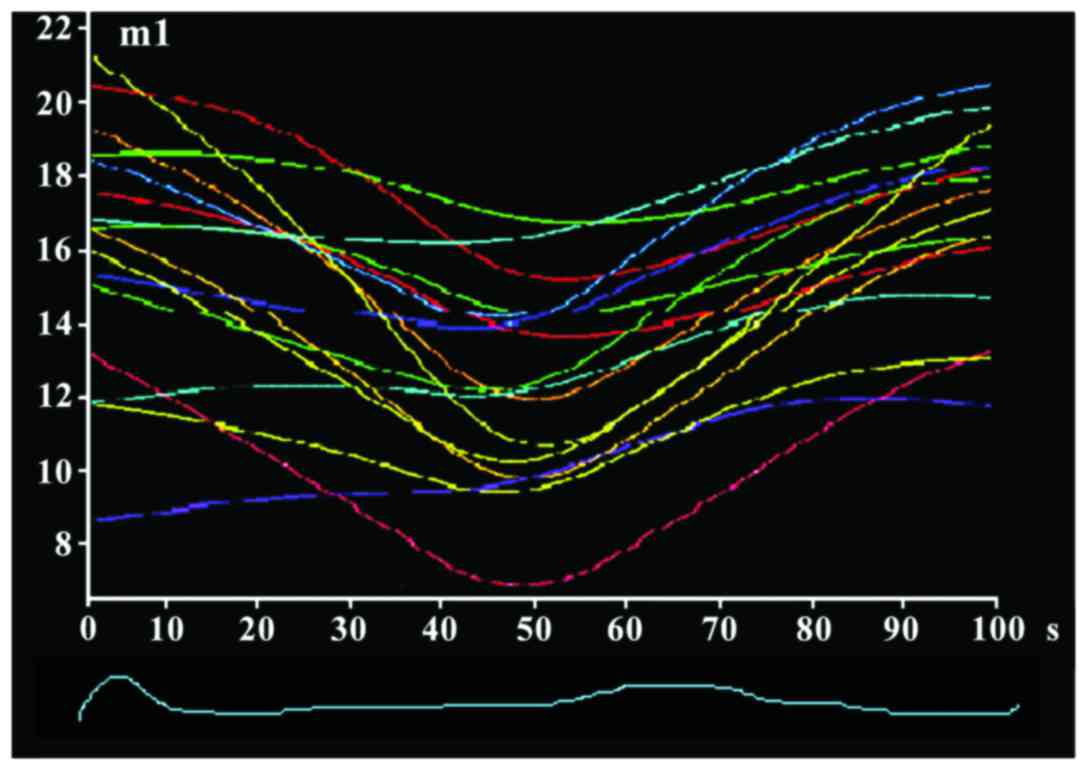
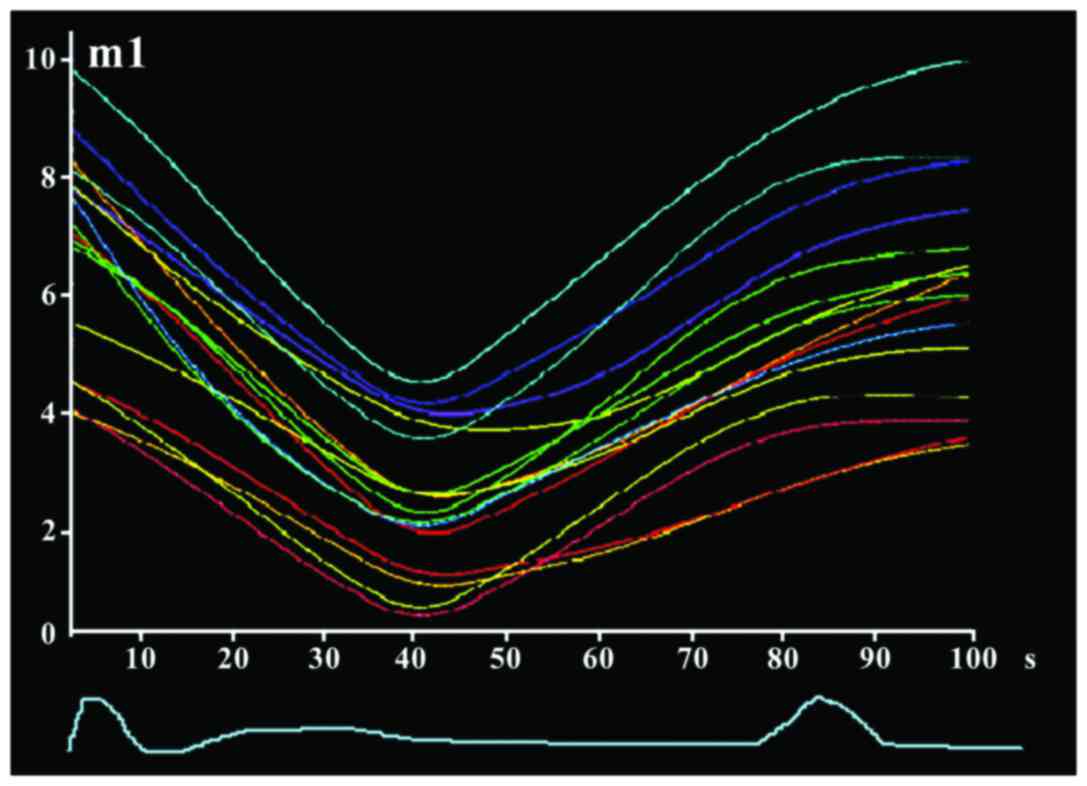
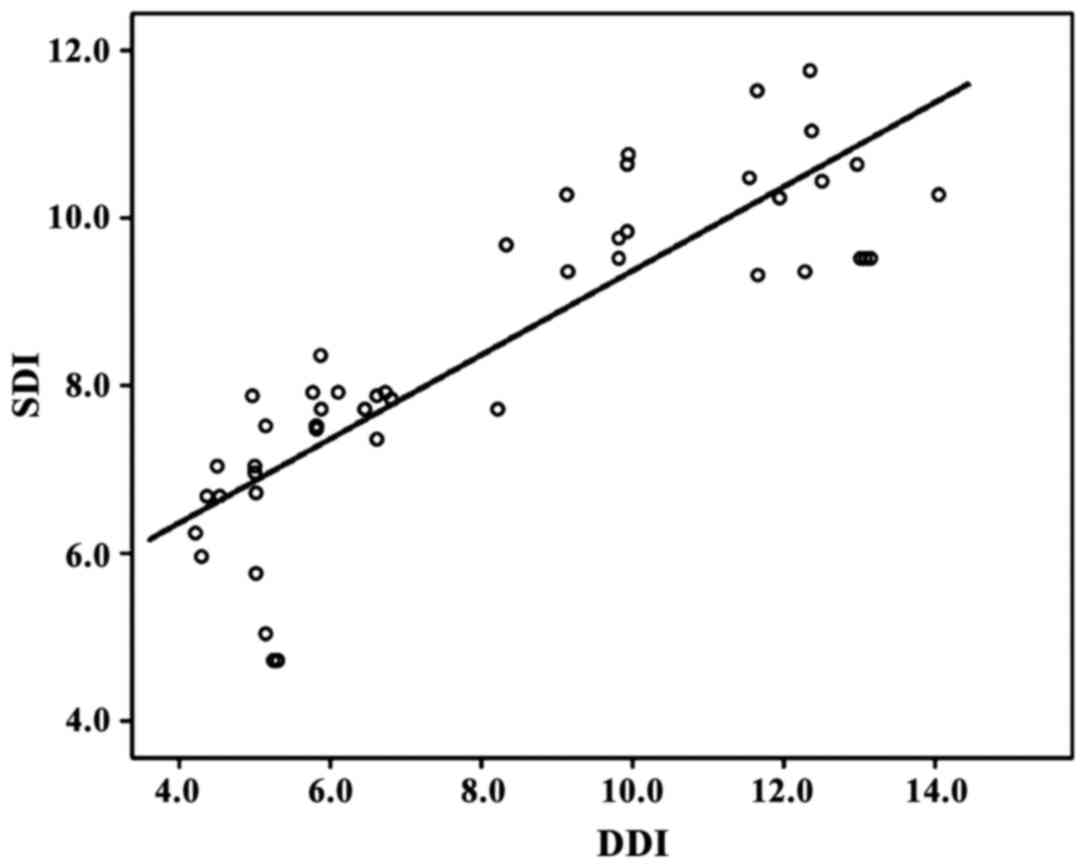
|
1
|
Semsarian C, Ingles J, Maron MS and Maron
BJ: New perspectives on the prevalence of hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1249–1254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maron BJ, Rowin EJ, Casey SA, Link MS,
Lesser JR, Chan RH, Garberich RF, Udelson JE and Maron MS:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in adulthood associated with low
cardiovascular mortality with contemporary management strategies. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1915–1928. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elliott PM, Anastasakis A, Borger MA,
Borggrefe M, Cecchi F, Charron P, Hagege AA, Lafont A, Limongelli
G, Mahrholdt H, et al: Authors/Task Force members: 2014 ESC
Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy: The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology
(ESC). Eur Heart J. 35:2733–2779. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wasilewska M, Gardziejczyk W and
Gierasimiuk P: Evaluation of skid resistance using CTM, DFT and
SRT-3 devices. Transportat Res Proced. 14:3050–3059. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cai Q and Ahmad M: Left ventricular
dyssynchrony by three-dimensional echocardiography: Current
understanding and potential future clinical applications.
Echocardiography. 32:1299–1306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kalsi KK, Smolenski RT, Pritchard RD,
Khaghani A, Seymour AM and Yacoub MH: Energetics and function of
the failing human heart with dilated or hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy. Eur J Clin Invest. 29:469–477. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dubourg O, Mansencal N and Charron P:
Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy in 2014. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 108:151–155. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alfares AA, Kelly MA, McDermott G, Funke
BH, Lebo MS, Baxter SB, Shen J, McLaughlin HM, Clark EH, Babb LJ,
et al: CORRIGENDUM: Results of clinical genetic testing of 2,912
probands with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Expanded panels offer
limited additional sensitivity. Genet Med. 17:3192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cardim N, Galderisi M, Edvardsen T, Plein
S, Popescu BA, D'Andrea A, Bruder O, Cosyns B, Davin L, Donal E, et
al: Role of multimodality cardiac imaging in the management of
patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: An expert consensus of
the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging endorsed by the
Saudi Heart Association. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging.
16:2802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hensley N, Dietrich J, Nyhan D, Mitter N,
Yee MS and Brady M: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A review. Anesth
Analg. 120:554–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nomura A, Konno T, Fujita T, Tanaka Y,
Nagata Y, Tsuda T, Hodatsu A, Sakata K, Nakamura H, Kawashiri MA,
et al: Fragmented QRS predicts heart failure progression in
patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ J. 79:136–143.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ho CY, Lakdawala NK, Cirino AL, Lipshultz
SE, Sparks E, Abbasi SA, Kwong RY, Antman EM, Semsarian C, González
A, et al: Diltiazem treatment for pre-clinical hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy sarcomere mutation carriers: A pilot randomized
trial to modify disease expression. JACC Heart Fail. 3:180–188.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu M, Ashraf M, Zhang Z, Streiff C,
Shimada E, Kimura S, Schaller T, Song X and Sahn DJ: Real time
three-dimensional echocardiographic evaluations of fetal left
ventricular stroke volume, mass, and myocardial strain: In vitro
and in vivo experimental study. Echocardiography. 32:1697–1706.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maron BJ, Casey SA, Chan RH, Garberich RF,
Rowin EJ and Maron MS: Independent assessment of the European
Society of Cardiology sudden death risk model for hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 116:757–764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Patel P, Dhillon A, Popovic ZB, Smedira
NG, Rizzo J, Thamilarasan M, Agler D, Lytle BW, Lever HM and Desai
MY: Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction in hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy patients without severe septal hypertrophy:
Implications of mitral valve and papillary muscle abnormalities
assessed using cardiac magnetic resonance and echocardiography.
Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 8:e0031322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu KJ, Chen JX, Profitis K, Kearney LG,
DeSilva D, Smith G, Ord M, Harberts S, Calafiore P, Jones E, et al:
Right ventricular global longitudinal strain is an independent
predictor of right ventricular function: A multimodality study of
cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, real time three-dimensional
echocardiography and speckle tracking echocardiography.
Echocardiography. 32:966–974. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elsayed M, Hsiung MC, Meggo-Quiroz LD,
Elguindy M, Uygur B, Tandon R, Guvenc T, Keser N, Vural MG, Bulur
S, et al: Incremental value of live/real time three-dimensional
over two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography in the
assessment of atrial septal pouch. Echocardiography. 32:1858–1867.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wada Y, Aiba T, Matsuyama TA, Nakajima I,
Ishibashi K, Miyamoto K, Yamada Y, Okamura H, Noda T, Satomi K, et
al: Clinical and pathological impact of tissue fibrosis on lethal
arrhythmic events in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients with
impaired systolic function. Circ J. 79:1733–1741. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao B, Wang S, Chen J, Ji Y, Wang J, Tian
X and Zhi G: Echocardiographic characterization of hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy in Chinese patients with myosin-binding protein C3
mutations. Exp Ther Med. 13:995–1002. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parthiban A, Li L, Kindel SJ, Shirali G,
Roessner B, Marshall J, Schuster A, Klas B, Danford DA and Kutty S:
Mechanical dyssynchrony and abnormal regional strain promote
erroneous measurement of systolic function in pediatric heart
transplantation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 28:1161–1170. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|