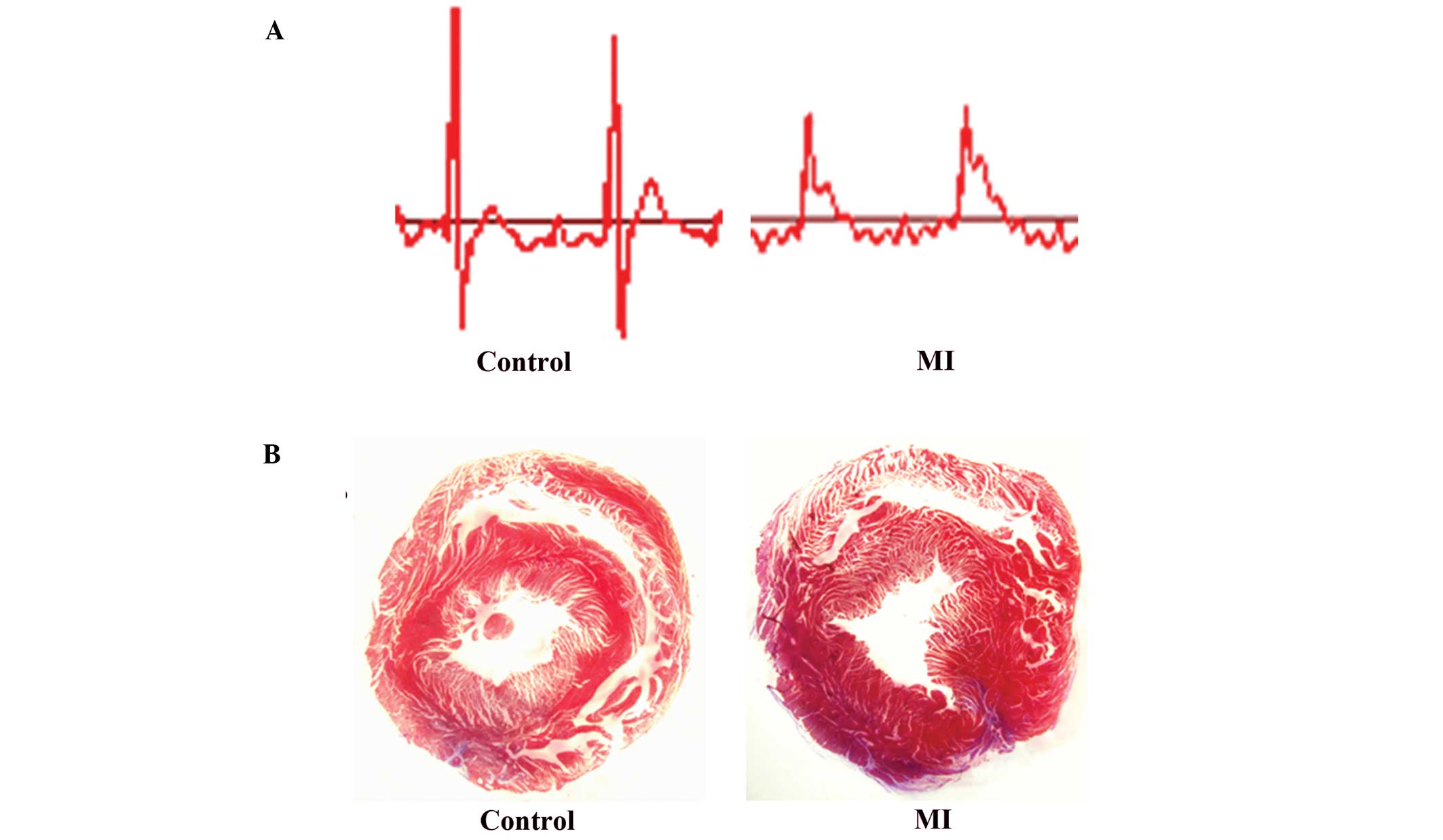
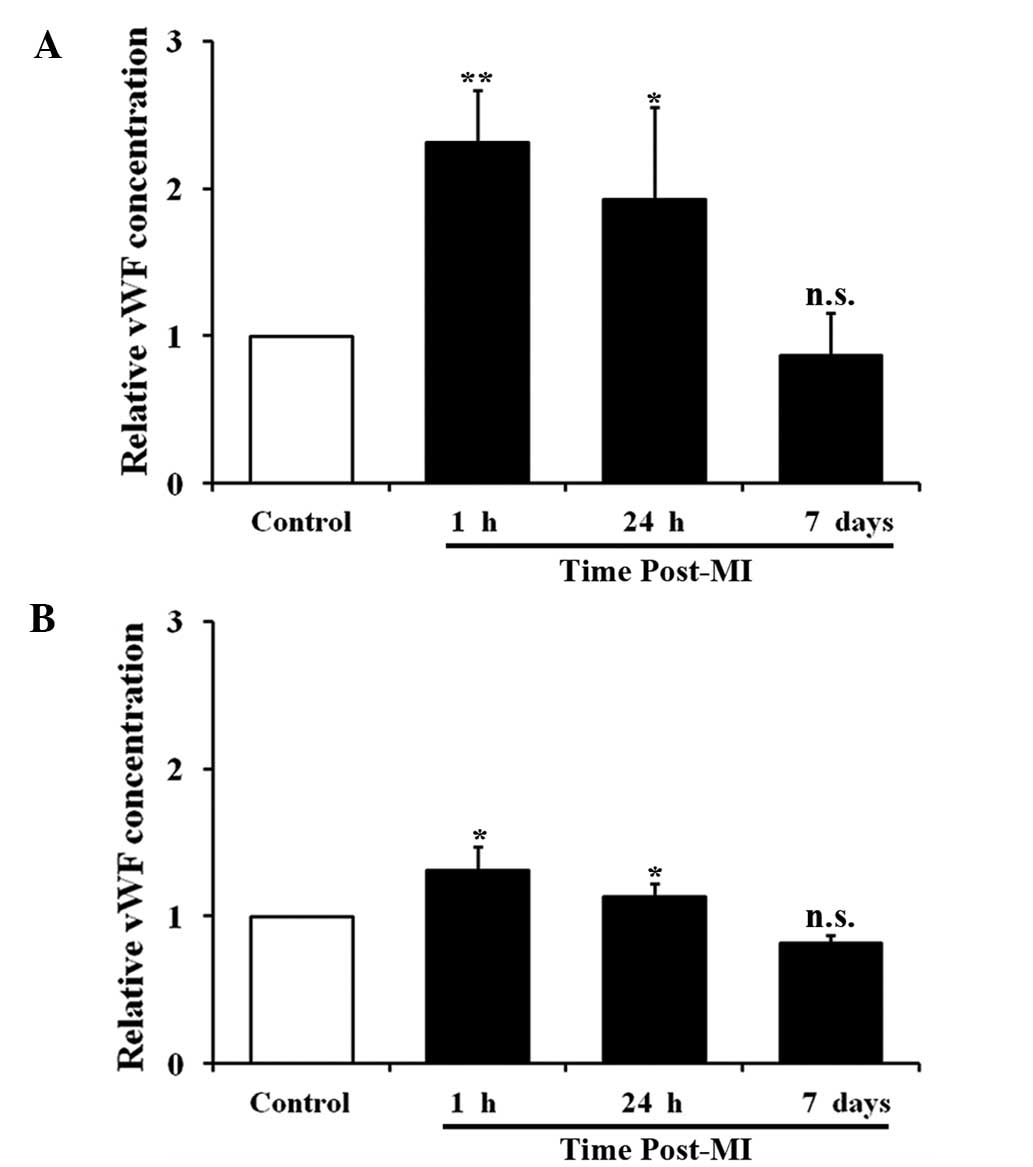
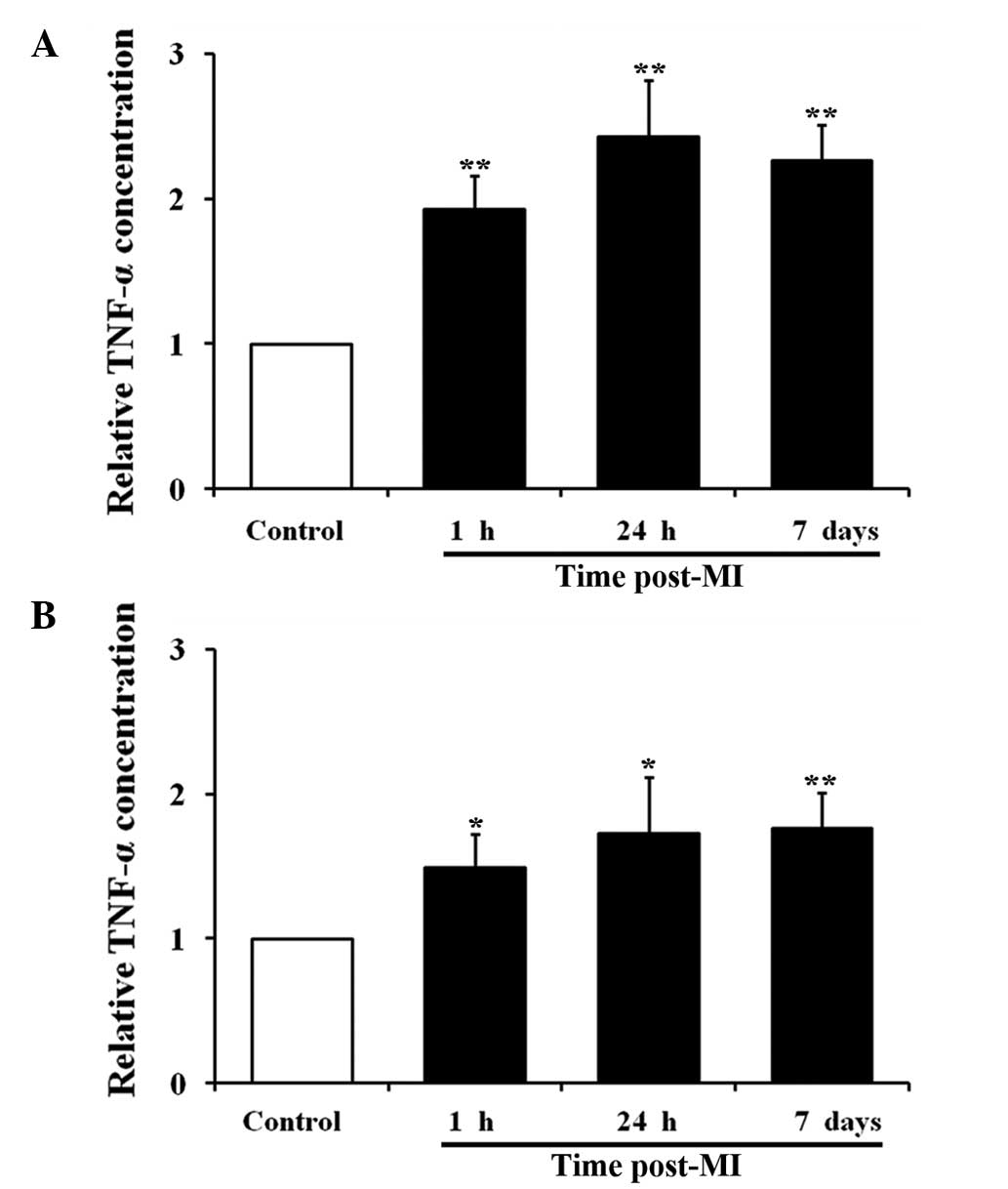
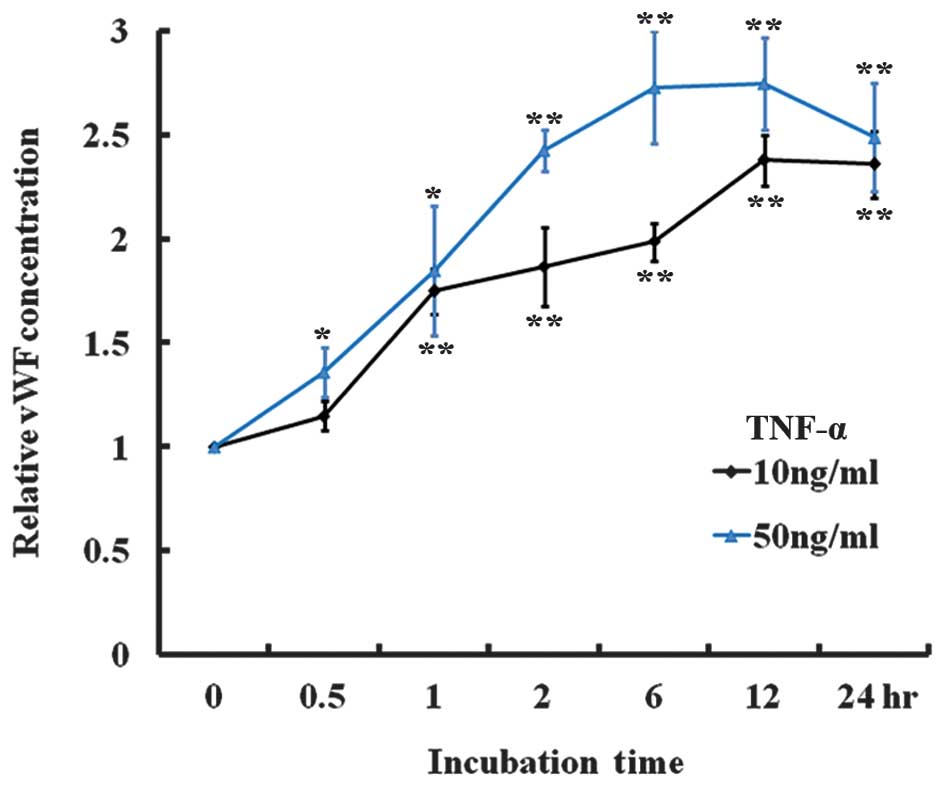
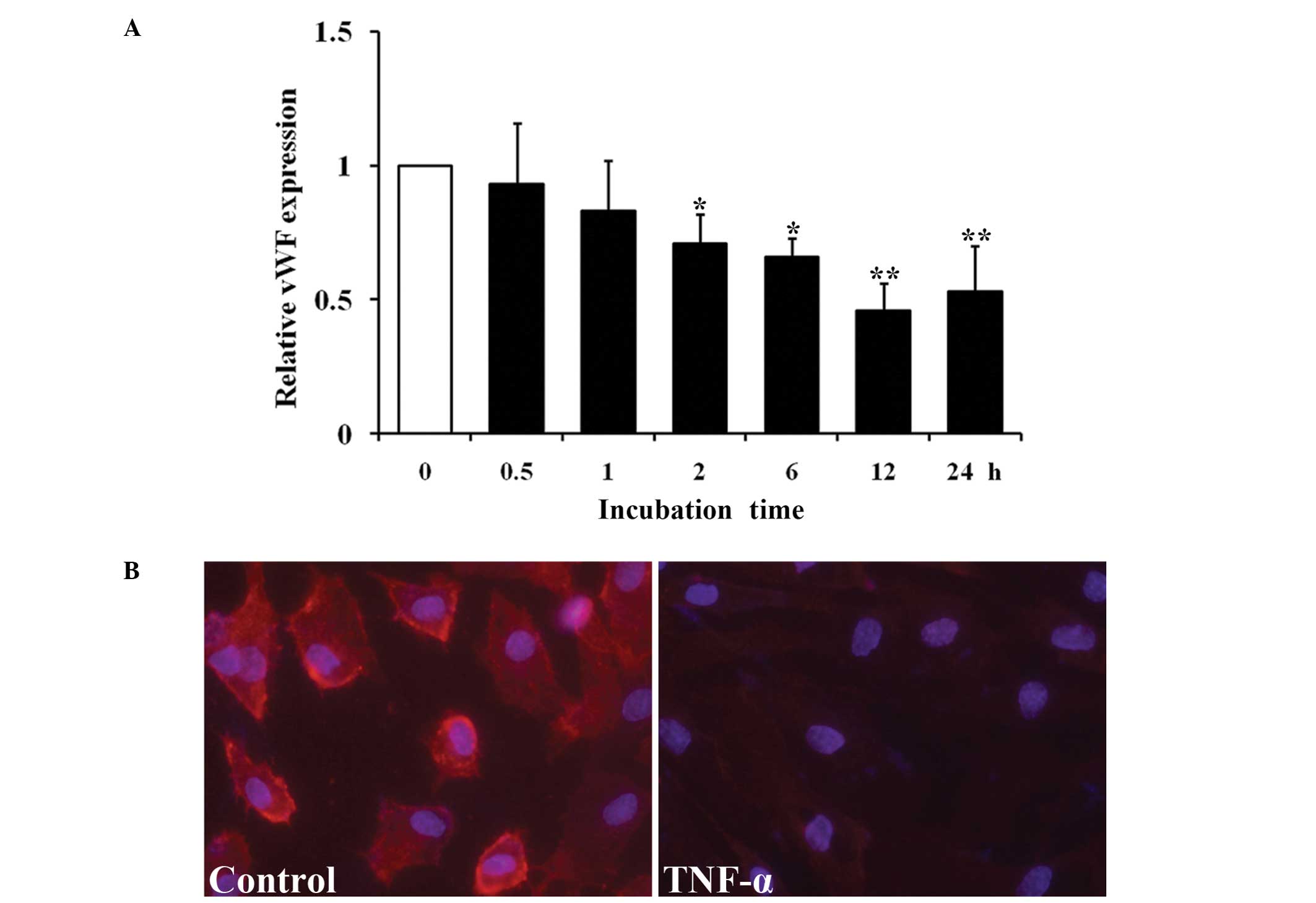
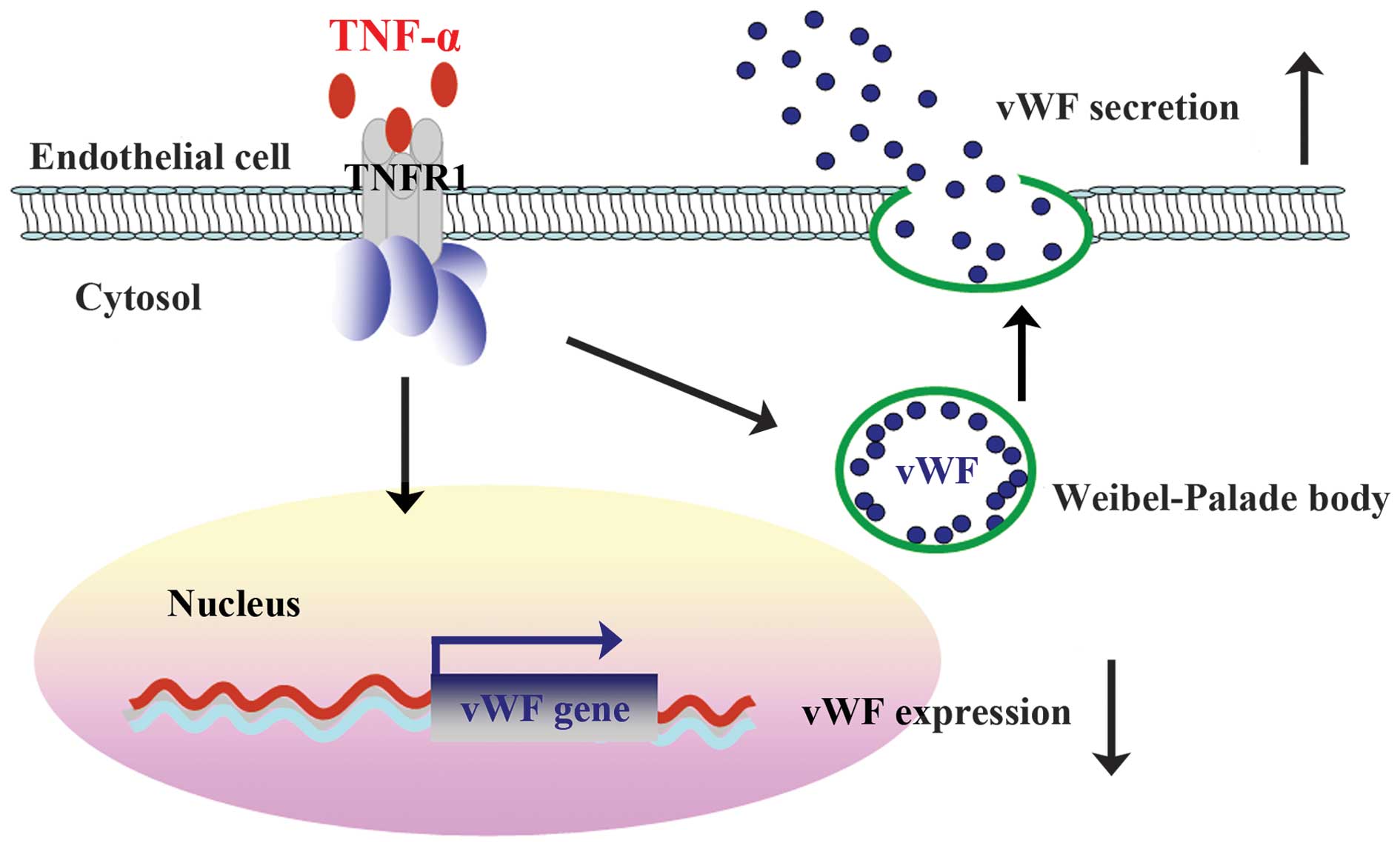
|
1
|
Ruggeri ZM: Von Willebrand factor,
platelets and endothelial cell interactions. J Thromb Haemost.
1:1335–1342. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lenting PJ, Christophe OD and Denis CV:
von Willebrand factor biosynthesis, secretion and clearance:
Connecting the far ends. Blood. 125:2019–2028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sadler JE: von Willebrand factor assembly
and secretion. J Thromb Haemost. 7(Suppl 1): S24–S27. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kanaji S, Fahs SA, Shi Q, Haberichter SL
and Montgomery RR: Contribution of platelet vs. endothelial VWF to
platelet adhesion and hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 10:1646–1652.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Metcalf DJ, Nightingale TD, Zenner HL,
Lui-Roberts WW and Cutler DF: Formation and function of
Weibel-Palade bodies. J Cell Sci. 121:19–27. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nightingale T and Cutler D: The secretion
of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells; an increasingly
complicated story. J Thromb Haemost. 11(Suppl 1): S192–S201. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yee A and Kretz CA: Von Willebrand factor:
Form for function. Semin Thromb Hemost. 40:17–27. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lenting PJ, Pegon JN, Groot E and de Groot
PG: Regulation of von Willebrand factor-platelet interactions.
Thromb Haemost. 104:449–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Franchini M, Frattini F, Crestani S,
Bonfanti C and Lippi G: von Willebrand factor and cancer: A renewed
interest. Thromb Res. 131:290–292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lenting PJ, Casari C, Christophe OD and
Denis CV: von Willebrand factor: The old, the new and the unknown.
J Thromb Haemost. 10:2428–2437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Randi AM, Laffan MA and Starke RD: Von
Willebrand factor, angiodysplasia and angiogenesis. Mediterr J
Hematol Infect Dis. 5:e20130602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jahroudi N and Lynch DC:
Endothelial-cell-specific regulation of von Willebrand factor gene
expression. Mol Cell Biol. 14:999–1008. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lillicrap D: von Willebrand disease:
Advances in pathogenetic understanding, diagnosis and therapy.
Blood. 122:3735–3740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto K, de Waard V, Fearns C and
Loskutoff DJ: Tissue distribution and regulation of murine von
Willebrand factor gene expression in vivo. Blood. 92:2791–2801.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aird WC, Jahroudi N, Weiler-Guettler H,
Rayburn HB and Rosenberg RD: Human von Willebrand factor gene
sequences target expression to a subpopulation of endothelial cells
in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:4567–4571. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aird WC, Edelberg JM, Weiler-Guettler H,
Simmons WW, Smith TW and Rosenberg RD: Vascular bed-specific
expression of an endothelial cell gene is programmed by the tissue
microenvironment. J Cell Biol. 138:1117–1124. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bertagna A and Jahroudi N: The NFY
transcription factor mediates induction of the von Willebrand
factor promoter by irradiation. Thromb Haemost. 85:837–844.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Kanki Y, Okada Y, Jin E, Yano K,
Shih SC, Minami T and Aird WC: A +220 GATA motif mediates basal but
not endotoxin-repressible expression of the von Willebrand factor
promoter in Hprt-targeted transgenic mice. J Thromb Haemost.
7:1384–1392. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mojiri A, Nakhaii-Nejad M, Phan WL, Kulak
S, Radziwon-Balicka A, Jurasz P, Michelakis E and Jahroudi N:
Hypoxia results in upregulation and de novo activation of von
Willebrand factor expression in lung endothelial cells.
Arterioscler, Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:1329–1338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kleinschmidt AM, Nassiri M, Stitt MS,
Wasserloos K, Watkins SC, Pitt BR and Jahroudi N: Sequences in
intron 51 of the von Willebrand factor gene target promoter
activation to a subset of lung endothelial cells in transgenic
mice. J Biol Chem. 283:2741–2750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nassiri M, Liu J, Kulak S, Uwiera RR, Aird
WC, Ballermann BJ and Jahroudi N: Repressors NFI and NFY
participate in organ-specific regulation of von Willebrand factor
promoter activity in transgenic mice. Arterioscler, Thromb Vasc
Biol. 30:1423–1429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Paulinska P, Spiel A and Jilma B: Role of
von Willebrand factor in vascular disease. Hamostaseologie.
29:32–38. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Spiel AO, Gilbert JC and Jilma B: von
Willebrand factor in cardiovascular disease: Focus on acute
coronary syndromes. Circulation. 117:1449–1459. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
White HD and Chew DP: Acute myocardial
infarction. Lancet. 372:570–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hori M and Nishida K: Oxidative stress and
left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction.
Cardiovasc Res. 81:457–464. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
White HD, Thygesen K, Alpert JS and Jaffe
AS: Clinical implications of the third universal definition of
myocardial infarction. Heart. 100:424–432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peyvandi F, Hollestelle MJ, Palla R,
Merlini PA, Feys HB, Vanhoorelbeke K, Lenting PJ and Mannucci PM:
Active platelet-binding conformation of plasma von Willebrand
factor in young women with acute myocardial infarction. J Haemost.
8:1653–1656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Goto S, Sakai H, Ikeda Y and Handa S:
Acute myocardial infarction plasma augments platelet thrombus
growth in high shear rates. Lancet. 349:543–544. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jansson JH, Nilsson TK and Johnson O: von
Willebrand factor in plasma: A novel risk factor for recurrent
myocardial infarction and death. Br Heart J. 66:351–355. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chion CK, Doggen CJ, Crawley JT, Lane DA
and Rosendaal FR: ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand factor and the risk
of myocardial infarction in men. Blood. 109:1998–2000. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu H, Xuan Y, Wang Y, Xue M, Suo F, Li X,
Cheng W, Li X, Yin J, Liu J and Yan S: Targeted NGF siRNA delivery
attenuates sympathetic nerve sprouting and deteriorates cardiac
dysfunction in rats with myocardial infarction. PloS One.
9:e951062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Liu J, Suo F, Hu HS, Xue M, Cheng
WJ, Xuan YL and Yan SH: Metoprolol-mediated amelioration of
sympathetic nerve sprouting after myocardial infarction.
Cardiology. 126:50–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang WB, Du QJ, Li H, Sun AJ, Qiu ZH, Wu
CN, Zhao G, Gong H, Hu K, Zou YZ and Ge JB: The therapeutic effect
of rosuvastatin on cardiac remodelling from hypertrophy to fibrosis
during the end-stage hypertension in rats. J Cell Mol Med.
16:2227–2237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Yuan L, Molema G, Regan E, Janes L,
Beeler D, Spokes KC, Okada Y, Minami T, Oettgen P and Aird WC:
Vascular bed-specific regulation of the von Willebrand factor
promoter in the heart and skeletal muscle. Blood. 117:342–351.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rutten B, Maseri A, Cianflone D, Laricchia
A, Cristell NA, Durante A, Spartera M, Ancona F, Limite L, Hu D, et
al: Plasma levels of active Von Willebrand factor are increased in
patients with first ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: A
multicenter and multiethnic study. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc
Care. 4:64–74. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sakai H, Goto S, Kim JY, Aoki N, Abe S,
Ichikawa N, Yoshida M, Nagaoka Y and Handa S: Plasma concentration
of von Willebrand factor in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb
Haemost. 84:204–209. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW and Entman ML:
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
53:31–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dinarello CA and Pomerantz BJ:
Proinflammatory cytokines in heart disease. Blood Purif.
19:314–321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hall G, Hasday JD and Rogers TB:
Regulating the regulator: NF-kappaB signaling in heart. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 41:580–591. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kleinbongard P, Schulz R and Heusch G:
TNFα in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, remodeling and heart
failure. Heart Fail Rev. 16:49–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mann DL: Tumor necrosis factor-induced
signal transduction and left ventricular remodeling. J Card Fail.
8(Suppl 6): S379–S386. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bradham WS, Bozkurt B, Gunasinghe H, Mann
D and Spinale FG: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and myocardial
remodeling in progression of heart failure: A current perspective.
Cardiovasc Res. 53:822–830. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jacobs M, Staufenberger S, Gergs U, Meuter
K, Brandstätter K, Hafner M, Ertl G and Schorb W: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha at acute myocardial infarction in rats and effects on
cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31:1949–1959. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Blake GJ: Inflammatory biomarkers of the
patient with myocardial insufficiency. Curr Opin Crit Care.
9:369–374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Schulz R, Aker S, Belosjorow S and Heusch
G: TNFalpha in ischemia/reperfusion injury and heart failure. Basic
Res Cardiol. 99:8–11. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang H, Park Y, Wu J, Chen Xp, Lee S,
Yang J, Dellsperger KC and Zhang C: Role of TNF-alpha in vascular
dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:219–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Madge LA and Pober JS: TNF signaling in
vascular endothelial cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 70:317–325. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
van der Poll T, van Deventer SJ,
Pasterkamp G, van Mourik JA, Büller HR and ten Cate JW: Tumor
necrosis factor induces von Willebrand factor release in healthy
humans. Thromb Haemost. 67:623–626. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Umetani M, Mataki C, Minegishi N, Yamamoto
M, Hamakubo T and Kodama T: Function of GATA transcription factors
in induction of endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 by
tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
21:917–922. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|