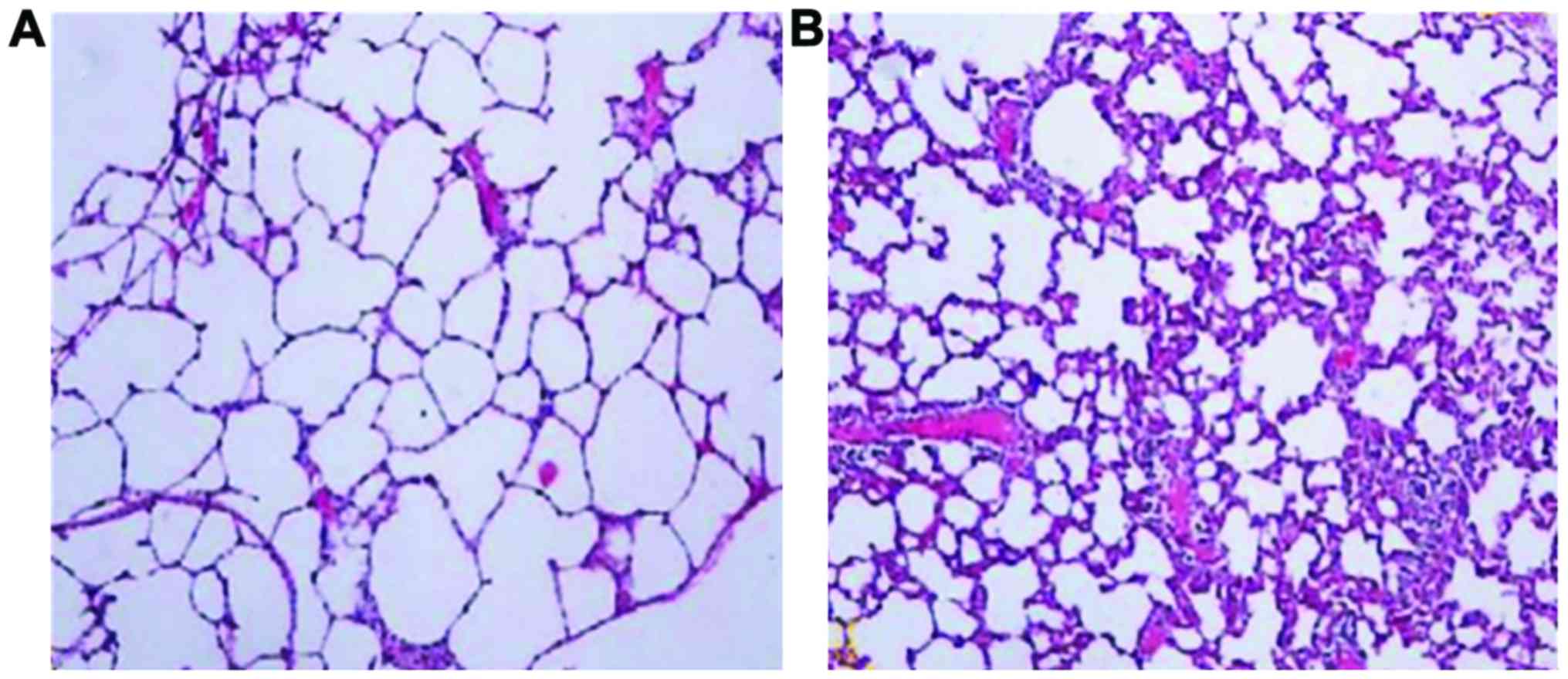
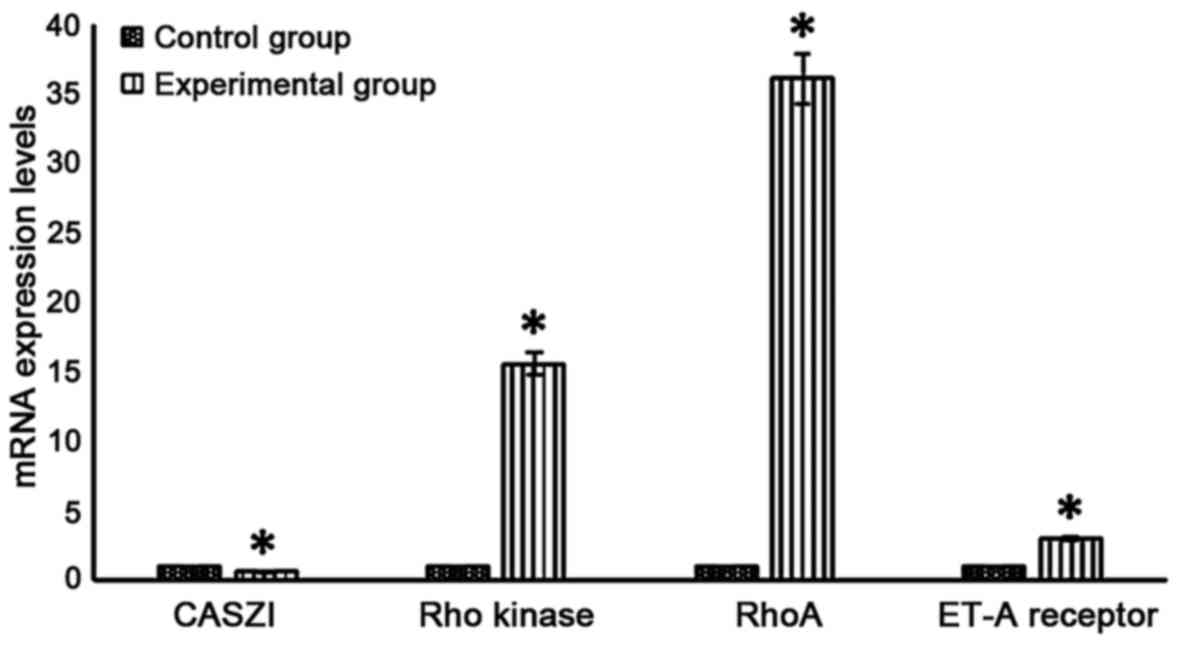
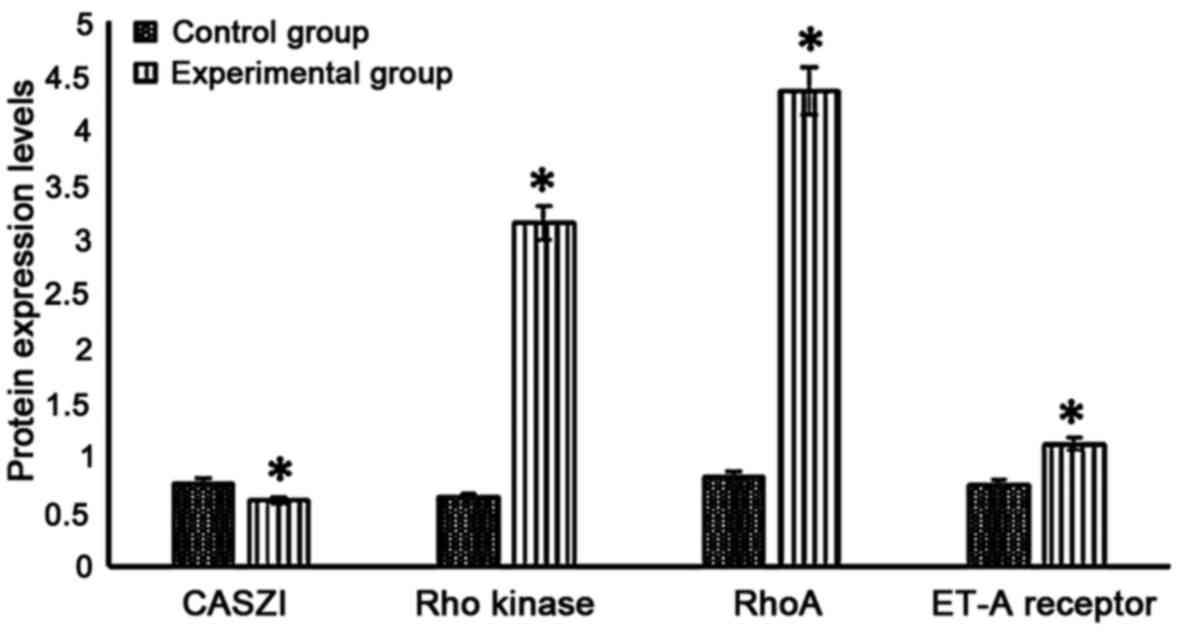
|
1
|
Gien J, Kinsella J, Thrasher J, Grenolds
A, Abman SH and Baker CD: Retrospective analysis of an
interdisciplinary ventilator care program intervention on survival
of infants with ventilator-dependent bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am
J Perinatol. 34:155–163. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nair V, Loganathan P and Soraisham AS:
Azithromycin andother macrolides for prevention of
bronchopulmonarydysplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Neonatology. 106:337–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gadhia MM, Cutter GR, Abman SH and
Kinsella JP: Effects of early inhaled nitric oxide therapy and
vitamin A supplementation on the risk for bronchopulmonary
dysplasia in premature newborns with respiratory failure. J
Pediatr. 164:744–748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu Q, Liu X and Zhou G: Effects of
ligustrazine on hypoxia-inducible factor pathway expression in
neonatal rats with BPD. J Pediatr Pharm. 20:1–5. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Golovnin AK, Kostyuchenko MV, Georgiev PG
and Melnikova LS: Mod(mdg4)-58.8, isoform of mod(mdg4) loci,
directly interacts with MTACP1A and MTACP1B proteins of
Drosophila melanogaster. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 466:5–8.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vom Hove M, Prenzel F, Uhlig HH and
Robel-Tillig E: Pulmonary outcome in former preterm, very low birth
weight children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A case-control
follow-up at school age. J Pediatr. 164:40–45.e4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Balany J and Bhandari V: Understanding the
impact of infection, inflammation, and their persistence in the
pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Front Med (Lausanne).
2:902015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Del Re DP, Miyamoto S and Brown JH:
RhoA/Rho kinase upregulate Bax to activate a mitochondrial death
pathway and induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
282:8069–8078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Monteiro CB, Midão L, Rebelo S, Reguenga
C, Lima D and Monteiro FA: Zinc finger transcription factor Casz1
expression is regulated by homeodomain transcription factor Prrxl1
in embryonic spinal dorsal horn late-born excitatory interneurons.
Eur J Neurosci. 43:1449–1459. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang L, Feng Z and Lv H: Expressions of
vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 in neonatal
rats with hypoxia-induced BPD and effects on lung development. J
Pract Med. 20:525–528. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Tang H: ‘Vascular hypothesi’ of BPD and
progress of Angiogenesis-promoting Treatment. J Clin Pediatr.
34:5532016.
|
|
12
|
Liu Z, Lam N and Thiele CJ: Zinc finger
transcription factor CASZ1 interacts with histones, DNA repair
proteins and recruits NuRD complex to regulate gene transcription.
Oncotarget. 6:27628–27640. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Q, Ma X and Zhang X: Pulmonary
microvascular development and CD34 expression in rats with
oxygen-induced BPD. J PLA Med. 26:25–28. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Sauzeau V, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Lehoux S,
Loirand G and Pacaud P: Sildenafil prevents change in RhoA
expression induced by chronic hypoxia in rat pulmonary artery. Circ
Res. 93:630–637. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pierro M, Ionescu L, Montemurro T, Vadivel
A, Weissmann G, Oudit G, Emery D, Bodiga S, Eaton F, Péault B, et
al: Short-term, long-term and paracrine effect of human umbilical
cord-derived stem cells in lung injury prevention and repair in
experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Thorax. 68:475–484. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stiles JM, Kurisetty V, Mitchell DC and
Bryan BA: Rho kinase proteins regulate global miRNA expression in
endothelial cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 10:251–263.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaya G, Sivasli E, Oztuzcu S, Melekoglu
NA, Ozkara E, Sarikabadayi U and Demiryürek AT: Association of
Rho-kinase gene polymorphisms with respiratory distress syndrome in
preterm neonates. Pediatr Neonatol. 58:36–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|