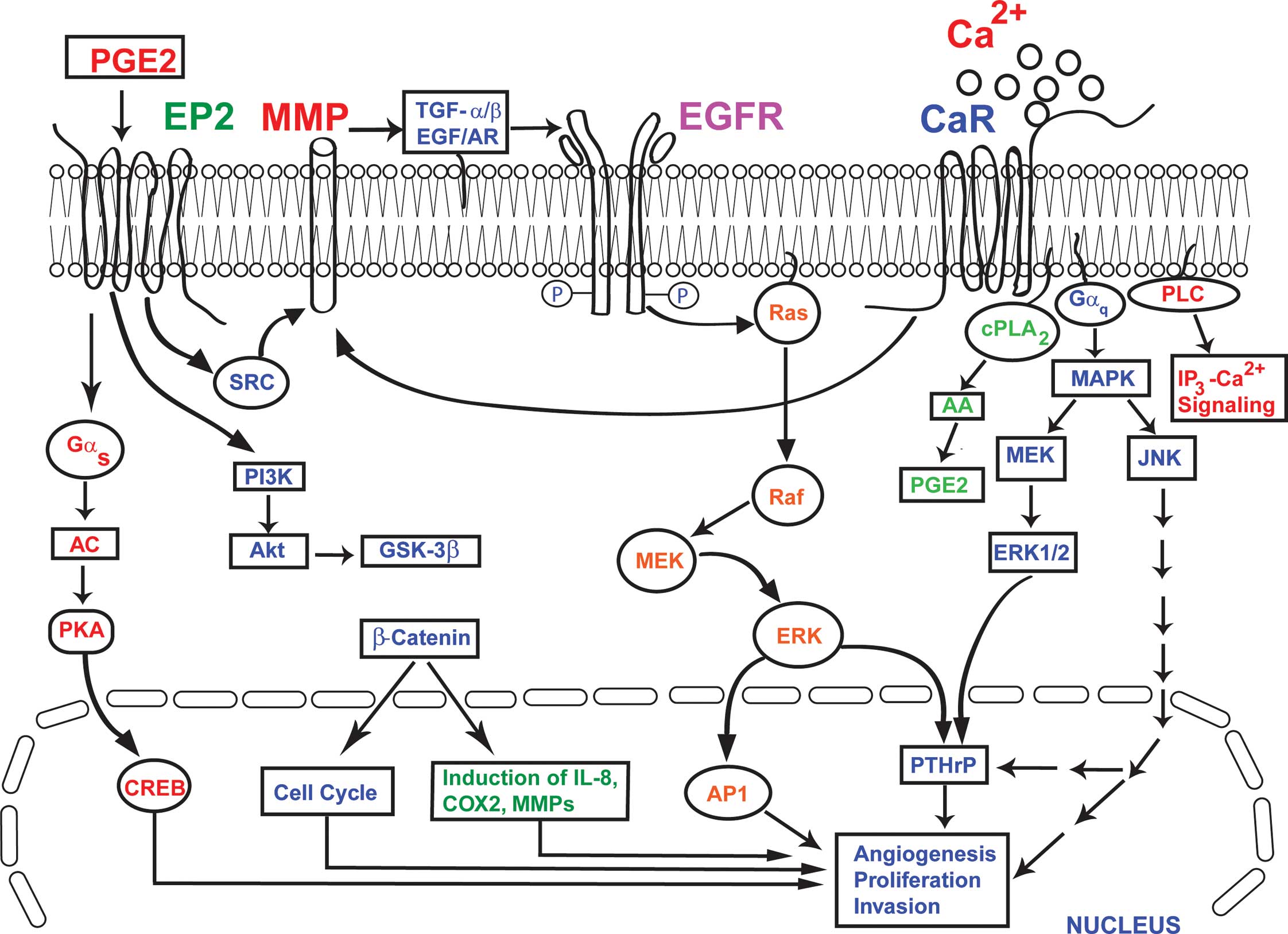
|
1.
|
Kingsley LA, Fournier PGJ, Chirgwin JM and
Guise TA: Molecular biology of bone metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:2609–2617. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kozlow W and Guise TA: Breast cancer
metastasis to bone: mechanisms of osteolysis and implications for
therapy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 10:169–180. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis. The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003.
|
|
4.
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancers of breast. Lancet. 1:571–573. 1889. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Kakonen SM and Mundy GR: Mechanisms of
osteolytic bone metastases in breast carcinoma. Cancer. 97:834–839.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Doherty TM, Uzui H, Fitzpatrick LA,
Tripathi PV, Dunstan CR, Asotra K and Rajavashisth TB: Mechanism of
arterial calcification in the context of atherosclerosis. FASEB J.
16:577–582. 2002.
|
|
7.
|
Doherty TM, Asotra K, Fitzpatrick LA,
Dunstan CR, Qiao J-H, Wilkin DJ, Detrano RC, Shah PK and
Rajavashisth TB: Calcification in atherosclerosis: bone biology and
chronic inflammation at the arterial crossroads. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:11201–11206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Parkash J, Chaudhry MA and Rhoten WB:
Calbindin-D28k and calcium sensing receptor cooperate in MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 24:1111–1119.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Sanders JL, Chattopadhyay N, Kifor O,
Yamaguchi T, Butters RR and Brown EM: Extracellular calcium-sensing
receptor expression and its potential role in regulating
parathyroid hormone-related peptide secretion in human breast
cancer cell lines. Endocrinology. 141:4357–4364. 2000.
|
|
10.
|
Schafer B, Gschwind A and Ullrich A:
Multiple G-protein receptor signals converge on the epidermal
growth factor receptor to promote migration and invasion. Oncogene.
23:991–999. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Chang SH, Ai Y, Breyer RM, Lane TF and Hla
T: The prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 is required for cyclooxygenase
2-mediated mammary hyperplasia. Cancer Res. 65:4496–4499. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hiraga T, Myoui A, Choi ME, Yoshikawa H
and Yoneda T: Stimulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by
bone-derived transforming growth factor-β enhances bone metastases
in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:2067–2073. 2006.
|
|
13.
|
Mazhar D, Ang R and Waxman J: COX
inhibitors and breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 94:346–350. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, et al:
Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal
adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med. 352:1092–1102. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Fulton AM, Ma X and Kundu N: Targeting
prostaglandin E EP receptors to inhibit metastasis. Cancer Res.
66:9794–9797. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Dorsam RT and Gutkind JS: G-protein
coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev. 7:79–94. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Pai R, Soreghan B, Szabo IL, Pavelka M,
Baatar D and Tarnawski AS: Prostaglandin E2 transactivates EGF
receptor: a novel mechanism for promoting colon cancer growth and
gastrointestinal hypertrophy. Nat Med. 8:289–293. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Willmarth NE, Baillo A, Dziubinski ML,
Wilson K, Riese DJ II and Ethier SP: Altered EGFR localization and
degradation in human breast cancer cells with an amphiregulin/EGFR
autocrine loop. Cell Signal. 21:212–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Doherty TM, Asotra K, Pei D, Uzui H,
Wilkin DJ, Shah PK and Rajavashisth TB: Therapeutic developments in
matrix metal-loproteinase inhibition. Expert Opinion Therapeutic
Patents. 12:665–707. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Brown EM and MacLeod RJ: Extracellular
calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev.
81:239–297. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Lindemann RK, Braig M, Hauser CA, Nordheim
A and Dittmer J: Ets2 and protein kinase C epsilon are important
regulators of parathyroid hormone-related protein expression in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochem J. 372:787–797. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Nemeth EF, Delmar EG, Heaton WL, et al:
Calcilytic compounds: potent and selective Ca2+ –
receptor antagonists that stimulate secretion of parathyroid
hormone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 299:323–331. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Brown EM: Clinical lessons from the
calcium-sensing receptor. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab.
3:122–133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Mihai R, Stevens J, McKinney C and Ibrahim
NB: Expression of the calcium receptor in human breast cancer – a
potential new marker predicting the risk of bone metastases. Eur J
Surg Oncol. 32:511–515. 2006.
|
|
25.
|
Woodward DF, Pepperl DJ, Burkey TH and
Regan JW: 6-Isopropoxy-9-oxoanthene-2-carboxylic acid (AH6809), a
human EP2 receptor antagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 50:1731–1733.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Silva J, Chang K, Hannon GJ and Rivas FV:
RNA-interference-based functional genomics in mammalian cells:
reverse genetics coming of age. Oncogene. 23:8401–8409. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Paddison PJ, Caudy AA, Bernstein E, Hannon
GJ and Conklin DS: Short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) induce
sequence-specific silencing in mammalian cells. Genes Dev.
16:948–958. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Parkash J, Chaudhry MA and Rhoten WB:
Tumor necrosis factor-α induced changes in insulin-producing
β-cells. Anatom Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 286A:982–993.
2005.
|
|
29.
|
Parkash J, Felty Q and Roy D: Estrogen
exerts a spatial and temporal influence on reactive oxygen species
generation that precedes calcium uptake in high capacity
mitochondria: implications for rapid nongenomic signaling of cell
growth. Biochemistry. 45:2872–2881. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Gupta GP, Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, et al:
Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in
lung metastasis. Nature. 446:765–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Dhurjati R, Krishnan V, Shuman LA, Mastro
AM and Vogler EA: Metastatic breast cancer cells colonize and
degrade three-dimensional osteoblastic tissue in vitro. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:741–752. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Fisher OM, Hart S, Gshwind A and Ullrich
A: EGFR signal trans-activation in cancer cells. Biochem Soc Trans.
31:1203–1208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Prenzel N, Zwick E, Daub H, Leserer M,
Abraham R, Wallasch C and Ullrich A: EGF receptor transactivation
by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage
of proHB-EGF. Nature. 402:884–888. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Gilmore JL, Scott JA, Bouizar Z, Robling
A, Pitfield SE, Riese DJ II and Foley J: Amphiregulin-EGFR
signaling regulates PTHrP gene expression in breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 110:493–505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
MacLeod RJ, Yano S, Chattopadhyay N and
Brown EM: Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor transactivates the
epidermal growth factor receptor by a triple-membrane-spanning
signaling mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 320:455–460. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|