phase 1/2 trial. Int J Infect Dis. 114:165–174.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
AstraZeneca: AZD1222 US Phase III primary
analysis confirms safety and efficacy. AstraZeneca, 2021. Available
at: https://www.astrazeneca.com/content/astraz/media-centre/press-releases/2021/azd1222-us-phase-iii-primary-analysis-confirms-safety-and-efficacy.html.
|
|
137
|
Khan KH: DNA vaccines: Roles against
diseases. Germs. 3:26–35. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Zhao G, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Hou J, Liu Y,
Zhang M, Sui C, Wang L, Xu X, Gao X and Kou Z: A DNA vaccine
encoding the full-length spike protein of beta variant (B.1.351)
elicited broader cross-reactive immune responses against other
SARS-CoV-2 variants. Vaccines (Basel). 11(513)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Chavda VP, Jogi G, Dave S, Patel BM,
Vineela Nalla L and Koradia K: mRNA-Based vaccine for COVID-19:
They are new but not unknown! Vaccines (Basel).
11(507)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Hussain A, Yang H, Zhang M, Liu Q,
Alotaibi G, Irfan M, He H, Chang J, Liang XJ, Weng Y and Huang Y:
mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 and diverse diseases. J Control Release.
345:314–333. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Gordon CJ, Tchesnokov EP, Woolner E, Perry
JK, Feng JY, Porter DP and Götte M: Remdesivir is a direct-acting
antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe
acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J Biol
Chem. 295:6785–6797. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Grein J, Ohmagari N, Shin D, Diaz G,
Asperges E, Castagna A, Feldt T, Green G, Green ML and Lescure FX:
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19.
N Engl J Med. 382:2327–2336. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Chen C, Zhang Y, Huang J, Yin P, Cheng Z,
Wu J, Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen B, Lu M, et al: Favipiravir versus
arbidol for clinical recovery rate in moderate and severe adult
COVID-19 Patients: A prospective, multicenter, open-label,
randomized controlled clinical trial. Front Pharmacol.
12(683296)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Joshi S, Parkar J, Ansari A, Vora A,
Talwar D, Tiwaskar M, Patil S and Barkate H: Role of favipiravir in
the treatment of COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis. 102:501–508.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Lei ZN, Wu ZX, Dong S, Yang DH, Zhang L,
Ke Z, Zou C and Chen ZS: Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the
treatment of malaria and repurposing in treating COVID-19.
Pharmacol Ther. 216(107672)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Mallat J, Hamed F, Balkis M, Mohamed MA,
Mooty M, Malik A, Nusair A and Bonilla MF: Hydroxychloroquine is
associated with slower viral clearance in clinical COVID-19
patients with mild to moderate disease. Medicine (Baltimore).
99(e23720)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Yang G, Tan Z, Zhou L, Yang M, Peng L, Liu
J, Cai J, Yang R, Han J, Huang Y and He S: Effects of Angiotensin
II receptor blockers and ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)
inhibitors on virus infection, inflammatory status, and clinical
outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and hypertension: A
single-center retrospective study. Hypertension. 76:51–58.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Eastman RT, Roth JS, Brimacombe KR,
Simeonov A, Shen M, Patnaik S and Hall MD: Remdesivir: A review of
its discovery and development leading to emergency use
authorization for treatment of COVID-19. ACS Cent Sci. 6:672–683.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Uzunova K, Filipova E, Pavlova V and Vekov
T: Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir,
lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting
the new SARS-CoV-2. Biomed Pharmacother. 131(110668)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Bahsoun A, Fakih Y, Zareef R, Bitar F and
Arabi M: Corticosteroids in COVID-19: Pros and cons. Front Med
(Lausanne). 10(1202504)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Venditto VJ, Haydar D, Abdel-Latif A,
Gensel JC, Anstead MI, Pitts MG, Creameans J, Kopper TJ, Peng C and
Feola DJ: Immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin revisited:
Potential applications to COVID-19. Front Immunol.
12(574425)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Peng HT, Rhind SG and Beckett A:
Convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: A
systematic review and quantitative analysis. JMIR Public Health
Surveill. 7(e25500)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Pandey A, Nikam AN, Shreya AB, Mutalik SP,
Gopalan D, Kulkarni S, Padya BS, Fernandes G, Mutalik S and Prassl
R: Potential therapeutic targets for combating SARS-CoV-2: Drug
repurposing, clinical trials and recent advancements. Life Sci.
256(117883)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Aiyegbusi OL, Hughes SE, Turner G, Rivera
SC, McMullan C, Chandan JS, Haroon S, Price G, Davies EH,
Nirantharakumar K, et al: Symptoms, complications and management of
long COVID: A review. J R Soc Med. 114:428–442. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Hosseinzadeh P, Zareipour M, Baljani E and
Moradali MR: Social consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. A
systematic review. Invest Educ Enferm. 40(e10)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Wouters OJ, Shadlen KC, Salcher-Konrad M,
Pollard AJ, Larson HJ, Teerawattananon Y and Jit M: Challenges in
ensuring global access to COVID-19 vaccines: Production,
affordability, allocation, and deployment. Lancet. 397:1023–1034.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
McNeely JA: Nature and COVID-19: The
pandemic, the environment, and the way ahead. Ambio. 50:767–781.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Keusch GT, Amuasi JH, Anderson DE, Daszak
P, Eckerle I, Field H, Koopmans M, Lam SK, Das Neves CG, Peiris M,
et al: Pandemic origins and a One Health approach to preparedness
and prevention: Solutions based on SARS-CoV-2 and other RNA
viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 119(e2202871119)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Morens DM, Taubenberger JK and Fauci AS:
Universal coronavirus vaccines-an urgent need. N Engl J Med.
386:297–299. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Loh EH, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Olival KJ,
Bogich TL, Johnson CK, Mazet JA, Karesh W and Daszak P: Targeting
transmission pathways for emerging zoonotic disease surveillance
and control. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 15:432–437. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Pike J, Bogich T, Elwood S, Finnoff DC and
Daszak P: Economic optimization of a global strategy to address the
pandemic threat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:18519–18523.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
AlShurman BA, Khan AF, Mac C, Majeed M and
Butt ZA: What demographic, social, and contextual factors influence
the intention to use COVID-19 vaccines: A scoping review. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 18(9342)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Dinnes J, Sharma P, Berhane S, van Wyk SS,
Nyaaba N, Domen J, Taylor M, Cunningham J, Davenport C, Dittrich S,
et al: Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of
SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
7(CD013705)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Malekzadeh R, Abedi G, Ziapour A, Yıldırım
M and Amirkhanlou A: Analysis of ethical considerations of COVID-19
vaccination: Lessons for future. BMC Med Ethics.
24(91)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Jalilian H, Amraei M, Javanshir E,
Jamebozorgi K and Faraji-Khiavi F: Ethical considerations of the
vaccine development process and vaccination: A scoping review. BMC
Health Serv Res. 23(255)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Chung JY, Thone MN and Kwon YJ: COVID-19
vaccines: The status and perspectives in delivery points of view.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 170:1–25. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Forman R, Shah S, Jeurissen P, Jit M and
Mossialos E: COVID-19 vaccine challenges: What have we learned so
far and what remains to be done? Health Policy. 125:553–567.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|