Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), caused by median nerve
(MN) compression at the wrist, is the most prevalent type of
entrapment neuropathy of the wrist (1). The median nerve distribution is
affected by symptoms, such as pain, tingling and numbness, and the
global incidence of this condition has been reported to range from
0.24 to 0.4% (1,2).
A clinical evaluation and nerve conduction studies
(NCS) are the two requirements for reaching a diagnosis;
nevertheless, NCS tests are not only uncomfortable, but are also
time-consuming and prone to producing misleading results (3,4). The
measurement of the MN cross-sectional area (CSA) at the flexor
retinaculum using ultrasound (US) is a promising alternative that
does not involve any invasive procedures. This method enables the
direct measurement of the MN CSA (5). In comparison to electrodiagnostic
examinations, it is more convenient, less costly and provides
morphological data (6). However,
the connection between CSA-D and NCS latencies is not yet fully
understood, despite the fact that it has the potential to be
significant.
The present study thus aimed to determine the
correlation between the MN CSA at the distal wrist (CSA-D) with the
severity of CTS, as graded by NCS.
Patients and methods
Study design and setting
The present prospective, cross-sectional study was
carried out at the Al-Imamen Al-Kadhmin Medical Teaching Hospital
(a primary teaching hospital affiliated with the College of
Medicine, Al-Nahrain University) in Baghdad, Iraq during the months
of September, 2023 and July, 2024. The study cohort comprised 60
female patients. The sample comprised only females as the
prevalence of CTS is markedly higher in females than males. There
were no male patients during patient recruitment period. Patients
were presenting with clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of CTS,
as assessed by an orthopedic surgeon. Clinical indicators of CTS
included tingling and/or numbness, nocturnal symptoms mostly in MN
distribution and positive results on a clinical examination (Phalen
test or compression test).
Ethical considerations
Research approval was obtained from the
institutional Review Board of Al-Khadimain Teaching Hospital
(Reference no. 5563 on April 24, 2023). Following the explanation
of the objectives of the study, each participant completed a
consent form before the commencement of data collection.
Participants were informed of their unconditional right to withdraw
at any time, and the confidentiality of all collected data was
strictly maintained.
Patient population and data
collection
Direct interviews were used to obtain patient
demographics [age and body mass index (BMI)]. The inclusion
criteria were the following: The presence of typical CTS symptoms,
such as numbness, tingling, burning, or pain in the median nerve
distribution (thumb, index, middle fingers); a duration of symptoms
persisting for a minimum period (e.g., ≥3 months); and clinical
signs, i.e., positive provocative tests, such as Phalen s test
or Tinel s sign, as assessed by an orthopedic surgeon.
The exclusion criteria were the following: Patients
were excluded if they had a history of concomitant illnesses, such
as cervical radiculopathy, prior ipsilateral CTS surgery,
rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disease, pregnancy, brachial
plexopathy, wrist fractures and polyneuropathy.
NCS and severity grading
An electrophysiologist blinded to the findings of
the clinical and US investigations conducted NCS, which consisted
of five different motor and sensory nerve measurements. Compound
muscle action potentials (CMAPs) and distal motor latencies (DMLs)
were recorded for this investigation, and motor latencies were
measured over 5-6 cm segments over the MN.
Measurements of sensory nerve action potentials
(SNAPs) and distal sensory latencies were made in addition to
sensory latencies recorded over 12-13 cm segments of the MN. NCS
results were deemed normal when the following criteria were met: MN
motor latency <4.0 msec, CMAP amplitude >10 mV, MN sensory
latency <3.5 msec, and SNAP amplitude >6 µV. The thresholds
were obtained from previous studies on CTS, as well as guidelines
from clinical neurology (7-11).
The inability to satisfy any of these requirements was the defining
characteristic of a positive electrodiagnostic test result for
CTS.
Electrophysiological severity
grading
The severity of CTS was classified as mild, moderate
or severe based on the findings of NCS, in accordance with the
electrodiagnostic guidelines that have been developed (12): i) Mild CTS: Prolonged median
sensory latency (>3.5 msec) with normal median motor distal
latency (≤4.0 msec); ii) moderate CTS: Prolonged median sensory
latency and prolonged median motor distal latency (>4.0 msec)
with a preserved CMAP amplitude; iii) severe CTS: Prolonged median
motor and sensory latencies with either a low CMAP amplitude
(<4.5 mV) and/or electrophysiological evidence of axonal loss.
In the present study, it was confirmed that all 65 wrists (as in 5
patients, both wrists were affected) were classified using these
specific, quantitative metrics.
Ultrasonographic examination
A radiologist, blinded to the results of the
electrodiagnostic testing, conducted the ultrasonography of the
median nerve. The carpal tunnel entrance at the pisiform bone was
utilized to measure the CSA of the MN. A 4-12 MHz linear array
transducer (US machine: Affiniti 30 Ultrasound system; Philips
Medical System) was employed for the ultrasonography, positioned
vertical to the forearm.
On the examination table, the patients lay on their
backs, elbows bent at 90˚, and forearms widely splayed. An ellipse
function was employed by the US machine to determine the CSA. The
hyperechoic epineurium interior area can be determined using this
function, which forms an ellipse around the target region (13).
Assessment of measurement
reliability
An intra-observer variability assessment was carried
out to guarantee the accuracy and reproducibility of the
ultrasonographic measurements. Following 1 week, 15 patients
(representing 25% of the total sample) were re-measured for CSA-D
by the same radiologist who had been blinded to the
electrodiagnostic results.
Reproducibility was high, with an intra-class
correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.94 (95% CI, 0.87-0.98) for
intra-observer reliability. To reduce the possibility of operator
error, the NCS relied on a single, highly trained
electrophysiologist to conduct each test according to a
predetermined procedure. In conformity with the standards set forth
by the American Association of Neuromuscular &
Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM), all subjects had identical
equipment settings and electrode placements (12).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were executed using SPSS
software (version 25.0). Continuous data that were not normally
distributed data were analyzed using the Kruskal Wallis test
followed by Dunn s multiple comparisons test. The
discriminative ability of the MN CSA in distinguishing between
mild, moderate and CTS was assessed using receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Pearson s correlation
analysis was used to examine potential correlations between MN CSA
and other variables. A P-value <0.05 was considered to indicate
a statistically significant difference.
Results
Demographic and clinical
characteristics of the patients
The study population had a mean age of 49.7±11.34
years. The cohort, comprising exclusively female participants, had
a mean BMI of 28.58±3.1 kg/m2, categorizing the majority
of the patients as overweight or obese. In total, 58.46% of the
patients had an involvement of the right wrist (Table I).
 | Table IDemographic characteristics of the
patients with carpal tunnel syndrome in the present study
(n=60). |
Table I
Demographic characteristics of the
patients with carpal tunnel syndrome in the present study
(n=60).
| Variables | Value |
|---|
| Age, years | |
|
Mean ±
SD | 49.7±11.34 |
|
Range | 25-68 |
| Height, cm | |
|
Mean ±
SD | 165.5±9.4 |
|
Range | 150-179 |
| Weight, kg | |
|
Mean ±
SD | 75.18±9.0 |
|
Range | 67-102 |
| Body mass index,
kg/m2 | |
|
Mean ±
SD | 28.58±3.1 |
|
Range | 23.2-35.0 |
| Patients (n=60) | Unilateral CTS:
55 |
| | Bilateral CTS: 5 |
| Wrists (n=65) | Right: 38
(58.46%) |
| | Left: 27
(41.54%) |
Electrophysiological parameters and
ultrasonography
The mean DML and CMAP of the affected MN were
5.43±2.08 msec and 5.81±1.89 msec, respectively. Abnormalities in
conduction velocities and sensory latencies were prevalent, with a
mean motor conduction velocity of 53.0±6.42 m/sec, mean sensory
latency of 4.56±2.57 msec, and mean sensory conduction velocity of
30.98±23.91 m/sec. The ultrasonography findings revealed that the
mean CSA of the affected MN at its distal segment was 17.9±4.1
mm2 (Table II).
 | Table IIElectrophysiological parameters and
sonography (60 wrists). |
Table II
Electrophysiological parameters and
sonography (60 wrists).
| Variables | Mean ± SD | Range |
|---|
| MN distal motor
latency, msec | 5.43±2.08 | 2.8-11.2 |
| MN compound muscle
action potential (msec) | 5.81±1.89 | 1.9-9.7 |
| MN motor conduction
velocity, msec | 53.0±6.42 | 35.5-68.8 |
| MN sensory latency
msec | 4.56±2.57 | 2.5-11 |
| MN sensory action
potentials amplitude, µv | 30.98±23.91 | 3.5-98.4 |
| MN sensory
conduction velocity, msec | 31.66±10.77 | 10.8-48.0 |
| MN cross sectional
area, mm2 | 17.9±4.1 | 10.0-31.0 |
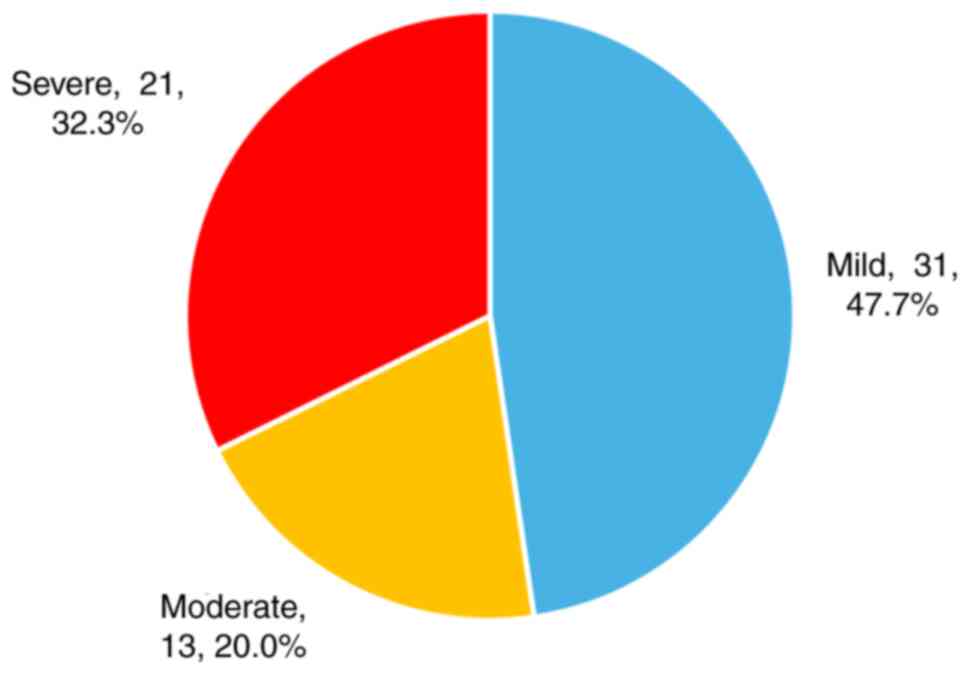
Distribution of disease severity
Based on the American criteria for CTS
classification (14), of the 65
affected wrists, 31 (47.69%) were categorized as having mild
disease, 13 (20%) as moderate disease, and 21 (32.3%) as severe
disease (Fig. 1).
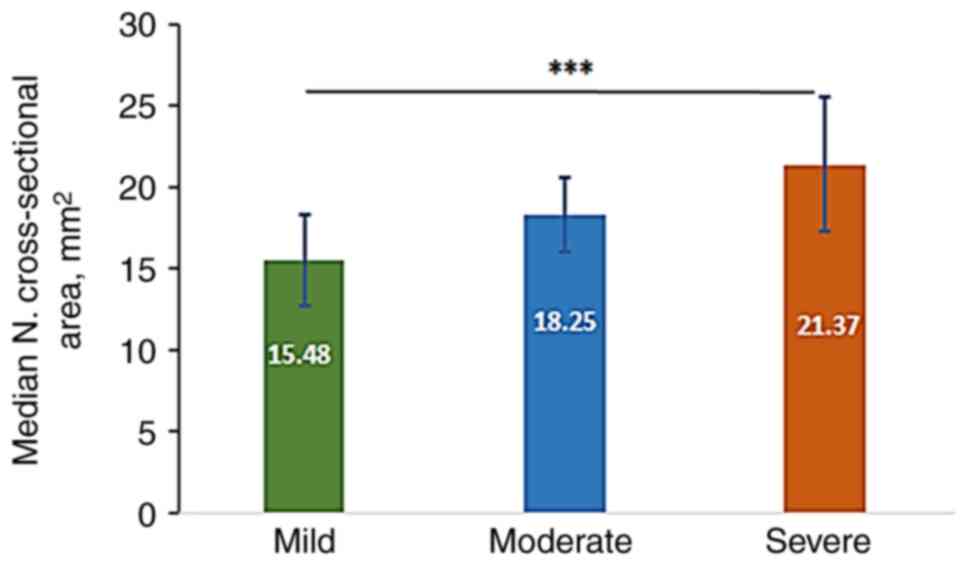
Association between median nerve CSA-D
and disease severity
The mean CSA-D in mild, moderate and severe cases
was 15.48±2.82, 18.25±2.62 and 21.37±4.14 mm2,
respectively, with highly significant differences observed between
mild and severe categories, as analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis
test followed by Dunn s test for multiple comparisons
(Fig. 2).
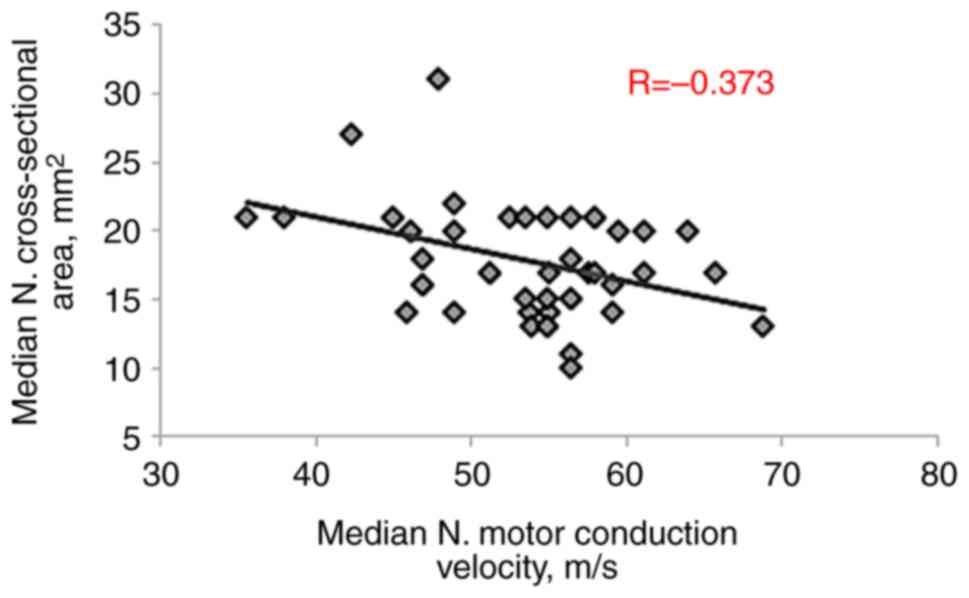
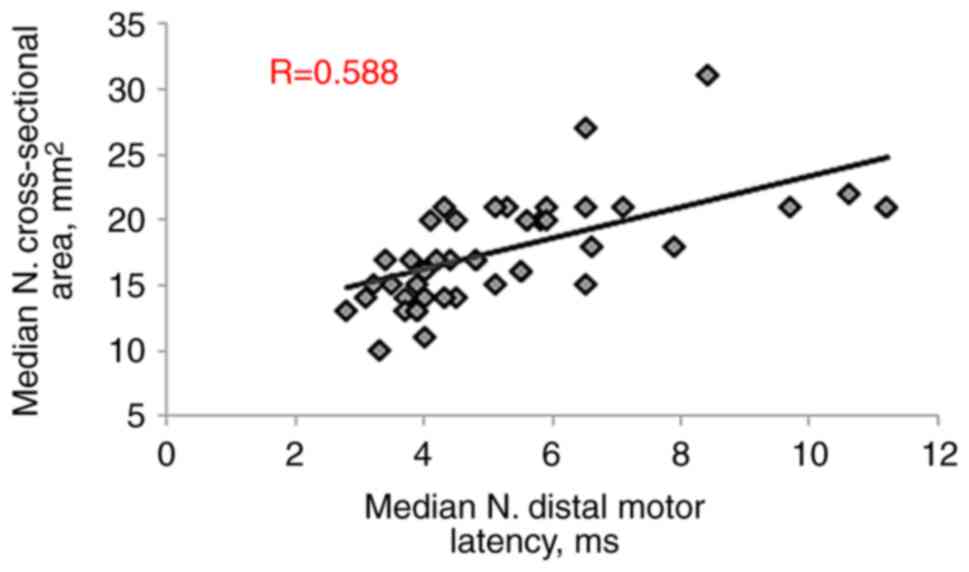
Correlation of CSA-D with
electrophysiological parameters
Pearson s correlation analysis was performed to
examine the correlation between the CSA-D and other parameters in
patients with CTS. The CSA-D exhibited a significant positive
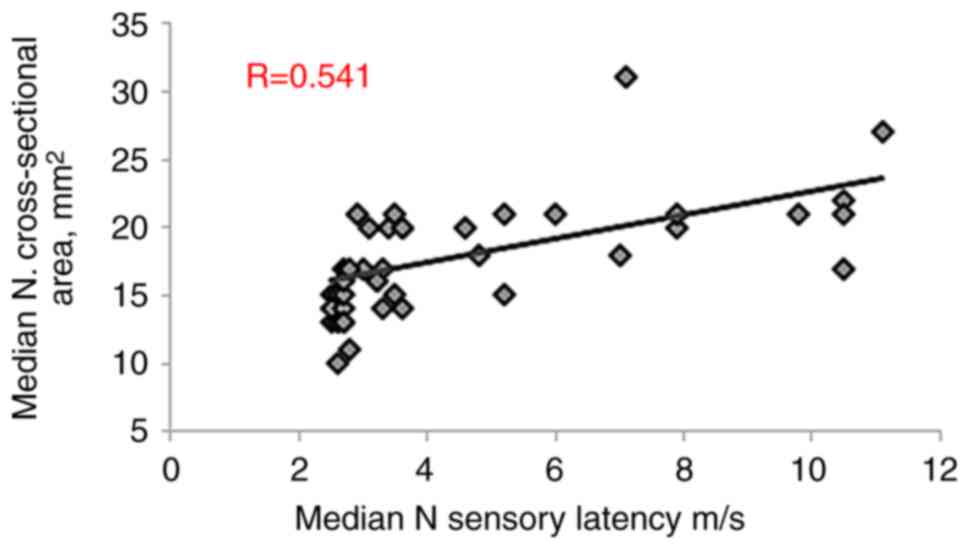
correlation with both MN distal motor latency (R=0.588, P<0.001)
and MN sensory latency (R=0.541, P<0.001). Conversely,
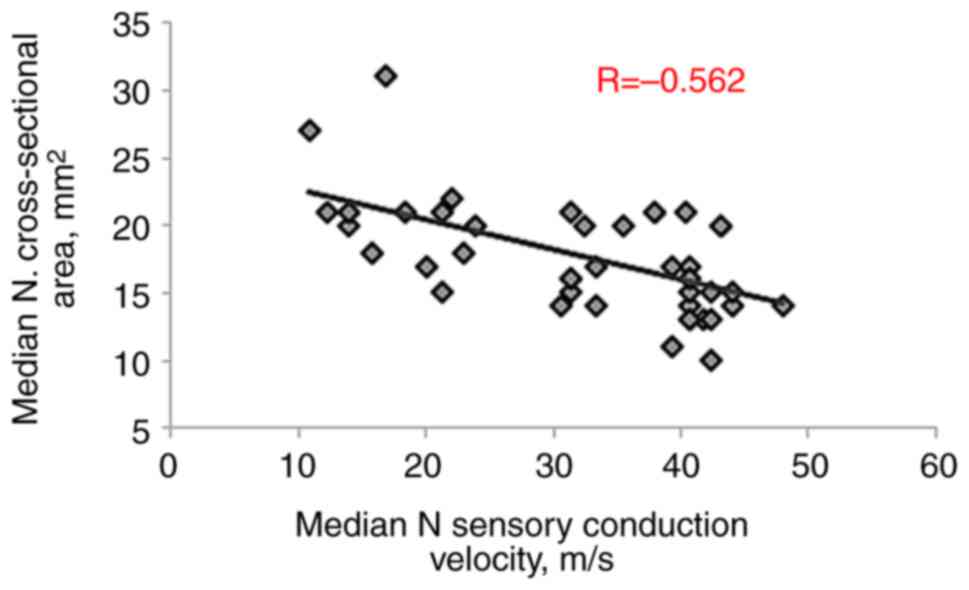
significant negative correlations were observed with MN motor
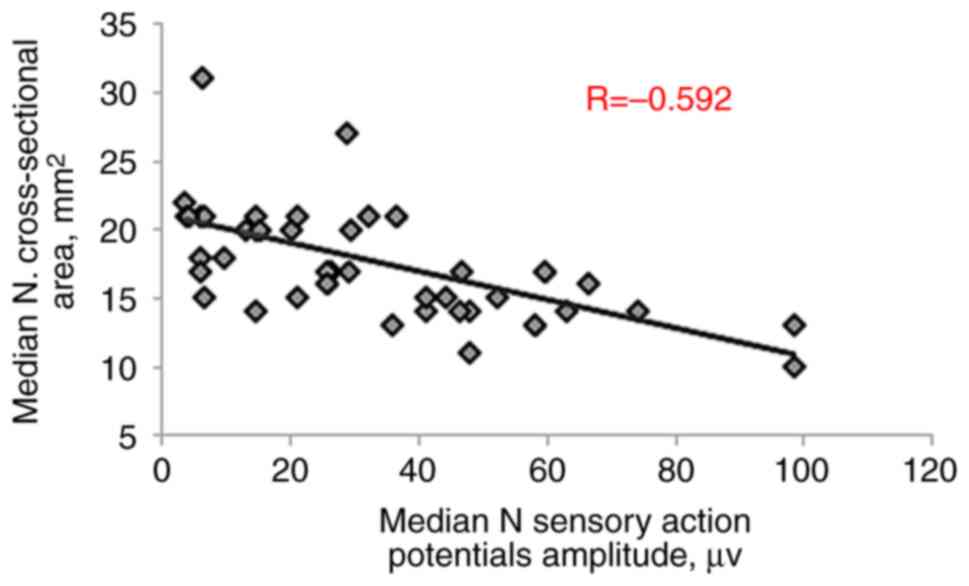
conduction velocity (R=-0.373, P=0.003), sensory action potential
amplitude (R=-0.592, P<0.001) and sensory conduction velocity
(R=-0.562, P<0.001), as presented in Table III and Fig. 3, Fig.
4, Fig. 5, Fig. 6 and Fig. 7.
 | Table IIIPearson s correlation between MN
cross sectional area at distal wrist with other parameters in
patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. |
Table III
Pearson s correlation between MN
cross sectional area at distal wrist with other parameters in
patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.
| Variables | Coefficient | P-value |
|---|
| MN. distal motor
latency, msec | 0.588 | <0.001 |
| MN compound muscle
action potential (msec) | -0.215 | 0.098 |
| MN. motor
conduction velocity, msec | -0.373 | 0.003 |
| MN sensory action
potentials amplitude, µv | -0.592 | <0.001 |
| MN sensory latency
msec | 0.541 | <0.001 |
| MN sensory
conduction velocity, msec | -0.562 | <0.001 |
| Age, years | 0.112 | 0.396 |
| Height, cm | 0.091 | 0.489 |
| Weight, kg | 0.099 | 0.453 |
| Body mass index,
kg/m2 | 0.178 | 0.175 |
Diagnostic performance of
ultrasonography
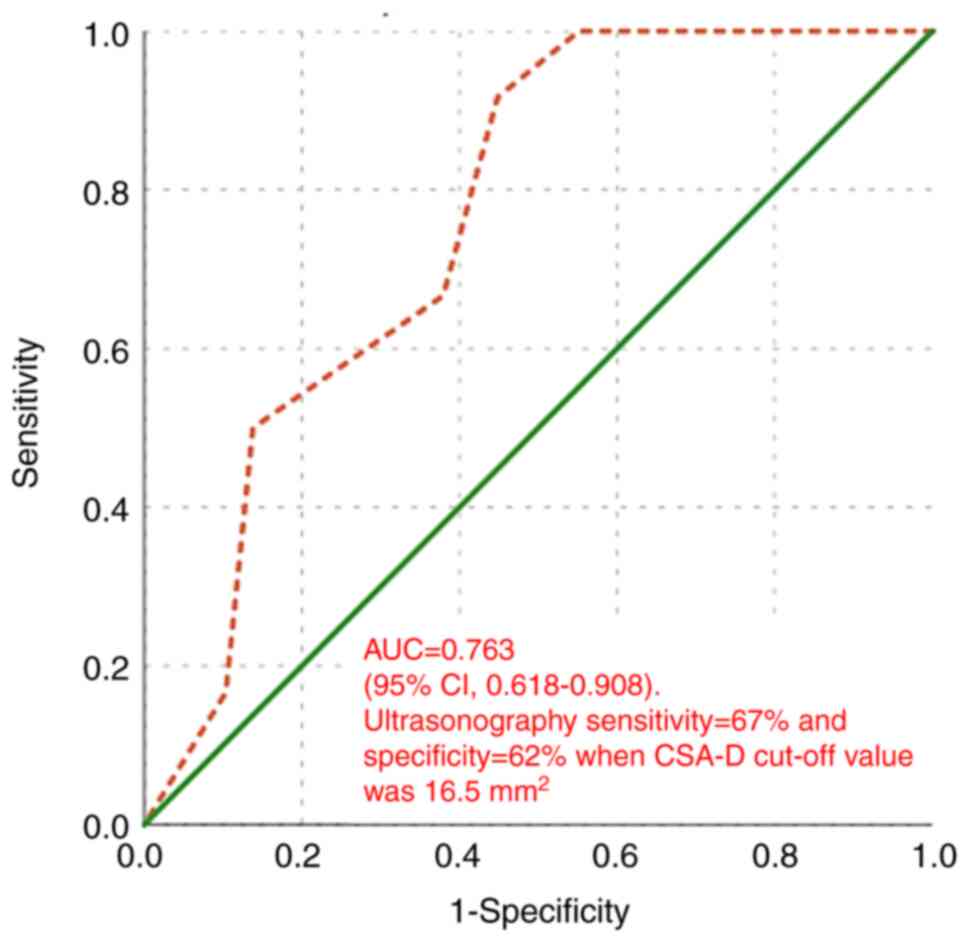
The diagnostic accuracy of MN CSA-D measured by US
in detecting and differentiating CTS was assessed using the ROC
curve. When comparing mild and moderate CTS, the area under the
curve (AUC) was 0.763 (95% CI, 0.618-0.908; P=0.009). As shown in
Fig. 8, ultrasonography exhibited
a sensitivity of 67% and a specificity of 62% when the cut-off
value of CSA-D was 16.5 mm2.
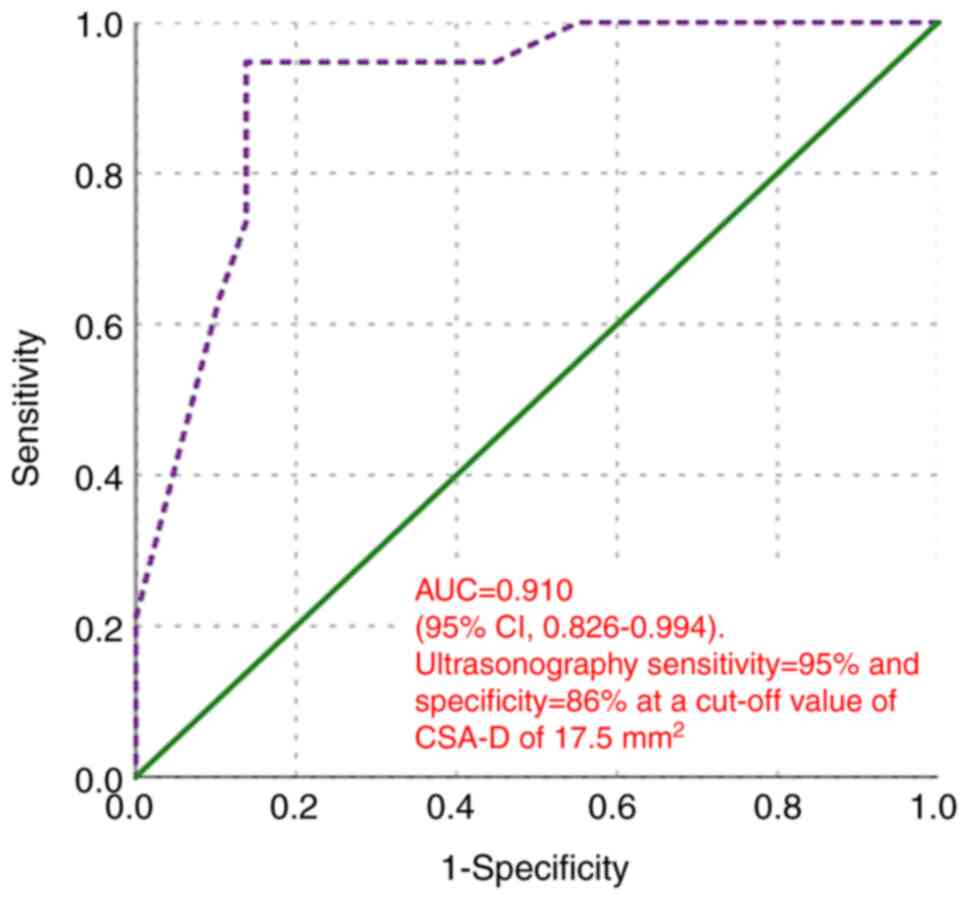
In distinguishing between mild and severe CTS, the
AUC was 0.910 (95% CI, 0.826-0.994; P<0.001). At a cut-off value
of CSA-D of 17.5 mm2, ultrasonography exhibited a
sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 86% (Fig. 9).
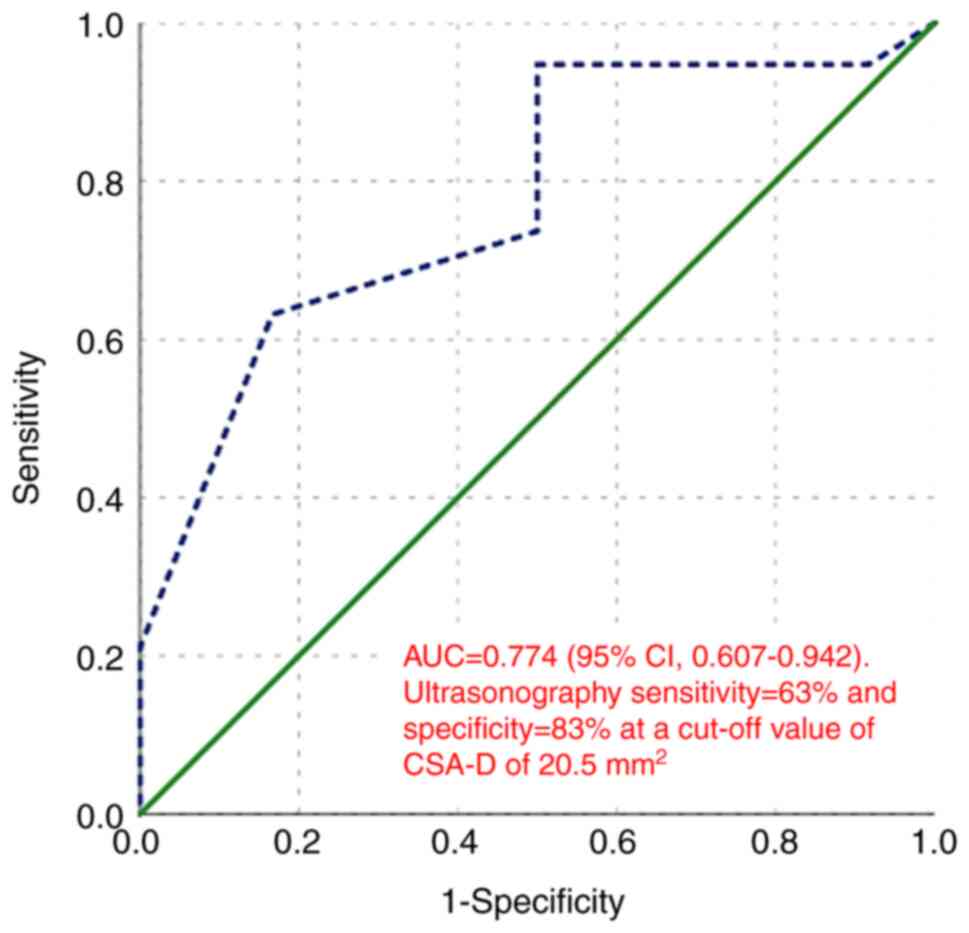
For distinguishing between moderate and severe CTS,
the AUC was 0.774 (95% CI, 0.607-0.942, P=0.011). At a cut-off
value of CSA-D of 20.5 mm2, ultrasonography demonstrated
a sensitivity of 63% and a specificity of 83% (Fig. 10).
Discussion
A positive electrodiagnostic test is primarily used
to corroborate the diagnosis of CTS, which is often based on
characteristic clinical signs and symptoms (15). According to recent research, MN
sonography can detect CTS with sensitivity that is comparable to
that of the gold-standard electrophysiological testing (16,17).
The present study identified a positive correlation
between the CSA-D of MN and both MN distal motor latency and
sensory latency. Conversely, the CSA-D demonstrated a significant
negative correlation with MN motor conduction velocity, sensory
action potential amplitude, and sensory conduction velocity. These
results validate the utility of US in diagnosing CTS and align with
findings from other studies (18-21).
Reported cut-off values for the CSA of the MN at the
pisiform bone using US vary widely, ranging from 9 to 14
mm2 (16,22,23)
which affect the sensitivity and specificity of this parameter for
diagnosing CTS. In the present study, the CSA cut-off value was
17.5 mm2. The cutoff value of 17.5 mm2 for
distinguishing mild from severe CTS use in the present study is
higher than the range of 9-14 mm2 frequently reported in
other populations (24-26).
This disparity does not necessarily constitute a contradiction;
rather, it draws attention to significant elements that have an
impact on sonographic findings and the therapeutic application of
these measurements. It is possible that this disparity is due to a
variety of factors, such as: i) The characteristics of the
population: The population in the present study comprised solely of
Iraqi females who had a BMI that was defined as overweight, namely
28.58±3.1 kg/m2. It is a well-established fact that
demographic parameters, such as sex, race and body habitus have an
effect on the size of the nerves. Studies have demonstrated that a
higher BMI is associated with a larger median nerve CSA. This could
potentially result in an upward shift of the ideal diagnostic
cutoff in communities that have a higher prevalence of obesity in
comparison to general populations in which lower cut-off values
were established (27,28). ii) Measurement methodology: While
the present study adhered to standard techniques, subtle
differences in measurement protocols, such as the precise level of
the pisiform bone, the use of the ellipse tracing function vs.
manual trace and the pressure applied with the transducer can
systematically influence the absolute CSA values obtained. The
consistent application of the method used herein ensures internal
validity; however, cross-study comparisons must account for these
potential technical variations (29).
In the present study, US had a sensitivity of 95%
and a specificity of 86%, suggesting that US is most effective in
distinguishing mild from severe CTS. For differentiating mild from
moderate CTS, the sensitivity and specificity at a cut-off value of
16.5 mm2 were 67 and 62%, respectively. In the same
manner, a cut-off value of 20.5 mm2 for moderate to
severe CTS yielded a sensitivity of 63% and a specificity of
83%.
Probably distinct aspects of the process of the
condition are being investigated by ultrasonography and nerve
conduction investigations individually. US is used to examine the
structural reaction of the nerve to external compression, whereas
nerve conduction investigations are used to evaluate the functional
capacity of the nerve to convey information. Rather than being
considered contradictory with one another, these diagnostic tools
ought to be regarded as complementary.
It is possible that the distinct pathological
processes that are present at different phases of the disease are
responsible for the greater efficacy of ultrasonography in
separating mild from severe cases of CTS. On the other hand, the
effectiveness of US in discriminating between mild and moderate
cases is restricted.
The major pathophysiology of CTS is typically
localized demyelination, which is caused by compression and
ischemia in the early (mild) phases of the condition. Despite the
fact that this functional deficit manifests electrophysiologically
as longer sensory and motor latencies, it is possible that it did
not cause a significant and long-lasting structural expansion of
the nerve (9).
There is a possibility that the nerve will exhibit
transitory swelling that is influenced by the symptoms; however,
the average CSA-D in the group with mild CTS in the present study
was only slightly higher than the typical upper limits, which range
from 9-14 mm2. This results in a threshold that is less
sensitive and specific in terms of differentiating between mild and
moderate instances, as the CSA differences between the two types of
cases become less distinct. By contrast, prolonged compression
induces increasingly severe structural alterations as the severity
of CTS increases, including the persistent endoneurial edema, the
disturbance of the blood-nerve barrier, fibrosis, and ultimately,
axonal degeneration (30).
The fact that in the present study, the group with
severe CTS had a significantly higher mean CSA-D (21.37
mm2) provides evidence that the accumulated structural
damage induces nerve swelling that is both chronic and
considerable. Ultrasonography is a powerful instrument that can
differentiate between moderate and severe manifestations of disease
due to the exceptional clarity it possesses.
US is sensitive to the significant nerve damage that
is associated with advanced illness, as evidenced by the fact that
it is able to differentiate between moderate and severe cases of
CTS. It is possible that functional electrophysiological changes,
which NCS is able to detect, may occur prior to lasting
morphological alterations. This is suggested by the observation
that US is not very effective at identifying the early phases of
the condition.
The fact that NCS exposes structural compromise,
while US indicates functional integrity adds validity to the
hypothesis that functional integrity and structural compromise are
two different sorts of information that they provide. As a result
of this, combining the two methods may possibly provide a more
realistic portrayal of the severity of the condition.
The results of the present study demonstrate a
robust correlation between MN CSA and electrophysiologically
assessed disease severity. Nevertheless, additional studies are
required to investigate the impact of sonographic parameters on
patient-reported clinical outcomes. For the purpose of clinical
decision-making, it is essential to use a validated instrument such
as the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ) (31) to determine whether nerve
enlargement, as shown through ultrasonography, correlates with the
severity of symptoms and functional impairment.
The authors acknowledge that the study population
may not fully represent the complexity of all patients presenting
with CTS-like symptoms in general practice due to the exclusion of
patients with comorbidities, such thyroid disease, polyneuropathy
and cervical radiculopathy. The primary objective of these criteria
was to isolate the association between the morphology of the MN and
its electrical activity in cases of CTS, excluding other disorders
that may mimic or exacerbate CTS symptoms. Cervical radiculopathy
may present with overlapping sensory symptoms (32), whereas polyneuropathy may cause
aberrant nerve conduction tests and widespread nerve enlargement
(33).
The present study had certain limitations which
should be mentioned. First, the sample size was relatively small.
Further multicenter studies with larger cohorts are thus warranted
to validate the proposed cut-off values and improve the
generalizability of the findings. Second, the present study
employed a cross sectional design by selectively enlisting patients
with a clinical suspicion of CTS. This may render the test to
appear more precise than it actually is due to a high pre-test
probability, a phenomenon known as spectrum bias. Third, the
present study only demonstrated a link between the MN sonography
tests and the electrodiagnostic examination. The present study does
not indicate whether NCS or ultrasonography appropriately captures
the clinical manifestations of CTS. Finally, the present study did
not incorporate a correlation with standardized clinical symptom
scores, such as the BCTQ. Therefore, while CSA may be related to
electrophysiological severity, its direct association with the
subjective experiences of patients, such as pain, numbness and
functional limitations remains a key area for future
investigations.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that
CSA-D and NCS are positively correlated, and the CSA-D is more
sensitive in differentiating between mild and severe CTS, than
between mild and moderate CTS. As regards the evaluation of
structural and functional integrity, US and NCS provide
complimentary information. When used in conjunction, they provide a
more comprehensive evaluation of the nerve, which may be useful in
clinical therapy and in the stratification of prognostic factors.
Future research is required to focus on correlating these objective
measures with clinical symptom scores in order to fully integrate
ultrasonography into patient-centered care pathways.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors contributions
JMK was involved in the conception and design of the
study, in the literature search, in clinical analyses, in data
analysis and in statistical analysis, as well as in manuscript
preparation and in the reviewing of the manuscript. AMJAM was
involved in the conception and design of the study and in data
analysis, as well as in manuscript preparation and in the reviewing
of the manuscript. IAM and AKA were involved in the conception and
design of the study, manuscript preparation and in the reviewing of
the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final
manuscript. All authors confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Research approval was obtained from the
institutional Review Board of Al-Khadimain Teaching Hospital
(Reference no. 5563 on April 24, 2023). A written informed consent
to participate in the study as specified in the Declaration of
Helsinki was obtained from each patient.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Ghasemi M, Masoumi S, Ansari B,
Fereidan-Esfahani M and Mousavi SM: Determination of cut-off point
of cross-sectional area of median nerve at the wrist for diagnosing
carpal tunnel syndrome. Iran J Neurol. 16:164–167. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ibrahim I, Khan WS, Goddard N and Smitham
P: Carpal tunnel syndrome: A review of the recent literature. Open
Orthop J. 6:69–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Park JS, Won HC, Oh JY, Kim DH, Hwang SC
and Yoo JI: Value of cross-sectional area of median nerve by MRI in
carpal tunnel syndrome. Asian J Surg. 43:654–659. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fowler JR, Munsch M, Tosti R, Hagberg WC
and Imbriglia JE: Comparison of ultrasound and electrodiagnostic
testing for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome: Study using a
validated clinical tool as the reference standard. J Bone Joint
Surg Am. 96(e148)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Al-Hashel JY, Rashad HM, Nouh MR, Amro HA,
Khuraibet AJ, Shamov T, Tzvetanov P and Rousseff RT: Sonography in
carpal tunnel syndrome with normal nerve conduction studies. Muscle
Nerve. 51:592–597. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Suk JI, Walker FO and Cartwright MS:
Ultrasonography of peripheral nerves. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
13(328)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nkrumah G, Blackburn AR, Goitz RJ and
Fowler JR: Ultrasonography findings in severe carpal tunnel
syndrome. Hand (NY). 15:64–68. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen X, Cao J, Lao J, Liu A and Rui J:
Evaluation of electrophysiological examinations for the diagnosis
of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Orthop Surg Res.
20(680)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Werner RA and Andary M: Carpal tunnel
syndrome: Pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin
Neurophysiol. 113:1373–1381. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Joshi A, Patel K, Mohamed A, Oak S, Zhang
MH, Hsiung H, Zhang A and Patel UK: Carpal tunnel syndrome:
Pathophysiology and comprehensive guidelines for clinical
evaluation and treatment. Cureus. 14(e27053)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pelosi L, Arányi Z, Beekman R, Bland J,
Coraci D, Hobson-Webb LD, Padua L, Podnar S, Simon N, van Alfen N,
et al: Expert consensus on the combined investigation of carpal
tunnel syndrome with electrodiagnostic tests and neuromuscular
ultrasound. Clin Neurophysiol. 135:107–116. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zivkovic S, Gruener G, Arnold M, Winter C,
Nuckols T and Narayanaswami P: the Quality Improvement Committee of
the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic
Medicine. Quality measures in electrodiagnosis: Carpal tunnel
syndrome-An AANEM quality measure set. Muscle Nerve. 61:460–465.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kanagasabai K: Ultrasound of median nerve
in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome-correlation with
electrophysiological studies. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 32:16–29.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
AAOS. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Clinical
Practice Guideline on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, 2024. Available from:
https://www.aaos.org/quality/quality-programs/upper-extremity-programs/carpal-tunnel-syndrome/.
|
|
15
|
Vo NQ, Nguyen THD, Nguyen DD, Le TB, Le
NTN and Nguyen TT: The value of sonographic quantitative parameters
in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome in the Vietnamese
population. J Int Med Res. 49(3000605211064408)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Billakota S and Hobson-Webb LD: Standard
median nerve ultrasound in carpal tunnel syndrome: A retrospective
review of 1,021 cases. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2:188–191.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
El-Najjar AR, Abu-Elsoaud AM, Sabbah DA
and Zeid AF: Emerging role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of
carpal tunnel syndrome: Relation to risk factors, clinical and
electrodiagnostic severity. Egypt Rheumatol. 43:341–345. 2021.
|
|
18
|
Baiee RH, Al-Mukhtar NJ, Al-Rubiae SJ,
Hammoodi ZH and Abass FN: Neurophysiological findings in patients
with carpal tunnel syndrome by nerve conduction study in comparing
with ultrasound study. J Nat Sci Res. 5:111–128. 2015.
|
|
19
|
Mohamed RE, Amin MA, Aboelsafa AA and
Elsayed SE: Contribution of power Doppler and gray-scale ultrasound
of the median nerve in evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome. Egypt
J Radiol Nucl Med. 45:191–201. 2014.
|
|
20
|
Elnady B, Rageh EM, Ekhouly T, Fathy SM,
Alshaar M, Fouda ES, Attar M, Abdelaal AM, El Tantawi A, Algethami
MM and Bong D: Diagnostic potential of ultrasound in carpal tunnel
syndrome with different etiologies: Correlation of sonographic
median nerve measures with electrodiagnostic severity. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 20(634)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chan KY, George J, Goh KJ and Ahmad TS:
Ultrasonography in the evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome:
Diagnostic criteria and comparison with nerve conduction studies.
Neurol Asia. 16:57–64. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Ng AWH, Griffith JF, Lee RKL, Tse WL, Wong
CWY and Ho PC: Ultrasound carpal tunnel syndrome: Additional
criteria for diagnosis. Clin Radiol. 73:214.e11–214.e18.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gelfman R, Melton Iii LJ III, Yawn BP,
Wollan PC, Amadio PC and Stevens JC: Long-term trends in carpal
tunnel syndrome. Neurology. 72:33–41. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Duncan I, Sullivan P and Lomas F:
Sonography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 173:681–684. 1999.
|
|
25
|
Cartwright MS, Hobson-Webb LD, Boon AJ,
Alter KE, Hunt CH, Flores VH, Werner RA, Shook SJ, Thomas TD,
Primack SJ, et al: Evidence-based guideline: Neuromuscular
ultrasound for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle
Nerve. 46:287–293. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wong SM, Griffith JF, Hui ACF, Lo SK, Fu M
and Wong KS: Carpal tunnel syndrome: Diagnostic usefulness of
sonography. Radiology. 232:93–99. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Klauser AS, Faschingbauer R, Bauer T, Wick
MC, Gabl M, Arora R, Cotton A, Martinoli C and Jaschke WR:
Entrapment neuropathies II: carpal tunnel syndrome. Semin
Musculoskelet Radiol. 14:487–500. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Won SJ, Kim BJ, Park KS, Yoon JS and Choi
H: Reference values for nerve ultrasonography in the upper
extremity. Muscle Nerve. 47:864–871. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Seok JI: A beginner s guide to
peripheral nerve ultrasound. Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 24:46–52.
2022.
|
|
30
|
Aboonq MS: Pathophysiology of carpal
tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 20:4–9. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy
LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH and Katz JN: A self-administered
questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and
functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
75:1585–1592. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kaddoori HG: Electrophysiological study in
patients with cervical radiculopathy. Iraqi J Med Sci: Jun 6, 2024
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
33
|
Nasr-Eldin YK, Cartwright MS, Hamed A, Ali
LH and Abdel-Nasser AM: Neuromuscular ultrasound in
polyneuropathies. J Ultrasound Med. 43:1181–1198. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|