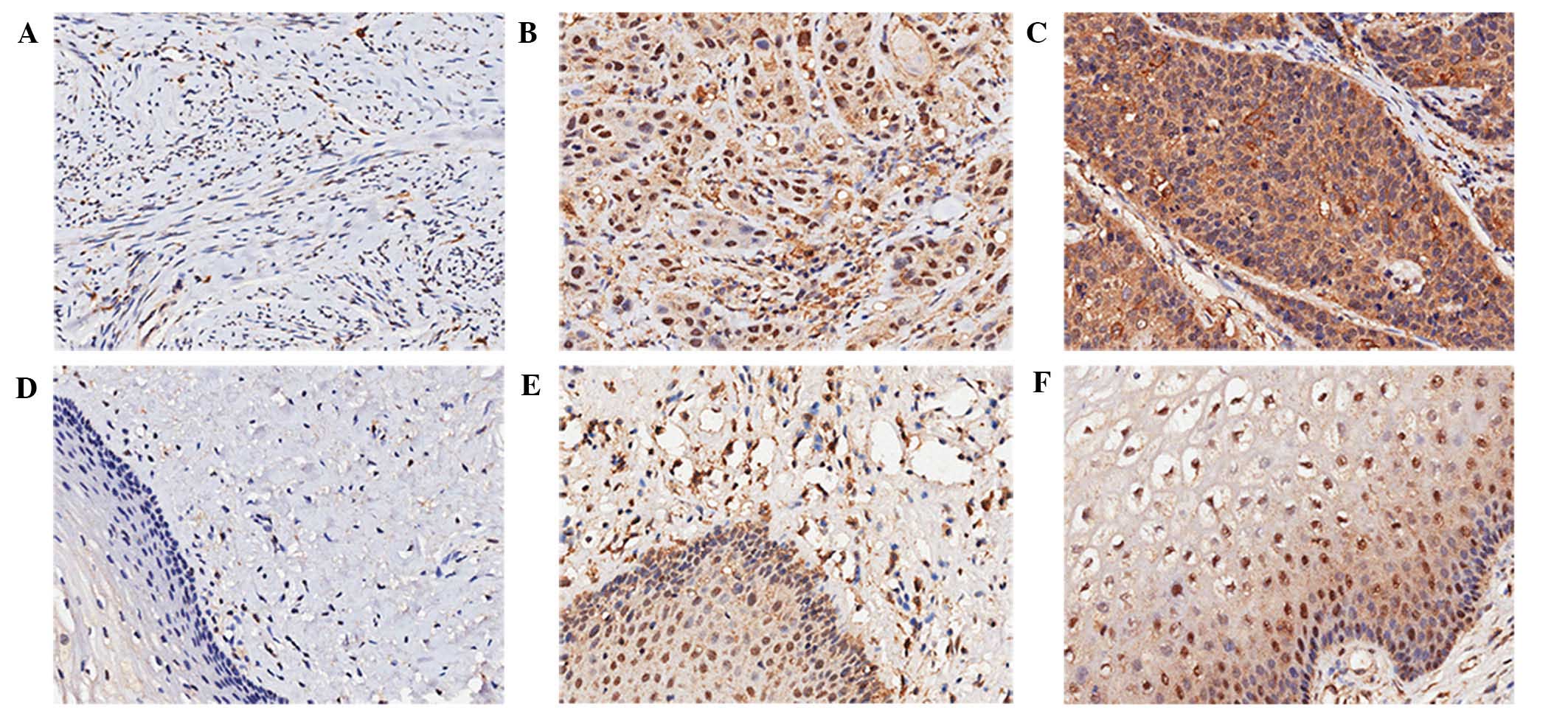
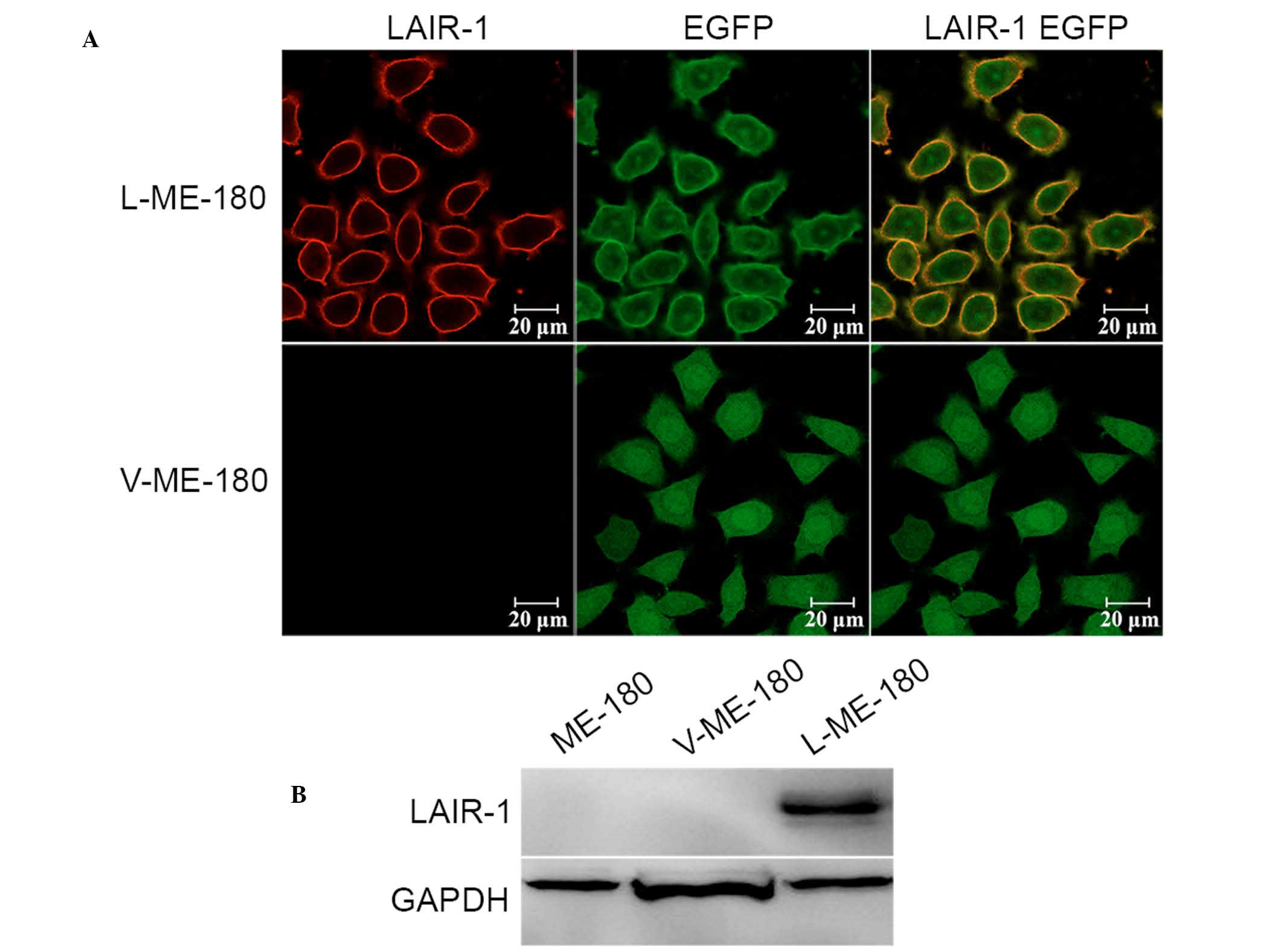
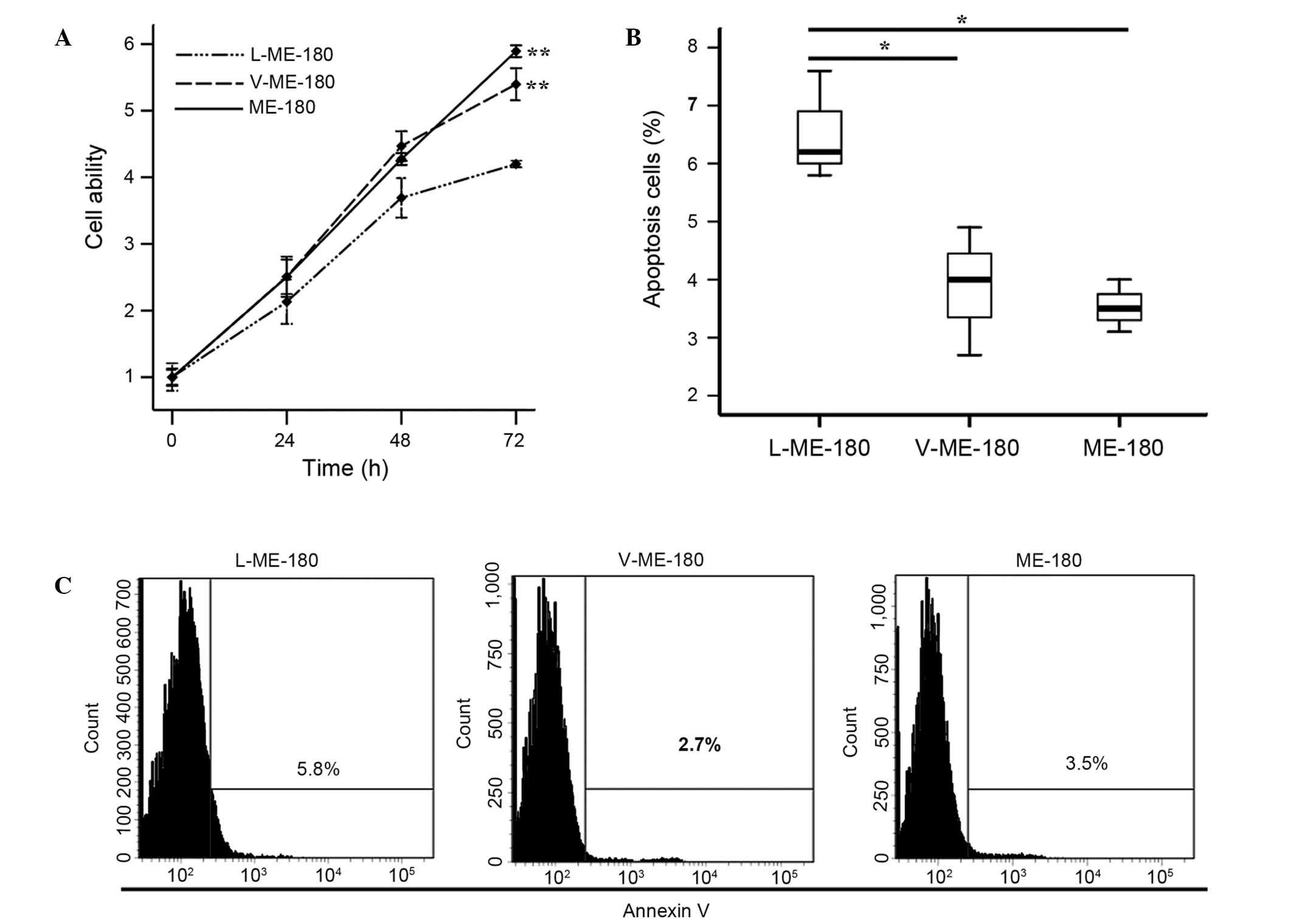
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global Cancer Statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dhillon PK, Yeole BB, Dikshit R, Kurkure
AP and Bray F: Trends in breast, ovarian and cervical cancer
incidence in Mumbai, India over a 30-year period, 1976–2005: An
age-period-cohort analysis. Br J Cancer. 105:723–730. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gadducci A, Barsotti C, Cosio S, Domenici
L and Genazzani A Riccardo: Smoking habit, immune suppression, oral
contraceptive use, and hormone replacement therapy use and cervical
carcinogenesis: A review of the literature. Gynecol Endocrinol.
27:597–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Benedet JL, Bender H, Jones H III, Ngan HY
and Pecorelli S: FIGO staging classifications and clinical practice
guidelines in the management of gynecologic cancers. FIGO Committee
on Gynecologic Oncology. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 70:209–262. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cain JM and Howett MK: Preventing cervical
cancer. Science. 288:1753–1755. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meyaard L: LAIR and collagens in immune
regulation. Immunol Lett. 128:26–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xue J, Zhang X, Zhao H, Fu Q, Cao Y, Wang
Y, Feng X and Fu A: Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like
receptor-1 is expressed on human megakaryocytes and negatively
regulates the maturation of primary megakaryocytic progenitors and
cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:128–133. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Ding Y, Huang Y, Zhang C, Boquan
J and Ran Z: Expression of leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like
receptor-1 (LAIR-1) on osteoclasts and its potential role in
rheumatoid arthritis. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 68:475–481. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Poggi A, Catellani S, Bruzzone A,
Caligaris-Cappio F, Gobbi M and Zocchi MR: Lack of the
leukocyte-associated Ig-like receptor-1 expression in high-risk
chronic lymphocytic leukaemia results in the absence of a negative
signal regulating kinase activation and cell division. Leukemia.
22:980–988. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao Q, Fu A, Yang S, He X, Wang Y, Zhang
X, Zhou J, Luan X, Yu W and Xue J: Leukocyte-associated
immunoglobulin-like receptor-1 expressed in epithelial ovarian
cancer cells and involved in cell proliferation and invasion.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:399–404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu P, Weaver VM and Werb Z: The
extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell
Biol. 196:395–406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lebbink RJ, de Ruiter T, Adelmeijer J,
Brenkman AB, van Helvoort JM, Koch M, Farndale RW, Lisman T,
Sonnenberg A, Lenting PJ and Meyaard L: Collagens are functional,
high affinity ligands for the inhibitory immune receptor LAIR-1. J
Exp Med. 203:1419–1425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tewari KS, Sill MW, Long HJ, Penson RT,
Huang H, Ramondetta LM, Landrum LM, Oaknin A, Reid TJ, Leitao MM,
Michael HE and Monk BJ: Improved survival with Bevacizumab in
advanced cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 370:734–743. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahasrabuddhe VV, Luhn P and Wentzensen N:
Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer: Biomarkers for improved
prevention efforts. Future Microbiol. 6:1083–1098. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meyaard L, Adema GJ, Chang C, Woollatt E,
Sutherland GR, Lanier LL and Phillips JH: LAIR-1, a novel
inhibitory receptor expressed on human mononuclear leukocytes.
Immunity. 7:283–290. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ouyang W, Ma D, Lin D, Sun Y, Liu X, Li Q,
Jia W, Cao Y, Zhu Y and Jin B: 9.1C3 is identical to LAIR-1, which
is expressed on hematopoietic progenitors. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 310:1236–1240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maasho K, Masilamani M, Valas R, Basu S,
Coligan JE and Borrego F: The inhibitory leukocyte-associated
Ig-like receptor-1 (LAIR-1) is expressed at high levels by human
naive T cells and inhibits TCR mediated activation. Mol Immunol.
42:1521–1530. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Poggi A, Pellegatta F, Leone BE, Moretta L
and Zocchi MR: Engagement of the leukocyte-associated Ig-like
receptor-1 induces programmed cell death and prevents NF-kappaB
nuclear translocation in human myeloid leukemias. Eur J Immunol.
30:2751–2758. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zocchi MR, Pellegatta F, Pierri I, Gobbi M
and Poggi A: Leukocyte-associated Ig-like receptor-1 prevents
granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor-dependent
proliferation and Akt1/PKB alpha activation in primary acute
myeloid leukemia cells. Eur J Immunol. 31:3667–3675. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seo DW, Li H, Qu CK, Oh J, Kim YS, Diaz T,
Wei B, Han JW and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Shp-1 mediates the
antiproliferative activity of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-2 in human microvascular endothelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 281:3711–3721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yip SS, Crew AJ, Gee JM, Hui R, Blamey RW,
Robertson JF, Nicholson RI, Sutherland RL and Daly RJ:
Up-regulation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in human
breast cancer and correlation with GRB2 expression. Int J Cancer.
88:363–368. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang J, Jin MS, Kong F, Wang YP, Jia ZF,
Cao DH, Ma HX, Suo J and Cao XY: Increased expression of tyrosine
phosphatase SHP-2 in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:575–580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng F, Zhao X and Zhang S: Expression and
significance of SHP-2 in human papillomavirus infected cervical
cancer. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 32:247–251. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tao XH, Shen JG, Pan WL, Dong YE, Meng Q,
Honn KV and Jin R: Significance of SHP-1 and SHP-2 expression in
human papillomavirus infected Condyloma acuminatum and cervical
cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 14:365–371. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Verbrugge A, Rijkers ES, de Ruiter T and
Meyaard L: Leukocyte-associated Ig-like receptor-1 has SH2
domain-containing phosphatase-independent function and recruits
C-terminal Src kinase. Eur J Immunol. 36:190–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|