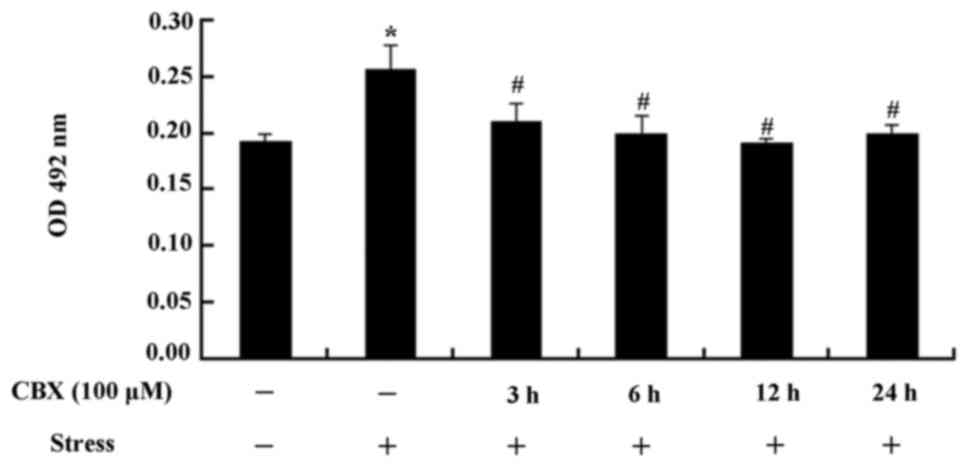
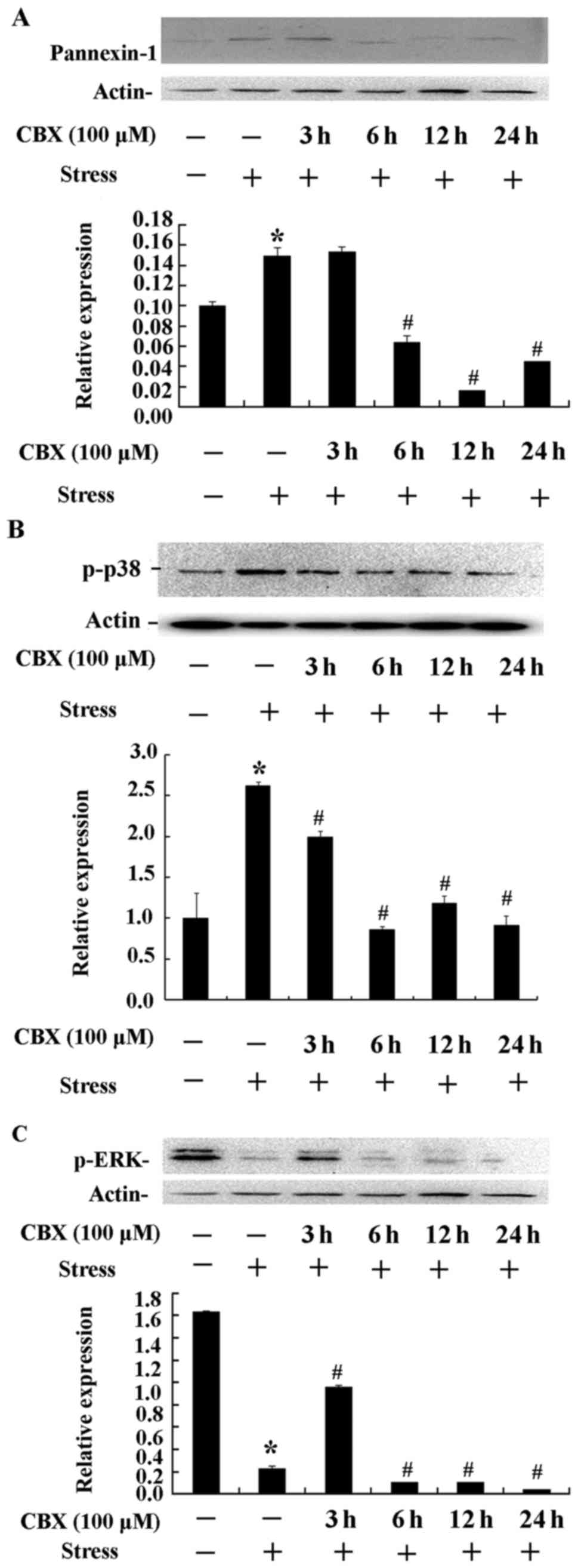
|
1
|
Awad HA, Butler DL, Boivin GP, Smith FN,
Malaviya P, Huibregtse B and Caplan AI: Autologous mesenchymal stem
cell-mediated repair of tendon. Tissue Eng. 5:267–277. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kopen GC, Prockop DJ and Phinney DG:
Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum,
and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into
neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:pp. 10711–10716.
1999; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang W, Ma A, Wang T, Han K, Liu Y, Zhang
Y, Zhao X, Dong A, Du Y, Huang X, et al: Intravenous
transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac
performance after acute myocardial ischemia in female rats. Transpl
Int. 19:570–580. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Triplett JW, O'Riley R, Tekulve K, Norvell
SM and Pavalko FM: Mechanical loading by fluid shear stress
enhances IGF-1 receptor signaling in osteoblasts in A
PKCzeta-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biomech. 4:13–25.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Klein-Nulend J, van der Plas A, Semeins
CM, Ajubi NE, Frangos JA, Nijweide PJ and Burger EH: Sensitivity of
osteocytes to biomechanical stress in vitro. FASEB J. 9:441–445.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trexler EB, Bennett M, Bargiello TA and
Verselis VK: Voltage gating and permeation in a gap junction
hemichannel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:pp. 5836–5841. 1996;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iyyathurai J, Himpens B, Bultynck G and
D'hondt C: Calcium wave propagation triggered by local mechanical
stimulation as a method for studying gap junctions and
hemichannels. Methods Mol Biol. 1437:203–211. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Ma M, Locovei S, Keane RW and Dahl
G: Modulation of membrane channel currents by gap junction protein
mimetic peptides: Size matters. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
293:C1112–C1119. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Escalona Y, Garate JA, Araya-Secchi R,
Huynh T, Zhou R and Perez-Acle T: Exploring the membrane potential
of simple dual-membrane systems as models for gap-junction
channels. Biophys J. 110:2678–2688. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meda P and Spray DC: Gap junction
function. Adv Mol Cell Biology. 30:263–322. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Panchina Y, Kelmanson I, Matz M, Lukyanov
K, Usman N and Lukyanov S: A ubiquitous family of putative gap
junction molecules. Curr Biol. 10:R473–474. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Penuela S, Celetti SJ, Bhalla R, Shao Q
and Laird DW: Diverse subcellular distribution profiles of pannexin
1 and pannexin 3. Cell Commun Adhes. 15:133–142. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Penuela S, Bhalla R, Gong XQ, Cowan KN,
Celetti SJ, Cowan BJ, Bai D, Shao Q and Laird DW: Pannexin 1 and
pannexin 3 are glycoproteins that exhibit many distinct
characteristics from the connexin family of gap junction proteins.
J Cell Sci. 120:3772–3783. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Romanov RA, Bystrova MF, Rogachevskaya OA
and Kolesnikov SS: Channel activity of recombinant pannexin 1.
Biochem Suppl. 5:343–349. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Owan I, Burr DB, Turner CH, Qiu J, Tu Y,
Onyia JE and Duncan RL: Mechanotransduction in bone: Osteoblasts
are more responsive to fluid forces than mechanical strain. Am J
Physiol. 273:C810–C815. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Genge BR, Sauer GR, Wu LN, McLean FM and
Wuthier RE: Correlation between loss of alkaline phosphatase
activity and accumulation of calcium during matrix vesicle-mediated
mineralization. J Biol Chem. 263:18513–18519. 1989.
|
|
17
|
Akbari M, Nikbakht M and Sobhani A:
Expression of alkaline phosphatase during osteogenic
differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Cell J.
43:94–106. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Rodríguez JP, González M, Ríos S and
Cambiazo V: Cytoskeletal organization of human mesenchymal stem
cells (MSC) changes during their osteogenic differentiation. J Cell
Biochem. 93:721–731. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ryder KD and Duncan RL: Parathyroid
hormone enhances fluid shear-induced [Ca2+]i signaling in
osteoblastic cells through activation of mechanosensitive and
voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. J Bone Miner Res. 16:240–248.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng JJ, Kronbergs A, Fomin VP, Usatyuk
PV, Natarajan V and Duncan RL: Protein Kinase C (PKC)-mediated
actin disruption regulates [Ca2+]i responses to mechanical load in
osteoblasts. FASEB J. 21:A9132007.
|
|
21
|
Lu L, Tu J and Ballard HJ:
Connexin-hemichannels are involved in acidosis-induced ATP release
from skeletal myocytes. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Scientific
Meeting of the Institute of Cardiovascular Science and Medicine
(ICSM 2013), Hong Kong, China. Journal of the Hong Kong College of
Cardiology. pp. 672013;
|
|
22
|
Huang YJ, Maruyama Y, Dvoryanchikov G,
Pereira E, Chaudhari N and Roper SD: The role of pannexin 1
hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse
taste buds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 6436–6441. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ransford GA, Fregien NF, Qiu F, Dahl G,
Conner GE and Salathe M: Pannexin 1 contributes to ATP release in
airway epithelia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 41:525–534. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krick S, Wang J, St-Pierre M, Gonzalez C,
Dahl G and Salathe M: Dual oxidase 2 (Duox2) regulates pannexin
1-mediated ATP release in primary human airway epithelial cells via
changes in intracellular pH and not H2O2 production. J Biol Chem.
291:6423–6432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Orellana JA, Froger N, Ezan P, Jiang JX,
Bennett MV, Naus CC, Giaume C and Sáez JC: ATP and glutamate
released via astroglial connexin 43 hemichannels mediate neuronal
death through activation of pannexin 1 hemichannels. J Neurochem.
118:826–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishikawa M, Iwamoto T, Nakamura T, Doyle
A, Fukumoto S and Yamada Y: Pannexin 3 functions as an ER Ca(2+)
channel, hemichannel, and gap junction to promote osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Biol. 193:1257–1274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saunders MM, You J, Zhou Z, Li Z,
Yellowley CE, Kunze EL, Jacobs CR and Donahue HJ: Fluid
flow-induced prostaglandin E2 response of osteoblastic ROS 17/2.8
cells is gap junction-mediated and independent of cytosolic
calcium. Bone. 32:350–356. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jørgensen NR, Teilmann SC, Henriksen Z,
Meier E, Hansen SS, Jensen JE, Sørensen OH and Petersen JS: The
antiarrhythmic peptide analog rotigaptide (ZP123) stimulates gap
junction intercellular communication in human osteoblasts and
prevents decrease in femoral trabecular bone strength in
ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 146:4745–4754. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jaiswal RK, Jaiswal N, Bruder SP,
Mbalaviele G, Marshak DR and Pittenger MF: Adult human mesenchymal
stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic or adipogenic lineage
is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem.
275:9645–9652. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|