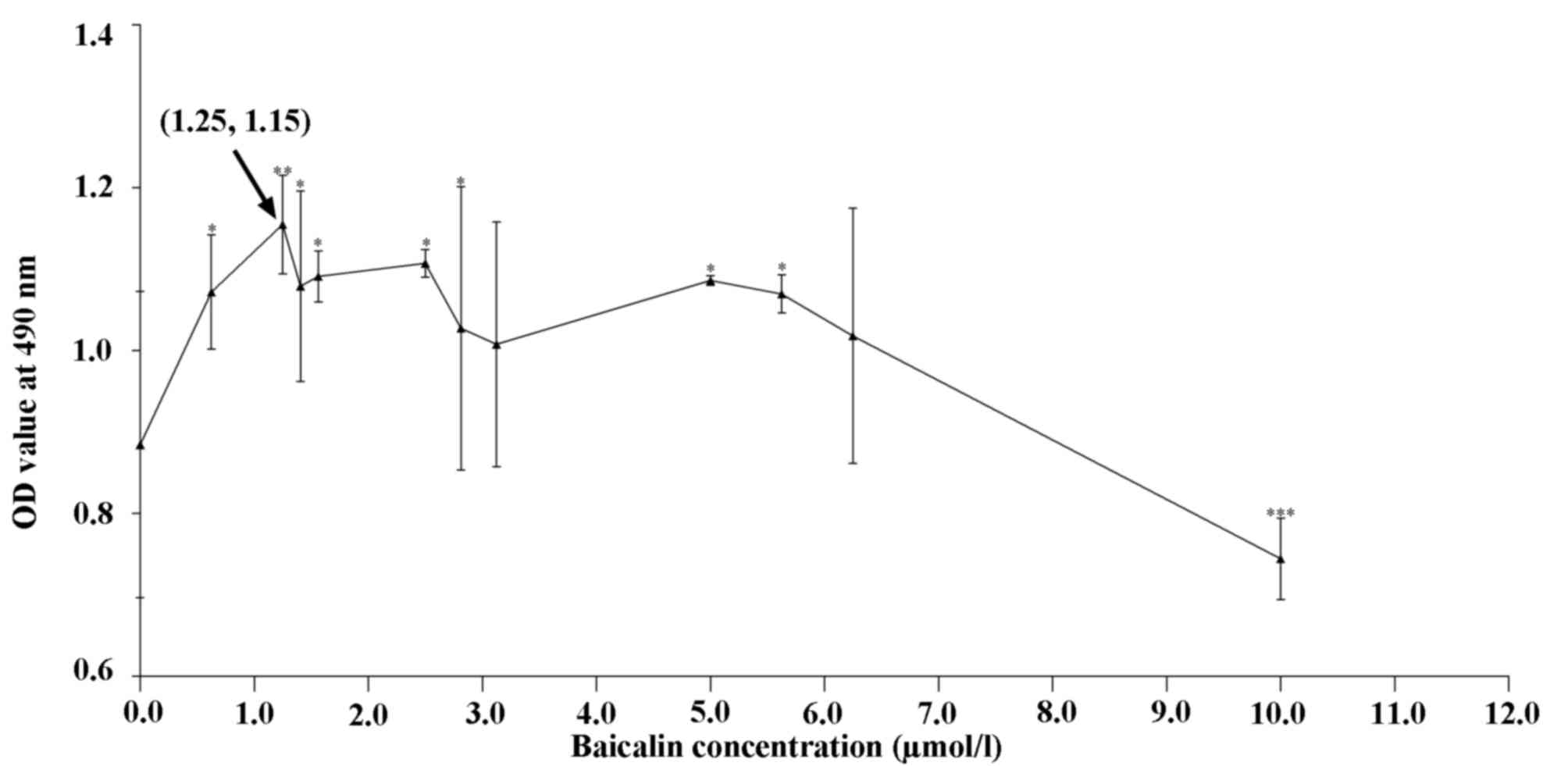
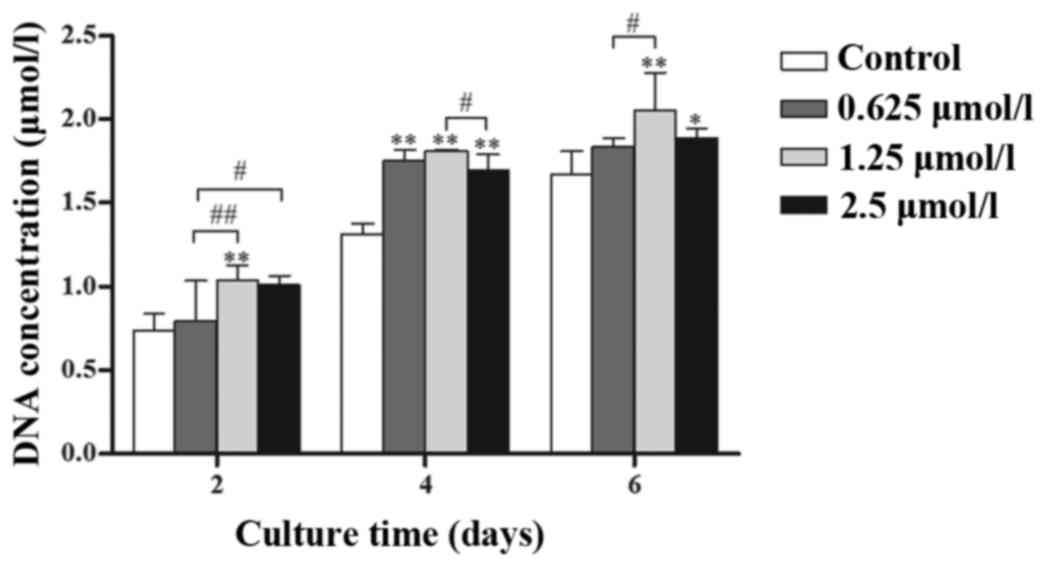
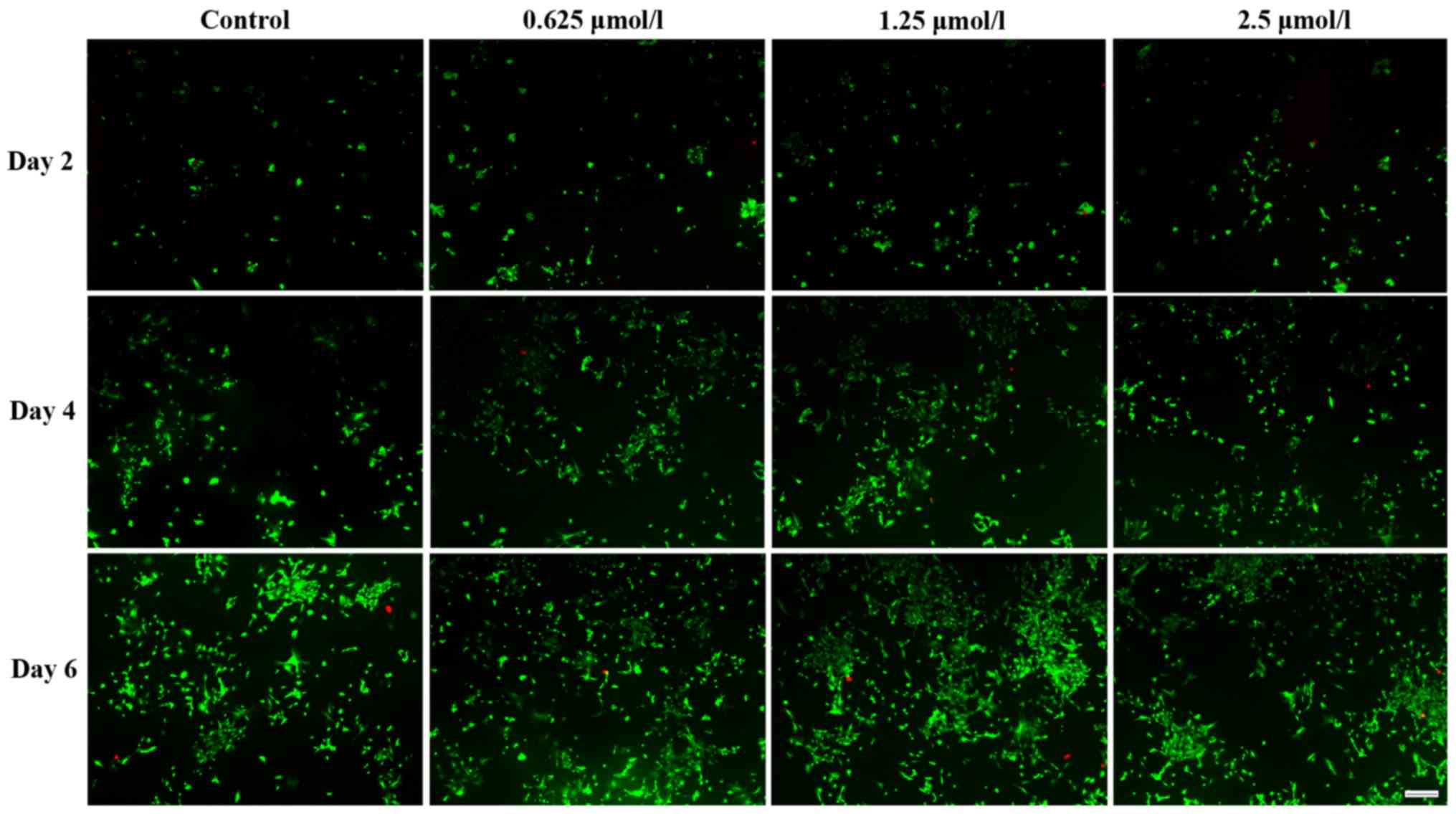
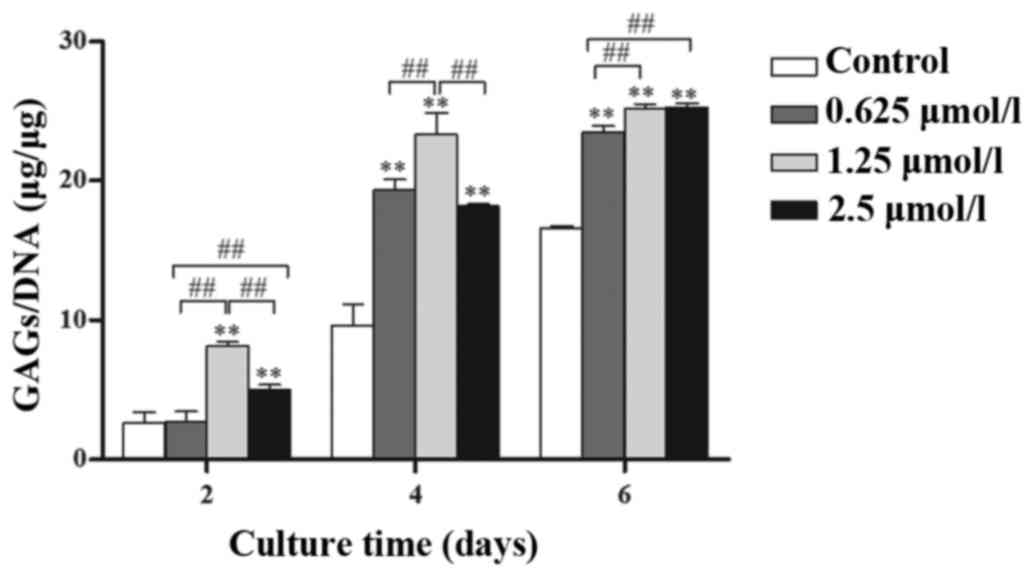
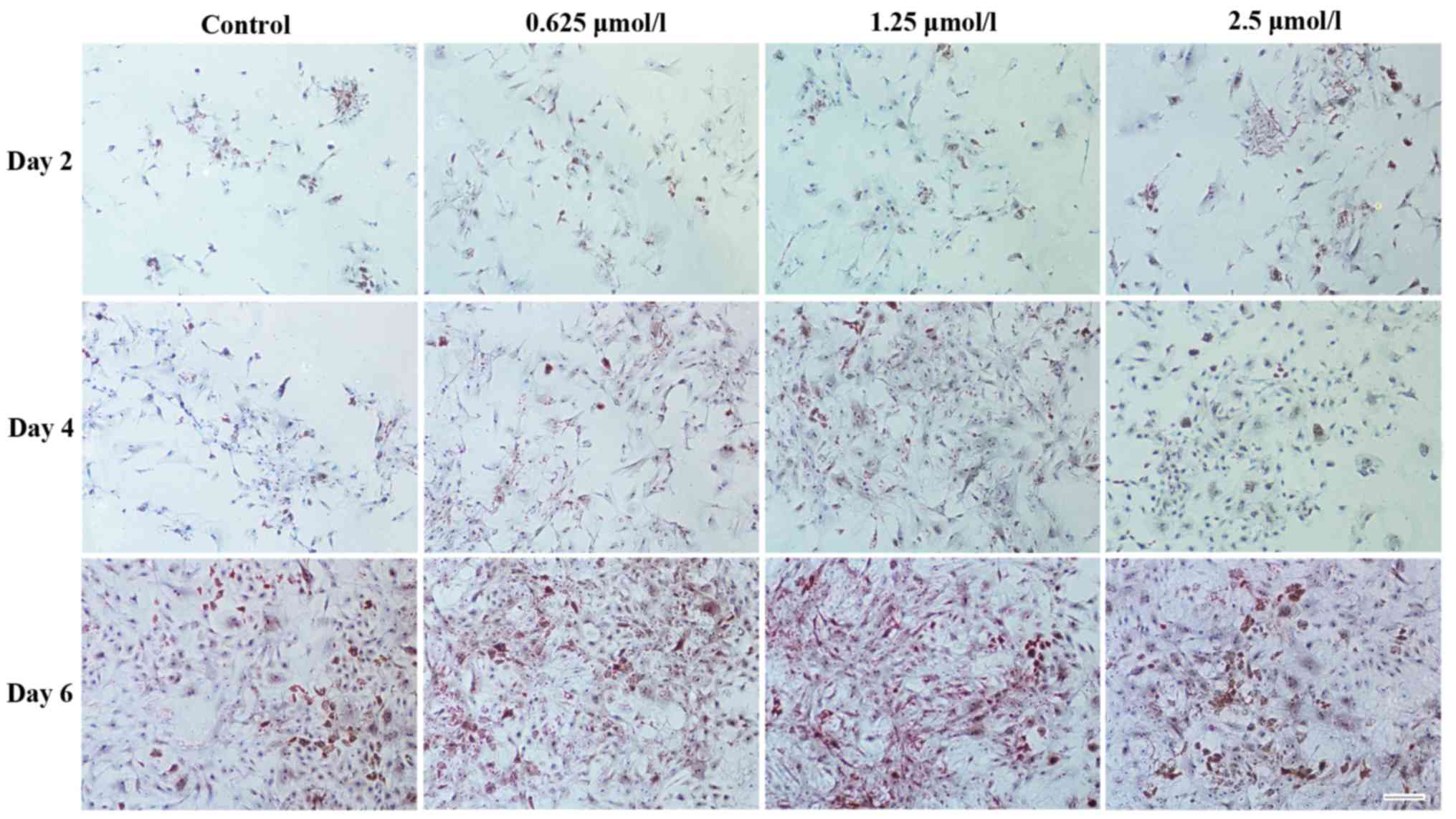
|
1
|
Pasold J, Zander K, Heskamp B, Gruttner C,
Luthen F, Tischer T, Jonitz-Heincke A and Bader R: Positive impact
of IGF-1-coupled nanoparticles on the differentiation potential of
human chondrocytes cultured on collagen scaffolds. Int J
Nanomedicine. 10:1131–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ishii I, Mizuta H, Sei A, Hirose J, Kudo S
and Hiraki Y: Healing of full-thickness defects of the articular
cartilage in rabbits using fibroblast growth factor-2 and a fibrin
sealant. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 89:693–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oda K and Minata M: Drug free remission
after steroid-dependent disappearance of lymphoproliferative
disorder in rheumatoid arthritis patient treated with TNF-alpha
blockade: Case study. Springerplus. 4:412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buckwalter JA and Mankin HJ: Articular
cartilage: Tissue design and chondrocyte-matrix interactions. Instr
Course Lect. 47:477–486. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rahman R Abdul, Sukri N Mohamad, Md Nazir
N, Radzi MA Ahmad, Zulkifly AH, Che Ahmad A, Hashi AA, Rahman S
Abdul and Sha'ban M: The potential of 3-dimensional construct
engineered from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/fibrin hybrid
scaffold seeded with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for in
vitro cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Cell. 47:420–430. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kojima K, Bonassar LJ, Roy AK, Mizuno H,
Cortiella J and Vacanti CA: A composite tissue-engineered trachea
using sheep nasal chondrocyte and epithelial cells. FASEB J.
17:823–828. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kojima K, Bonassar LJ, Roy AK, Vacanti CA
and Cortiella J: Autologous tissue-engineered trachea with sheep
nasal chondrocytes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 123:1177–1184. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ting SY, Montagne K, Nishimura Y, Ushida T
and Furukawa KS: Modulation of the effect of transforming growth
factor-β3 by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on scaffold-free
dedifferentiated articular bovine chondrocyte tissues. Tissue Eng
Part C Methods. 21:1005–1014. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Q, Li J, Hartstone-Rose A, Wang J, Li
J, Janicki JS and Fan D: Chinese herbal compounds for the
prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis: Experimental EVIDENCE
AND MECHANISMS. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2015:7526102015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu J, Wang JS and Kong LY:
Anti-inflammatory effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction, its two
fractions and four typical compounds. J Ethnopharmacol.
134:911–918. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu P, Yang L, Sun Y, Ye L, Cao Z and Tang
K: Target network differences between western drugs and Chinese
herbal ingredients in treating cardiovascular disease. BMC
Bioinformatics. 15 Suppl 4:S32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dun RL, Yao M, Yang L, Cui XJ, Mao JM,
Peng Y and Qi GC: Traditional Chinese herb combined with surgery
versus surgery for varicocele infertility: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:6890562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsai CC, Lin MT, Wang JJ, Liao JF and
Huang WT: The antipyretic effects of baicalin in
lipopolysaccharide-evoked fever in rabbits. Neuropharmacology.
51:709–717. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He Z, Li B, Rankin GO, Rojanasakul Y and
Chen YC: Selecting bioactive phenolic compounds as potential agents
to inhibit proliferation and VEGF expression in human ovarian
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 9:1444–1450. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao JR, Do CW and To CH: Potential
therapeutic effects of baicalein, baicalin, and wogonin in ocular
disorders. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 30:605–614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shen YC, Chiou WF, Chou YC and Chen CF:
Mechanisms in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of baicalin
and baicalein in human leukocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 465:171–181.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding Y, Dou J, Teng Z, Yu J, Wang T, Lu N,
Wang H and Zhou C: Antiviral activity of baicalin against influenza
A (H1N1/H3N2) virus in cell culture and in mice and its inhibition
of neuraminidase. Arch Virol. 159:3269–3278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao Z, Huang K and Xu H: Protective
effects of flavonoids in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis
Georgi against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in
HS-SY5Y cells. Pharmacol Res. 43:173–178. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang CP, Huang WT, Cheng BC, Hsu CC and
Lin MT: The flavonoid baicalin protects against cerebrovascular
dysfunction and brain inflammation in experimental heatstroke.
Neuropharmacology. 52:1024–1033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu Q, Noor M, Wong YF, Hylands PJ,
Simmonds MS and Xu Q, Jiang D, Hendry BM and Xu Q: In vitro
anti-fibrotic activities of herbal compounds and herbs. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 24:3033–3041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y and Yao X: Role of c-Jun
N-terminal kinase and p38/activation protein-1 in
interleukin-1β-mediated type I collagen synthesis in rat hepatic
stellate cells. APMIS. 120:101–107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu L, Liu Q, Lin X, Wei QJ and Zheng L:
Effect of JEZTC, a synthetic compound, on proliferation and
phenotype maintenance of rabbit articular chondrocytes in vitro. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 50:982–991. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Farndale RW, Buttle DJ and Barrett AJ:
Improved quantitation and discrimination of sulphated
glycosaminoglycans by use of dimethylmethylene blue. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 883:173–177. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smith GD, Knutsen G and Richardson JB: A
clinical review of cartilage repair techniques. J Bone Joint Surg
Br. 87:445–449. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vega A, Martin-Ferrero MA, Del Canto F,
Alberca M, García V, Munar A, Orozco L, Soler R, Fuertes JJ, Huguet
M, et al: Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with allogeneic bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells: A randomized controlled trial.
Transplantation. 99:1681–1690. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee JH, Ahn J, Kim JW, Lee SG and Kim HP:
Flavonoids from the aerial parts of Houttuynia cordata attenuate
lung inflammation in mice. Arch Pharm Res. 38:1304–1311. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu JJ, Huang TS, Cheng WF and Lu FJ:
Baicalein and baicalin are potent inhibitors of angiogenesis:
Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation, migration and
differentiation. Int J Cancer. 106:559–565. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang D, Huang B, Xiong C and Yue Z:
Pinocembrin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase expression in
chondrocytes. IUBMB Life. 67:36–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizuguchi S, Uyama T, Kitagawa H, Nomura
KH, Dejima K, Gengyo-Ando K, Mitani S, Sugahara K and Nomura K:
Chondroitin proteoglycans are involved in cell division of
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 423:443–448. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ancsin JB: Amyloidogenesis: Historical and
modern observations point to heparan sulfate proteoglycans as a
major culprit. Amyloid. 10:67–79. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi S, Wang C, Acton AJ, Eckert GJ and
Trippel SB: Role of Sox9 in growth factor regulation of articular
chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 116:1391–1400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Davies SR, Chang LW, Patra D, Xing X,
Posey K, Hecht J, Stormo GD and Sandell LJ: Computational
identification and functional validation of regulatory motifs in
cartilage-expressed genes. Genome Res. 17:1438–1447. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Tew SR, Russell AM, Gonzalez KR,
Hardingham TE and Hawkins RE: Transduction of passaged human
articular chondrocytes with adenoviral, retroviral, and lentiviral
vectors and the effects of enhanced expression of SOX9. Tissue Eng.
10:575–584. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zamani S, Hashemibeni B, Esfandiari E,
Kabiri A, Rabbani H and Abutorabi R: Assessment of TGF-b3 on
production of aggrecan by human articular chondrocytes in pellet
culture system. Adv Biomed Res. 3:542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Svala E, Löfgren M, Sihlbom C, Rüetschi U,
Lindahl A, Ekman S and Skiöldebrand E: An inflammatory equine model
demonstrates dynamic changes of immune response and cartilage
matrix molecule degradation in vitro. Connect Tissue Res.
56:315–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xing R, Kong Q, Xiang Z, Yang J, Luo J,
Deng L and Xie H: Preliminary study on microRNA regulated
osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of mouse stem cells.
Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 28:1009–1016. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang X, Trehan SK, Guan Y, Sun C, Moore
DC, Jayasuriya CT and Chen Q: Matrilin-3 inhibits chondrocyte
hypertrophy as a bone morphogenetic protein-2 antagonist. J Biol
Chem. 289:34768–34779. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|