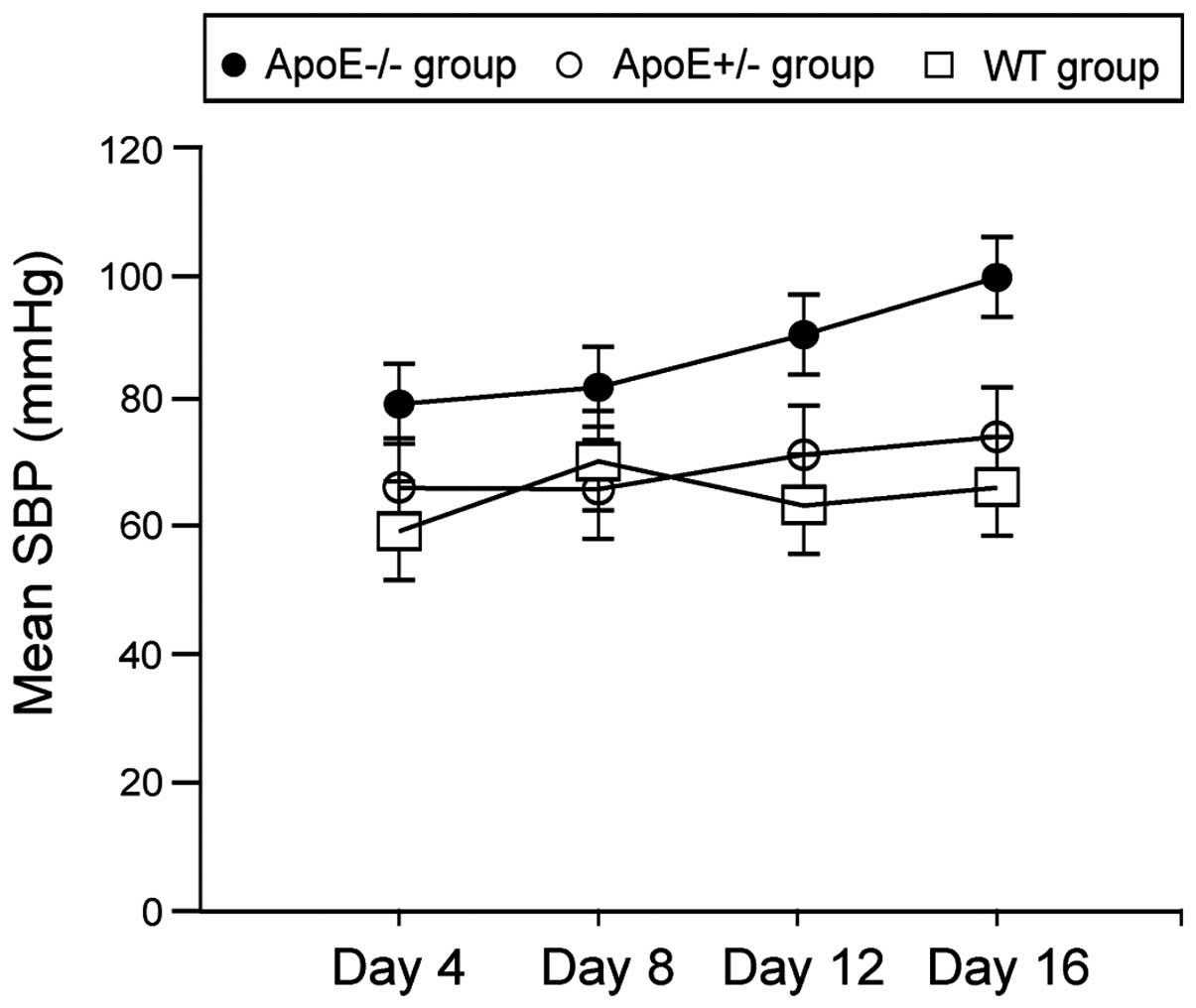
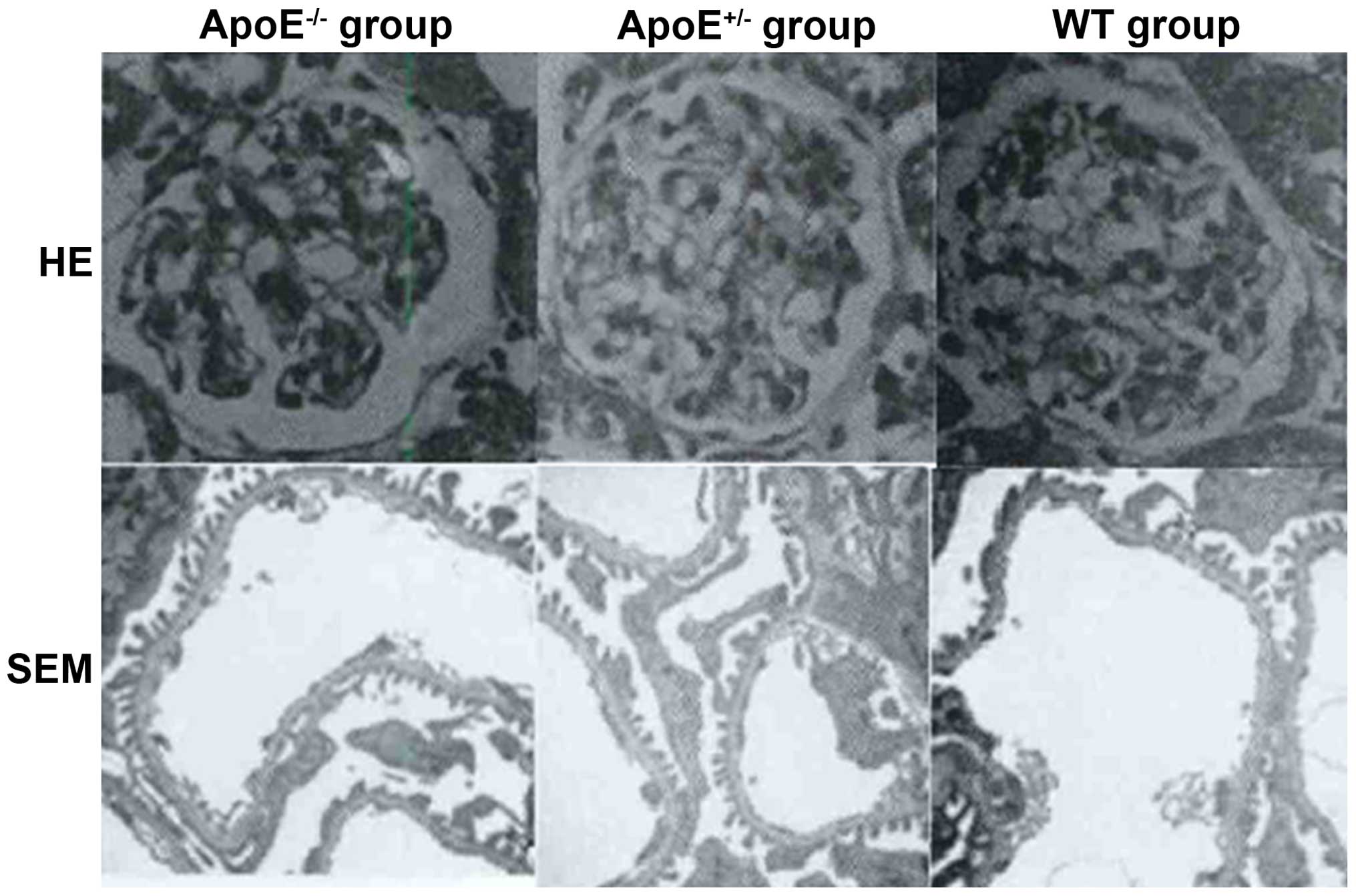
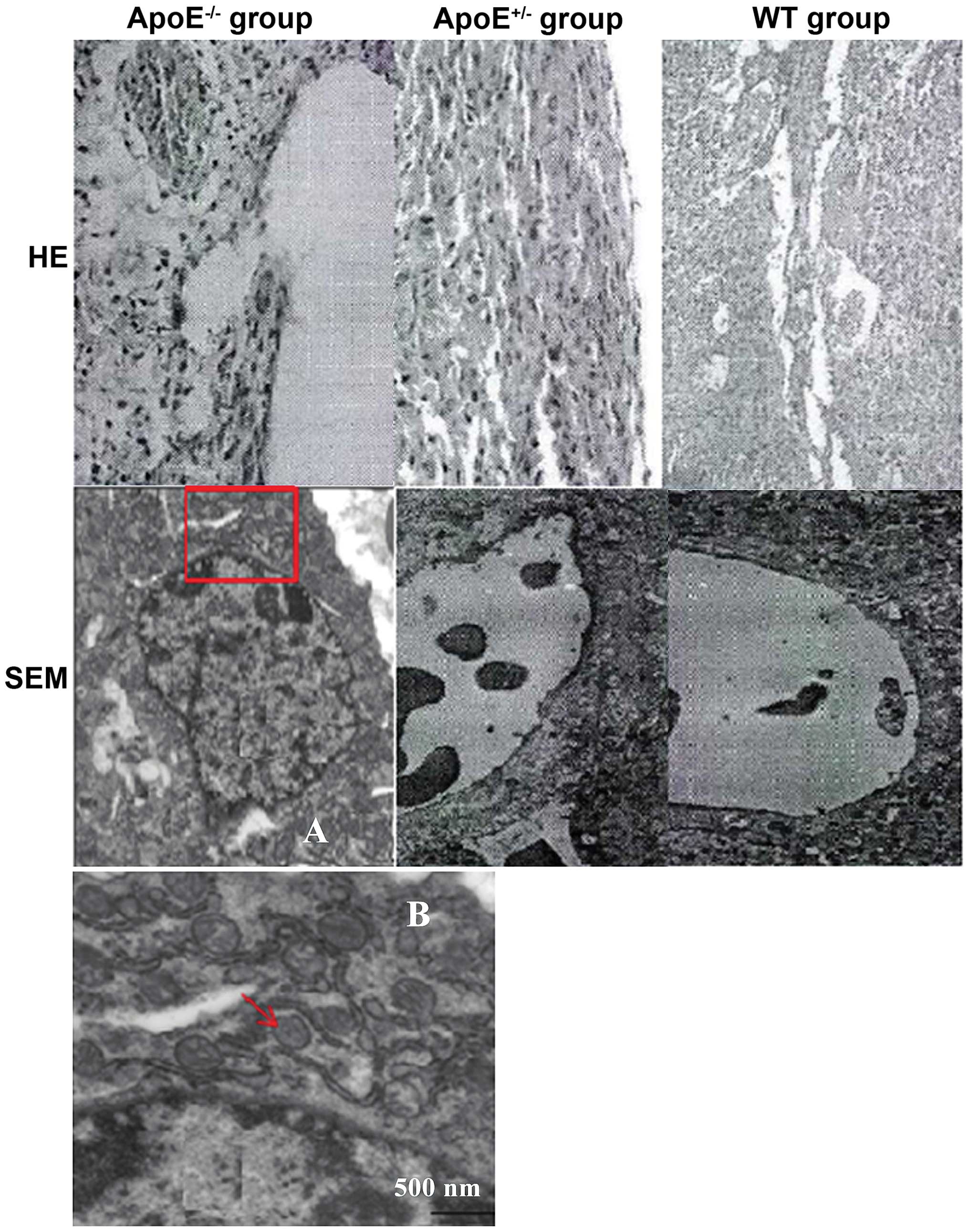
|
1
|
Gong YH, Jia J, Lü DH, Dai L, Bai Y and
Zhou R: Outcome and risk factors of early onset severe
preeclampsia. Chin Med J (Engl). 125:2623–2627. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang X, Wang F, Lau WB, Zhang S, Zhang S,
Liu H and Ma XL: Autoantibodies isolated from preeclamptic patients
induce endothelial dysfunction via interaction with the angiotensin
II AT1 receptor. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 14:21–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mannarino E and Pirro M: Endothelial
injury and repair: a novel theory for atherosclerosis. Angiology.
59 Suppl 2:69S–72S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Podjarny E, Baylis C and Losonczy G:
Animal models of preeclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 23:2–13. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sircar M, Thadhani R and Karumanchi SA:
Pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens.
24:131–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Redman CW, Sacks GP and Sargent IL:
Preeclampsia: an excessive maternal inflammatory response to
pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 180:499–506. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bayhan G, Koçyigit Y, Atamer A, Atamer Y
and Akkus Z: Potential atherogenic roles of lipids, lipoprotein(a)
and lipid peroxidation in preeclampsia. Gynecol Endocrinol. 21:1–6.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsuo K, Kooshesh S, Dinc M, Sun CC,
Kimura T and Baschat AA: Late postpartum eclampsia: report of two
cases managed by uterine curettage and review of the literature. Am
J Perinatol. 24:257–266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cekmen MB, Erbagci AB, Balat A, Duman C,
Maral H, Ergen K, Ozden M, Balat O and Kuskay S: Plasma lipid and
lipoprotein concentrations in pregnancy induced hypertension. Clin
Biochem. 36:575–578. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Francoual J, Audibert F, Trioche P, Chalas
J, Capel L, Lindenbaum A, Labrune P and Frydman R: Is a
polymorphism of the apolipoprotein E gene associated with
preeclampsia? Hypertens Pregnancy. 21:127–133. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Belo L, Gaffney D, Caslake M, Santos-Silva
A, Pereira-Leite L, Quintanilha A and Rebelo I: Apolipoprotein E
and cholesteryl ester transfer protein polymorphisms in normal and
preeclamptic pregnancies. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
112:9–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kobayashi K, Oyama S, Numata A, Rahman MM
and Kumura H: Lipopolysaccharide disrupts the milk-blood barrier by
modulating claudins in mammary alveolar tight junctions. PLoS One.
8:e621872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee KM and Seong SY: Partial role of TLR4
as a receptor responding to damage-associated molecular pattern.
Immunol Lett. 125:31–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Banas MC, Banas B, Hudkins KL, Wietecha
TA, Iyoda M, Bock E, Hauser P, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ, Smith KD,
et al: TLR4 links podocytes with the innate immune system to
mediate glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:704–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suzuki H, Ohkuchi A, Matsubara S, Takei Y,
Murakami M, Shibuya M, Suzuki M and Sato Y: Effect of recombinant
placental growth factor 2 on hypertension induced by full-length
mouse soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 adenoviral vector in
pregnant mice. Hypertension. 54:1129–1135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin M, Yiu WH, Li RX, Wu HJ, Wong DW, Chan
LY, Leung JC, Lai KN and Tang SC: The TLR4 antagonist CRX-526
protects against advanced diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int.
83:887–900. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|