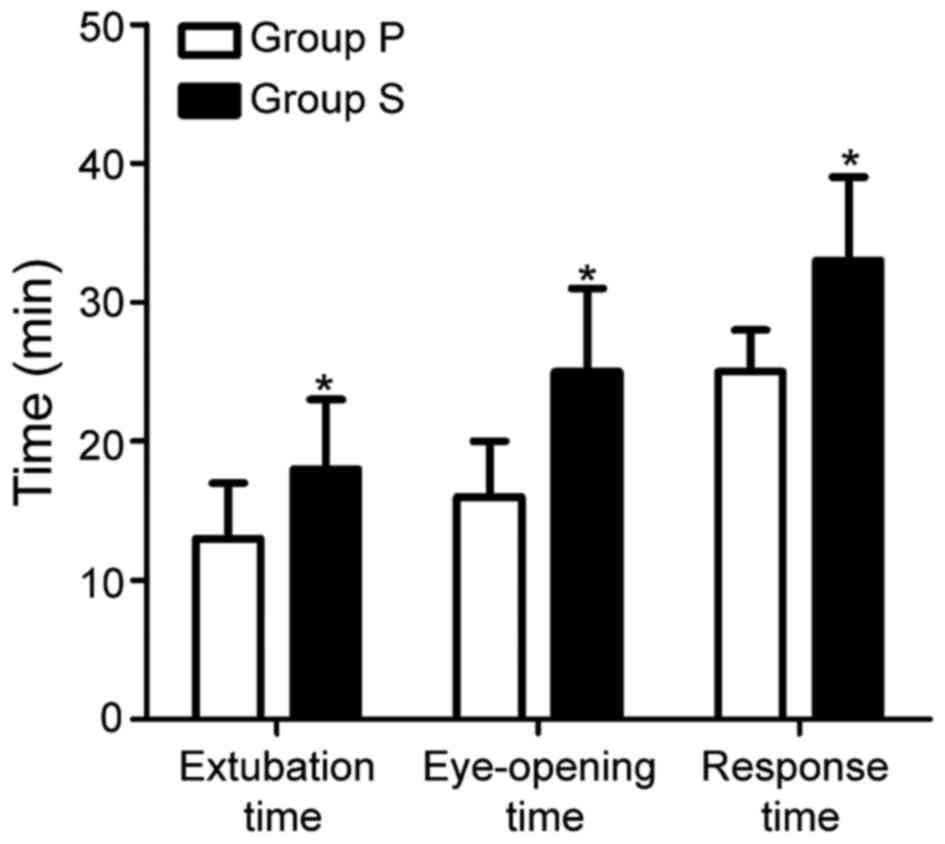
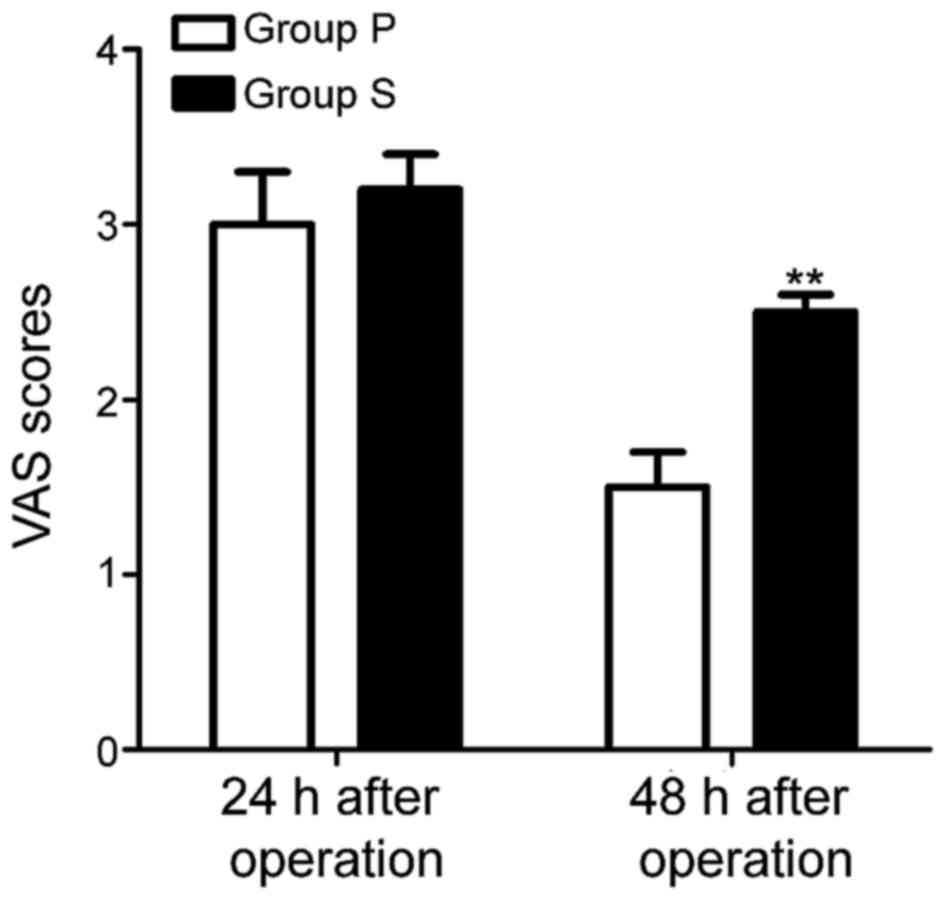
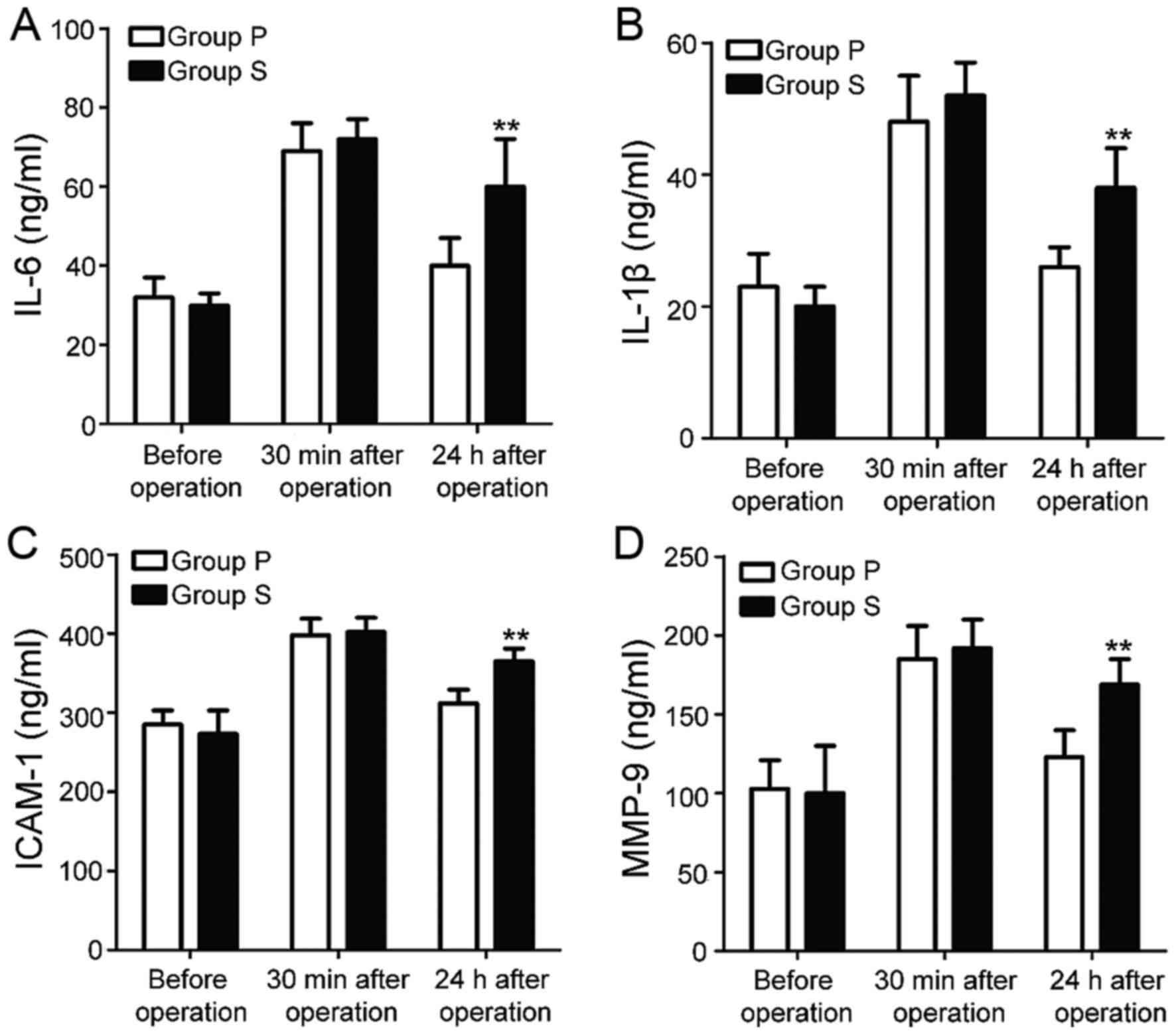
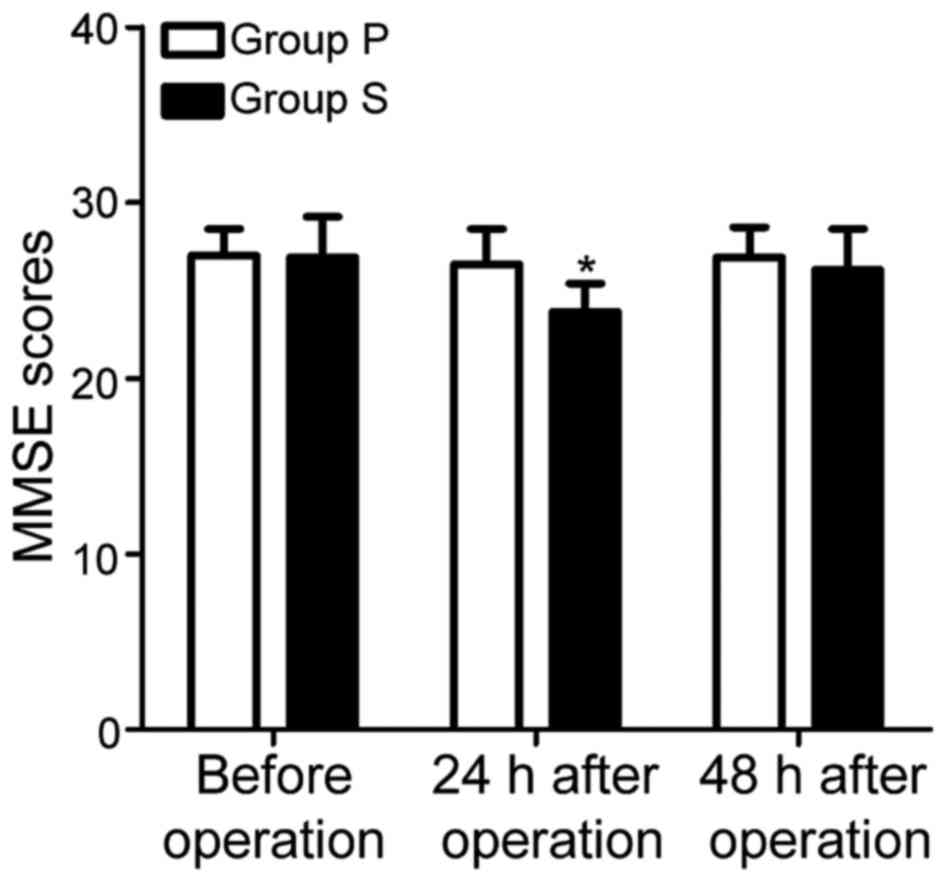
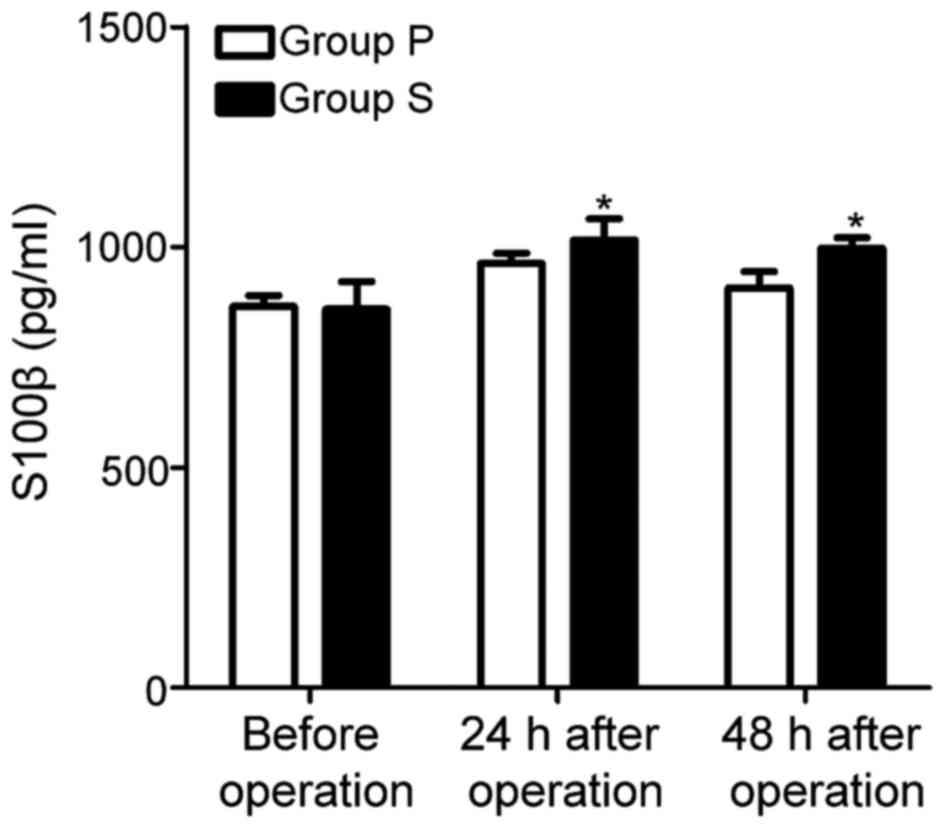
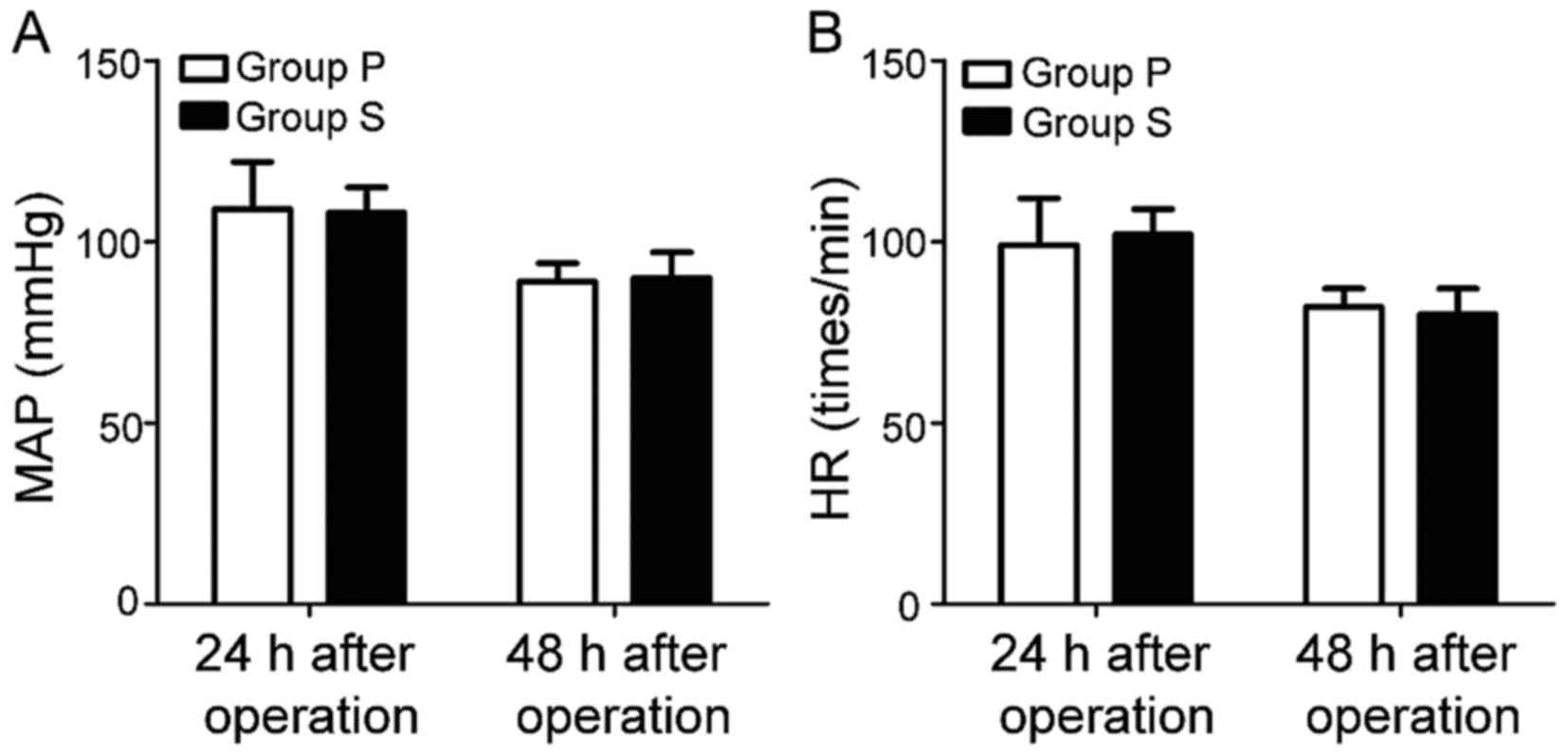
|
1
|
Health Quality Ontario, . Vertebral
augmentation involving vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for
cancer-related vertebral compression fractures: A systematic
review. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 16:1–202. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Yu WY, Lou C, Liu FJ and He DW: Clinical
efficacy of one stage posterior debridement joint graft fixation
for lumbar vertebral fractures in spinal tuberculosis patients with
compression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3161–3167.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malgo F, Hamdy NAT, Ticheler CHJM, Smit F,
Kroon HM, Rabelink TJ, Dekkers OM and Appelman-Dijkstra NM: Value
and potential limitations of vertebral fracture assessment (VFA)
compared to conventional spine radiography: Experience from a
fracture liaison service (FLS) and a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int.
28:2955–2965. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cawthon PM, Schousboe JT, Harrison SL,
Ensrud KE, Black D, Cauley JA, Cummings SR, Le Blanc ES, Laughlin
GA, Nielson CM, et al: Osteoporotic fractures in men (MrOS) study
research group: Sex hormones, sex hormone binding globulin, and
vertebral fractures in older men. Bone. 84:271–278. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao J, Xie H, Sun Y, Zhu J, Ying M, Qiao
S, Shao Q, Wu H and Wang C: Sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces
rat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through an increase in
NOS and a decrease in phopshorylated NHE1 levels. Int J Mol Med.
36:1529–1537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou L, Wang Z, Zhou H, Liu T, Lu F, Wang
S, Li J, Peng S and Zuo Z: Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane may not
cause learning and memory deficits and behavioral abnormality in
the childhood of Cynomolgus monkeys. Sci Rep. 5:111452015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
De Conno E, Steurer MP, Wittlinger M,
Zalunardo MP, Weder W, Schneiter D, Schimmer RC, Klaghofer R, Neff
TA, Schmid ER, et al: Anesthetic-induced improvement of the
inflammatory response to one-lung ventilation. Anesthesiology.
110:1316–1326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Visvabharathy L, Xayarath B, Weinberg G,
Shilling RA and Freitag NE: Propofol increases host susceptibility
to microbial infection by reducing subpopulations of mature immune
effector cells at sites of infection. PLoS One. 10:e01380432015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Katzman WB, Vittinghoff E, Kado DM, Lane
NE, Ensrud KE and Shipp K: Thoracic kyphosis and rate of incident
vertebral fractures: The fracture intervention trial. Osteoporos
Int. 27:899–903. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Waterloo S, Nguyen T, Ahmed LA, Center JR,
Morseth B, Nguyen ND, Eisman JA, Søgaard AJ and Emaus N: Important
risk factors and attributable risk of vertebral fractures in the
population-based Tromsø study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
13:1632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Waterloo S, Søgaard AJ, Ahmed LA, Damsgård
E, Morseth B and Emaus N: Vertebral fractures and self-perceived
health in elderly women and men in a population-based
cross-sectional study: The Tromsø Study 2007–08. BMC Geriatr.
13:1022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang JQ, Xu WY and Xu CQ: Neonatal
propofol and etomidate exposure enhance inhibitory synaptic
transmission in hippocampal cornus ammonis 1 pyramidal neurons.
Chin Med J (Engl). 129:2714–2724. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mu DL, Li LH, Wang DX, Li N, Shan GJ, Li
J, Yu QJ and Shi CX: High postoperative serum cortisol level is
associated with increased risk of cognitive dysfunction early after
coronary artery bypass graft surgery: A prospective cohort study.
PLoS One. 8:e776372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang R, Chen J and Wu G: Variable lung
protective mechanical ventilation decreases incidence of
postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction during open
abdominal surgery. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:21208–21214.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papadopoulos G, Karanikolas M,
Liarmakopoulou A, Papathanakos G, Korre M and Beris A: Cerebral
oximetry and cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing
surgery for hip fractures: A prospective observational study. Open
Orthop J. 6:400–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sclar DA: Remifentanil, fentanyl, or the
combination in surgical procedures in the United States: Predictors
of use in patients with organ impairment or obesity. Clin Drug
Investig. 35:53–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YH, Kwon HJ and Kim DS: Matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9)-dependent processing of βig-h3 protein
regulates cell migration, invasion, and adhesion. J Biol Chem.
287:38957–38969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu PP, Yuan SG, Liao Y, Qin LL and Liao
WJ: High level of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 affects
prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7254–7263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Xu M and Chen G:
Autophagy is involved in the sevoflurane anesthesia-induced
cognitive dysfunction of aged rats. PLoS One. 11:e1535052016.
|
|
20
|
Sato C, Sekiguchi A, Kawai M, Kotozaki Y,
Nouchi R, Tada H, Takeuchi H, Ishida T, Taki Y, Kawashima R and
Ohuchi N: Postoperative structural brain changes and cognitive
dysfunction in patients with breast cancer. PLoS One.
10:e1406552015. View Article : Google Scholar
|