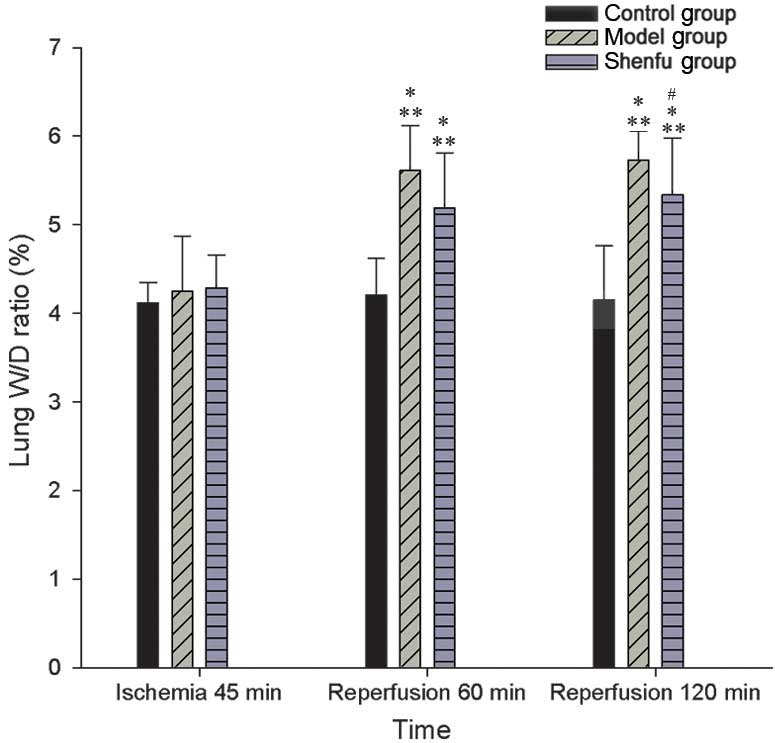
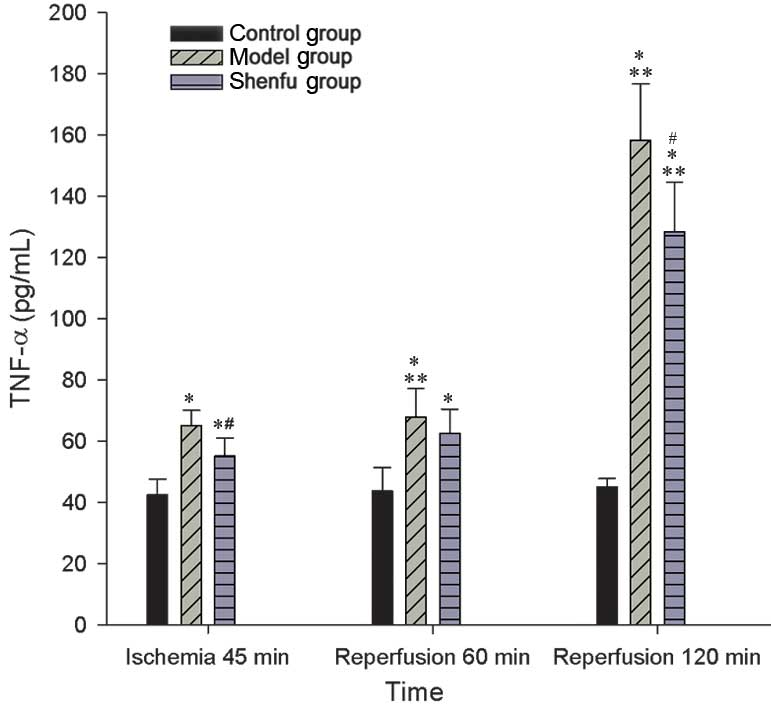
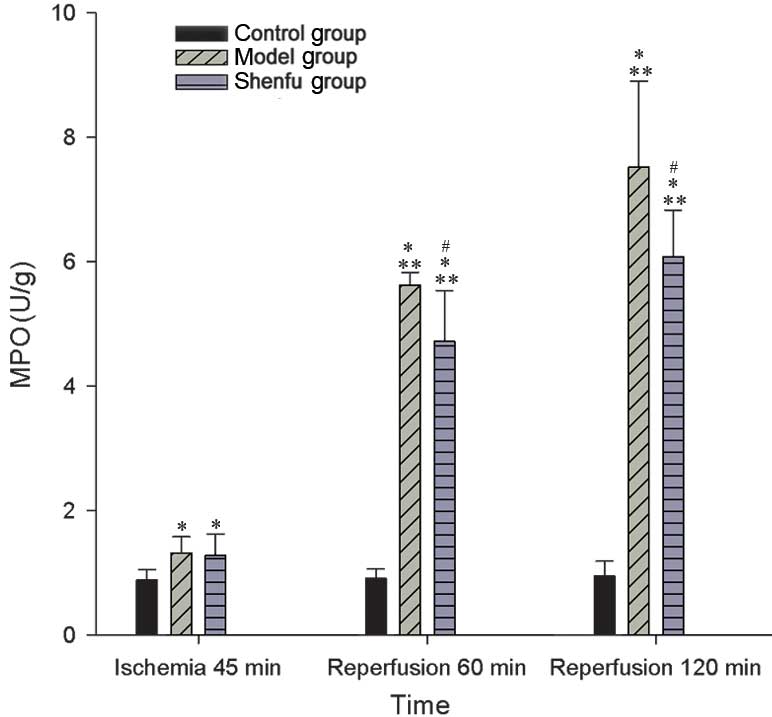
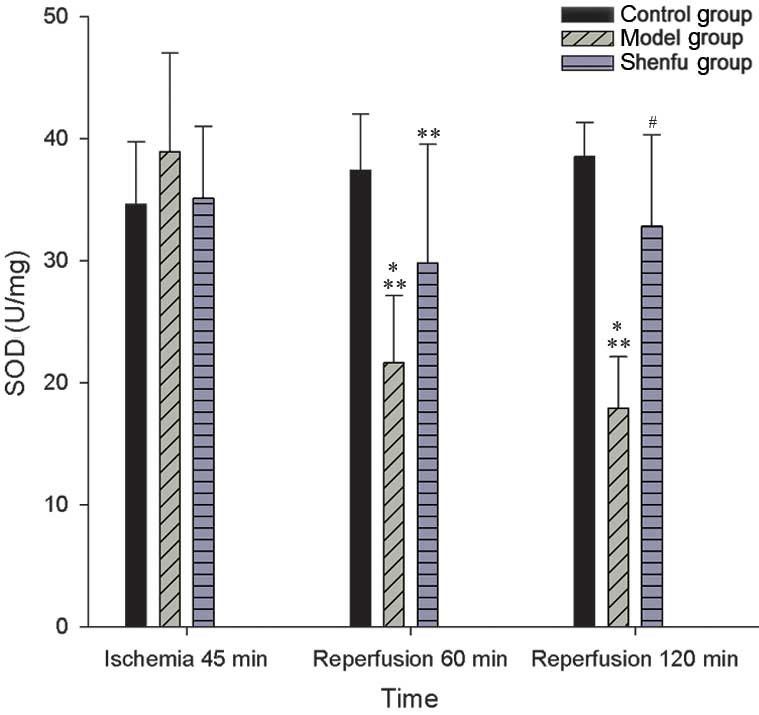
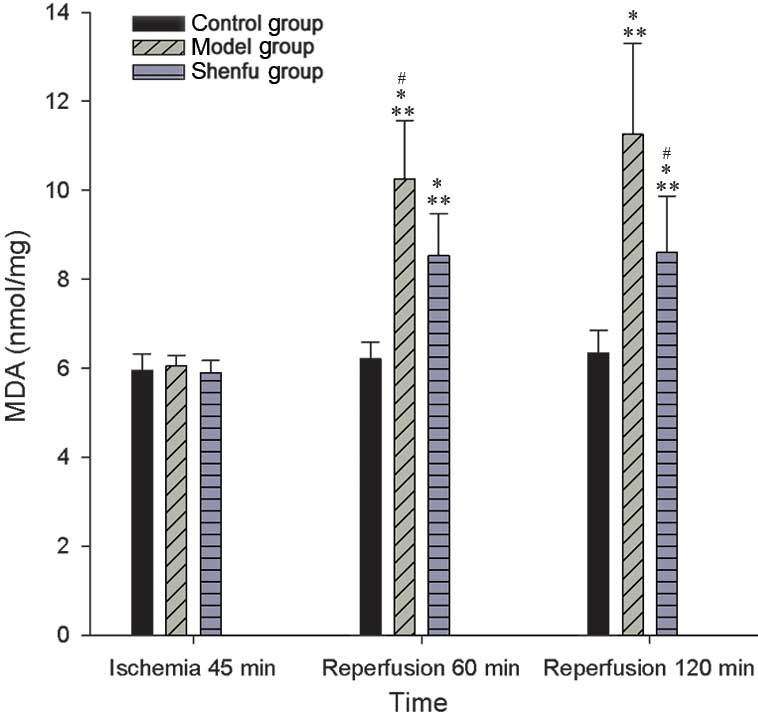
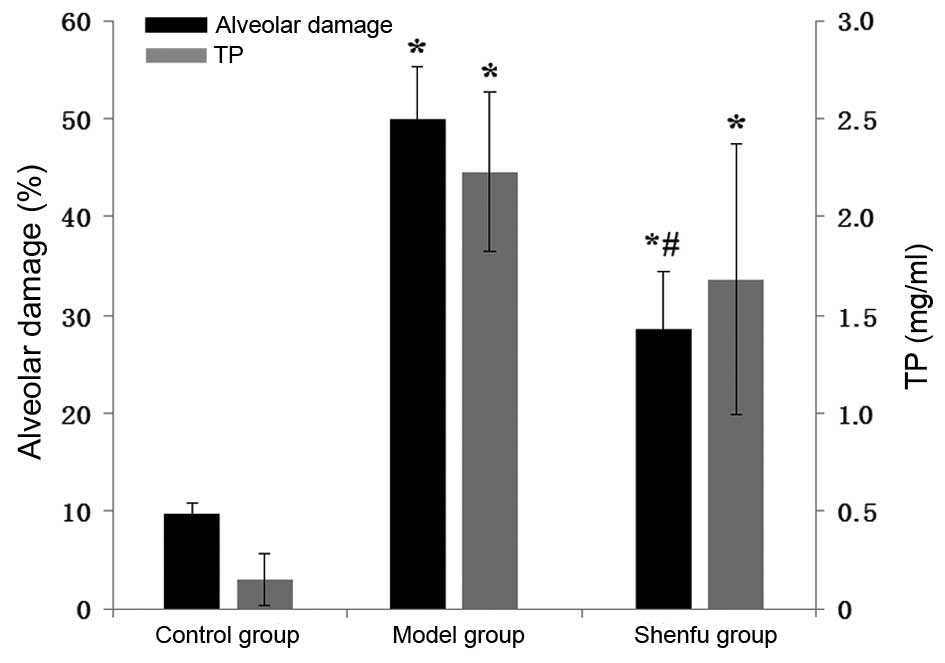
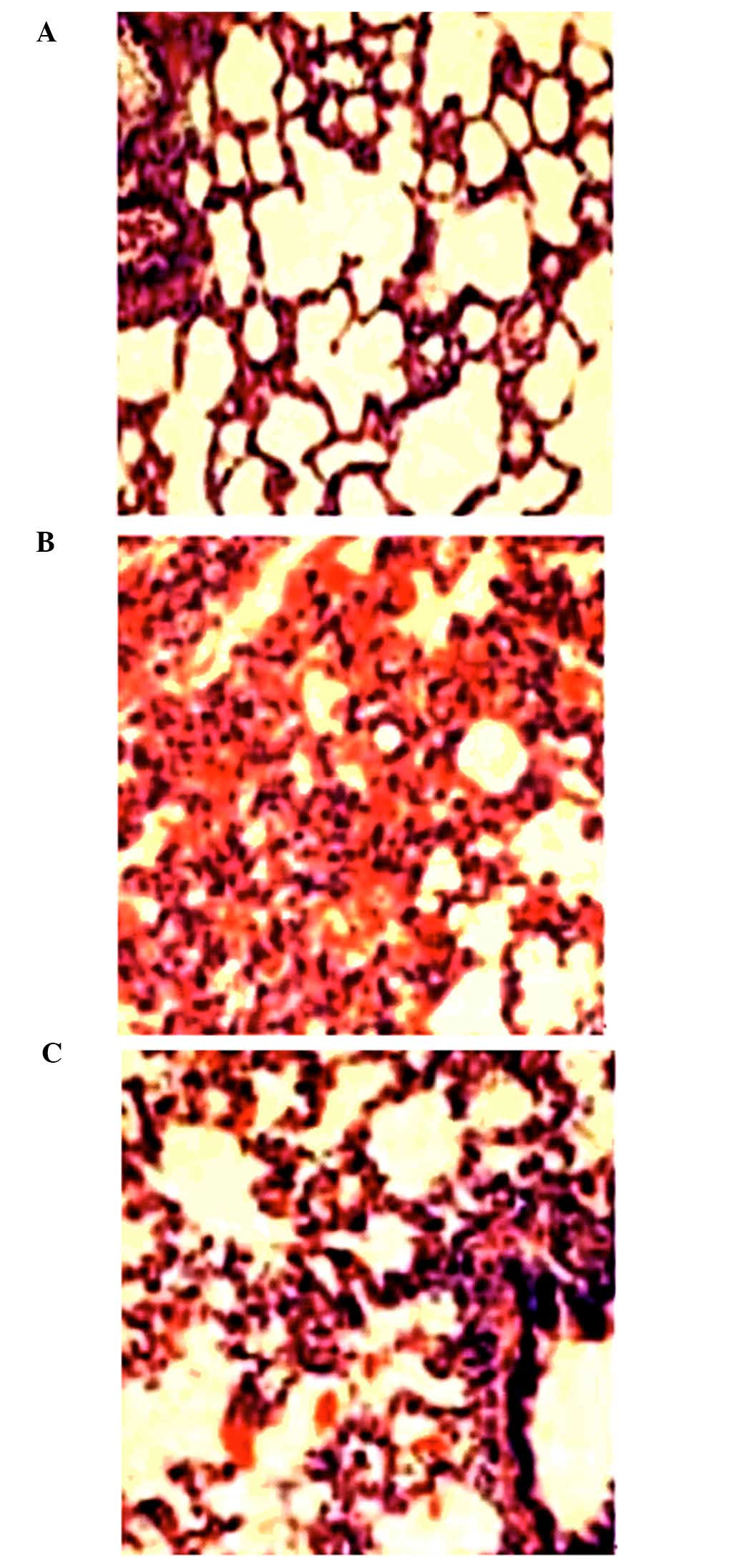
|
1
|
Yang CL, Tsai PS and Huang CJ: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on regulating pulmonary inflammation in a rat model
of ventilator-induced lung injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
46:151–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harada M, Oto T, Otani S and Miyoshi K: A
neutrophil elastase inhibitor improves lung function during ex vivo
lung perfusion. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 63:645–651. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Belaïdi E, Béguin PC, Ribuot C and
Godin-Ribuot D: Hypoxic preconditioning: Role of transcription
factor HIF-1alpha. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 55:70–73. 2006.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurt A, Tumkaya L, Kalkan Y, Turut H, Cure
MC, Cure E, Sehitoglu I, Bilgin H and Usta M: Is adalimumab
protective in ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung? Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 18:1093–1099. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang XJ, Song L, Zhou ZG and Wang XM:
Effect of shenfu injection on gastrointestinal microcirculation in
rabbits after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:4389–4391. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dong G and Shen B: Clinical effect of
shenfu injection in the sepsis bundle treatment of septic shock.
Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Ji Zheng. 23:944–945. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Zheng SY, Sun J, Zhao X and Xu JG:
Protective effect of shen-fu on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rats. Am J Chin Med. 32:209–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang SL, Feng ZQ, Wu LS and Li LH: Shenfu
injection prevents kidney from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rabbits. Zhong Guo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi. 19:353–356. 2003.(In
Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Long SQ, Liao GY, He WF, Wang B, Deng H,
Zhang HB, Chai XS, Cau JZ and Wu WY: Influence of shenfu injection
on the quality of life of lung cancer patients receiving
chemotherapy. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:2090–2092. 2011.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang F, Chen X and Zhu J: Clinical study
on the effects of shenfu injection in children with bronchial
asthma. Zhong Guo Xian Dai Yi Sheng. 52:70–72. 2014.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Fang M: Clinical observation on treatment
of 32 cases of chronic obstructive lung disease with Chinese
medicine combined with Western medicine. Jiang Su Zhong Yi Yao.
39:22–23. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Qiao LF and Yang GT: Role of
Shenfu Injection in rats with systemic inflammatory response
syndrome. Chin J Integr Med. 14:51–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu G, Liu XY, Xia ZY and Xiong GX: The
effect of shenfu injection on the expression of NF-κB, ICAM-1,
TNF-α after ischemia-reperfusion of intestinal mucosa in rats. Tong
Ji Da Xue Xue Bao. 24:381–384. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Yun QC: Effect of combined
methylprednisolone with shenfu injection on the treatment of
children systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Zhong Guo Zhong
Xi Yi Jie He Ji Jiu Za Zhi. 9:155–156. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Zhang Q, Li CS, Wang S and Gu W: Effects
of Chinese medicine Shen-Fu injection on the expression of
inflammatory cytokines and complements during post-resuscitation
immune dysfunction in a porcine model. Chin J Integr Med.
22:101–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chai J, Wang DW and Shen J: Effect of
sevoflurane on pulmonary oxygen free radicals in
ischemia-reperfusion rats. Shi Yong Yao Wu Yu Lin Chuang.
12:156–159. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Du JZ and Dong BR: The effect of
atorvastatin on pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.
Zhong Guo Ji Ceng Yi Yao. 13:2027–2028. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Song J, Jiang M, Qi G, Xie Y, Wang H, Tian
Y, Qu J, Zhang X and Li H: Effect of airway humidification on lung
injury induced by mechanical ventilation. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing
Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 26:884–889. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dawn B and Bolli R: HO-1 induction by
HIF-1: A new mechanism for delayed cardioprotection? Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 289:H522–H524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Laubach VE and Sharma AK: Mechanisms of
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant.
21:246–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lehmann S, Barten MJ, Topf C, Garbade J,
Dhein S, Mohr FW and Bittner HB: Donor type impact on
ischemia-reperfusion injury after lung transplantation. Ann Thorac
Surg. 93:913–919; discussion 919–920. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Shen H, Qin HD, Ma MZ and Xu Y:
Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine against pneumocyte apoptosis
during ischemia/reperfusion injury of lung in rats. Zhongguo Wei
Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 24:111–115. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reyes YA, Shimoyama T, Akamatsu H and
Sunamori M: MCI-186 (edaravone), a free radical scavenger,
attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury and activation of
phospholipase A(2) in an isolated rat lung model after 18 h of cold
preservation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 29:304–311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ferrari RS and Andrade CF: Oxidative
Stress and Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015:5909872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Xia ZY, Meng QT, Zhu J, Lei S, Xu J
and Dou J: Shen-Fu injection preconditioning inhibits myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats: Activation of eNOS
via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:3846272011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jin WY, Sun W, Zhang YZ, Li HY and Chen
MZ: Effect of benidipine on plasma level of calcitonin gene-related
peptide in essential hypertension. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi.
43:747–749. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma RH, Li Y and Wang YX: Postconditioning
with shenfu injection protects against pulmonary
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats MA. Zhong Guo Yao Wu Yu Lin
Chuang. 13:437–439. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Xia ZY, Meng QT, Zhang F and Chen XD:
Effect of shenfu injection (ginesenoside and aconite alkaloid) on
the apoptosis of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells and its
mechanism during ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Zhong Hua Chuang
Shang Za Zhi. 7:363–367. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Wang ZF: The protective of Shenfu
injections on hemodynamics and myocardial enzyme after myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za
Zhi. 27:155–157. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gu W, Hou X, Zhou H and Li C: Protective
effect of shen-fu injection on neuronal mitochondrial function in a
porcine model of prolonged cardiac arrest. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2014:5238472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Christie JD, Edward LB, Aurora P, Dobbels
F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Stehlik J, Taylor DO, Kucheryavaya AY and
Hertz MI: The Registry of the International Society for Heart and
Lung Transplantation: Twenty-sixth Official Adult Lung and
Heart-Lung Transplantation Report - 2009. J Heart Lung Transplant.
28:1031–1049. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ng CS, Wan S, Yim AP and Arifi AA:
Pulmonary dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Chest. 121:1269–1277.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Friedrich I, Spillner J, Lu EX, Bartling
B, Barnscheid M, Sablotzki A, Schade U, Reidemeister JC, Silber RE,
Gunther A and Borgermann J: Ischemic pre-conditioning of 5 minutes
but not of 10 minutes improves lung function after warm ischemia in
a canine model. J Heart Lung Transplant. 20:985–995. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hanci V, Yurdakan G, Yurtlu S, Turan IO
and Sipahi EY: Protective effect of dexmedetomidine in a rat model
of α-naphthylthiourea-induced acute lung injury. J Surg Res.
178:424–430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kesici S, Turkmen UA, Kesici U, Altan A
and Pulat E: Effects of enteral and parenteral glutamine on
intestinal mucosa and on levels of blood glutamine, tumor necrosis
factor-alpha, and interleukin-10 in an experimental sepsis model.
Saudi Med J. 33:262–271. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fu PK, Wu CL, Tsai TH and Hsieh CL:
Anti-inflammatory and anticoagulative effects of paeonol on
LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:224546872012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Inci I, Dutly A, Inci D, Boehler A and
Weder W: Recipient treatment with trimetazidine improves graft
function and protects energy status after lung transplantation. J
Heart Lung Transplant. 20:1115–1122. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li YC and Jiang Z: Ulinastatin, a human
protease inhibitor, attenuates ischemia-reperfusion lung injury. Fu
Dan Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban Bian Ji Wei Yuan Hui. 31:182–186. 2004.(In
Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Xu M, Wen XH, Chen SP, An XX and Xu HY:
Addition of ulinastatin to preservation solution promotes
protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbit lung. Chin
Med J (Engl). 124:2179–2183. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|