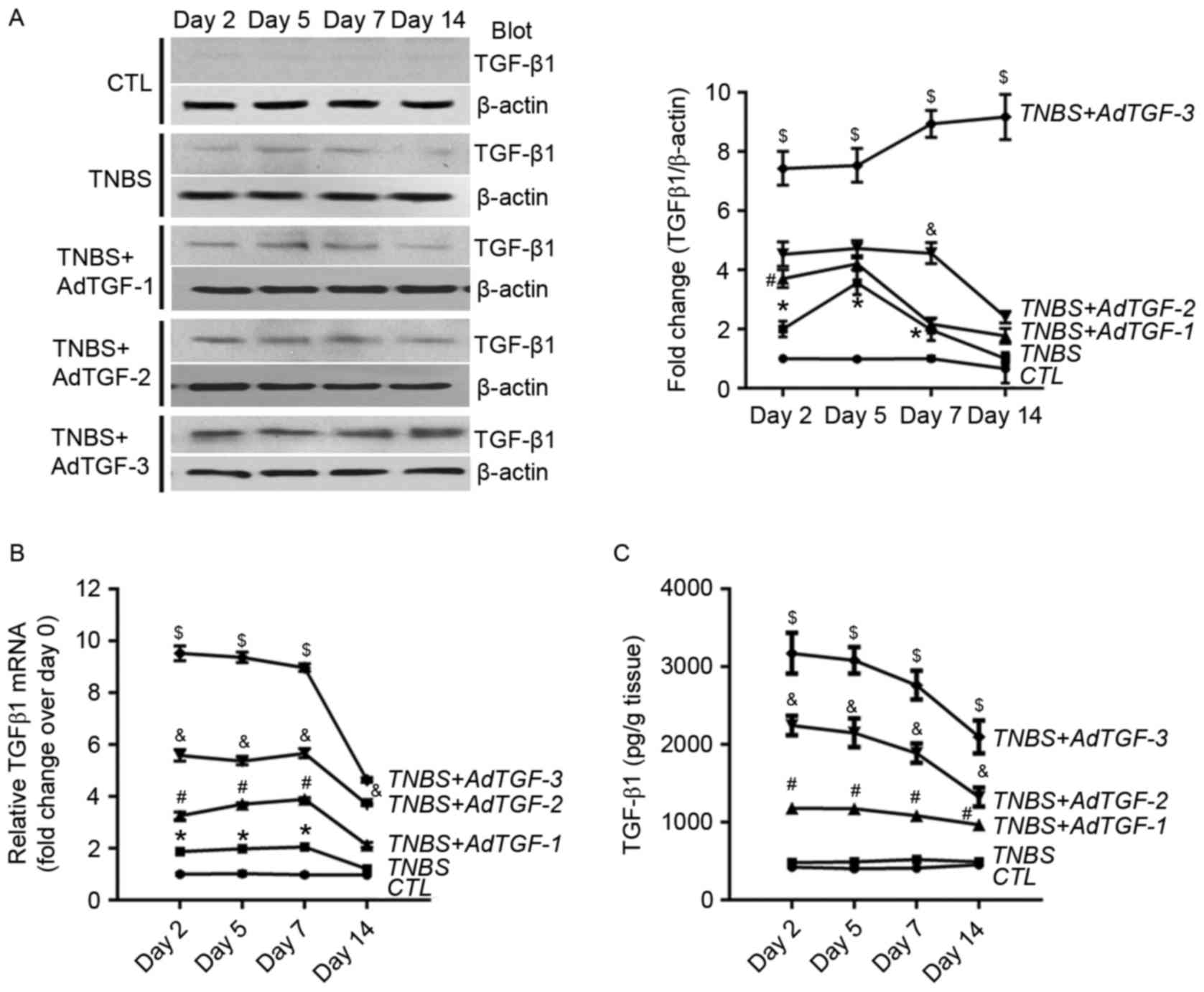
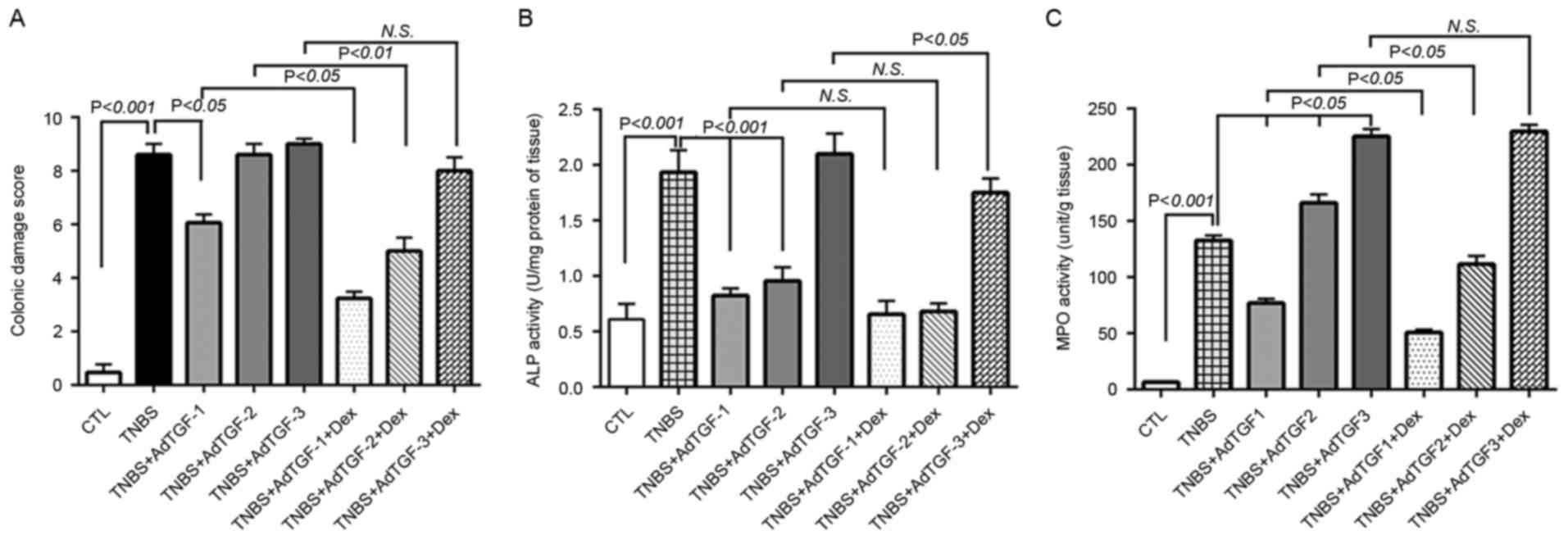
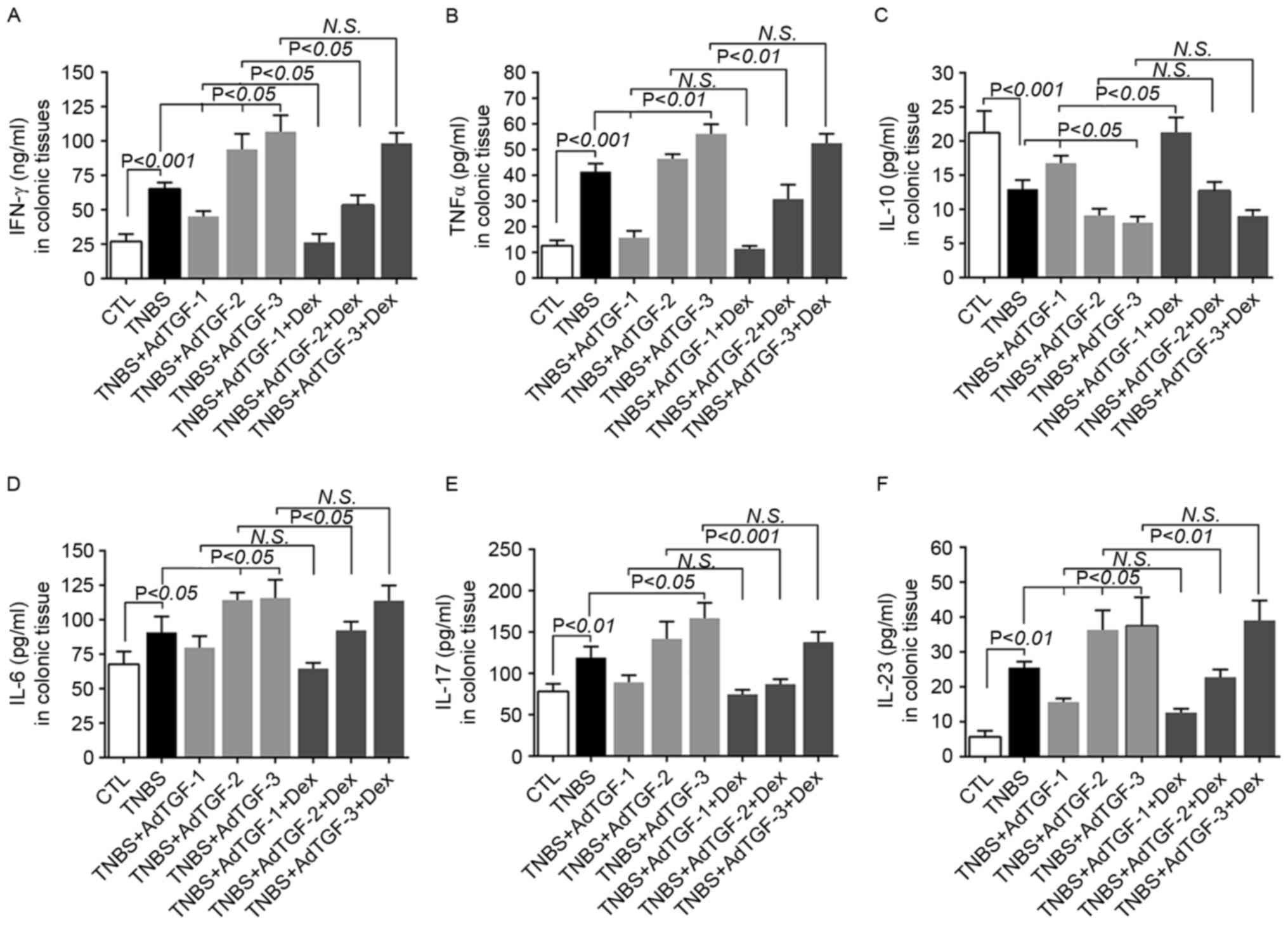
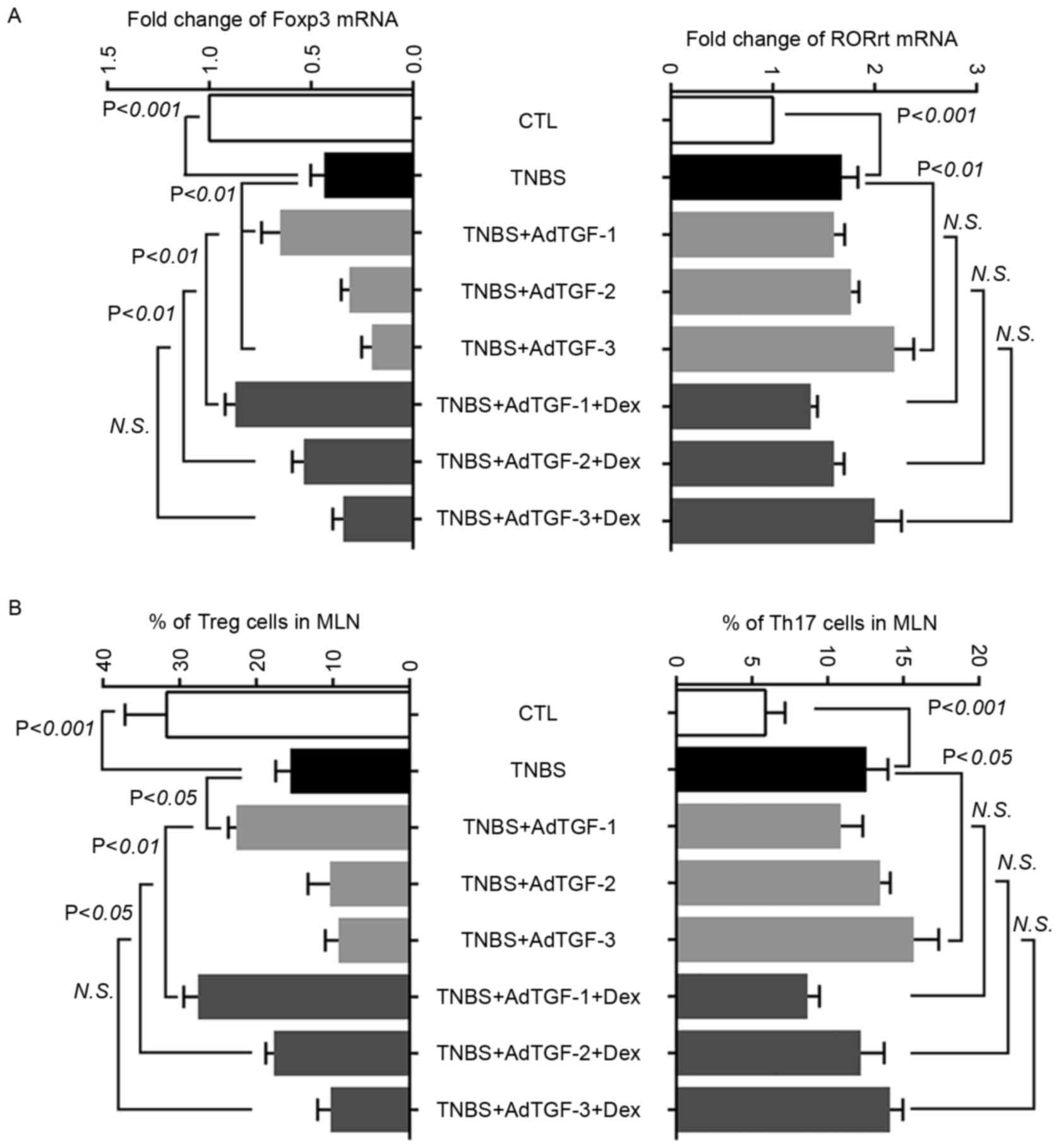
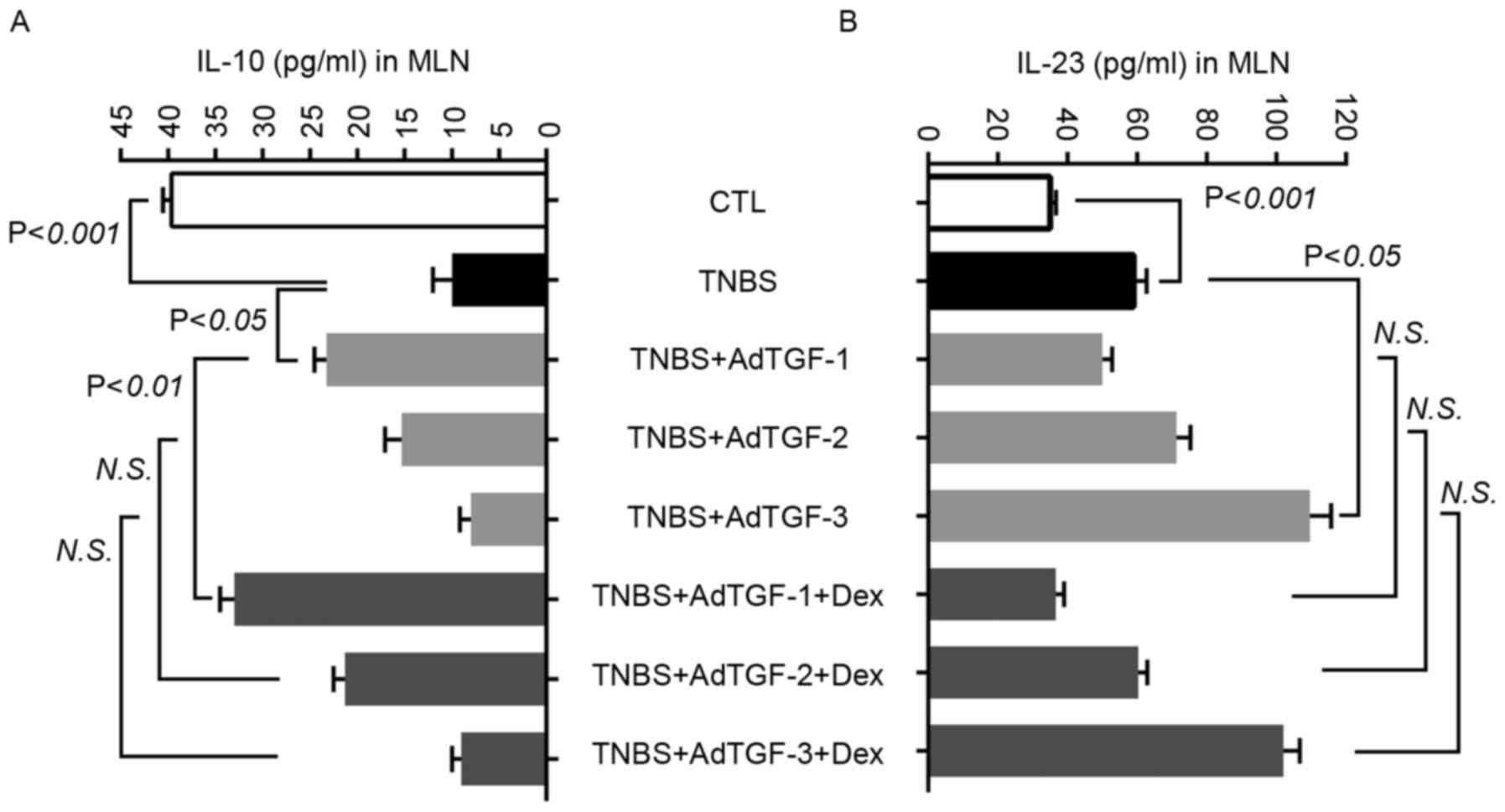
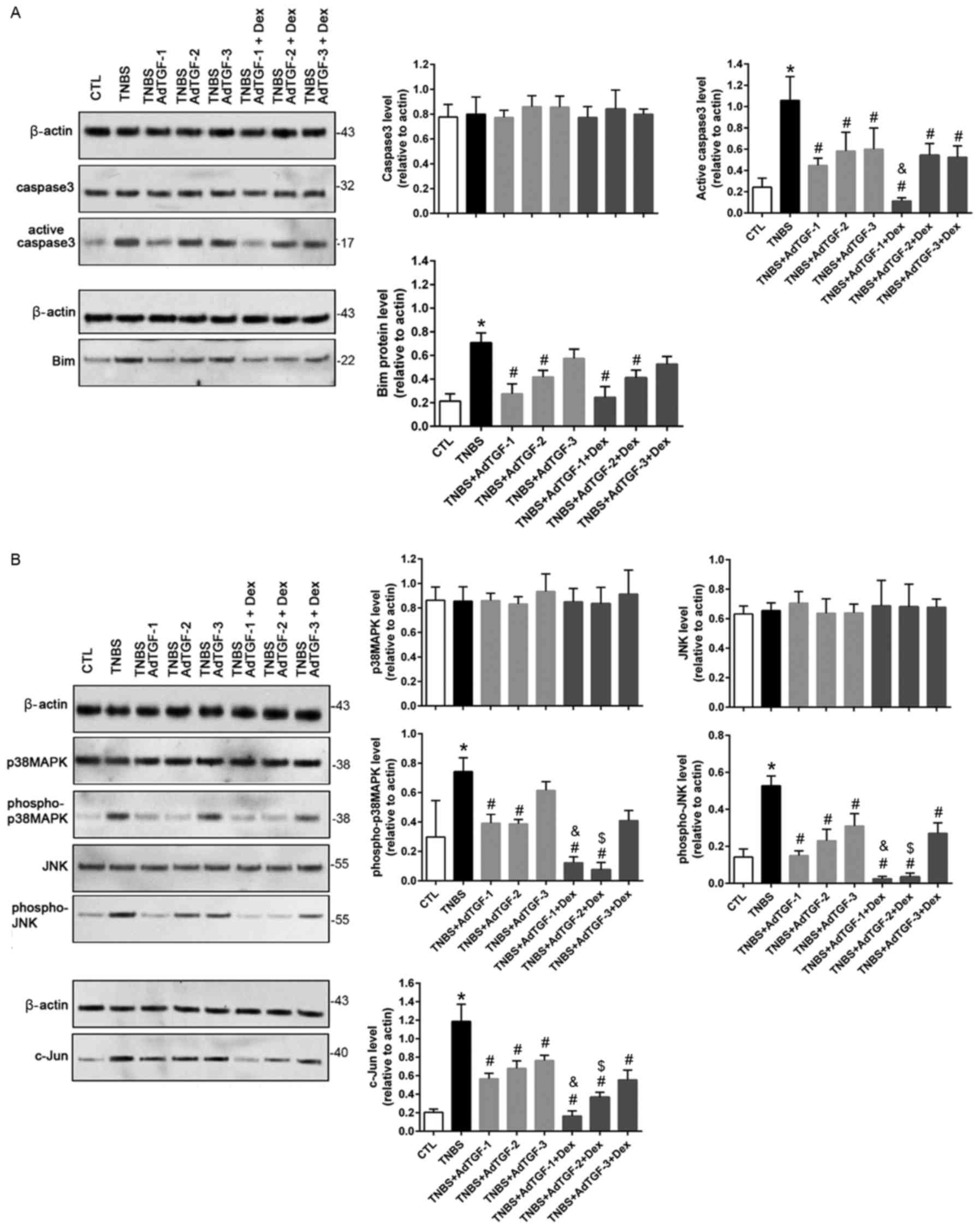
|
1
|
Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, Ghali WA,
Ferris M, Chernoff G, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Barkema
HW and Kaplan GG: Increasing incidence and prevalence of the
inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review.
Gastroenterology. 142:46–54.e42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Lange KM and Barrett JC: Understanding
inflammatory bowel disease via immunogenetics. J Autoimmun.
64:91–100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kaistha A and Levine J: Inflammatory bowel
disease: The classic gastrointestinal autoimmune disease. Curr
Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 44:328–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee YK and Mazmanian SK: Has the
microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive
immune system? Science. 330:1768–1773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Powrie F, Leach MW, Mauze S, Caddle LB and
Coffman RL: Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T
cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C.
B-17 scid mice. Int Immunol. 5:461–471. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Himmel ME, Yao Y, Orban PC, Steiner TS and
Levings MK: Regulatory T-cell therapy for inflammatory bowel
disease: More questions than answers. Immunology. 136:115–122.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neurath MF: Cytokines in inflammatory
bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:329–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Goettel JA, Scott Algood HM,
Olivares-Villagómez D, Washington MK, Chaturvedi R, Wilson KT, Van
Kaer L and Polk DB: KSR1 protects from interleukin-10
deficiency-induced colitis in mice by suppressing T-lymphocyte
interferon-γ production. Gastroenterology. 140:265–274. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strober W and Fuss IJ: Proinflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Gastroenterology. 140:1756–1767. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feagins LA: Role of transforming growth
factor-β in inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon
cancer. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:1963–1968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Borgiel-Marek H and
Kos-Kudła B: Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) in physiology
and pathology. Endokrynol Pol. 64:384–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marafini I, Zorzi F, Codazza S, Pallone F
and Monteleone G: TGF-Beta signaling manipulation as potential
therapy for IBD. Curr Drug Targets. 14:1400–1404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vallance BA, Gunawan MI, Hewlett B, Bercik
P, Van Kampen C, Galeazzi F, Sime PJ, Gauldie J and Collins SM:
TGF-beta1 gene transfer to the mouse colon leads to intestinal
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physio. 289:G116–G128.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kitani A, Fuss IJ, Nakamura K, Schwartz
OM, Usui T and Strober W: Treatment of experimental
(Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid) colitis by intranasal
administration of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 plasmid:
TGF-beta1-mediated suppression of T helper cell type 1 response
occurs by interleukin (IL)-10 induction and IL-12 receptor beta2
chain downregulation. J Exp Med. 192:41–52. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wallace JL and Keenan CM: An orally active
inhibitor of leukotriene synthesis accelerates healing in a rat
model of colitis. Am J Physiol. 258:G527–G534. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng L, Gao ZQ and Wang SX: A chronic
ulcerative colitis model in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 6:150–152.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sánchez de Medina F, Martinez-Augustin O,
González R, Ballester I, Nieto A, Gálvez J and Zarzuelo A:
Induction of alkaline phosphatase in the inflamed intestine: A
novel pharmacological target for inflammatory bowel disease.
Biochem Pharmacol. 68:2317–2326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Friend DR: Review article: Issues in oral
administration of locally acting glucocorticosteroids for treatment
of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 12:591–603.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Mattos BR, Garcia MP, Nogueira JB,
Paiatto LN, Albuquerque CG, Souza CL, Fernandes LG, Tamashiro WM
and Simioni PU: Inflammatory bowel disease: An overview of immune
mechanisms and biological treatments. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:4930122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scheinman RI, Gualberto A, Jewell CM,
Cidlowski JA and Baldwin AS Jr: Characterization of mechanisms
involved in transrepression of NF-kappa B by activated
glucocorticoid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 15:943–953. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Quaglio AE, Castilho AC and Di Stasi LC:
Experimental evidence of heparanase, Hsp70 and NF-κB gene
expression on the response of anti-inflammatory drugs in
TNBS-induced colonic inflammation. Life Sci. 141:179–187. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Del Zotto B, Mumolo G, Pronio AM,
Montesani C, Tersigni R and Boirivant M: TGF-beta1 production in
inflammatory bowel disease: Differing production patterns in
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Clin Exp Immunol.
134:120–126. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Monteleone G, Boirivant M, Pallone F and
MacDonald TT: TGF-beta1 and Smad7 in the regulation of IBD. Mucosal
Immunology. 1 Suppl 1:S50–S53. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Giladi E, Raz E, Karmeli F, Okon E and
Rachmilewitz D: Transforming growth factor-beta gene therapy
ameliorates experimental colitis in rats. Eur J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 7:341–347. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schmitt N and Ueno H: Regulation of human
helper T cell subset differentiation by cytokines. Curr Opin
Immunol. 34:130–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Erdogan Kayhan G, Gul M, Kayhan B, Gedik
E, Ozgul U, Kurtoglu EL, Durmus M and Ersoy MÖ: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis by inducing immunomodulator
effect. J Surg Res. 183:733–741. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Marwaha AK, Leung NJ, McMurchy AN and
Levings MK: TH17 cells in autoimmunity and immunodeficiency:
Protective or pathogenic? Front Immunol. 3:1292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McGeachey MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, Tato
CM, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T and Cua DJ: TGF-beta and IL-6
drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain
T(H)-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat Immunol. 8:1390–1397. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hartog A, Belle FN, Bastiaans J, de Graaff
P, Garssen J, Harthoorn LF and Vos AP: A potential role for
regulatory T-cells in the amelioration of DSS induced colitis by
dietary non-digestible polysaccharides. J Nutr Biochem. 26:227–233.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang D, Wang L, Yan L, Miao X, Gong C,
Xiao M, Ni R and Tang Q: Vacuolar protein sorting 4B regulates
apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells via p38 MAPK in Crohn's
disease. Exp Mol Pathol. 98:55–64. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Reinecke K, Eminel S, Dierck F, Roessner
W, Kersting S, Chromik AM, Gavrilova O, Laukevicience A, Leuschner
I, Waetzig V, et al: The JNK inhibitor XG-102 protects against
TNBS-induced colitis. PLoS One. 7:e309852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|