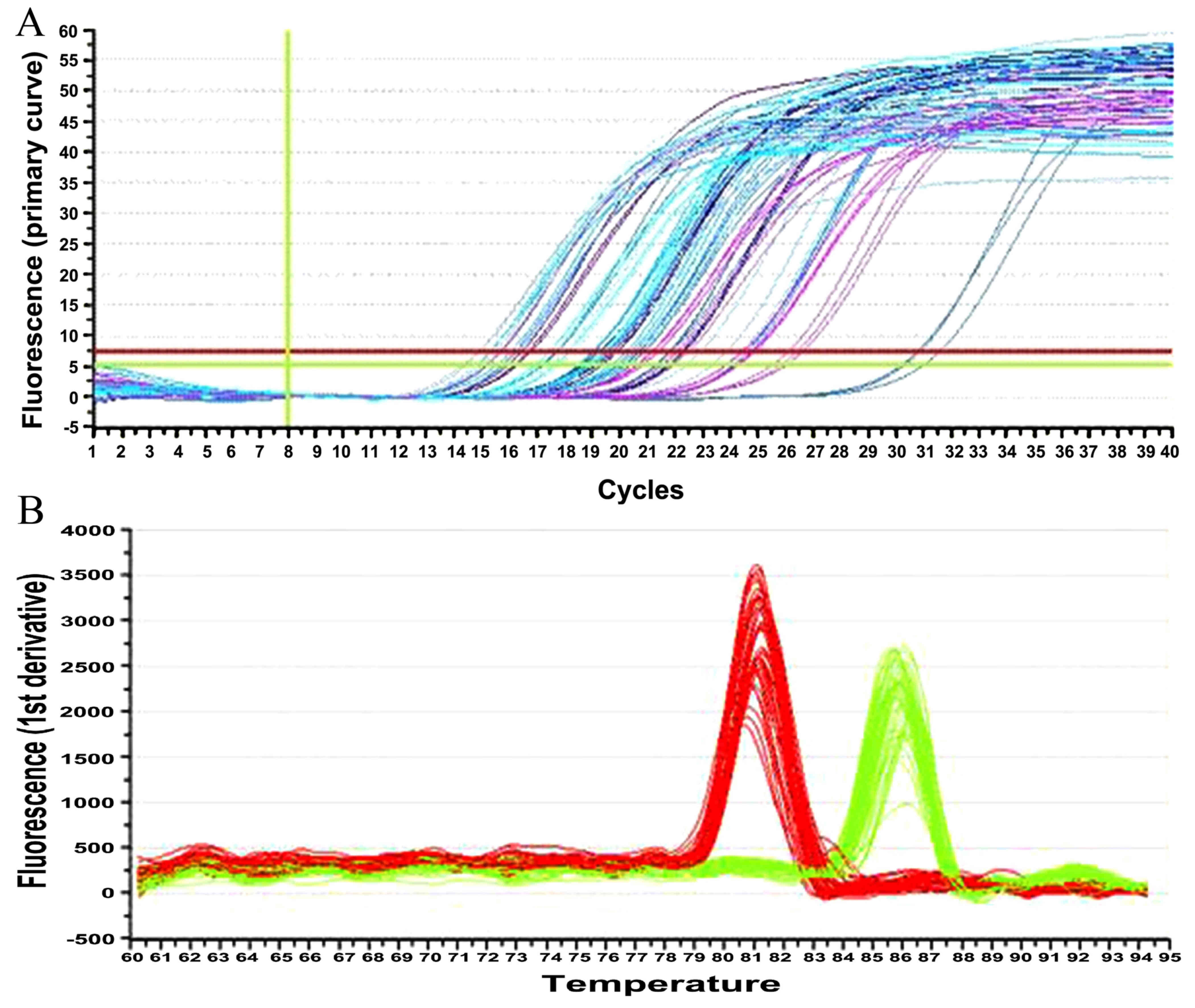
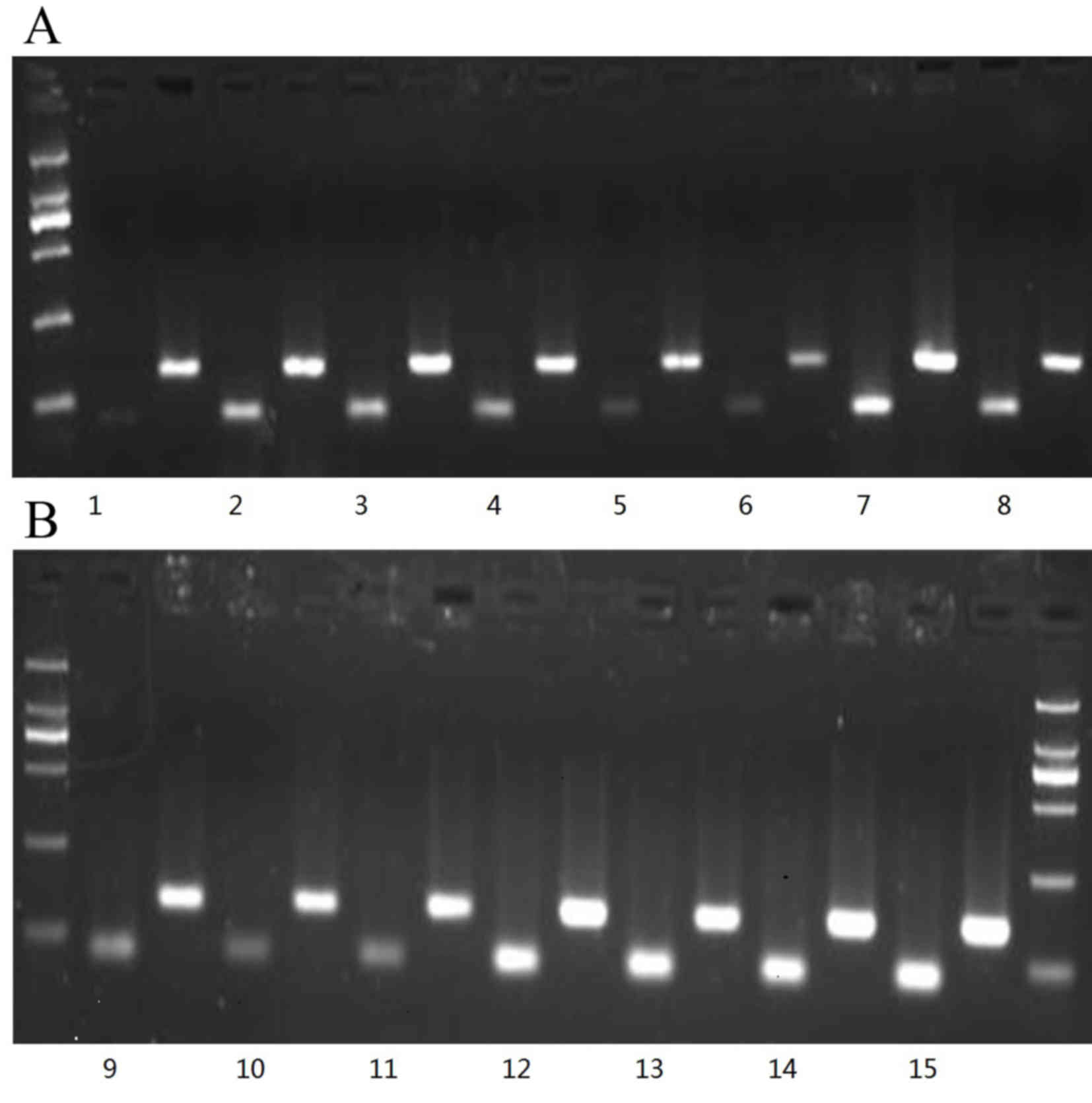
|
1
|
Bergogne-Bérézin E and Towner KJ:
Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Microbiological,
clinical, and epidemiological features. Clin Microbiol Rev.
9:148–165. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guardado Rodríguez A, Blanco A, Asensi V,
Pérez F, Rial JC, Pintado V, Bustillo E, Lantero M, Tenza E,
Alvarez M, et al: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter
meningitis in neurosurgical patients with intraventricular
catheters: Assessment of different treatments. J Antimicrob
Chemother. 61:908–913. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Magnet S, Courvalin P and Lambert T:
Resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in
aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain
BM4454. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45:3375–3380. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peleg AY, Adams J and Paterson DL:
Tigecycline efflux as a mechanism for nonsusceptibility in
Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
51:2065–2069. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute (CLSI): Performance Standards for Antimicrobial
Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-First Informational SupplementCLSI
documen M100-S22. CLSI; Wayne, PA: 2012
|
|
6
|
Shi WF, Jiang JP, Xu N, Huang ZM and Wang
YY: Inhibitory effects of reserpine and carbonyl cyanide
m-chloro-phenylhydrazone on fluoroquinolone resistance of
Acinetobacter baumannii. Chin Med J (Engl). 118:340–343.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giannouli M, Cuccurullo S, Crivaro V, Di
Popolo A, Bernardo M, Tomasone F, Amato G, Brisse S, Triassi M,
Utili R and Zarrilli R: Molecular epidemiology of
multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary
care hospital in Naples, Italy, shows the emergence of a novel
epidemic clone. J Clin Microbiol. 48:1223–1230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fernandez-Cuenca F, Martínez-Martínez L,
Conejo MC, Ayala JA, Perea EJ and Pascual A: Relationship between
beta-lactamase production, outer membrane protein and
penicillin-binding protein profiles on the activity of carbapenems
against clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 51:565–574. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee JK, Martínez-Martínez L, Conejo MC,
Ayala JA, Perea EJ and Pascual A: Mutations in the gyrA and gyrC
genes in ciprofloxacin-resistant clinical isolates of
Acinetobacter baumannii in Korea. Microbiol Immunol.
49:647–653. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yoon EJ, Courvalin P and Grillot-Courvalin
C: RND-type efflux pumps in multidrug-resistant clinical isolates
of Acinetobacter baumannii: Major role for AdeABC
overexpression and AdeRS mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
57:2989–2995. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rajamohan G, Srinivasan VB and Gebreyes
WA: Molecular and functional characterization of a novel efflux
pump, AmvA, mediating antimicrobial and disinfectant resistance in
Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother.
65:1919–1925. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ni W, Li Y, Guan J, Zhao J, Cui J, Wang R
and Liu Y: Effects of efflux pump inhibitors on colistin resistance
in multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 60:3215–3218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Principe L, D'Arezzo S, Capone A,
Petrosillo N and Visca P: In vitro activity of tigecycline in
combination with various antimicrobials against multidrug resistant
Acinetobacter baumannii. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob.
8:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ruzin A, Keeney D and Bradford PA: AdeABC
multidrug efflux pump is associated with decreased susceptibility
to tigecycline in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter
baumannii complex. J Antimicrob Chemother. 59:1001–1004. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin L, Ling BD and Li XZ: Distribution of
the multidrug efflux pump genes, adeABC, adeDE and adeIJK, and
class 1 integron genes in multiple-antimicrobial-resistant clinical
isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-Acinetobacter
calcoaceticus complex. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 33:27–32. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Poole K: Outer membranes and efflux: The
path to multidrug resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 3:77–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang JP, Zhu W, Tian SF, Chu YZ and Chen
BY: Molecular characteristics and resistant mechanisms of
imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in
Shenyang, China. J Microbiol. 48:689–694. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heritier C, Poirel L, Lambert T and
Nordmann P: Contribution of acquired carbapenem-hydrolyzing
oxacillinases to carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter
baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 49:3198–3202. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu WS, Yao SM, Fung CP, Hsieh YP, Liu CP
and Lin JF: An OXA-66/OXA-51-like carbapenemase and possibly an
efflux pump are associated with resistance to imipenem in
Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
51:3844–3852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rhomberg PR and Jones RN: MYSTIC Program
(USA) Study Group: Antimicrobial spectrum of activity for meropenem
and nine broad spectrum antimicrobials: Report from the MYSTIC
program (2002) in North America. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
47:365–372. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|