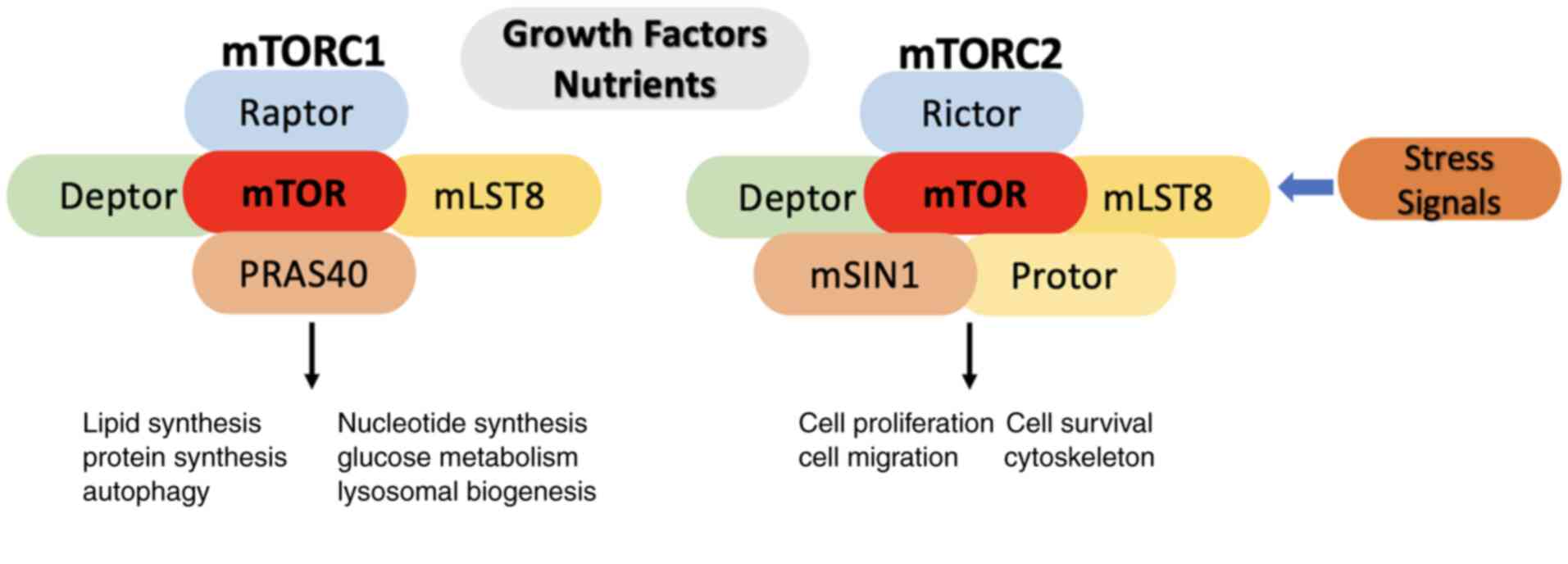
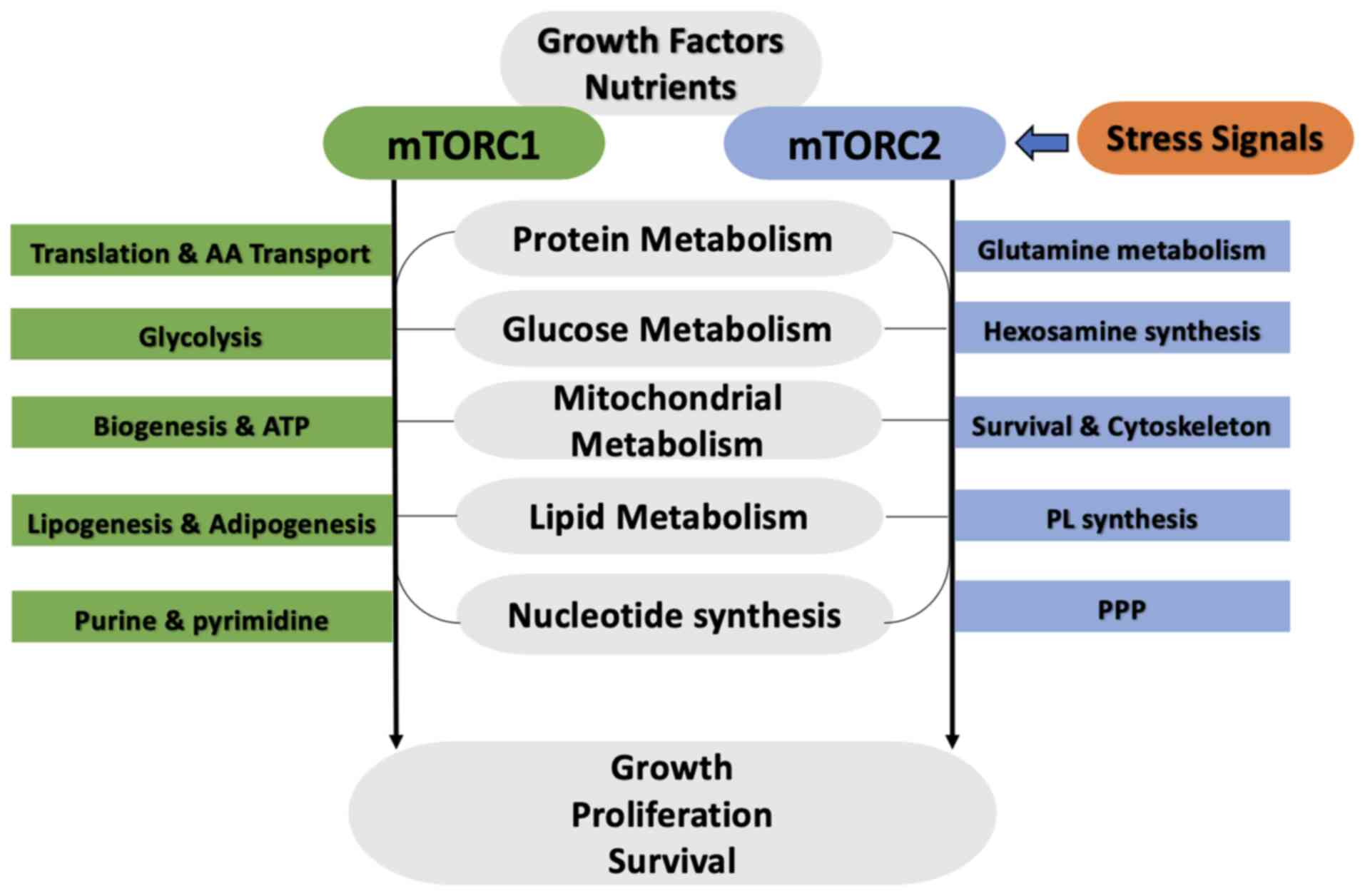
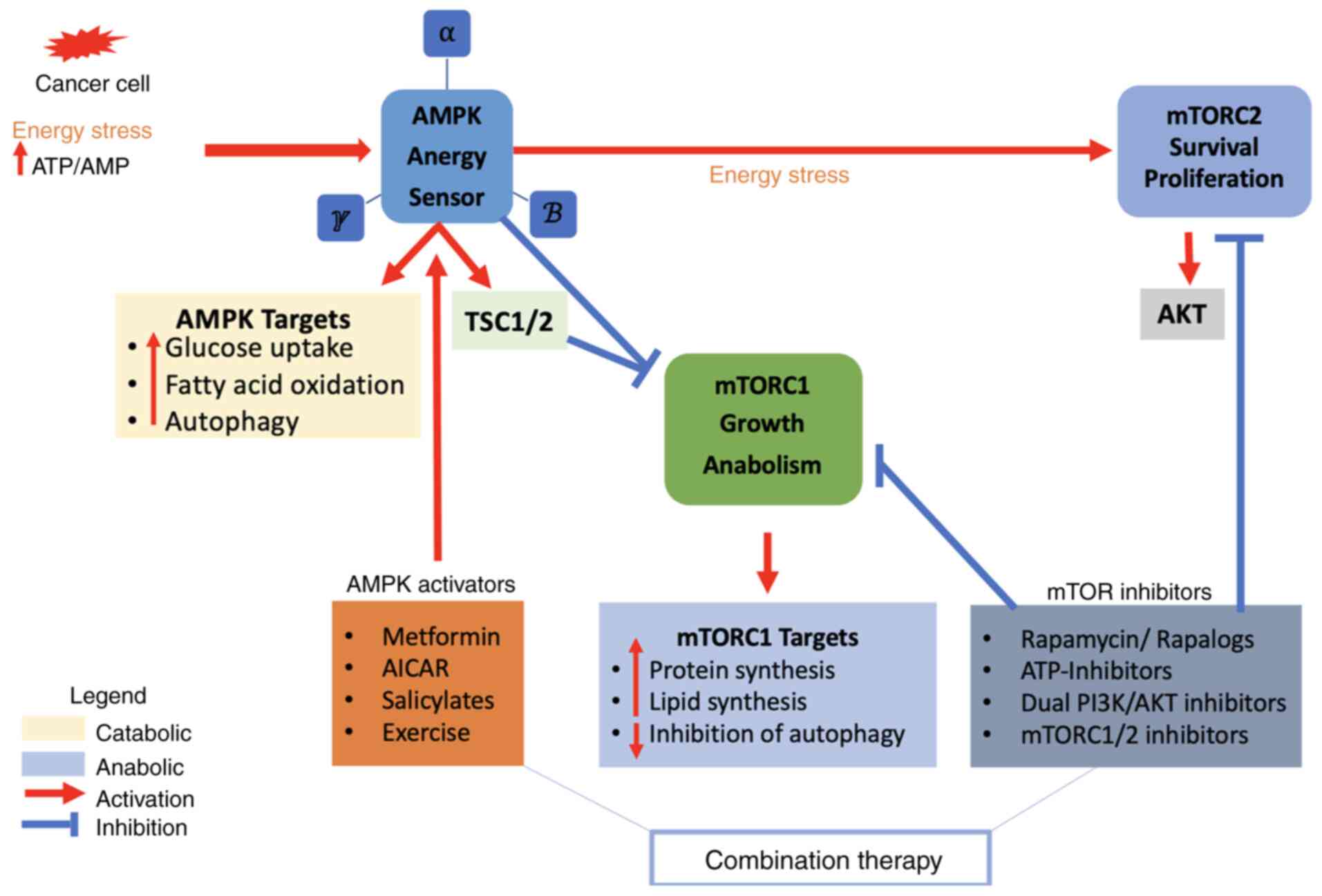
|
1
|
Fan H, Wu Y, Yu S, Li X, Wang A, Wang S,
Chen W and Lu Y: Critical role of mTOR in regulating aerobic
glycolysis in carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 58:9–19.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H, Wang J, Luo T and
Jiang Y: Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol.
12(71)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zarogoulidis P, Lampaki S, Turner JF,
Huang H, Kakolyris S, Syrigos K and Zarogoulidis K: mTOR pathway: A
current, up-to-date mini-review (review). Oncol Lett. 8:2367–2370.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lien EC, Lyssiotis CA and Cantley LC:
Metabolic reprogramming by the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway in cancer.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 207:39–72. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mossmann D, Park S and Hall MN: mTOR
signaling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:744–757. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ramanathan A and Schreiber SL: Direct
control of mitochondrial function by mTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:22229–22232. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang N, Wang B, Maswikiti EP, Yu Y, Song
K, Ma C, Han X, Ma H, Deng X, Yu R and Chen H: AMPK-a key factor in
crosstalk between tumor cell energy metabolism and immune
microenvironment? Cell Death Discov. 10(237)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Torres Acosta MA, Gurkan JK, Liu Q,
Mambetsariev N, Reyes Flores C, Helmin KA, Joudi AM,
Morales-Nebreda L, Cheng K, Abdala-Valencia H, et al: AMPK is
necessary for Treg functional adaptation to microenvironmental
stress during malignancy and viral pneumonia. J Clin Invest.
135(e179572)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Marafie SK, Al-Mulla F and Abubaker J:
mTOR: Its critical role in metabolic diseases, cancer, and the
aging process. Int J Mol Sci. 25(6141)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Smiles WJ, Ovens AJ, Kemp BE, Galic S,
Petersen J and Oakhill JS: New developments in AMPK and mTORC1
cross-talk. Essays Biochem. 68:321–336. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Keerthana CK, Rayginia TP, Shifana SC,
Anto NP, Kalimuthu K, Isakov N and Anto RJ: The role of AMPK in
cancer metabolism and its impact on the immunomodulation of the
tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. 14(1114582)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang T, Wang X, Alexander PG, Feng P and
Zhang J: An analysis of AMPK and ferroptosis in cancer: A potential
regulatory axis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
30(36618)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liao H, Wang Y, Zou L, Fan Y, Wang X, Tu
X, Zhu Q, Wang J, Liu X and Dong C: Relationship of mTORC1 and
ferroptosis in tumors. Discov Oncol. 15(107)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sun Z, Liu L, Liang H and Zhang L:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide induces autophagy and ferroptosis via
AMPK/mTOR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
63:577–588. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang X, Tan X, Zhang J, Wu J and Shi H:
The emerging roles of MAPK-AMPK in ferroptosis regulatory network.
Cell Commun Signal. 21(200)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee H, Zandkarimi F, Zhang Y, Meena JK,
Kim J, Zhuang L, Tyagi S, Ma L, Westbrook TF, Steinberg GR, et al:
Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat
Cell Biol. 22:225–234. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun Q, Zhen P, Li D, Liu X, Ding X and Liu
H: Amentoflavone promotes ferroptosis by regulating reactive oxygen
species (ROS)/5'AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/mammalian
target of rapamycin (mTOR) to inhibit the malignant progression of
endometrial carcinoma cells. Bioengineered. 13:13269–13279.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen W, Zhao H and Li Y: Mitochondrial
dynamics in health and disease: Mechanisms and potential targets.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8(333)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Crosas-Molist E, Graziani V, Maiques O,
Pandya P, Monger J, Samain R, George SL, Malik S, Salise J, Morales
V, et al: AMPK is a mechano-metabolic sensor linking cell adhesion
and mitochondrial dynamics to Myosin-dependent cell migration. Nat
Commun. 14(2740)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu Q, Zhang L, Zou Y, Tao Y, Wang B, Li
B, Liu R, Wang B, Ding L, Cui Q, et al: Modulating p-AMPK/mTOR
pathway of mitochondrial dysfunction caused by MTERF1 abnormal
expression in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
23(12354)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu A, Lu X, Song Y, Pei J and Wei R: ACK1
condensates promote STAT5 signaling in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 25(237)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mehta S and Zhang J: Liquid-liquid phase
separation drives cellular function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 22:239–252. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Peng Q, Tan S, Xia L, Wu N, Oyang L, Tang
Y, Su M, Luo X, Wang Y, Sheng X, et al: Phase separation in cancer:
From the impacts and mechanisms to treatment potentials. Int J Biol
Sci. 18:5103–5122. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Maqsood Q, Sumrin A, Saleem MZ, Perveen R,
Hussain N, Mahnoor M, Akhtar MW, Wajid A and Ameen E: An insight
into cancer from biomolecular condensates. Cancer Screen Prev.
2:177–190. 2023.
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Feng Y, Geng S, Xu F and Guo H: The
role of liquid-liquid phase separation in defining cancer EMT. Life
Sci. 353(122931)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Warburg O and Minami S: Versuche an
Überlebendem carcinom-gewebe. Klin Wochenschr. 2:776–777. 1923.
|
|
29
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Koppenol WH, Bounds PL and Dang CV: Otto
Warburg's contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:325–337. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tochigi T, Shuto K, Kono T, Ohira G, Tohma
T, Gunji H, Hayano K, Narushima K, Fujishiro T, Hanaoka T, et al:
Heterogeneity of glucose metabolism in esophageal cancer measured
by fractal analysis of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography image: Correlation between metabolic heterogeneity and
survival. Dig Surg. 34:186–191. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Larson SM: Positron emission
tomography-based molecular imaging in human cancer: Exploring the
link between hypoxia and accelerated glucose metabolism. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:2203–2204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
DeBerardinis RJ and Chandel NS:
Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci Adv.
2(e1600200)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ward PS and Thompson CB: Metabolic
reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate.
Cancer Cell. 21:297–308. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hsu PP and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 134:703–707. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li ZY and Zhang HF: Reprogramming of
glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism for cancer
progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:377–392. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim SY: Cancer energy metabolism: Shutting
power off cancer factory. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:39–44.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Corbet C and Feron O: Cancer cell
metabolism and mitochondria: Nutrient plasticity for TCA cycle
fueling. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1868:7–15.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Weinberg F and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial
metabolism and cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1177:66–73. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhao L, Mao Y, Zhao Y, Cao Y and Chen X:
Role of multifaceted regulators in cancer glucose metabolism and
their clinical significance. Oncotarget. 7:31572–31585.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Finley LWS: What is cancer metabolism?
Cell. 186:1670–1688. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stine ZE, Schug ZT, Salvino JM and Dang
CV: Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:141–162. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vander Heiden MG, Locasale JW, Swanson KD,
Sharfi H, Heffron GJ, Amador-Noguez D, Christofk HR, Wagner G,
Rabinowitz JD, Asara JM and Cantley LC: Evidence for an alternative
glycolytic pathway in rapidly proliferating cells. Science.
329:1492–1499. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kalyanaraman B, Cheng G, Hardy M, Ouari O,
Lopez M, Joseph J, Zielonka J and Dwinell MB: A review of the
basics of mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and related
signaling pathways in cancer cells: Therapeutic targeting of tumor
mitochondria with lipophilic cationic compounds. Redox Biol.
14:316–327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Stepien M, Duarte-Salles T, Fedirko V,
Floegel A, Barupal DK, Rinaldi S, Achaintre D, Assi N, Tjønneland
A, Overvad K, et al: Alteration of amino acid and biogenic amine
metabolism in hepatobiliary cancers: Findings from a prospective
cohort study. Int J Cancer. 138:348–360. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Frezza C: Cancer metabolism: Addicted to
serine. Nat Chem Biol. 12:389–390. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gordan JD, Thompson CB and Simon MC: HIF
and c-Myc: Sibling rivals for control of cancer cell metabolism and
proliferation. Cancer Cell. 12:108–113. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
West MJ, Stoneley M and Willis AE:
Translational induction of the c-myc oncogene via activation of the
FRAP/TOR signalling pathway. Oncogene. 17:769–780. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kalkat M, De Melo J, Hickman KA, Lourenco
C, Redel C, Resetca D, Tamachi A, Tu WB and Penn LZ: MYC
deregulation in primary human cancers. Genes (Basel).
8(151)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Goetzman ES and Prochownik EV: The role
for Myc in coordinating glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation,
glutaminolysis, and fatty acid metabolism in normal and neoplastic
tissues. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(129)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Pourdehnad M, Truitt ML, Siddiqi IN,
Ducker GS, Shokat KM and Ruggero D: Myc and mTOR converge on a
common node in protein synthesis control that confers synthetic
lethality in Myc-driven cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:11988–11993. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sukumaran A, Choi K and Dasgupta B:
Insight on transcriptional regulation of the energy sensing AMPK
and biosynthetic mTOR pathway genes. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8(671)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Khan MW, Biswas D, Ghosh M, Mandloi S,
Chakrabarti S and Chakrabarti P: mTORC2 controls cancer cell
survival by modulating gluconeogenesis. Cell Death Discov.
1(15016)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sun Q, Chen X, Ma J, Peng H, Wang F, Zha
X, Wang Y, Jing Y, Yang H, Chen R, et al: Mammalian target of
rapamycin up-regulation of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 is
critical for aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:4129–4134. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wei H, Dong C and Shen Z:
Kallikrein-related peptidase (KLK10) cessation blunts colorectal
cancer cell growth and glucose metabolism by regulating the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Neoplasma. 67:889–897. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Iqbal MA, Siddiqui FA, Gupta V,
Chattopadhyay S, Gopinath P, Kumar B, Manvati S, Chaman N and
Bamezai RN: Insulin enhances metabolic capacities of cancer cells
by dual regulation of glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase M2. Mol
Cancer. 12(72)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Buller CL, Loberg RD, Fan MH, Zhu Q, Park
JL, Vesely E, Inoki K, Guan KL and Brosius FC III: A
GSK-3/TSC2/mTOR pathway regulates glucose uptake and GLUT1 glucose
transporter expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C836–C843.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Shi LZ, Wang R, Huang G, Vogel P, Neale G,
Green DR and Chi H: HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway
orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17
and Treg cells. J Exp Med. 208:1367–1376. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Siska PJ, van der Windt GJW, Kishton RJ,
Cohen S, Eisner W, MacIver NJ, Kater AP, Weinberg JB and Rathmell
JC: Suppression of Glut1 and glucose metabolism by decreased
Akt/mTORC1 signaling drives T cell impairment in B cell leukemia. J
Immunol. 197:2532–2540. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Feng Y and Wu L: mTOR up-regulation of
PFKFB3 is essential for acute myeloid leukemia cell survival.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:897–903. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Finlay DK, Rosenzweig E, Sinclair LV,
Feijoo-Carnero C, Hukelmann JL, Rolf J, Panteleyev AA, Okkenhaug K
and Cantrell DA: PDK1 regulation of mTOR and hypoxia-inducible
factor 1 integrate metabolism and migration of CD8+ T cells. J Exp
Med. 209:2441–2453. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chen X, Zhu Y, Wang Z, Zhu H, Pan Q, Su S,
Dong Y, Li L, Zhang H, Wu L, et al: mTORC1 alters the expression of
glycolytic genes by regulating KPNA2 abundances. J Proteomics.
136:13–24. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Li Y, He ZC, Liu Q, Zhou K, Shi Y, Yao XH,
Zhang X, Kung HF, Ping YF and Bian XW: Large intergenic non-coding
RNA-RoR inhibits aerobic glycolysis of glioblastoma cells via Akt
pathway. J Cancer. 9:880–889. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Holloway RW and Marignani PA: Targeting
mTOR and glycolysis in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 13(2922)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Dibble CC and Manning BD: Signal
integration by mTORC1 coordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic
output. Nat Cell Biol. 15:555–564. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kullmann L and Krahn MP: Controlling the
master-upstream regulation of the tumor suppressor LKB1. Oncogene.
37:3045–3057. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Zhang J, Pavlova NN and Thompson CB:
Cancer cell metabolism: The essential role of the nonessential
amino acid, glutamine. EMBO J. 36:1302–1315. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Altman BJ, Stine ZE and Dang CV: From
Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:619–634. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Choi YK and Park KG: Targeting glutamine
metabolism for cancer treatment. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:19–28.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Masui K, Tanaka K, Akhavan D, Babic I,
Gini B, Matsutani T, Iwanami A, Liu F, Villa GR, Gu Y, et al: mTOR
complex 2 controls glycolytic metabolism in glioblastoma through
FoxO acetylation and upregulation of c-Myc. Cell Metab. 18:726–739.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Prieto J, García-Cañaveras JC, León M,
Sendra R, Ponsoda X, Izpisúa Belmonte JC, Lahoz A and Torres J:
c-MYC triggers lipid remodelling during early somatic cell
reprogramming to pluripotency. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 17:2245–2261.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Khan MW, Layden BT and Chakrabarti P:
Inhibition of mTOR complexes protects cancer cells from glutamine
starvation induced cell death by restoring Akt stability. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:2040–2052. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Csibi A, Lee G, Yoon SO, Tong H, Ilter D,
Elia I, Fendt SM, Roberts TM and Blenis J: The mTORC1/S6K1 pathway
regulates glutamine metabolism through the eIF4B-dependent control
of c-Myc translation. Curr Biol. 24:2274–2280. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Shaw E, Talwadekar M, Rashida Z, Mohan N,
Acharya A, Khatri S, Laxman S and Kolthur-Seetharam U: Anabolic
SIRT4 exerts retrograde control over TORC1 signaling by glutamine
sparing in the mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol. 40:e00212–19.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wang D, He J, Huang B, Liu S, Zhu H and Xu
T: Emerging role of the Hippo pathway in autophagy. Cell Death Dis.
11(880)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Trejo-Solís C, Serrano-García N,
Castillo-Rodríguez RA, Robledo-Cadena DX, Jimenez-Farfan D,
Marín-Hernández Á, Silva-Adaya D, Rodríguez-Pérez CE and
Gallardo-Pérez JC: Metabolic dysregulation of tricarboxylic acid
cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in glioblastoma. Rev Neurosci.
35:813–838. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Morita M, Gravel SP, Chénard V, Sikström
K, Zheng L, Alain T, Gandin V, Avizonis D, Arguello M, Zakaria C,
et al: mTORC1 controls mitochondrial activity and biogenesis
through 4E-BP-dependent translational regulation. Cell Metab.
18:698–711. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Wise DR, DeBerardinis RJ, Mancuso A, Sayed
N, Zhang XY, Pfeiffer HK, Nissim I, Daikhin E, Yudkoff M, McMahon
SB and Thompson CB: Myc regulates a transcriptional program that
stimulates mitochondrial glutaminolysis and leads to glutamine
addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18782–18787. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Byun JK, Choi YK, Kim JH, Jeong JY, Jeon
HJ, Kim MK, Hwang I, Lee SY, Lee YM, Lee IK and Park KG: A positive
feedback loop between Sestrin2 and mTORC2 is required for the
survival of glutamine-depleted lung cancer cells. Cell Rep.
20:586–599. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Durán RV, Oppliger W, Robitaille AM,
Heiserich L, Skendaj R, Gottlieb E and Hall MN: Glutaminolysis
activates Rag-mTORC1 signaling. Mol Cell. 47:349–358.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Chiu M, Tardito S, Barilli A, Bianchi MG,
Dall'Asta V and Bussolati O: Glutamine stimulates mTORC1
independent of the cell content of essential amino acids. Amino
Acids. 43:2561–2567. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Bodineau C, Tomé M, Courtois S, Costa ASH,
Sciacovelli M, Rousseau B, Richard E, Vacher P, Parejo-Pérez C,
Bessede E, et al: Two parallel pathways connect glutamine
metabolism and mTORC1 activity to regulate glutamoptosis. Nat
Commun. 12(4814)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Dennis MD, Jefferson LS and Kimball SR:
Role of p70S6K1-mediated phosphorylation of eIF4B and PDCD4
proteins in the regulation of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem.
287:42890–42899. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Dalle Pezze P, Ruf S, Sonntag AG,
Langelaar-Makkinje M, Hall P, Heberle AM, Razquin Navas P, van
Eunen K, Tölle RC, Schwarz JJ, et al: A systems study reveals
concurrent activation of AMPK and mTOR by amino acids. Nat Commun.
7(13254)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Nicklin P, Bergman P, Zhang B,
Triantafellow E, Wang H, Nyfeler B, Yang H, Hild M, Kung C, Wilson
C, et al: Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and
autophagy. Cell. 136:521–534. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Selwan EM and Edinger AL: Branched chain
amino acid metabolism and cancer: The importance of keeping things
in context. Transl Cancer Res. 6 (Suppl 3):S578–S584.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
McCracken AN and Edinger AL: Nutrient
transporters: The Achilles' heel of anabolism. Trends Endocrin Met.
24:200–208. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Kawasome H, Papst P, Webb S, Keller GM,
Johnson GL, Gelfand EW and Terada N: Targeted disruption of
p70(s6k) defines its role in protein synthesis and rapamycin
sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:5033–5038. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Martineau Y, Wang X, Alain T, Petroulakis
E, Shahbazian D, Fabre B, Bousquet-Dubouch MP, Monsarrat B,
Pyronnet S and Sonenberg N: Control of Paip1-eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 3 interaction by amino acids through S6 kinase.
Mol Cell Biol. 34:1046–1053. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Iadevaia V, Liu R and Proud CG: mTORC1
signaling controls multiple steps in ribosome biogenesis. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 36:113–120. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Abetov DA, Kiyan VS, Zhylkibayev AA,
Sarbassova DA, Alybayev SD, Spooner E, Song MS, Bersimbaev RI and
Sarbassov DD: Formation of mammalian preribosomes proceeds from
intermediate to composed state during ribosome maturation. J Biol
Chem. 294:10746–10757. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Gentilella A, Kozma SC and Thomas G: A
liaison between mTOR signaling, ribosome biogenesis and cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:812–820. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
He J, Yang Y, Zhang J, Chen J, Wei X, He J
and Luo L: Ribosome biogenesis protein Urb1 acts downstream of mTOR
complex 1 to modulate digestive organ development in zebrafish. J
Genet Genomics. 44:567–576. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Rad E, Murray JT and Tee AR: Oncogenic
signalling through mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR): A driver
of metabolic transformation and cancer progression. Cancers
(Basel). 10(5)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Qin L, Cheng X, Wang S, Gong G, Su H,
Huang H, Chen T, Damdinjav D, Dorjsuren B, Li Z, et al: Discovery
of novel aminobutanoic acid-based ASCT2 inhibitors for the
treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Med Chem. 67:988–1007.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Leibowitz BJ, Zhao G, Xia W, Wang Y, Ruan
H, Zhang L and Yu J: mTOR inhibition suppresses Myc-driven
polyposis by inducing immunogenic cell death. Oncogene.
42:2007–2016. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Elkon R, Loayza-Puch F, Korkmaz G, Lopes
R, van Breugel PC, Bleijerveld OB, Altelaar AF, Wolf E, Lorenzin F,
Eilers M and Agami R: Myc coordinates transcription and translation
to enhance transformation and suppress invasiveness. EMBO Rep.
16:1723–1736. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Peng T, Golub TR and Sabatini DM: The
immunosuppressant rapamycin mimics a starvation-like signal
distinct from amino acid and glucose deprivation. Mol Cell Biol.
22:5575–5584. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Rosario FJ, Kanai Y, Powell TL and Jansson
T: Mammalian target of rapamycin signalling modulates amino acid
uptake by regulating transporter cell surface abundance in primary
human trophoblast cells. J Physiol. 591:609–625. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Rosario FJ, Dimasuay KG, Kanai Y, Powell
TL and Jansson T: Regulation of amino acid transporter trafficking
by mTORC1 in primary human trophoblast cells is mediated by the
ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2. Clin Sci (Lond). 130:499–512.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Park Y, Reyna-Neyra A, Philippe L and
Thoreen CC: mTORC1 balances cellular amino acid supply with demand
for protein synthesis through post-transcriptional control of ATF4.
Cell Rep. 19:1083–1090. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Gu Y, Albuquerque CP, Braas D, Zhang W,
Villa GR, Bi J, Ikegami S, Masui K, Gini B, Yang H, et al: mTORC2
regulates amino acid metabolism in cancer by phosphorylation of the
cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT. Mol Cell. 67:128–138.e7.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Toda K, Kawada K, Iwamoto M, Inamoto S,
Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Hasegawa S and Sakai Y: Metabolic
alterations caused by KRAS mutations in colorectal cancer
contribute to cell adaptation to glutamine depletion by
upregulation of asparagine synthetase. Neoplasia. 18:654–665.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Pupo E, Avanzato D, Middonti E, Bussolino
F and Lanzetti L: KRAS-driven metabolic rewiring reveals novel
actionable targets in cancer. Front Oncol. 9(848)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Gwinn DM, Lee AG, Briones-Martin-Del-Campo
M, Conn CS, Simpson DR, Scott AI, Le A, Cowan TM, Ruggero D and
Sweet-Cordero EA: Oncogenic KRAS regulates amino acid homeostasis
and asparagine biosynthesis via ATF4 and alters sensitivity to
L-asparaginase. Cancer Cell. 33:91–107.e6. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Long Y, Tsai WB, Wangpaichitr M, Tsukamoto
T, Savaraj N, Feun LG and Kuo MT: Arginine deiminase resistance in
melanoma cells is associated with metabolic reprogramming, glucose
dependence, and glutamine addiction. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2581–2590.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Selvarajah B, Azuelos I, Platé M,
Guillotin D, Forty EJ, Contento G, Woodcock HV, Redding M, Taylor
A, Brunori G, et al: mTORC1 amplifies the ATF4-dependent de novo
serine-glycine pathway to supply glycine during
TGF-β1-induced collagen biosynthesis. Sci Signal.
12(eaav3048)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Kma L and Baruah TJ: The interplay of ROS
and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl
Biochem. 69:248–264. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Horton JD, Goldstein JL and Brown MS:
SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty
acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 109:1125–1131.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Randle PJ: Regulatory interactions between
lipids and carbohydrates: The glucose fatty acid cycle after 35
years. Diabetes Metab Rev. 14:263–283. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Chen Y and Li P: Fatty acid metabolism and
cancer development. Sci Bull. 61:1473–1479. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Alasadi A, Humaish HH and Al-hraishawi H:
Evaluation the predictors of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. Syst Rev
Pharm. 11:421–430. 2020.
|
|
113
|
Mullen AR, Wheaton WW, Jin ES, Chen PH,
Sullivan LB, Cheng T, Yang Y, Linehan WM, Chandel NS and
DeBerardinis RJ: Reductive carboxylation supports growth in tumour
cells with defective mitochondria. Nature. 481:385–388.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Metallo CM, Gameiro PA, Bell EL, Mattaini
KR, Yang J, Hiller K, Jewell CM, Johnson ZR, Irvine DJ, Guarente L,
et al: Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis
under hypoxia. Nature. 481:380–384. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Wise DR, Ward PS, Shay JE, Cross JR,
Gruber JJ, Sachdeva UM, Platt JM, DeMatteo RG, Simon MC and
Thompson CB: Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent
carboxylation of α-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth
and viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:19611–19616.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Schug ZT, Peck B, Jones DT, Zhang Q,
Grosskurth S, Alam IS, Goodwin LM, Smethurst E, Mason S, Blyth K,
et al: Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 promotes acetate utilization and
maintains cancer cell growth under metabolic stress. Cancer Cell.
27:57–71. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Green CR, Wallace M, Divakaruni AS,
Phillips SA, Murphy AN, Ciaraldi TP and Metallo CM: Branched-chain
amino acid catabolism fuels adipocyte differentiation and
lipogenesis. Nat Chem Biol. 12:15–21. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Eberlé D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, Ferré P
and Foufelle F: SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of
lipid homeostasis. Biochimie. 86:839–848. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Nakamura MT, Cheon Y, Li Y and Nara TY:
Mechanisms of regulation of gene expression by fatty acids. Lipids.
39:1077–1083. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Pégorier JP, Le May C and Girard J:
Control of gene expression by fatty acids. J Nutr. 134:2444S–2449S.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Düvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P,
Lipovsky AI, Souza AL, Triantafellow E, Ma Q, Gorski R, Cleaver S,
et al: Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream
of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell. 39:171–183. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ and Thompson CB:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent modulation of carnitine
palmitoyltransferase 1A expression regulates lipid metabolism
during hematopoietic cell growth. J Biol Chem. 281:37372–37380.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Hao YJ, Samuels Y, Li QL, Krokowski D,
Brunengraber H, Hatzoglou M, Zhang GF, Vogelstein B and Wang Z:
Abstract 1125: Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations reprogram glutamine
metabolism in colorectal cancers. Cancer Res. 75 (15
Suppl)(S1125)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Liu C, Zhou X, Pan Y, Liu Y and Zhang Y:
Pyruvate carboxylase promotes thyroid cancer aggressiveness through
fatty acid synthesis. BMC Cancer. 21(722)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Schiliro C and Firestein BL: Mechanisms of
metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells supporting enhanced growth
and proliferation. Cells. 10(1056)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Andrade-Vieira R, Han JH and Marignani PA:
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid promotes the inhibition of
glycolytic enzymes and mTOR signaling by regulating the tumor
suppressor LKB1. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:1050–1058. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A,
Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T and Mizushima N: The
role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period.
Nature. 432:1032–1036. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Alasadi AH, Guo J, Tao H and Jin S:
Preventing and treating hepatic metastatic colon and pancreatic
cancers by targeting cell metabolism. Cancer Res. 76 (14
Suppl)(S45)2016.
|
|
129
|
Aird KM and Zhang R: Nucleotide
metabolism, oncogene-induced senescence and cancer. Cancer Lett.
356:204–210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Cantor JR and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: One hallmark, many faces. Cancer Discov. 2:881–898.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Vander Heiden MG: Targeting cancer
metabolism: A therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
10:671–684. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Ben-Sahra I, Howell JJ, Asara JM and
Manning BD: Stimulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis by growth
signaling through mTOR and S6K1. Science. 339:1323–1328.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Robitaille AM, Christen S, Shimobayashi M,
Cornu M, Fava LL, Moes S, Prescianotto-Baschong C, Sauer U, Jenoe P
and Hall MN: Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveal mTORC1 activates
de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Science. 339:1320–1323.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
He L, Wei X, Ma X, Yin X, Song M,
Donninger H, Yaddanapudi K, McClain CJ and Zhang X: Simultaneous
quantification of nucleosides and nucleotides from biological
samples. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 30:987–1000. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Qian X, Li X, Tan L, Lee JH, Xia Y, Cai Q,
Zheng Y, Wang H, Lorenzi PL and Lu Z: Conversion of PRPS hexamer to
monomer by AMPK-mediated phosphorylation inhibits nucleotide
synthesis in response to energy stress. Cancer Discov. 8:94–107.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Yecies JL, Zhang HH, Menon S, Liu S,
Yecies D, Lipovsky AI, Gorgun C, Kwiatkowski DJ, Hotamisligil GS,
Lee CH and Manning BD: Akt stimulates hepatic SREBP1c and
lipogenesis through parallel mTORC1-dependent and independent
pathways. Cell Metab. 14:21–32. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Chen J, Yang S, Li Y, Ziwen X, Zhang P,
Song Q, Yao Y and Pei H: De novo nucleotide biosynthetic pathway
and cancer. Genes Dis. 10:2331–2338. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Qian J, Chen Y, Meng T, Ma L, Meng L, Wang
X, Yu T, Zask A, Shen J and Yu K: Molecular regulation of apoptotic
machinery and lipid metabolism by mTORC1/mTORC2 dual inhibitors in
preclinical models of HER2+/PIK3CAmut breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:67071–67086. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Evert M, Calvisi DF, Evert K, De Murtas V,
Gasparetti G, Mattu S, Destefanis G, Ladu S, Zimmermann A, Delogu
S, et al: V-AKT murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog/mammalian
target of rapamycin activation induces a module of metabolic
changes contributing to growth in insulin-induced
hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 55:1473–1484. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Cheng J, Huang Y, Zhang X, Yu Y, Wu S,
Jiao J, Tran L, Zhang W, Liu R, Zhang L, et al: TRIM21 and PHLDA3
negatively regulate the crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT pathway and
PPP metabolism. Nat Commun. 11(1880)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Saha A, Connelly S, Jiang J, Zhuang S,
Amador DT, Phan T, Pilz RB and Boss GR: Akt phosphorylation and
regulation of transketolase is a nodal point for amino acid control
of purine synthesis. Mol Cell. 55:264–276. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Wang W and Guan KL: AMP-activated protein
kinase and cancer. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 196:55–63. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Cantó C and Auwerx J: Calorie restriction:
Is AMPK a key sensor and effector? Physiology (Bethesda).
26:214–224. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Klaus S, Keipert S, Rossmeisl M and
Kopecky J: Augmenting energy expenditure by mitochondrial
uncoupling: A role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Genes Nutr.
7:369–386. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Fujii N, Aschenbach WG, Musi N, Hirshman
MF and Goodyear LJ: Regulation of glucose transport by the
AMP-activated protein kinase. Proc Nutr Soc. 63:205–210.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Haurie V, Boucherie H and Sagliocco F: The
Snf1 protein kinase controls the induction of genes of the iron
uptake pathway at the diauxic shift in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J
Biol Chem. 278:45391–45396. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Hawley SA, Fullerton MD, Ross FA,
Schertzer JD, Chevtzoff C, Walker KJ, Peggie MW, Zibrova D, Green
KA, Mustard KJ, et al: The ancient drug salicylate directly
activates AMP-activated protein kinase. Science. 336:918–922.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Daurio NA, Tuttle SW, Worth AJ, Song EY,
Davis JM, Snyder NW, Blair IA and Koumenis C: AMPK activation and
metabolic reprogramming by tamoxifen through estrogen
receptor-independent mechanisms suggests new uses for this
therapeutic modality in cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 76:3295–3306.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Xiao B, Heath R, Saiu P, Leiper FC, Leone
P, Jing C, Walker PA, Haire L, Eccleston JF, Davis CT, et al:
Structural basis for AMP binding to mammalian AMP-activated protein
kinase. Nature. 449:496–500. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Scott JW, Hawley SA, Green KA, Anis M,
Stewart G, Scullion GA, Norman DG and Hardie DG: CBS domains form
energy-sensing modules whose binding of adenosine ligands is
disrupted by disease mutations. J Clin Invest. 113:274–284.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Gowans GJ, Hawley SA, Ross FA and Hardie
DG: AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein
kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net
phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 18:556–566. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Hardie DG: Molecular pathways: Is AMPK a
friend or a foe in cancer? Clin Cancer Res. 21:3836–3840.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Faubert B, Vincent EE, Griss T, Samborska
B, Izreig S, Svensson RU, Mamer OA, Avizonis D, Shackelford DB,
Shaw RJ and Jones RG: Loss of the tumor suppressor LKB1 promotes
metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells via HIF-1α. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 111:2554–2559. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
El-Masry OS, Brown BL and Dobson PRM:
Effects of activation of AMPK on human breast cancer cell lines
with different genetic backgrounds. Oncol Lett. 3:224–228.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Hadad SM, Baker L, Quinlan PR, Robertson
KE, Bray SE, Thomson G, Kellock D, Jordan LB, Purdie CA, Hardie DG,
et al: Histological evaluation of AMPK signaling in primary breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 9(307)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Lee CW, Wong LLY, Tse EYT, Liu HF, Leong
VY, Lee JM, Hardie DG, Ng IO and Ching YP: AMPK promotes p53
acetylation via phosphorylation and inactivation of SIRT1 in liver
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 72:4394–4404. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Laderoute KR, Calaoagan JM, Chao WR, Dinh
D, Denko N, Duellman S, Kalra J, Liu X, Papandreou I, Sambucetti L
and Boros LG: 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) supports the
growth of aggressive experimental human breast cancer tumors. J
Biol Chem. 289:22850–22864. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Zheng L, Yang W, Wu F, Wang C, Yu L, Tang
L, Qiu B, Li Y, Guo L, Wu M, et al: Prognostic significance of AMPK
activation and therapeutic effects of metformin in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:5372–5380. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Faubert B, Boily G, Izreig S, Griss T,
Samborska B, Dong Z, Dupuy F, Chambers C, Fuerth BJ, Viollet B, et
al: AMPK is a negative regulator of the Warburg effect and
suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Cell Metab. 17:113–124.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller
M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM, Westra WH, Herman JG and Sidransky
D: Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinomas
of the lung. Cancer Res. 62:3659–3662. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara
K, Kozlowski P, Torrice C, Wu MC, Shimamura T, Perera SA, et al:
LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature.
448:807–810. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Wingo SN, Gallardo TD, Akbay EA, Liang MC,
Contreras CM, Boren T, Shimamura T, Miller DS, Sharpless NE,
Bardeesy N, et al: Somatic LKB1 mutations promote cervical cancer
progression. PLoS One. 4(e5137)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Hawley SA, Ross FA, Gowans GJ, Tibarewal
P, Leslie NR and Hardie DG: Phosphorylation by Akt within the ST
loop of AMPK-α1 down-regulates its activation in tumour cells.
Biochem J. 459:275–287. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Horman S, Vertommen D, Heath R, Neumann D,
Mouton V, Woods A, Schlattner U, Wallimann T, Carling D, Hue L and
Rider MH: Insulin antagonizes ischemia-induced Thr172
phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha-subunits in
heart via hierarchical phosphorylation of Ser485/491. J Biol Chem.
281:5335–5340. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Zhang Y, Li W, Niu J, Fan Z, Li X and
Zhang H: Reprogramming of glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer:
Mechanisms, implications, and therapeutic perspectives. Front
Immunol. 16(1586959)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Du W, Xu A, Huang Y, Cao J, Zhu H, Yang B,
Shao X, He Q and Ying M: The role of autophagy in targeted therapy
for acute myeloid leukemia. Autophagy. 17:2665–2679.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Mohanty SS, Warrier S and Rangarajan A:
Rethinking AMPK: A reversible switch fortifying cancer cell
stress-resilience. Yale J Biol Med. 98:33–52. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Baek SY, Hwang UW, Suk HY and Kim YW:
Hemistepsin A inhibits cell proliferation and induces G0/G1-phase
arrest, cellular senescence and apoptosis via the AMPK and p53/p21
signals in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomolecules.
10(713)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Wang EM, Akasaka H, Zhao J, Varadhachary
GR, Lee JE, Maitra A, Fleming JB, Hung MC, Wang H and Katz MHG:
Expression and clinical significance of protein kinase RNA-like
endoplasmic reticulum kinase and phosphorylated eukaryotic
initiation factor 2α in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas.
48:323–328. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Grenier A, Poulain L, Mondesir J, Jacquel
A, Bosc C, Stuani L, Mouche S, Larrue C, Sahal A, Birsen R, et al:
AMPK-PERK axis represses oxidative metabolism and enhances
apoptotic priming of mitochondria in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell
Rep. 38(110197)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Wang S, Li H, Yuan M, Fan H and Cai Z:
Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front Physiol.
13(1015500)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Panina SB, Pei J and Kirienko NV:
Mitochondrial metabolism as a target for acute myeloid leukemia
treatment. Cancer Metab. 9(17)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Liu Y and Ma Z: Leukemia and mitophagy: A
novel perspective for understanding oncogenesis and resistance. Ann
Hematol. 103:2185–2196. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Li Y, Sun R, Zou J, Ying Y and Luo Z: Dual
roles of the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in angiogenesis.
Cells. 8(752)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Carling D: AMPK hierarchy: A matter of
space and time. Cell Res. 29:425–426. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Uprety B and Abrahamse H: Targeting breast
cancer and their stem cell population through AMPK activation:
Novel insights. Cells. 11(576)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Jhaveri TZ, Woo J, Shang X, Park BH and
Gabrielson E: AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) regulates activity of
HER2 and EGFR in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:14754–14765.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Göbel A, Riffel RM, Hofbauer LC and
Rachner TD: The mevalonate pathway in breast cancer biology. Cancer
Lett. 542(215761)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Amengual-Cladera E, Morla-Barcelo PM,
Morán-Costoya A, Sastre-Serra J, Pons DG, Valle A, Roca P and
Nadal-Serrano M: Metformin: From diabetes to cancer-unveiling
molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Biology (Basel).
13(302)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Pei W, Dai L, Li M, Cao S, Xiao Y, Yang Y,
Ma M, Deng M, Mo Y and Liu M: Targeting mitochondrial quality
control for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer: From
molecular mechanisms to precision therapy. Biomolecules.
15(970)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Lim JS, Kim E, Song JS and Ahn S:
Energy-stress-mediated activation of AMPK sensitizes MPS1 kinase
inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
52(101)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Mustafa M, Abbas K, Alam M, Ahmad W,
Moinuddin Usmani N, Siddiqui SA and Habib S: Molecular pathways and
therapeutic targets linked to triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Mol Cell Biochem. 479:895–913. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Li C, Syed MU, Nimbalkar A, Shen Y, Vieira
MD, Fraser C, Inde Z, Qin X, Ouyang J, Kreuzer J, et al: LKB1
regulates JNK-dependent stress signaling and apoptotic dependency
of KRAS-mutant lung cancers. Nat Commun. 16(4112)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Huang Q, Ren Y, Yuan P, Huang M, Liu G,
Shi Y, Jia G and Chen M: Targeting the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway: A novel
therapeutic approach for acute lung injury. J Inflamm Res.
17:4683–4700. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Fatehi Hassanabad A and MacQueen KT:
Molecular mechanisms underlining the role of metformin as a
therapeutic agent in lung cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 44:1–18.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Bernasconi R, Soodla K, Sirp A, Zovo K,
Kuhtinskaja M, Lukk T, Vendelin M and Birkedal R: Higher AMPK
activation in mouse oxidative compared with glycolytic muscle does
not correlate with LKB1 or CaMKKβ expression. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 328:E21–E33. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Sumbly V and Landry I: Unraveling the role
of STK11/LKB1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cureus.
14(e21078)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
190
|
Shi Y, Zheng H, Wang T, Zhou S, Zhao S, Li
M and Cao B: Targeting KRAS: From metabolic regulation to cancer
treatment. Mol Cancer. 24(9)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
191
|
Liu H, Zhou D, Ou Y, Chen S, Long Y, Yuan
T, Li Y and Tan Y: Multiple signaling pathways in the frontiers of
lung cancer progression. Front Immunol. 16(1593793)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Yibcharoenporn C, Muanprasat C,
Moonwiriyakit A, Satitsri S and Pathomthongtaweechai N: AMPK in
intestinal health and disease: A multifaceted therapeutic target
for metabolic and inflammatory disorders. Drug Des Devel Ther.
19:3029–3058. 2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Li S, Wang Y, Zhang D, Wang H, Cui X,
Zhang C and Xin Y: Gliclazide reduces colitis-associated colorectal
cancer formation by deceasing colonic inflammation and regulating
AMPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Dig Dis Sci. 69:453–462.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
194
|
Su G, Wang D, Yang Q, Kong L, Ju X, Yang
Q, Zhu Y, Zhang S and Li Y: Cepharanthine suppresses APC-mutant
colorectal cancers by down-regulating the expression of β-catenin.
Nat Prod Bioprospect. 14(18)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Liu JY, Liu JX, Li R, Zhang ZQ, Zhang XH,
Xing SJ, Sui BD, Jin F, Ma B and Zheng CX: AMPK, a hub for the
microenvironmental regulation of bone homeostasis and diseases. J
Cell Physiol. 239(e31393)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Fakhri S, Moradi SZ, Moradi SY, Piri S,
Shiri Varnamkhasti B, Piri S, Khirehgesh MR and Bishayee A,
Casarcia N and Bishayee A: Phytochemicals regulate cancer
metabolism through modulation of the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway.
BMC Cancer. 24(1079)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Cheng D, Zhang M, Zheng Y, Wang M, Gao Y,
Wang X, Liu X, Lv W, Zeng X, Belosludtsev KN, et al:
α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver
mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the
AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway. Redox Biol. 74(103230)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Naiini MR, Shahouzehi B, Azizi S, Shafiei
B and Nazari-Robati M: Trehalose-induced SIRT1/AMPK activation
regulates SREBP-1c/PPAR-α to alleviate lipid accumulation in aged
liver. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 397:1061–1070.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Cunha V, Cotrim HP, Rocha R, Carvalho K
and Lins-Kusterer L: Metformin in the prevention of hepatocellular
carcinoma in diabetic patients: A systematic review. Ann Hepatol.
19:232–237. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
200
|
Tufail M, Jiang CH and Li N: Altered
metabolism in cancer: Insights into energy pathways and therapeutic
targets. Mol Cancer. 23(203)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Liu B, Liu L and Liu Y: Targeting cell
death mechanisms: The potential of autophagy and ferroptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Front Immunol.
15(1450487)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
202
|
Li A, Wang R, Zhao Y, Zhao P and Yang J:
Crosstalk between epigenetics and metabolic reprogramming in
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease-induced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A new sight. Metabolites.
14(325)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Nadile M, Sze NS, Fajardo VA and Tsiani E:
Inhibition of prostate cancer cell survival and proliferation by
carnosic acid is associated with inhibition of Akt and activation
of AMPK signaling. Nutrients. 16(1257)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Schooling CM, Yang G, Soliman GA and Leung
GM: A hypothesis that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
exert immediate and multifaceted effects by activating adenosine
monophosphate-activate protein kinase (AMPK). Life (Basel).
15(253)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Manoharan R: Salt-inducible kinases (SIKs)
in cancer: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic prospects. Drug
Discov Today. 30(104279)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Espitia-Pérez PJ, Espitia-Perez LM and
Negrette-Guzmán M: Targeting Prostate cancer metabolism through
transcriptional and epigenetic modulation: A multi-target approach
to therapeutic innovation. Int J Mol Sci. 26(6013)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Pujana-Vaquerizo M, Bozal-Basterra L and
Carracedo A: Metabolic adaptations in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
131:1250–1262. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Li H, Wang T, Lu F, Liu
R, Xie G, Song L, Huang B, Li X, et al: Enzalutamide inhibits PEX10
function and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ROS activators.
Cell Death Dis. 15(559)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Lemos G, Fernandes CMADS, Silva FH and
Calmasini FB: The role of autophagy in prostate cancer and
prostatic diseases: A new therapeutic strategy. Prostate Cancer
Prostatic Dis. 27:230–238. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Inoki K, Kim J and Guan KL: AMPK and mTOR
in cellular energy homeostasis and drug targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 52:381–400. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
211
|
Choi BH and Coloff JL: The diverse
functions of non-essential amino acids in cancer. Cancers (Basel).
11(675)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
212
|
Jin J, Byun JK, Choi YK and Park KG:
Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for
cancer. Exp Mol Med. 55:706–715. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
213
|
Halama A and Suhre K: Advancing cancer
treatment by targeting glutamine metabolism-A roadmap. Cancers
(Basel). 14(553)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Linke M, Fritsch SD, Sukhbaatar N,
Hengstschläger M and Weichhart T: mTORC1 and mTORC2 as regulators
of cell metabolism in immunity. FEBS Lett. 591:3089–3103.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Wang R, Dillon CP, Shi LZ, Milasta S,
Carter R, Finkelstein D, McCormick LL, Fitzgerald P, Chi H, Munger
J and Green DR: The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic
reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity. 35:871–882.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
216
|
Valvezan AJ and Manning BD: Molecular
logic of mTORC1 signalling as a metabolic rheostat. Nat Metab.
1:321–333. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
217
|
Nishitani S, Horie M, Ishizaki S and Yano
H: Branched chain amino acid suppresses hepatocellular cancer stem
cells through the activation of mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS
One. 8(e82346)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Kazyken D, Magnuson B, Bodur C,
Acosta-Jaquez HA, Zhang D, Tong X, Barnes TM, Steinl GK, Patterson
NE, Altheim CH, et al: AMPK directly activates mTORC2 to promote
cell survival during acute energetic stress. Sci Signal.
12(eaav3249)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Sadria M and Layton AT: Interactions among
mTORC, AMPK and SIRT: A computational model for cell energy balance
and metabolism. Cell Commun Signal. 19(57)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
220
|
Sujobert P, Poulain L, Paubelle E,
Zylbersztejn F, Grenier A, Lambert M, Townsend EC, Brusq JM,
Nicodeme E, Decrooqc J, et al: Co-activation of AMPK and mTORC1
induces cytotoxicity in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Rep.
11:1446–1457. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
221
|
Davie E, Forte GMA and Petersen J:
Nitrogen regulates AMPK to control TORC1 signaling. Curr Biol.
25:445–454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
222
|
Lie S, Wang T, Forbes B, Proud CG and
Petersen J: The ability to utilise ammonia as nitrogen source is
cell type specific and intricately linked to GDH, AMPK and mTORC1.
Sci Rep. 9(1461)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
223
|
Lu T, Sun L, Wang Z, Zhang Y, He Z and Xu
C: Fatty acid synthase enhances colorectal cancer cell
proliferation and metastasis via regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:3339–3347. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
224
|
Pereira O, Teixeira A, Sampaio-Marques B,
Castro I, Girão H and Ludovico P: Signalling mechanisms that
regulate metabolic profile and autophagy of acute myeloid leukaemia
cells. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4807–4817. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Chiang CT, Demetriou AN, Ung N, Choudhury
N, Ghaffarian K, Ruderman DL and Mumenthaler SM: mTORC2 contributes
to the metabolic reprogramming in EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
resistant cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett.
434:152–159. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
226
|
Zhang P, Fu HJ, Lv LX, Liu CF, Han C, Zhao
XF and Wang JX: WSSV exploits AMPK to activate mTORC2 signaling for
proliferation by enhancing aerobic glycolysis. Commun Biol.
6(361)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
227
|
He Z, Houghton PJ, Williams TM and Shen C:
Regulation of DNA duplication by the mTOR signaling pathway. Cell
Cycle. 20:742–751. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
228
|
Bu C, Zhao L, Wang L, Yu Z and Zhou J:
mTORC2 promotes pancreatic cancer progression and PARP inhibitor
resistance. Oncol Res. 31:495–503. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
229
|
Pournajaf S and Pourgholami MH: The mTOR
pathway in Gliomas: From molecular insights to targeted therapies.
Biomed Pharmacother. 189(118237)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22(138)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
231
|
Carew JS, Kelly KR and Nawrocki ST:
Mechanisms of mTOR inhibitor resistance in cancer therapy. Target
Oncol. 6:17–27. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
232
|
Dunn S, Eberlein C, Yu J, Gris-Oliver A,
Ong SH, Yelland U, Cureton N, Staniszewska A, McEwen R, Fox M, et
al: AKT-mTORC1 reactivation is the dominant resistance driver for
PI3Kβ/AKT inhibitors in PTEN-null breast cancer and can be overcome
by combining with Mcl-1 inhibitors. Oncogene. 41:5046–5060.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
233
|
Basnet R, Basnet BB, Gupta R, Basnet T,
Khadka S and Alam MS: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)
signalling pathway-a potential target for cancer intervention: A
short overview. Curr Mol Pharmacol.
17(e310323215268)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
234
|
Kim H, Lebeau B, Papadopoli D, Jovanovic
P, Russo M, Avizonis D, Morita M, Afzali F, Ursini-Siegel J,
Postovit LM, et al: MTOR modulation induces selective perturbations
in histone methylation which influence the anti-proliferative
effects of mTOR inhibitors. iScience. 27(109188)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
235
|
Faes S, Santoro T, Troquier L, Silva OD
and Dormond O: Rebound pathway overactivation by cancer cells
following discontinuation of PI3K or mTOR inhibition promotes
cancer cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:546–552.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Khorasani ABS, Hafezi N, Sanaei MJ,
Jafari-Raddani F, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A and Bashash D: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer: Review of
clinical trials and latest advances. Cell Biochem Funct.
42(e3998)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
237
|
Napolitano F, Lin CC, Ahuja K, Ye D,
Chica-Parrado MR, Uemoto Y, Luna P, Matsunaga Y, Mendiratta S, Unni
N, et al: Abstract 3003: Targeting mechanisms of adaptive
resistance to the PI3Kαmutant selective inhibitor RLY-2608 in
HR+/PIK3CA mutant breast cancer. Cancer Res. 85 (8 Suppl
1)(S3003)2025.
|
|
238
|
Elkanawati RY, Sumiwi SA and Levita J:
Impact of lipids on insulin resistance: Insights from human and
animal studies. Drug Des Devel Ther. 18:3337–3360. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
Martínez Báez A, Ayala G, Pedroza-Saavedra
A, González-Sánchez HM and Chihu Amparan L: Phosphorylation codes
in IRS-1 and IRS-2 are associated with the activation/inhibition of
insulin canonical signaling pathways. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
46:634–649. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
240
|
Banjac K, Obradovic M, Zafirovic S, Essack
M, Gluvic Z, Sunderic M, Nedic O and Isenovic ER: The involvement
of Akt, mTOR, and S6K in the in vivo effect of IGF-1 on the
regulation of rat cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase. Mol
Biol Rep. 51(517)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
241
|
Wright SCE, Vasilevski N, Serra V, Rodon J
and Eichhorn PJA: Mechanisms of resistance to PI3K inhibitors in
cancer: Adaptive responses, drug tolerance and cellular plasticity.
Cancers (Basel). 13(1538)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
242
|
Pourbarkhordar V, Rahmani S, Roohbakhsh A,
Hayes AW and Karimi G: Melatonin effect on breast and ovarian
cancers by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. IUBMB Life.
76:1035–1049. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
243
|
Vadla R and Haldar D: Mammalian target of
rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) controls glycolytic gene expression by
regulating Histone H3 Lysine 56 acetylation. Cell Cycle.
17:110–123. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|