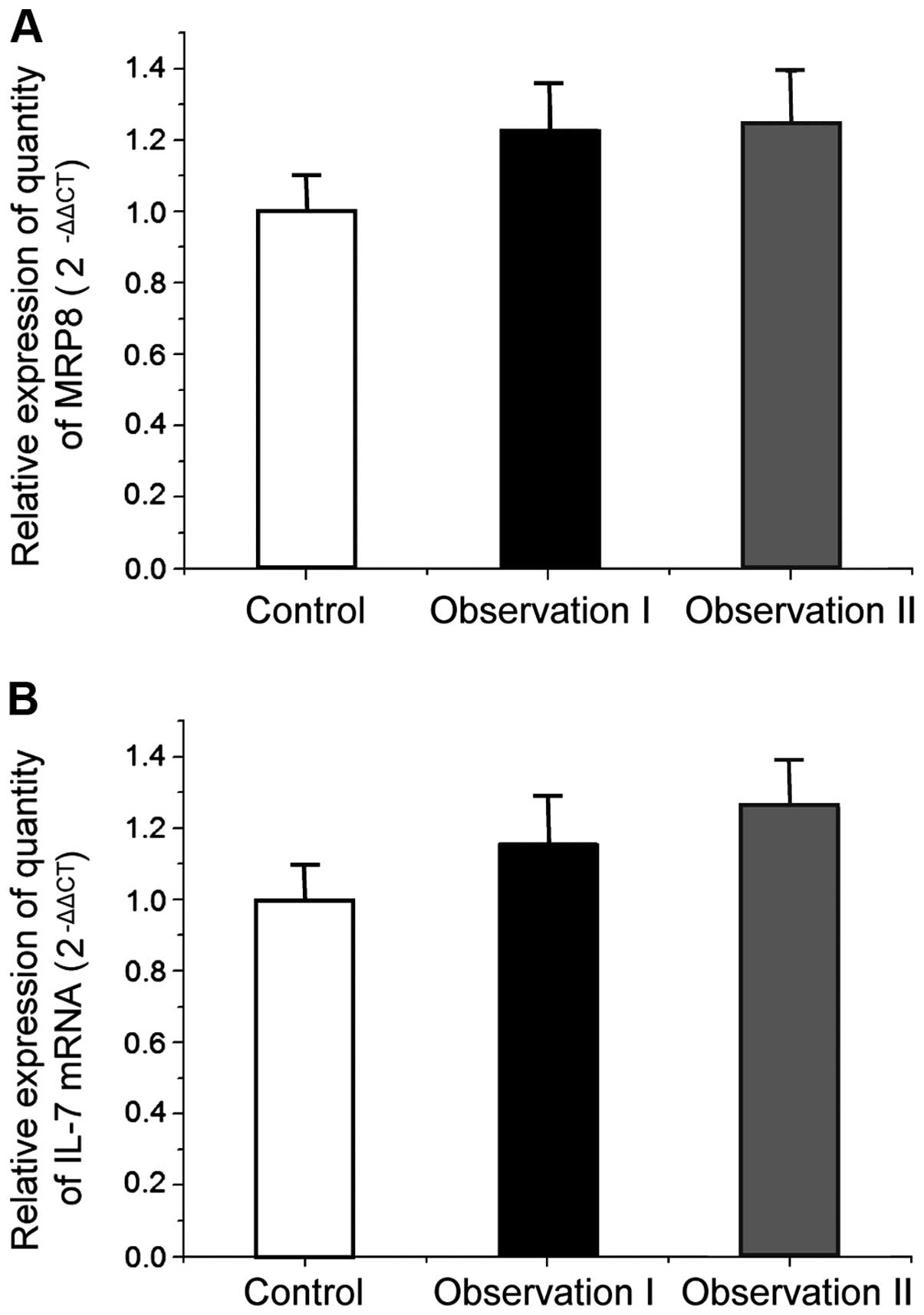
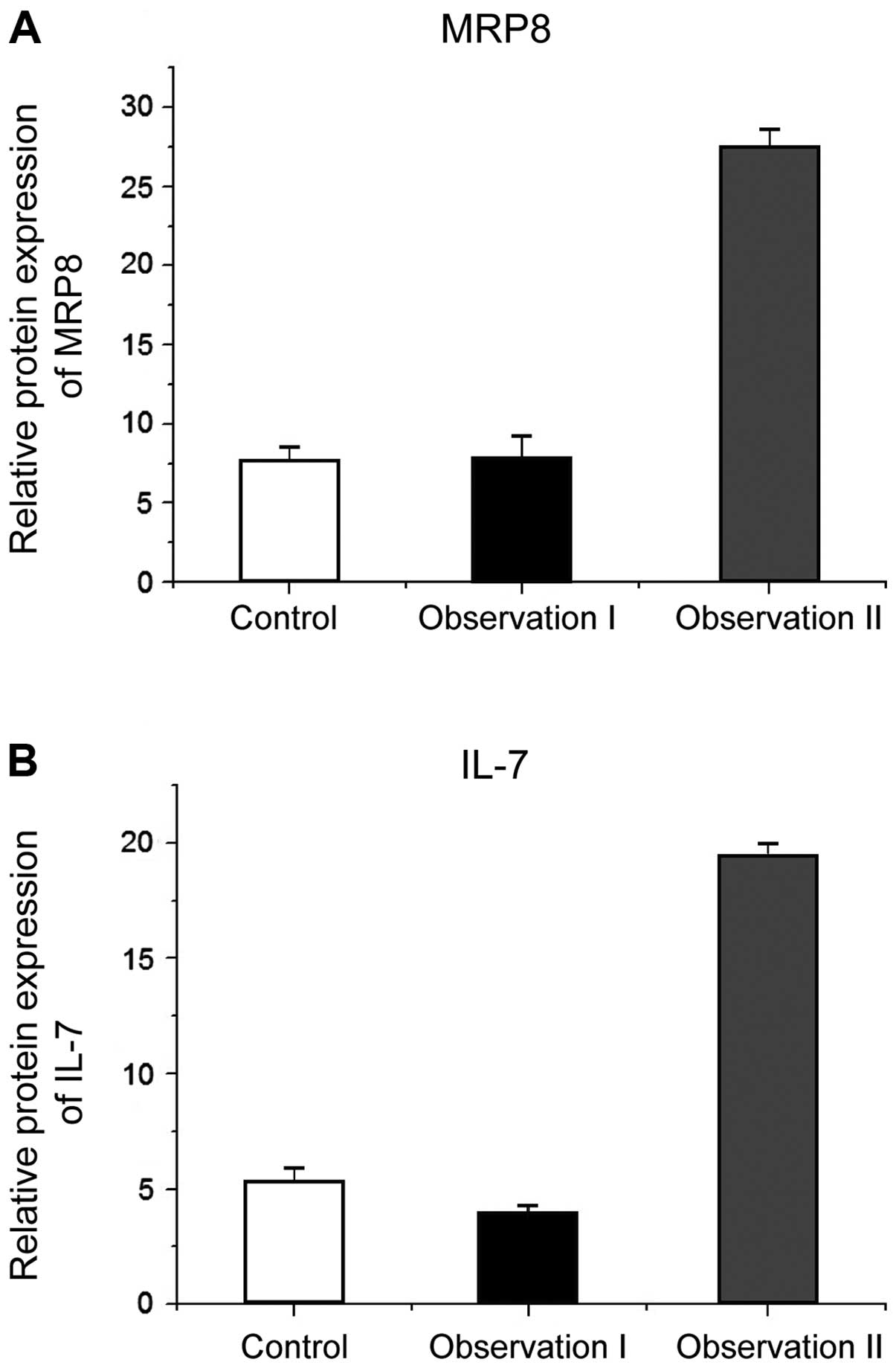
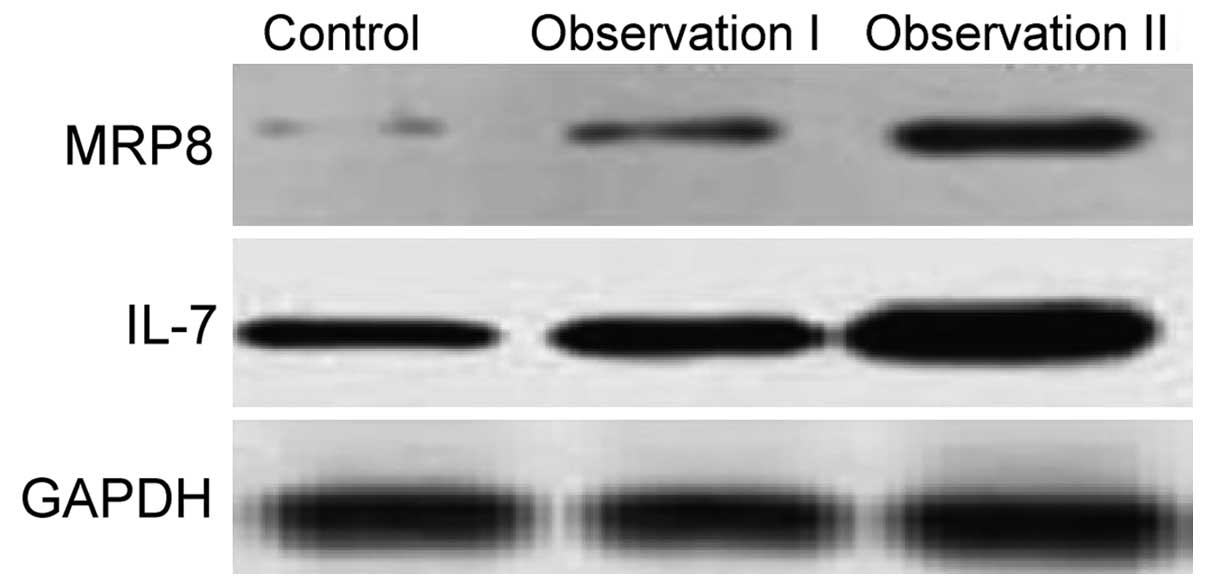
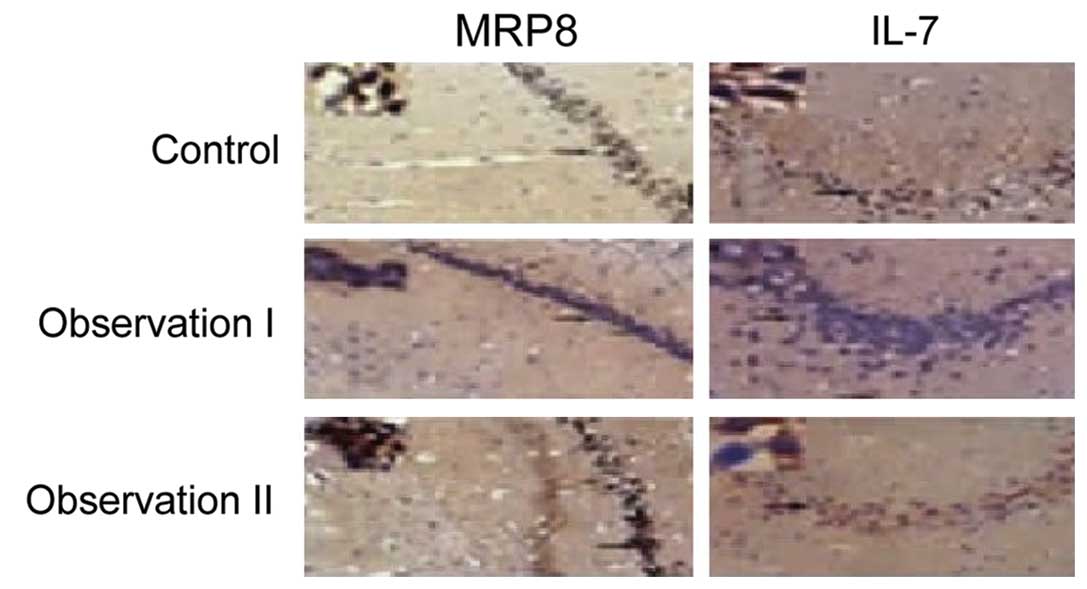
|
1
|
Ashhab MU, Omran A, Kong H, Gan N, He F,
Peng J and Yin F: Expressions of tumor necrosis factor alpha and
microRNA-155 in immature rat model of status epilepticus and
children with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci.
51:950–958. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sloan SA and Barres BA: Mechanisms of
astrocyte development and their contributions to neurodevelopmental
disorders. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 27:75–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Canpolat M, Per H, Gumus H, Yikilmaz A,
Unal E, Patiroglu T, Cinar L, Kurtsoy A and Kumandas S: Rapamycin
has a beneficial effect on controlling epilepsy in children with
tuberous sclerosis complex: results of 7 children from a cohort of
86. Childs Nerv Syst. 30:227–240. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang CL: Study on the relationship and
mechanism between dynamin-1 and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
(unpublished PhD thesis)Central South University; China: 2014
|
|
5
|
Kong H, Omran A, Ashhab MU, Gan N, Peng J,
He F, Wu L, Deng X and Yin F: Changes in microglial
inflammation-related and brain-enriched MicroRNAs expressions in
response to in vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation. Neurochem Res.
39:233–243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwon CH, Moon HJ, Park HJ, Choi JH and
Park Y: S100A8 and S100A9 promotes invasion and migration through
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent NF-κB activation in
gastric cancer cells. Mol Cells. 35:226–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pellegrini M, Calzascia T, Toe JG, Preston
SP, Lin AE, Elford AR, Shahinian A, Lang PA, Lang KS, Morre M, et
al: IL-7 engages multiple mechanisms to overcome chronic viral
infection and limit organ pathology. Cell. 144:601–613. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu YY, Wang Y, Li YP, Xu XX, Zhu SB and
Zhang XG: Interleukin-7 influences the development of thymic T
lymphocytes and thymic dendritic cells. Chinese J Immunol.
26:108–112. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Holtman L, van Vliet EA, Aronica E,
Wouters D, Wadman WJ and Gorter JA: Blood plasma inflammation
markers during epileptogenesis in post-status epilepticus rat model
for temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 54:589–595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiang QL, Zhang CL, Peng J, He F, Wu LW,
Ou M and Yin F: Expression of TLR4 and MRP8 in the developing
immature rats with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Apoplexy
Nervous Diseases. 7:580–584. 2012.(In Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZFSJ201207002.htm
|
|
11
|
Mohammad G, Siddiquei MM, Othman A,
Al-Shabrawey M and Abu El-Asrar AM: High-mobility group box-1
protein activates inflammatory signaling pathway components and
disrupts retinal vascular-barrier in the diabetic retina. Exp Eye
Res. 107:101–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schroten-Loef C, de Ridder CM, Reneman S,
Crezee M, Dalgleish A, Todryk SM, Bangma CH and Kraaij R: A
prostate cancer vaccine comprising whole cells secreting IL-7,
effective against subcutaneous challenge, requires local GM-CSF for
intra-prostatic efficacy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:373–381.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buchler T, Bortlicek Z, Poprach A,
Kubackova K, Kiss I, Zemanova M, Fiala O, Dusek L, Vyzula R and
Melichar B: Czech Renal Cancer Cooperative Group: Efficacy of
everolimus in second- and third-line therapy for metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: a registry-based analysis. Urol Oncol. 32:569–575.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hille A, Grüger S, Christiansen H, Wolff
HA, Volkmer B, Lehmann J, Dörr W and Rave-Fränk M: Effect of
tumour-cell-derived or recombinant keratinocyte growth factor (KGF)
on proliferation and radioresponse of human epithelial tumour cells
(HNSCC) and normal keratinocytes in vitro. Radiat Environ Biophys.
49:261–270. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yucel AF, Kanter M, Pergel A, Erboga M and
Guzel A: The role of curcumin on intestinal oxidative stress, cell
proliferation and apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. J Mol Histol. 42:579–587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu W, Huang Q, He F, Xiao M, Pang S, Guo
X, Brunk UT, Zhao K and Zhao M: Roles of mitogen-activated protein
kinases in the modulation of endothelial cell function following
thermal injury. Shock. 35:618–625. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lan L, Tao J, Chen A, Xie G, Huang J, Lin
J, Peng J and Chen L: Electroacupuncture exerts anti-inflammatory
effects in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via
suppression of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Int J Mol Med. 31:75–80.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schelbergen RF, Blom AB, van den Bosch MH,
Slöetjes A, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Schreurs BW, Mort JS, Vogl T, Roth
J, van den Berg WB, et al: Alarmins S100A8 and S100A9 elicit a
catabolic effect in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes that is
dependent on Toll-like receptor 4. Arthritis Rheum. 64:1477–1487.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang FL, Jiang JM, Wang F, Fu ZZ and Zhang
ZF: Expressions of interleukin 18 and prostaglandin E2 and their
correlation in the synoviocytes of patients with osteoarthritis. J
Southern Med University. 30:731–733. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Peng J, Omran A, Ashhab MU, Kong H, Gan N,
He F and Yin F: Expression patterns of miR-124, miR-134, miR-132,
and miR-21 in an immature rat model and children with mesial
temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci. 50:291–297. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|