|
1
|
Krupa A, Fol M, Rahman M, Stokes KY,
Florence JM, Leskov IL, Khoretonenko MV, Matthay MA, Liu KD, Calfee
CS, et al: Silencing Bruton's tyrosine kinase in alveolar
neutrophils protects mice from LPS/immune complex-induced acute
lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 307:L435–L448.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
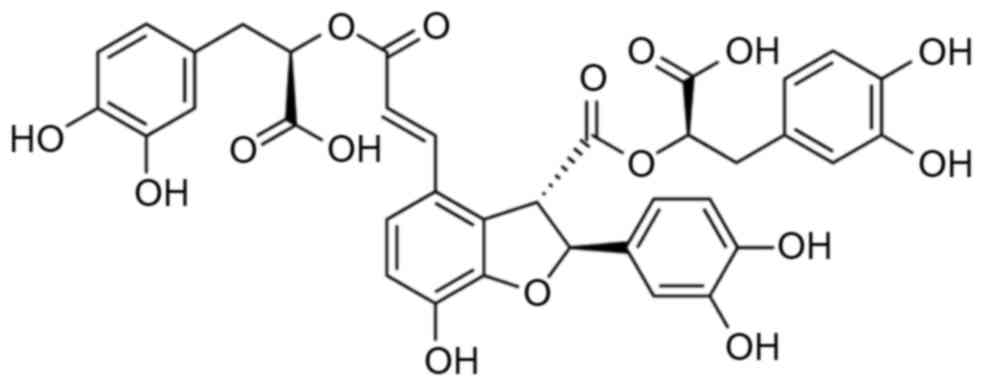
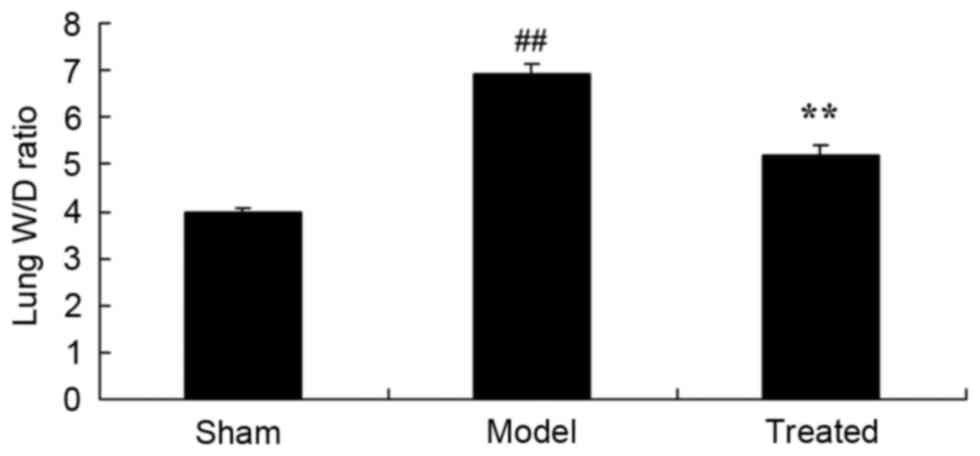
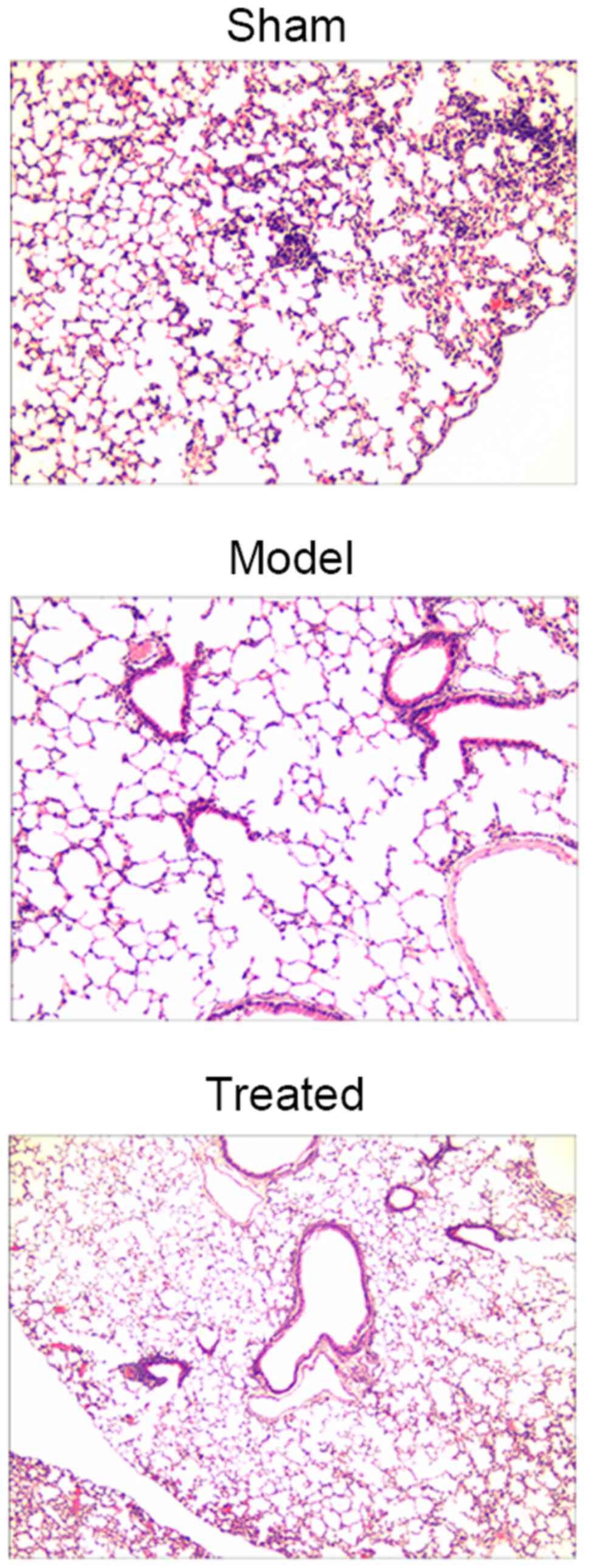
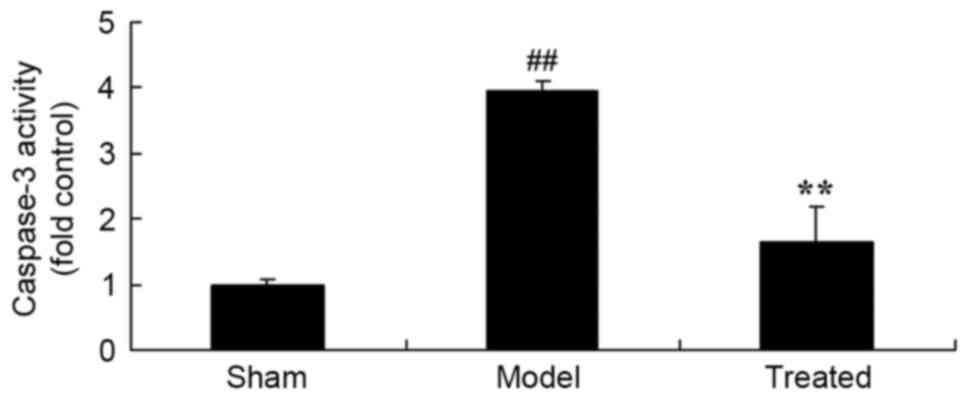
2
|
Stapleton RD, Martin TR, Weiss NS, Crowley
JJ, Gundel SJ, Nathens AB, Akhtar SR, Ruzinski JT, Caldwell E,
Curtis JR, et al: A phase II randomized placebo-controlled trial of
omega-3 fatty acids for the treatment of acute lung injury. Crit
Care Med. 39:1655–1662. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Calfee CS, Gallagher D, Abbott J, Thompson
BT and Matthay MA: NHLBI ARDS Network: Plasma angiopoietin-2 in
clinical acute lung injury: Prognostic and pathogenetic
significance. Crit Care Med. 40:1731–1737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McAuley DF, Laffey JG, O'Kane CM, Cross M,
Perkins GD, Murphy L, McNally C, Crealey G and Stevenson M; HARP-2
investigators; Irish Critical Care Trials Group, :
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibition with simvastatin in
acute lung injury to reduce pulmonary dysfunction (HARP-2) trial:
Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials.
13:1702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Needham DM, Wozniak AW, Hough CL, Morris
PE, Dinglas VD, Jackson JC, Mendez-Tellez PA, Shanholtz C, Ely EW,
Colantuoni E, et al: Risk factors for physical impairment after
acute lung injury in a national, multicenter study. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 189:1214–1224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Clark BJ, Williams A, Feemster LM, Bradley
KA, Macht M, Moss M and Burnham EL: NHLBI ARDS Network
Investigators: Alcohol screening scores and 90-day outcomes in
patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 41:1518–1525. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou L, Zhao D, An H, Zhang H, Jiang C and
Yang B: Melatonin prevents lung injury induced by hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion through anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis
effects. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:462–467. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Armstrong SM, Wang C, Tigdi J, Si X,
Dumpit C, Charles S, Gamage A, Moraes TJ and Lee WL: Influenza
infects lung microvascular endothelium leading to microvascular
leak: Role of apoptosis and claudin-5. PLoS One. 7:e473232012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kohira S, Oka N, Inoue N, Itatani K,
Hanayama N, Kitamura T, Fujii M, Takeda A, Oshima H, Tojo K, et al:
Effect of the neutrophil elastase inhibitor sivelestat on
perioperative inflammatory response after pediatric heart surgery
with cardiopulmonary bypass: A prospective randomized study. Artif
Organs. 37:1027–1033. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lv H, Yu Z, Zheng Y, Wang L, Qin X, Cheng
G and Ci X: Isovitexin exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant
activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by
inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB and activating HO-1/Nrf2 pathways. Int J
Biol Sci. 12:72–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu S, Zhong A, Bu X, Ma H, Li W, Xu X and
Zhang J: Salvianolic acid B inhibits platelets-mediated
inflammatory response in vascular endothelial cells. Thromb Res.
135:137–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen T, Liu W, Chao X, Zhang L, Qu Y, Huo
J and Fei Z: Salvianolic acid B attenuates brain damage and
inflammation after traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res Bull.
84:163–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xue L, Wu Z, Ji XP, Gao XQ and Guo YH:
Effect and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on the myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med.
7:280–284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang TL, Lin FY, Chen YH, Chiu JJ, Shiao
MS, Tsai CS, Lin SJ and Chen YL: Salvianolic acid B inhibits
low-density lipoprotein oxidation and neointimal hyperplasia in
endothelium-denuded hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. J Sci Food
Agric. 91:134–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Walkey AJ and Wiener RS: Utilization
patterns and patient outcomes associated with use of rescue
therapies in acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 39:1322–1328. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kowalski S, McMullen MC, Girling LG and
McCarthy BG: Biologically variable ventilation in patients with
acute lung injury: A pilot study. Can J Anaesth. 60:502–503. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Martin GS, Moss M, Wheeler AP, Mealer M,
Morris JA and Bernard GR: A randomized, controlled trial of
furosemide with or without albumin in hypoproteinemic patients with
acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 33:1681–1687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Afshari A, Brok J, Moller AM and
Wetterslev J: Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress
syndrome and acute lung injury in adults and children: A systematic
review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Anesth
Analg. 112:1411–1421. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grainge C, Brown R, Jugg BJ, Smith AJ,
Mann TM, Jenner J, Rice P and Parkhouse DA: Early treatment with
nebulised salbutamol worsens physiological measures and does not
improve survival following phosgene induced acute lung injury. J R
Army Med Corps. 155:105–109. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akcilar R, Akcilar A, Şimşek H, Koçak FE,
Koçak C, Yümün G and Bayat Z: Hyperbaric oxygen treatment
ameliorates lung injury in paraquat intoxicated rats. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:13034–13042. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ruchko MV, Gorodnya OM, Zuleta A, Pastukh
VM and Gillespie MN: The DNA glycosylase Ogg1 defends against
oxidant-induced mtDNA damage and apoptosis in pulmonary artery
endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 50:1107–1113. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ren M, Wang YM, Zhao J, Zhao J, Zhao ZM,
Zhang TF, He J, Ren SP and Peng SQ: Metallothioneins attenuate
paraquat-induced acute lung injury in mice through the mechanisms
of anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol.
73:140–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Y, Jacobi A, Vater C, Zou X and
Stiehler M: Salvianolic acid B protects human endothelial
progenitor cells against oxidative stress-mediated dysfunction by
modulating Akt/mTOR/4EBP1, p38 MAPK/ATF2 and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 90:34–49. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen WY, Huang YC, Yang ML, Lee CY, Chen
CJ, Yeh CH, Pan PH, Horng CT, Kuo WH and Kuan YH: Protective effect
of rutin on LPS-induced acute lung injury via down-regulation of
MIP-2 expression and MMP-9 activation through inhibition of Akt
phosphorylation. Int Immunopharmacol. 22:409–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen W, Ge X, Xu F, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Pan J,
Song J, Dai Y, Zhou J, Feng J and Liang G: Design, synthesis and
biological evaluation of paralleled Aza resveratrol-chalcone
compounds as potential anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment
of acute lung injury. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:2998–3004. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim J, Jeong SW, Quan H, Jeong CW, Choi JI
and Bae HB: Effect of curcumin (Curcuma longa extract) on
LPS-induced acute lung injury is mediated by the activation of
AMPK. J Anesth. 30:100–108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manickam N, Patel M, Griendling KK, Gorin
Y and Barnes JL: RhoA/Rho kinase mediates TGF-β1-induced kidney
myofibroblast activation through Poldip2/Nox4-derived reactive
oxygen species. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 307:F159–F171. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Hu J, Hao HZ, Yin Z, Liu G and Zou
XJ: Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate attenuates the transforming
growth factor-β1-induced differentiation of atrial fibroblasts into
myofibroblasts in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 35:1026–1032.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li S, Wang L, Yan X, Wang Q, Tao Y, Li J,
Peng Y, Liu P and Liu C: Salvianolic acid B attenuates rat hepatic
fibrosis via downregulating angiotensin II signaling. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:1607262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lv Z and Xu L: Salvianolic acid B inhibits
ERK and p38 MAPK signaling in TGF-β1-stimulated human hepatic
stellate cell line (LX-2) via distinct pathways. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:9601282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|