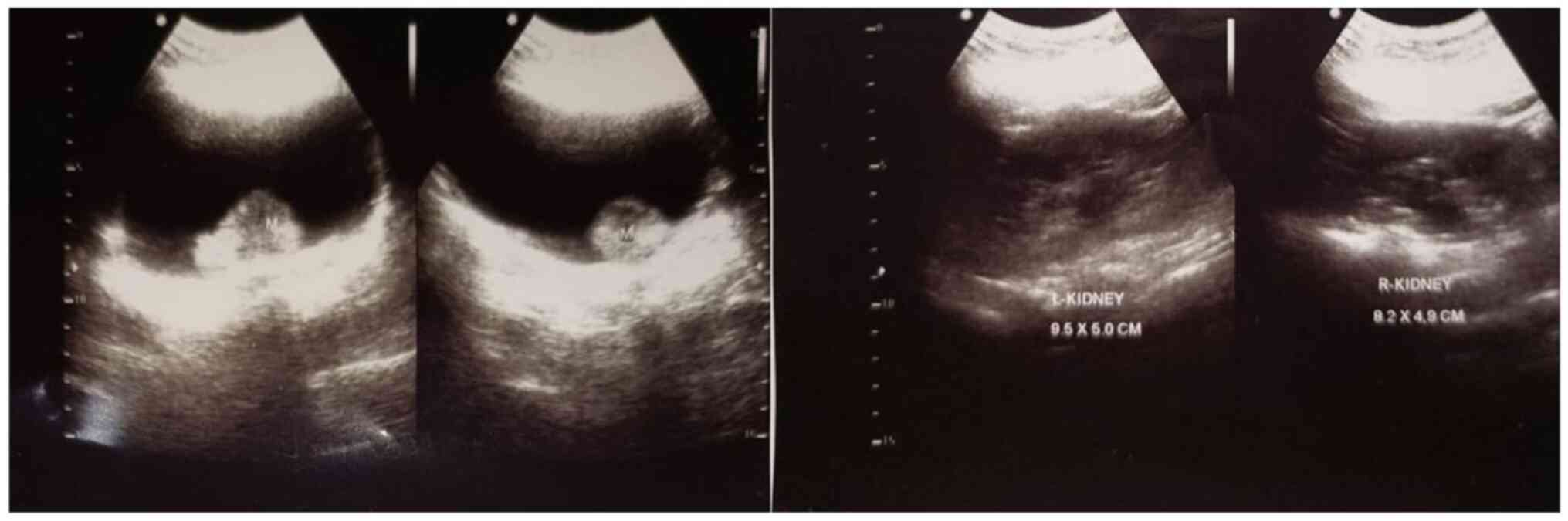
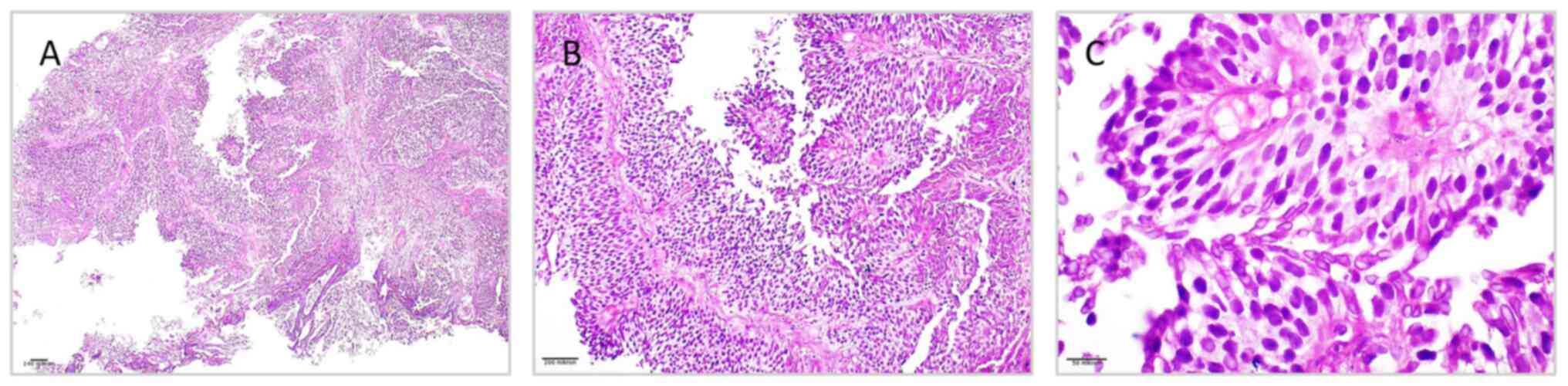
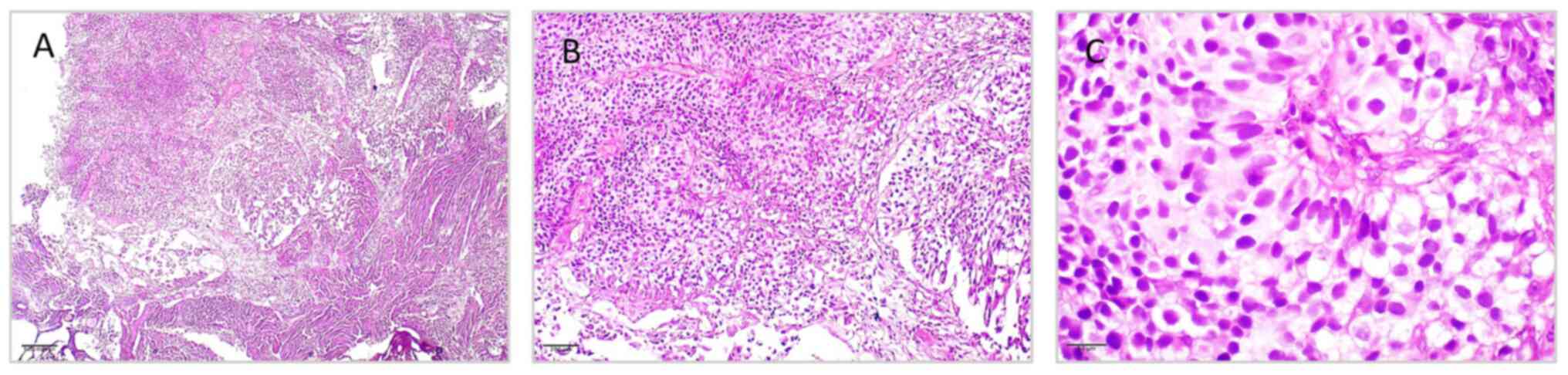
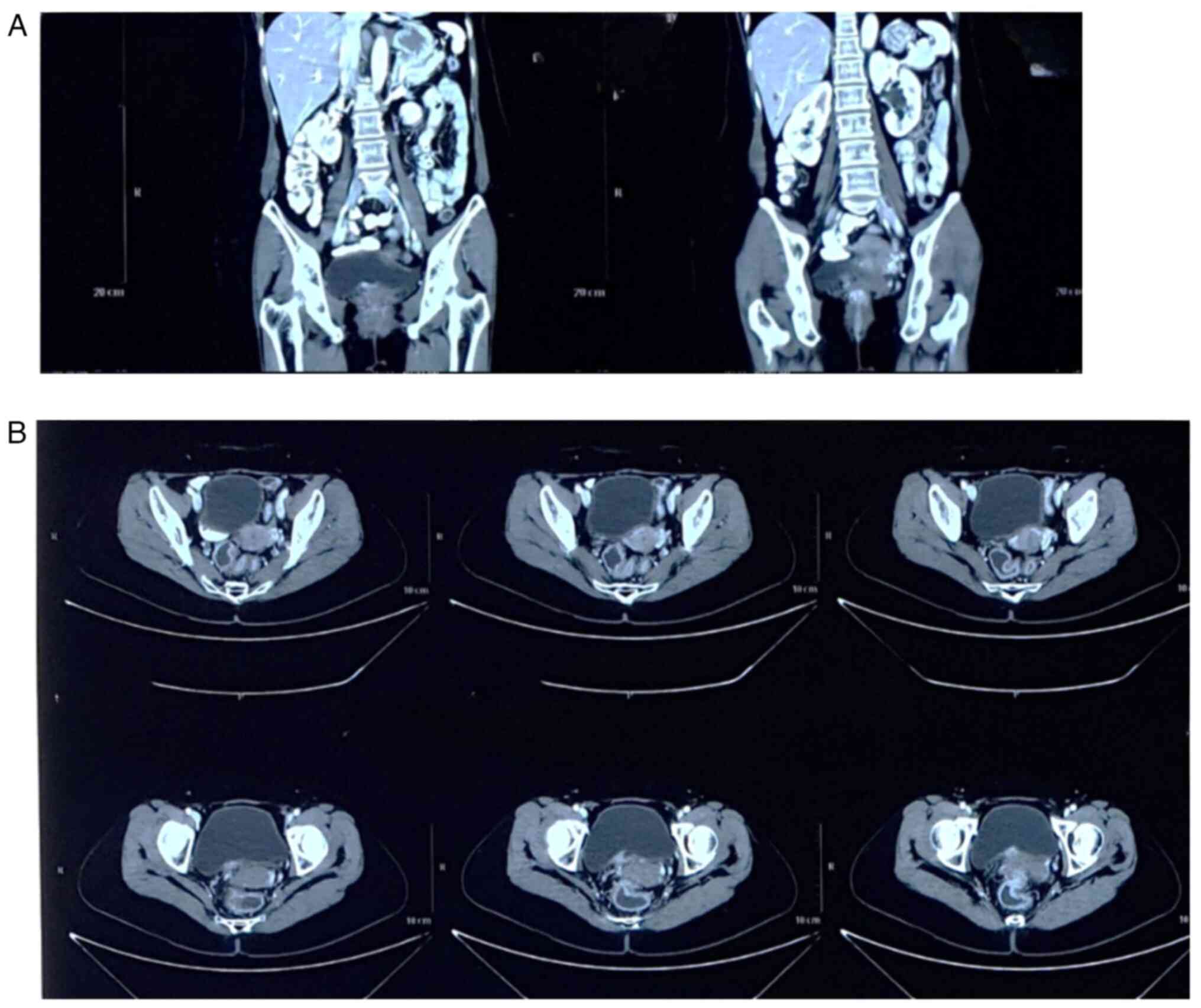
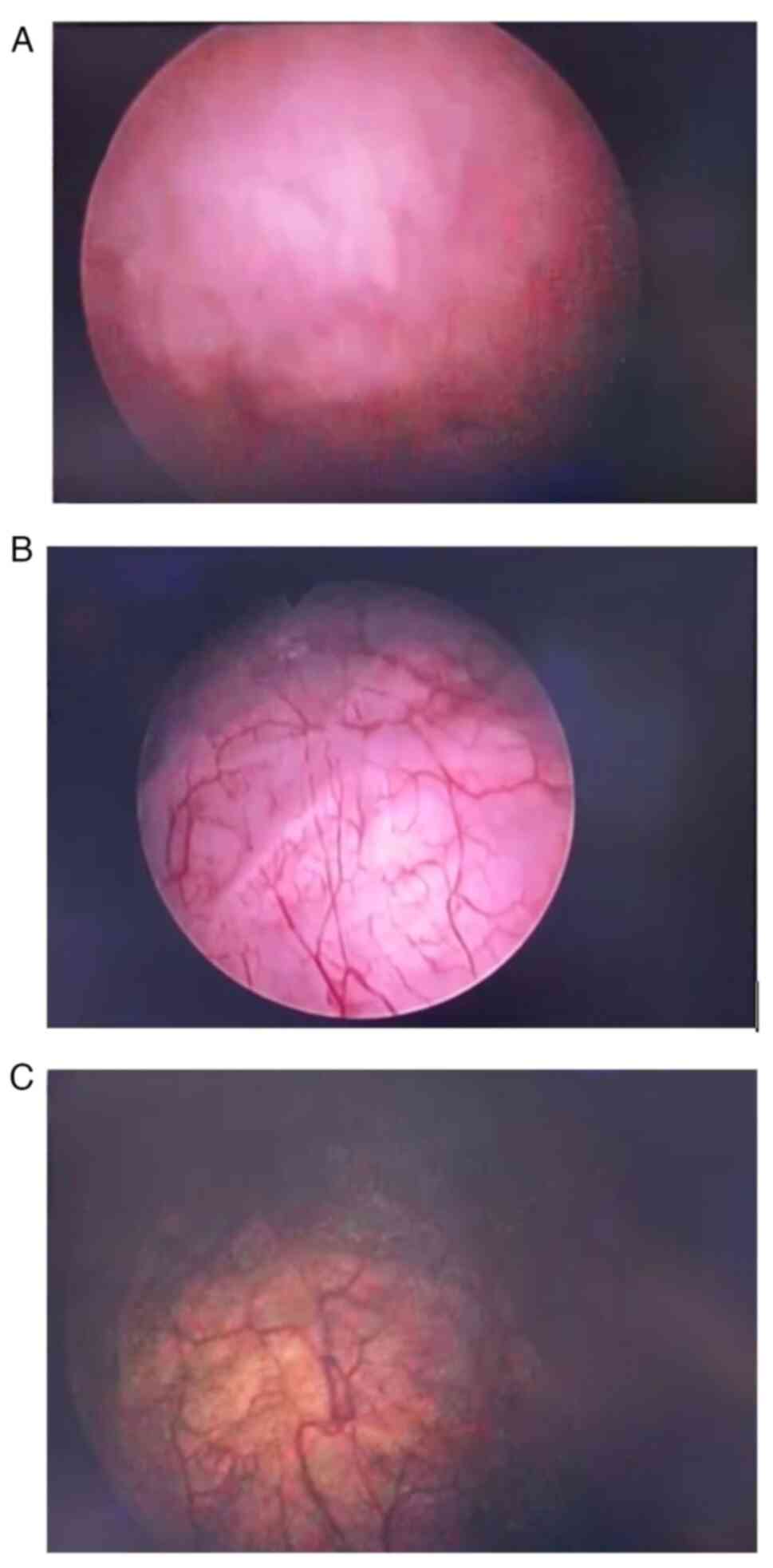
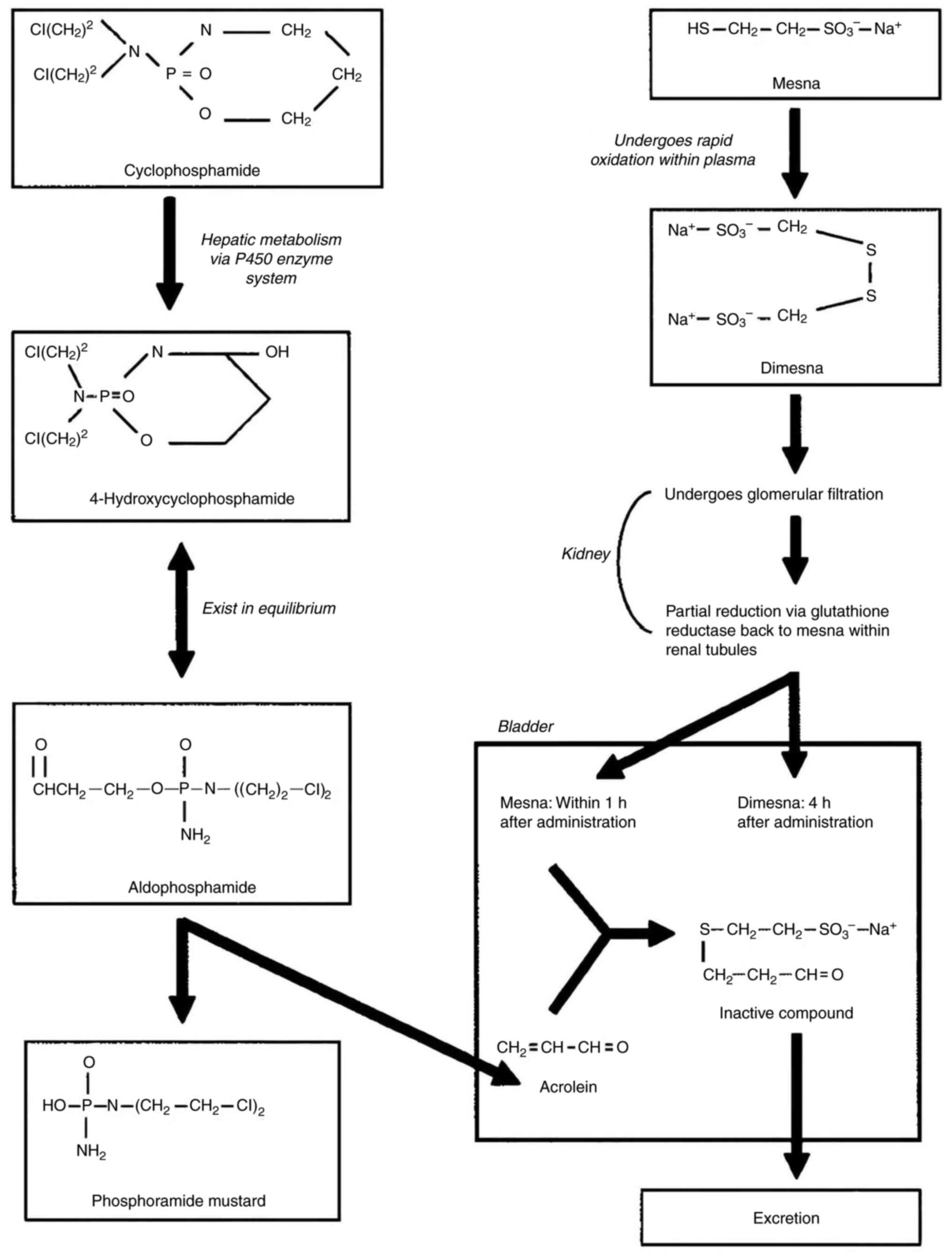
|
1
|
GLOBOCAN: All Cancer. The Global Cancer
Observatory, 2020.
|
|
2
|
Pedersen RN, Esen BÖ, Mellemkjær L,
Christiansen P, Ejlertsen B, Lash TL, Nørgaard M and Cronin-Fenton
D: The incidence of breast cancer recurrence 10-32 years after
primary diagnosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 114:391–399. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sinanoglu O, Yener AN, Ekici S, Midi A and
Aksungar FB: The protective effects of spirulina in
cyclophosphamide induced nephrotoxicity and urotoxicity in rats.
Urology. 80:1392.e1–e6. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Abraham P, Kanakasabapathy I and Sugumar
E: Decrease in the activities of lysosomal enzymes may contribute
to the urotoxicity of cyclophosphamide in the rat. Biomed Res.
18:131–136. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Volm T, Pfaff P, Gnann R and Kreienberg R:
Bladder carcinoma associated with cyclophosphamide therapy for
ovarian cancer occurring with a latency of 20 years. Gynecol Oncol.
82:197–199. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Veitch Z, Khan OF, Tilley D, Tang PA,
Ribnikar D, Stewart DA, Kostaras X, King K and Lupichuk S: Impact
of cumulative chemotherapy dose on survival with adjuvant FEC-D
chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 8:957–967.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liga EGK, Abdullah N, Tiro E, Maisuri S
and Chalid T: The effect of cyclophosphamide chemotherapy on
ovarian AntiMüllerian hormone levels in breast cancer patients.
Indonesian J Obstetr Gynecol. 6:64–67. 2018.
|
|
8
|
Kang YK, Si YR, An GY and Yuan P: Efficacy
and safety of cyclophosphamide in anthracycline- and Taxane-based
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Gland
Surg. 10:252–261. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Saoji VA: Cyclophosphamide-induced cancers
in pemphigus patients-A report of three cases. Indian J Drugs
Dermatol. 6:32–34. 2020.
|
|
10
|
Yilmaz N, Emmungil H, Gucenmez S, Ozen G,
Yildiz F, Balkarli A, Kimyon G, Coskun BN, Dogan I, Pamuk ON, et
al: Incidence of cyclophosphamide-induced urotoxicity and
protective effect of mesna in rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol.
42:1661–1666. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Emadi A, Jones RJ and Brodsky RA:
Cyclophosphamide and cancer: Golden anniversary. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 6:638–647. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Worth PH: Cyclophosphamide and the
bladder. Br Med J. 3(182)1971.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Monach PA, Arnold LM and Merkel PA:
Incidence and prevention of bladder toxicity from cyclophosphamide
in the treatment of rheumatic diseases: A data-driven review.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:9–21. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sohn HJ, Kim SH, Lee GW, Kim S, Kang HJ,
Ahn JH, Kim SB, Kim SW, Kim WK and Suh C: High-dose chemotherapy of
cyclophosphamide, thiotepa, and carboplatin (CTCb) followed by
autologous stem-cell transplantation for metastatic breast cancer
patients: A 6-year follow-up result. Cancer Res Treat. 37:24–30.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhou H, Liu D, Chen L, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Ge
Y, Liu M and Kong T: Metastasis to the bladder from primary breast
cancer: A case report and literature review. Oncol Lett.
27(249)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gor PP, Su HI, Gray RJ, Gimotty PA, Horn
M, Aplenc R, Vaughan WP, Tallman MS, Rebbeck TR and DeMichele A:
Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival
outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast
cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res.
12(R26)2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chou WH, McGregor B, Schmidt A, Carvalho
FLF, Hirsch MS, Chang SL, Kibel A and Mossanen M:
Cyclophosphamide-associated bladder cancers and considerations for
survivorship care: A systematic review. Urol Oncol. 39:678–685.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Warli SM, Prapiska FF, Siregar DIS and
Seja IA: Tumor markers as predictors of acute kidney injury
incidence and staging of the Muscle-invasive bladder cancer
receiving chemoradiation therapy. World J Oncol. 14:423–429.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Knight A, Askling J, Granath F, Sparen P
and Ekbom A: Urinary bladder cancer in Wegener's granulomatosis:
Risks and relation to cyclophosphamide. Ann Rheum Dis.
63:1307–1311. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Stillwell TJ, Benson RC Jr and Burgent EO
Jr: Cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in Ewing's
sarcoma. J Clin Onco. 6:76–82. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Warli SM, Prapiska FF, Siregar DIS and
Wijaya WS: Prediction of locally advanced bladder tumor using
preoperative clinical parameters. Urol Ann. 15:412–416.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Radis CD, Kahl LE, Baker GL, Wasko MC,
Cash JM, Gallatin A, Stolzer BL, Agarwal AK, Medsger TA Jr and Kwoh
CK: Effects of cyclophosphamide on the development of malignancy
and on long-term survival of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A
20-year followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 38:1120–1127.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tanaka T, Nakashima Y, Sasaki H, Masaki M,
Mogi A, Tamura K and Takamatsu Y: Severe hemorrhagic cystitis
caused by cyclophosphamide and capecitabine therapy in breast
cancer patients: Two case reports and literature review. Case Rep
Oncol. 12:69–75. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|