Introduction
The term ‘autism’ has been extensively utilized both
in specialist contexts, such as scientific, educational and
pedagogic research, and by public opinion.
To thoroughly define the term autism, we employed
the definition of the scientist Bonnie Evans, who affirms that:
‘Autism is an essential concept used in the description of child
development and its variances. Yet the phenomenal success of autism
diagnoses is relatively recent. Today, autistic spectrum disorder
is regarded as a developmental condition with genetic and
biochemical correlates that often persists into adulthood’
(1).
Problems associated with being on the autistic
spectrum are more common in male individuals. However, whether
there is a correlation with the testosterone levels to which babies
were exposed during intrauterine life is unclear (2).
The aim of the present study was to investigate,
through the digit ratio technique, the possible correlation between
testosterone exposition during intrauterine life and the
achievement of predetermined aims during the educational program
Treatment and Education of Autistic and Related Communication
Handicapped Children (TEACCH) (3,4) in a
group of subjects with different forms of autism. The results
showed that it is possible to measure the levels of prenatal
testosterone exposition in a non-invasive manner thanks to the
digit ratio technique, which involves measuring the ratio between
the second finger (index) and the fourth finger (ring finger) of
the left hand. Certain authors have previously observed that high
levels of prenatal testosterone exposition are associated with
specific competences (mathematics and academical performance) and
physiological and pathological personalities (5–8).
Subjects and methods
Subjects
A total of 60 boys on the autistic spectrum with a
mean age of 9±2.1 years participated in the study. Of the 60
subjects, 32 had a diagnosis of autism and mild mental retardation
and 28 had a diagnosis of high-functioning autism.
The parents of the subjects were informed about the
protocol of the research and gave their informed consent. The study
was approved and implemented by the organization ‘A Future for
Autism Onlus-Catania’ (http://www.autismo.net/).
A hand photocopy was made of all the subjects and
different activities were proposed to achieve the goals of the
TEACCH program (3).
TEACCH program
The TEACCH program, created and designed in 1960 by
Mesibov et al (3), has the
aim of improving the personal, social and professional life of the
autistic subject, by employing specific educational techniques to
develop the individual's personal capacities.
We selected activities that were not previously
conducted by the subjects, with the aim of excluding inferences
from previous learning (routine, execution and automatism). The
degree of achievement of predetermined aims was calculated by
conferring a score from 0 to 10.
The chosen activities, which correlated with the
objectives in the TEACCH program, are:
i) Recognition of colours and geometrical figures
involved work aiming to recognize colours (the subject had to put
the same colour cardboard inside the corresponding baskets of three
different colours: yellow, red, blue). The second assignment was to
pair up geometrical figures (triangle on triangle, square on
square, rectangle on rectangle).
ii) Another objective was autonomy in purchasing a
snack through social stories relating to the purchase of a snack in
a small shop. To reach the aim, the subject had to comprehend the
sequence of a social story regarding the purchase of a snack, and,
later, was required to use it as an acquired skill and employ it in
a natural context, such as s small shop.
iii) Refining manual skills, e.g., tying their own
shoelaces was checked. Manual labour was carried out on a table as
preparation for determining precision manual skill. The subject had
to tie his shoes with different types of shoelace, differing in
length and thickness, to arrive to the standard measure of tennis
shoes.
iv) Autonomy in personal hygiene, such as hand
washing and brushing of teeth was another objective. The aim was
achieved if the subject, after working with social stories and
after a ‘training’ with a tutor, could put soap on his hands, rub
the hands in the typical manner of washing hands, dry off with a
little towel and hang the towel back in its place, and then take
the beauty case from the bag and open it, take the toothbrush out,
remove the protective cap, take the toothpaste and twist off the
cap, brush his teeth, rinse the toothbrush, put on again the
protective cap, put the toothbrush in the glass, put on again the
cap on the toothpaste, place everything back in the beauty case,
and finally, place the beauty case back in the bag.
v) Recognizing road signs (pedestrian crossing,
pedestrian traffic light, stop, no entry, one-way road, impasse,
generic danger) only for the high-functioning autism group. The
objective was achieved if the subject was capable of distinguishing
the different road signs and at a later time could also use this
capacity in an outdoor environment.
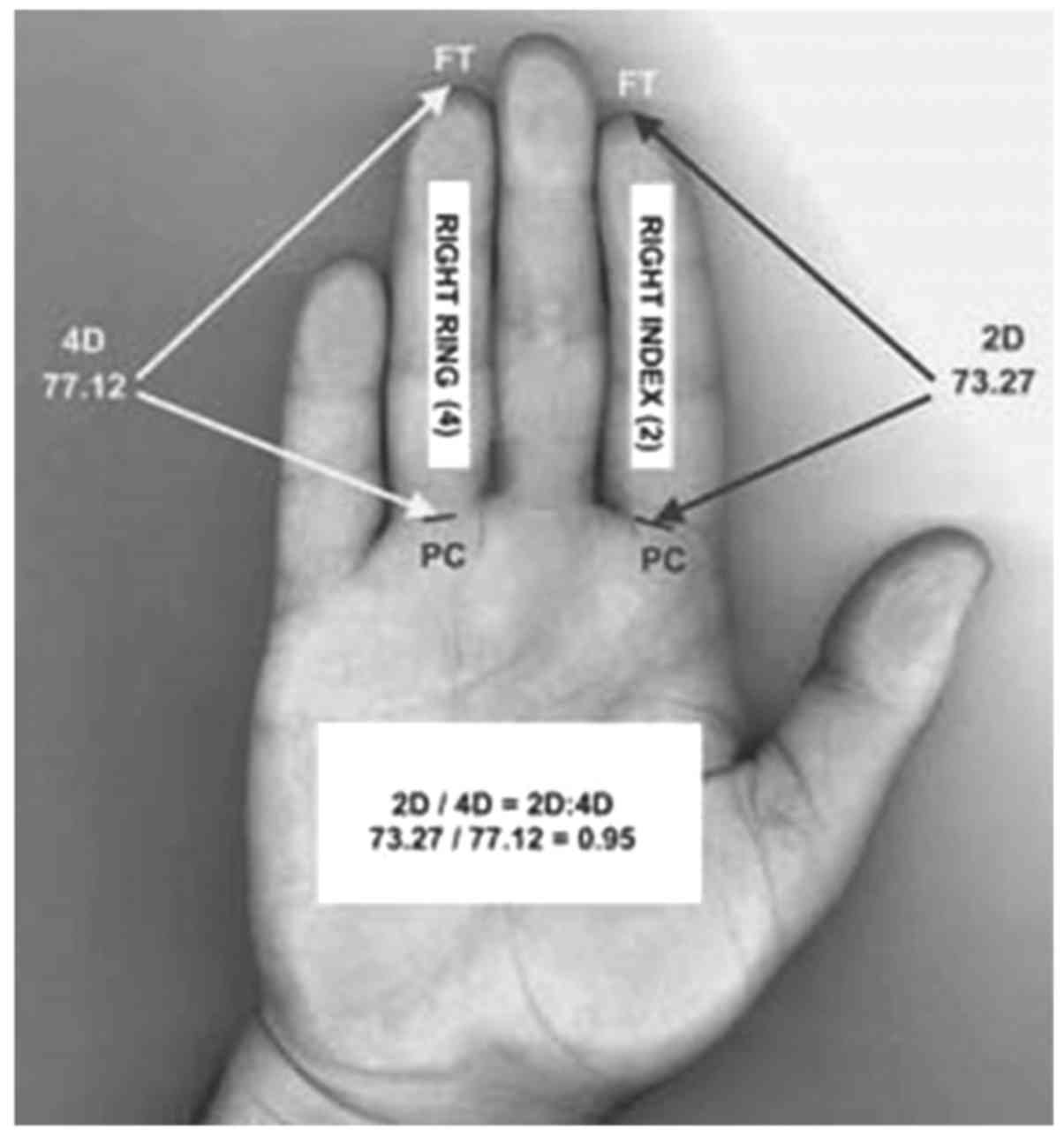
Digit ratio
At present, there is concensus on using the ratio
between index and ring fingers (2D:4D), termed digit ratio, as an
instrument to measure in the subject the exposure to testosterone
during intrauterine life. We photocopied the left hands of the
subjects and we measured the length of the fingers from the
meta-carpo-phalanx crease to the tip of the finger (Fig. 1). This crease, the nearest between
finger and palm, appears at approximately the ninth gestation week,
and is one of the primary or regular creases of the hand. It was
verified that finger length is directly associated with the
exposition of fetus to testosterone: A bigger length of ring finger
in comparison to index finger indicated a high quantity of
testosterone to which the baby has been exposed during pregnancy
(9).
Results
Both the autism and mild mental retardation and the
high-functioning autism groups showed an improvement in the TEACCH
program tasks.
The autism and mild mental retardation group
obtained a mean score of 4.037 (±0.80). The high-functioning autism
group obtained a mean score of 6.47 (±2.24).
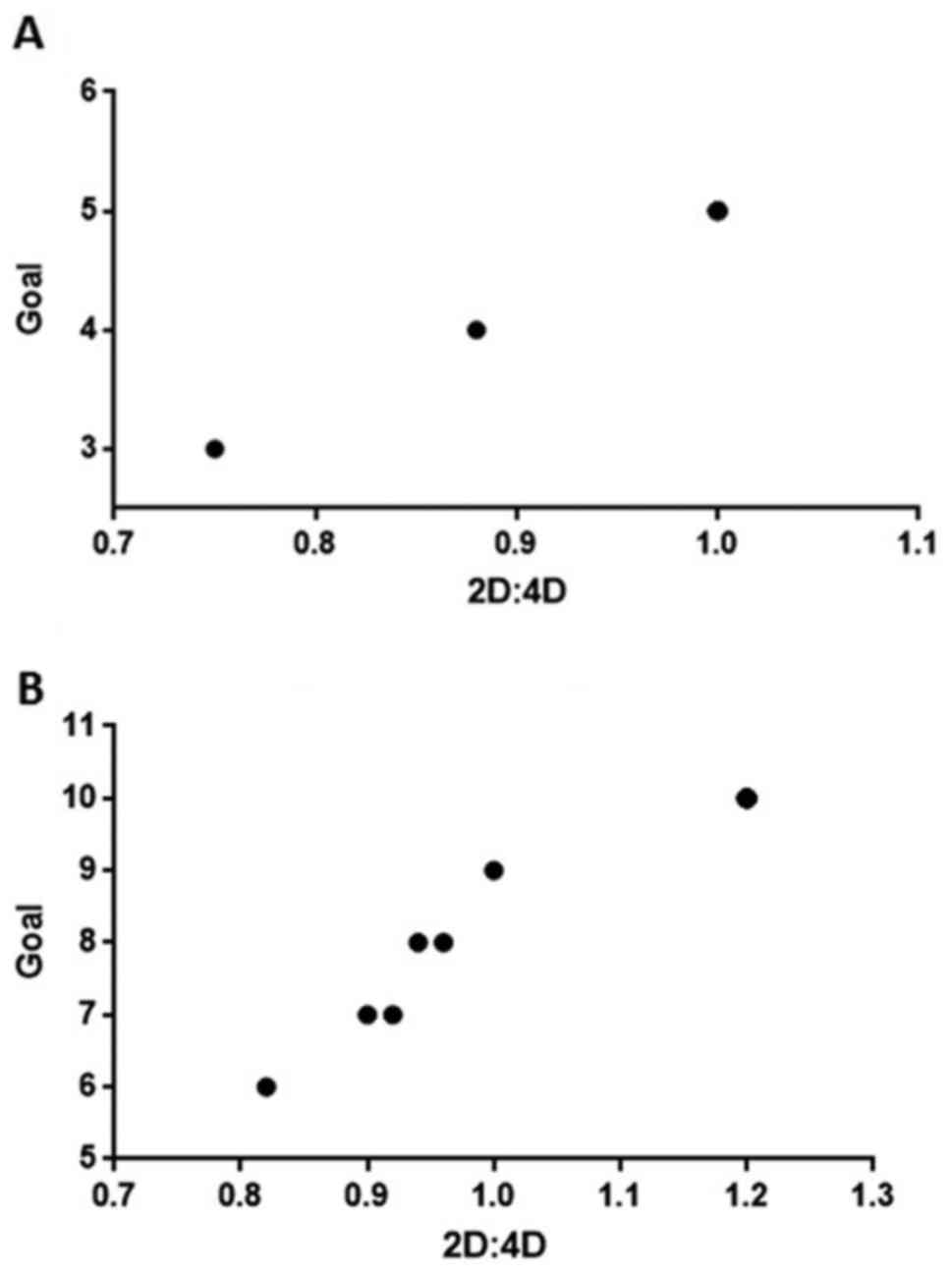
By correlating results of the TEACCH program with
the digit ratio (Fig. 2), we
observed a similar path in the two groups. This path indicated that
the less the quantity of testosterone to which the subject has been
exposed during intrauterine life is, the better is the
performance.
In Fig. 2 we can
observe how the results from the two groups, even if they start
from different base scores, if correlated to 2D:4D ratio, show a
similar path. Thus, an increase of the 2D:4D ratio also led to an
increase in the score obtained in the TEACCH program.
Discussion
Autism as a concept is not easy or definitive, and
is one that is constantly evolving, as evidenced by the constant
changes in diagnostic manuals used to make a definitive diagnosis.
The last version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders (DSM) (10) and of the
International Classification of Diseases (ICD) (11), include differences between the
diagnostic criteria of DSM-V and ICD-10, which were not previously
incorporated.
Concordant with the conclusions of Guyatt et
al (12), the subjects that
participated in our research exhibited a variability in 2D:4D
ratio.
The results obtained in the present study allow us
to observe a positive linear correlation, statistically relevant,
between index finger/ring finger and the capacity of achieving the
predetermined goals.
These conclusions are in agreement with previous
observations (5,6), which confirm that subjects with high
levels of testosterone are more instinctive and have a reduced
ability to concentrate during long performances, unlike subjects
less exposed to testosterone during intrauterine life, who are
capable of focusing on specific tasks with more regularity and
concentration. However, Richards (13) differs in opinion, as he does not
agree with the existence of a direct correlation between
testosterone production in the womb and the digit ratio and argues
that the studies demonstrating this have low statistical
significance.
Therefore, we hypothesize that a base screening may
be useful to pinpoint the optimal teaching strategies to obtain the
best possible performance from each subject.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank ‘A Future for Autism
Onlus-Catania’ for providing the opportunity to partner with
them.
Funding
The present study was supported by the current
research funds 2016 of Bonino Pulejo Neurolesi Center - IRCCS
(Messina, Italy).
Availability of data and materials
The data and the materials are available from the
corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author's contributions
RG, MC, ES and AB conceived and designed the
experiments. MCP, AB, ES, VP, MC, RG, GDG and LSGC performed the
experiments. MC analyzed the data. MCP, AB, VP and MC wrote the
paper.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The parents of the subjects were informed about the
protocol of the study and gave their informed consent. The present
study was approved and implemented by ‘A Future for Autism
Onlus-Catania’.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Evans B: The Metamorphosis of Autism. A
History of Child Development in Britain. 1st. Manchester University
Press; Manchester, UK: 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barona M, Kothari R, Skuse D and Micali N:
Social communication and emotion difficulties and second to fourth
digit ratio in a large community-based sample. Mol Autism.
6:682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mesibov GB, Shea V and Schopler E: The
TEACCH Approach to Autism Spectrum Disorders. Springer US; New
York, NY: 2004, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hauth I, de Bruijn YG, Staal W, Buitelaar
JK and Rommelse NN: Testing the extreme male brain theory of autism
spectrum disorder in a familial design. Autism Res. 7:491–500.
2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jeevanandam S and Muthu PK II: 2D:4D ratio
and its implications in medicine. J Clin Diagn Res. 10:CM01–CM03.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Coco M and Perciavalle V, Maci T,
Nicoletti F, Di Corrado D and Perciavalle V: The second-to-fourth
digit ratio correlates with the rate of academic performance in
medical school students. Mol Med Rep. 4:471–476. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perciavalle V, Di Corrado D, Petralia MC,
Gurrisi L, Massimino S and Coco M: The second-to-fourth digit ratio
correlates with aggressive behavior in professional soccer players.
Mol Med Rep. 7:1733–1738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coco M: The brain behaves as a muscle?
Neurol Sci. 38:1865–1868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paul SN, Kato BS, Hunkin JL, Vivekanandan
S, Spector TD and Fields KB: The big finger: The second to fourth
digit ratio is a predictor of sporting ability in women. Br J
Sports Med. 40:981–983. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
American Psychiatric Association (ed).
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th.
Washington, DC: 2013
|
|
11
|
World Health Organization, . ICD-10,
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related
Health Problems. 2:World Health Organization, Malta. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Guyatt AL, Heron J, Knight BC, Golding J
and Rai D: Digit ratio and autism spectrum disorders in the Avon
Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: A birth cohort study.
BMJ Open. 5:e0074332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Richards G: Digit ratio (2D:4D) and
prenatal/perinatal sex hormones: A response to Manning and Fink
(2017). Early Hum Dev. 113:75–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|