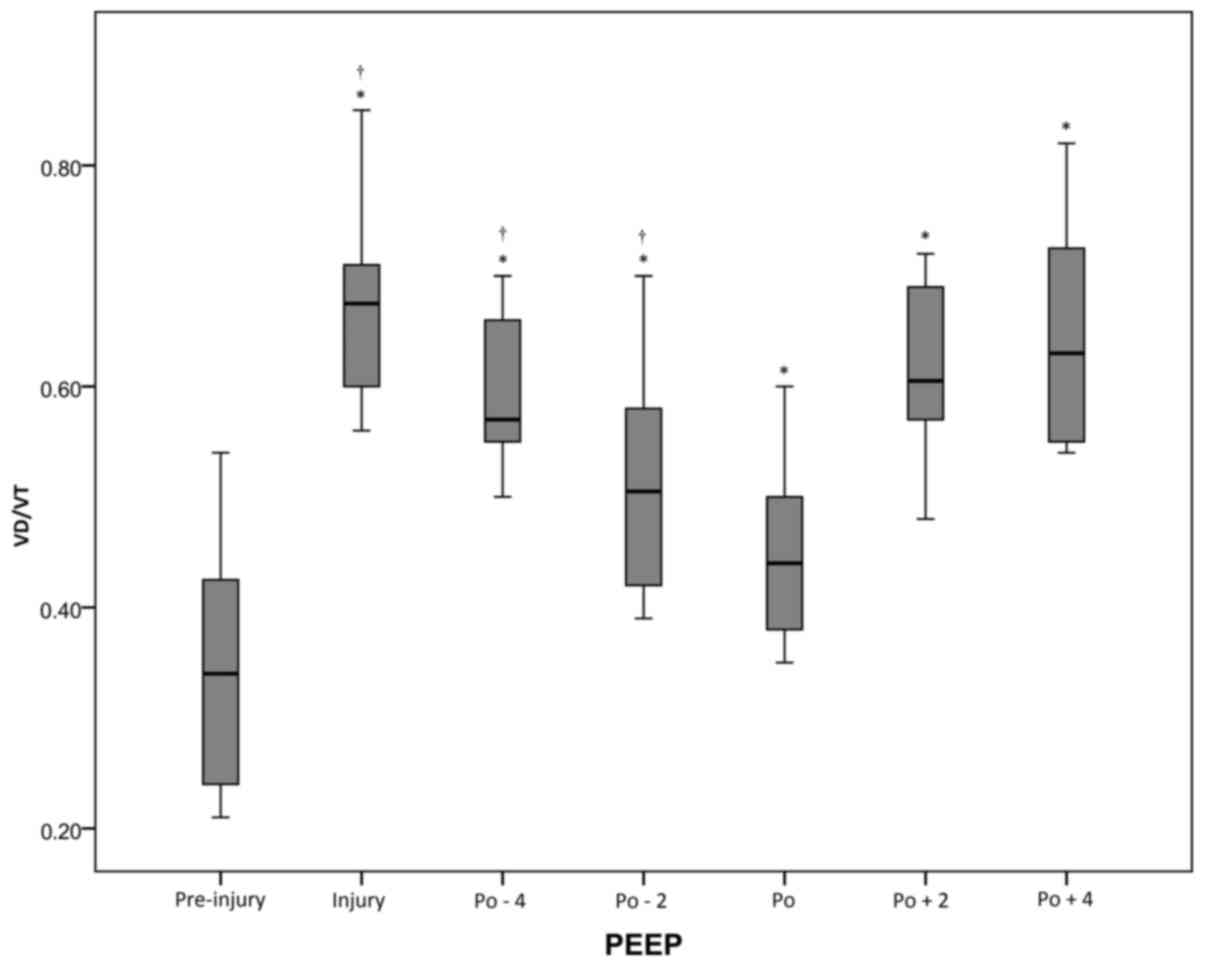
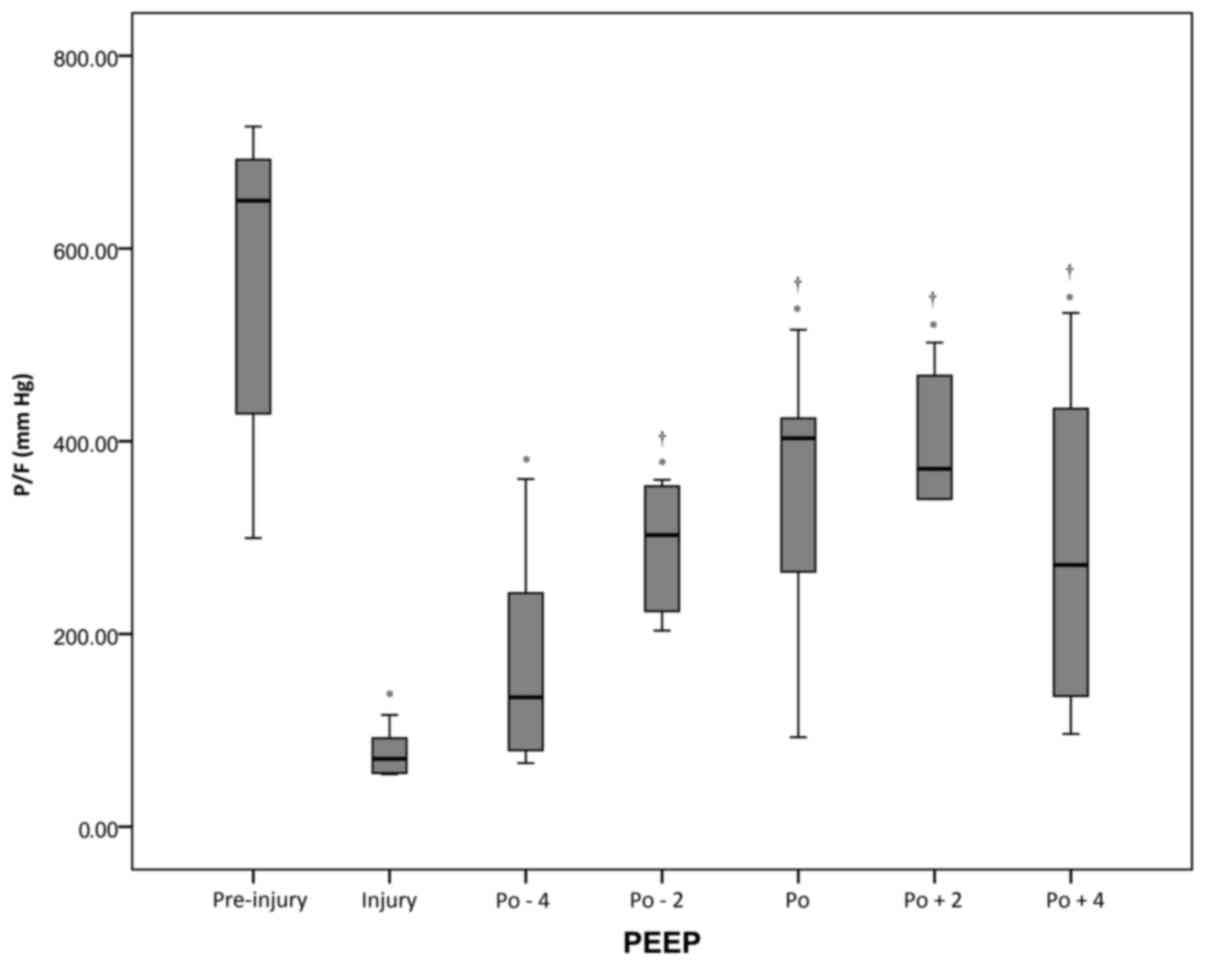
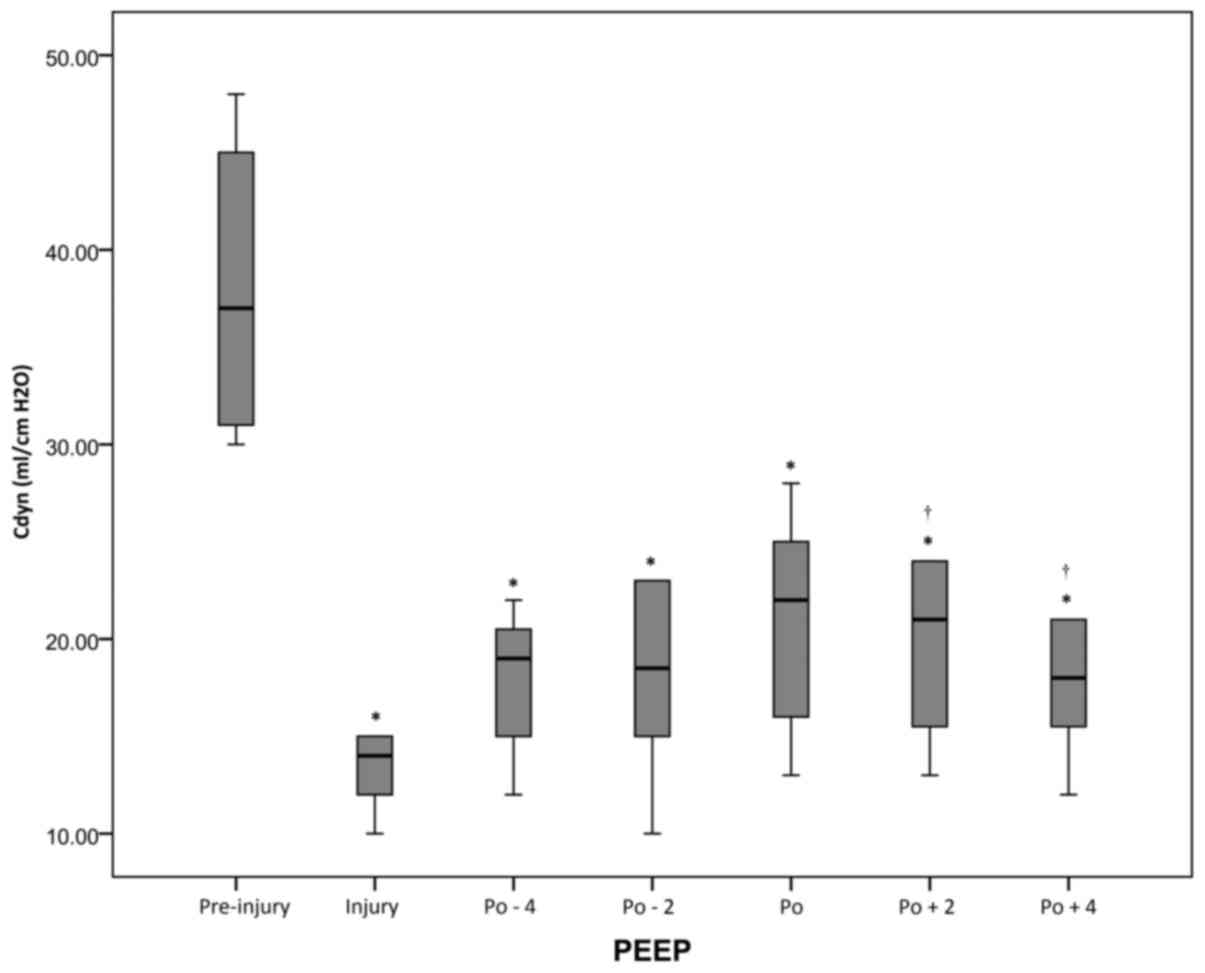
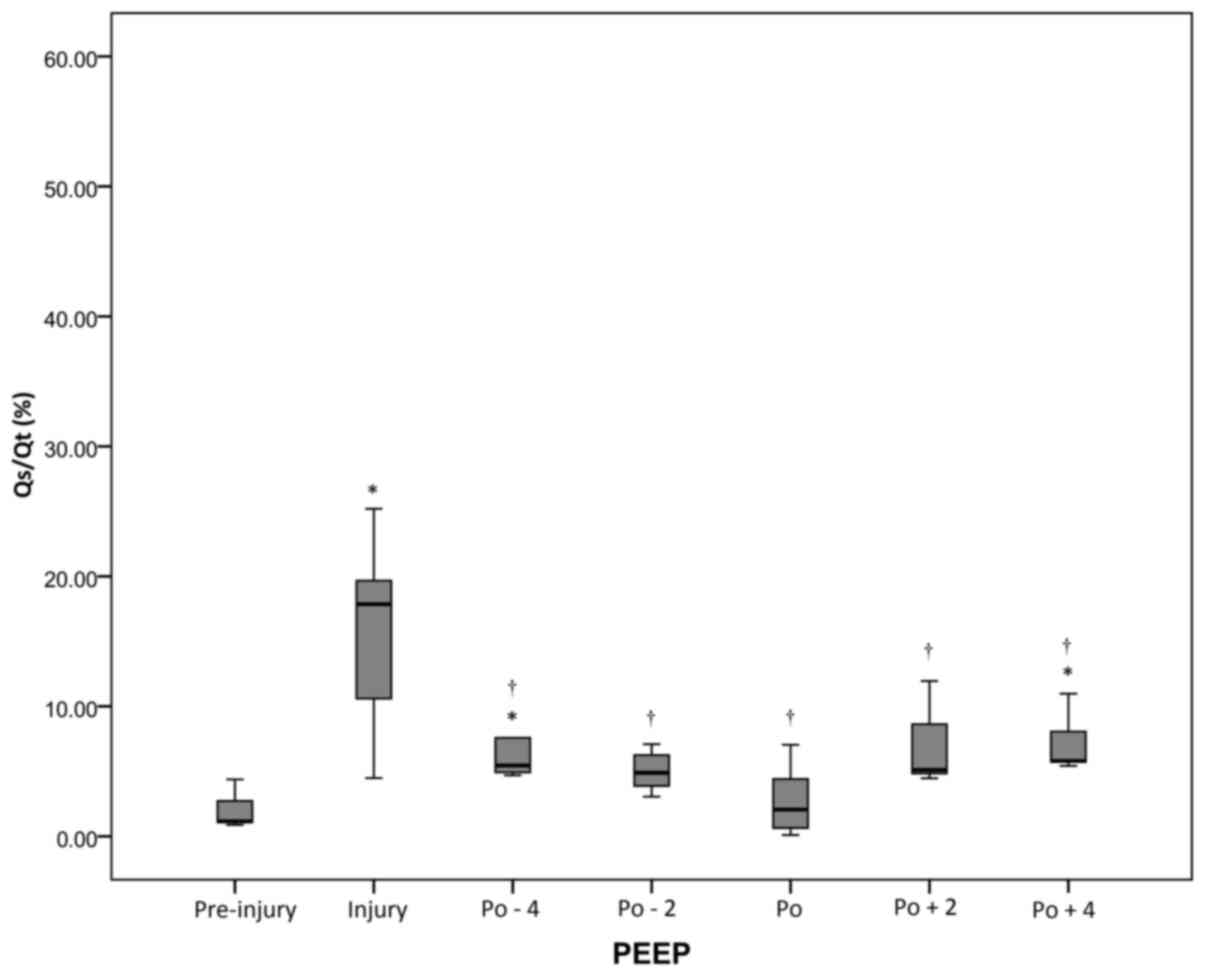
|
1
|
Phua J, Badia JR, Adhikari NK, Friedrich
JO, Fowler RA, Singh JM, Scales DC, Stather DR, Li A, Jones A, et
al: Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome
decreased over time? A systematic review. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 179:220–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petty TL: Acute respiratory distress
syndrome (ARDS). Dis Mon. 36:1–58. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Villar J, Blanco J, Añón JM, Santos-Bouza
A, Blanch L, Ambrós A, Gandía F, Carriedo D, Mosteiro F, Basaldúa
S, et al: The ALIEN study: Incidence and outcome of acute
respiratory distress syndrome in the era of lung protective
ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 37:1932–1941. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bull TM, Clark B, McFann K and Moss M:
National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood
Institute ARDS Network: Pulmonary vascular dysfunction is
associated with poor outcomes in patients with acute lung injury.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:1123–1128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lachmann B: Open up the lung and keep the
lung open. Intensive Care Med. 18:319–321. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi
RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D,
Munoz C, Oliveira R, et al: Effect of a protective-ventilation
strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N
Engl J Med. 338:347–354. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levy MM: PEEP in ARDS-how much is enough?
N Engl J Med. 351:389–391. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sakuramoto H, Shimojo N, Jesmin S, Unoki
T, Kamiyama J, Oki M, Miya K, Kawano S and Mizutani T: Repeated
open endotracheal suctioning causes gradual desaturation but does
not exacerbate lung injury compared to closed endotracheal
suctioning in a rabbit model of ARDS. BMC Anesthesiol. 13:472013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Charron C, Repesse X, Bouferrache K,
Bodson L, Castro S, Page B, Jardin F and Vieillard-Baron A: PaCO2
and alveolar dead space are more relevant than PaO2/FiO2 ratio in
monitoring the respiratory response to prone position in ARDS
patients: A physiological study. Crit Care. 15:R1752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fengmei G, Jin C, Songqiao L, Congshan Y
and Yi Y: Dead space fraction changes during PEEP titration
following lung recruitment in patients with ARDS. Respir Care.
57:1578–1585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gattinoni L, Caironi P, Cressoni M,
Chiumello D, Ranieri VM, Quintel M, Russo S, Patroniti N, Cornejo R
and Bugedo G: Lung recruitment in patients with the acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 354:1775–1786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tusman G, Suarez-Sipmann F, Böhm SH, Pech
T, Reissmann H, Meschino G, Scandurra A and Hedenstierna G:
Monitoring dead space during recruitment and PEEP titration in an
experimental model. Intensive Care Med. 32:1863–1871. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Uttman L, Bitzén U, De Robertis E,
Enoksson J, Johansson L and Jonson B: Protective ventilation in
experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome after
ventilator-induced lung injury: A randomized controlled trial. Br J
Anaesth. 109:584–594. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beydon L, Uttman L, Rawal R and Jonson B:
Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on dead space and its
partitions in acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med. 28:1239–1245.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blanch L, Lucangelo U, Lopez-Aguilar J,
Fernandez R and Romero P: Volumetric capnography in patients with
acute lung injury: Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure. Eur
Respir J. 13:1048–1054. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Higgs Z, Macafee D, Braithwaite B and
Maxwell-Armstrong C: The Seldinger technique: 50 years on. Lancet.
366:1407–1409. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marshall W: Arterial blood gas analysis.
Ann Clin Biochem. 47:283. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fletcher R, Jonson B, Cumming G and Brew
J: The concept of deadspace with special reference to the single
breath test for carbon dioxide. Br J Anaesth. 53:77–88. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fowler WS: Lung function studies; The
respiratory dead space. Am J Physiol. 154:405–416. 1948.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hofer CK, Furrer L, Matter-Ensner S,
Maloigne M, Klaghofer R, Genoni M and Zollinger A: Volumetric
preload measurement by thermodilution: A comparison with
transoesophageal echocardiography. Br J Anaesth. 94:748–755. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Quintel M, Pelosi P, Caironi P, Meinhardt
JP, Luecke T, Herrmann P, Taccone P, Rylander C, Valenza F,
Carlesso E and Gattinoni L: An increase of abdominal pressure
increases pulmonary edema in oleic acid-induced lung injury. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 169:534–541. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caramez MP, Kacmarek RM, Helmy M, Miyoshi
E, Malhotra A, Amato MB and Harris RS: A comparison of methods to
identify open-lung PEEP. Intensive Care Med. 35:740–747. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Borges JB, Okamoto VN, Matos GF, Caramez
MP, Arantes PR, Barros F, Souza CE, Victorino JA, Kacmarek RM,
Barbas CS, et al: Reversibility of lung collapse and hypoxemia in
early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 174:268–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL and
Levine BE: Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet. 2:319–323.
1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Greene R, Zapol WM, Snider MT, Reid L,
Snow R, O'Connell RS and Novelline RA: Early bedside detection of
pulmonary vascular occlusion during acute respiratory failure. Am
Rev Respir Dis. 124:593–601. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dantzker DR, Brook CJ, Dehart P, Lynch JP
and Weg JG: Ventilation-perfusion distributions in the adult
respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 120:1039–1052.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Idell S, Mazar AP, Bitterman P, Mohla S
and Harabin AL: Fibrin turnover in lung inflammation and neoplasia.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 163:578–584. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomashefski JF Jr, Davies P, Boggis C,
Greene R, Zapol WM and Reid LM: The pulmonary vascular lesions of
the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol. 112:112–126.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nuckton TJ, Alonso JA, Kallet RH, Daniel
BM, Pittet JF, Eisner MD and Matthay MA: Pulmonary dead-space
fraction as a risk factor for death in the acute respiratory
distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 346:1281–1286. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lucangelo U, Bernabè F, Vatua S, Degrassi
G, Villagrà A, Fernandez R, Romero PV, Saura P, Borelli M and
Blanch L: Prognostic value of different dead space indices in
mechanically ventilated patients with acute lung injury and ARDS.
Chest. 133:62–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maisch S, Reissmann H, Fuellekrug B,
Weismann D, Rutkowski T, Tusman G and Bohm SH: Compliance and dead
space fraction indicate an optimal level of positive end-expiratory
pressure after recruitment in anesthetized patients. Anaesth Analg.
106:175–181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Coffey RL, Albert RK and Robertson HT:
Mechanisms of physiological dead space response to PEEP after acute
oleic acid lung injury. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc
Physiol. 55:1550–1557. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Breen PH and Mazumdar B: How does positive
end-expiratory pressure decrease CO2 elimination from the lung?
Respir Physiol. 103:233–242. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Anderson CT and Breen PH: Carbon dioxide
kinetics and capnography during critical care. Crit Care.
4:207–215. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tang R, Huang Y, Chen Q, Hui X, Li Y, Yu
Q, Zhao H, Yang Y and Qiu H: The effect of alveolar dead space on
the measurement of end-expiratory lung volume by modified nitrogen
wash-out/wash-in in lavage-induced lung injury. Respir Care.
57:2074–2081. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Suwa K, Hedley-Whyte J and Bendixen HH:
Circulation and physiologic dead space changes on controlling the
ventilation of dogs. J Appl Physiol. 21:1855–1859. 1966.PubMed/NCBI
|