|
1
|
Lindsey BA, Markel JE and Kleinerman ES:
Osteosarcoma overview. Rheumatol Ther. 4:25–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maximov VV and Aqeilan RI: Genetic factors
conferring metastasis in osteosarcoma. Future Oncol. 12:1623–1644.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang S, Hui Y, Li X and Jia Q: Silencing
of lncRNA-CCDC26 restrains the growth and migration of glioma cells
in vitro and in vivo via targeting miR-203. Oncol Res.
26:1143–1154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Zi Y, Wang W and Li Y: LncRNA MEG3
inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in chronic myeloid
leukemia via targeting MiR-184. Oncol Res. 26:297–305. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu K, He Y, Xia C, Yan J, Hou J, Kong D,
Yang Y and Zheng G: MicroRNA-15a inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis in CNE1 nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Res.
24:145–151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou Y, Yang C, Wang K, Liu X and Liu Q:
MicroRNA-33b inhibits the proliferation and migration of
osteosarcoma cells via targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha.
Oncol Res. 25:397–405. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Dai Q, Zeng F and Liu H: MALAT1
promotes the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
activating the Rac1/JNK pathway via targeting miR-509. Oncol Res.
Apr 27–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Yang T, Zhang Z, Lu M, Zhao W,
Zeng X and Zhang W: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes migration and
invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-335-5p in osteosarcoma cells.
Cancer Sci. 108:859–867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilbert SL, Pehrson JR and Sharp PA: XIST
RNA associates with specific regions of the inactive X chromatin. J
Biol Chem. 275:36491–36494. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen DL, Chen LZ, Lu YX, Zhang DS, Zeng
ZL, Pan ZZ, Huang P, Wang FH, Li YH, Ju HQ and Xu RH: Long
noncoding RNA XIST expedites metastasis and modulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e30112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Z, Xu J, Lu H, Lin B, Cai S, Guo J,
Zang F and Chen R: LARP1 is regulated by the XIST/miR-374a axis and
functions as an oncogene in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 38:3659–3667. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu Y, Deng C, Zhang H, Zhang J, Peng B and
Hu C: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell growth and metastasis
through regulating miR-139-5p mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 8:94554–94568.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li C, Wan L, Liu Z, Xu G, Wang S, Su Z,
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Liu X, Lei Z and Zhang HT: Long non-coding RNA
XIST promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
regulating miR-367/141-ZEB2 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Lett. 418:185–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
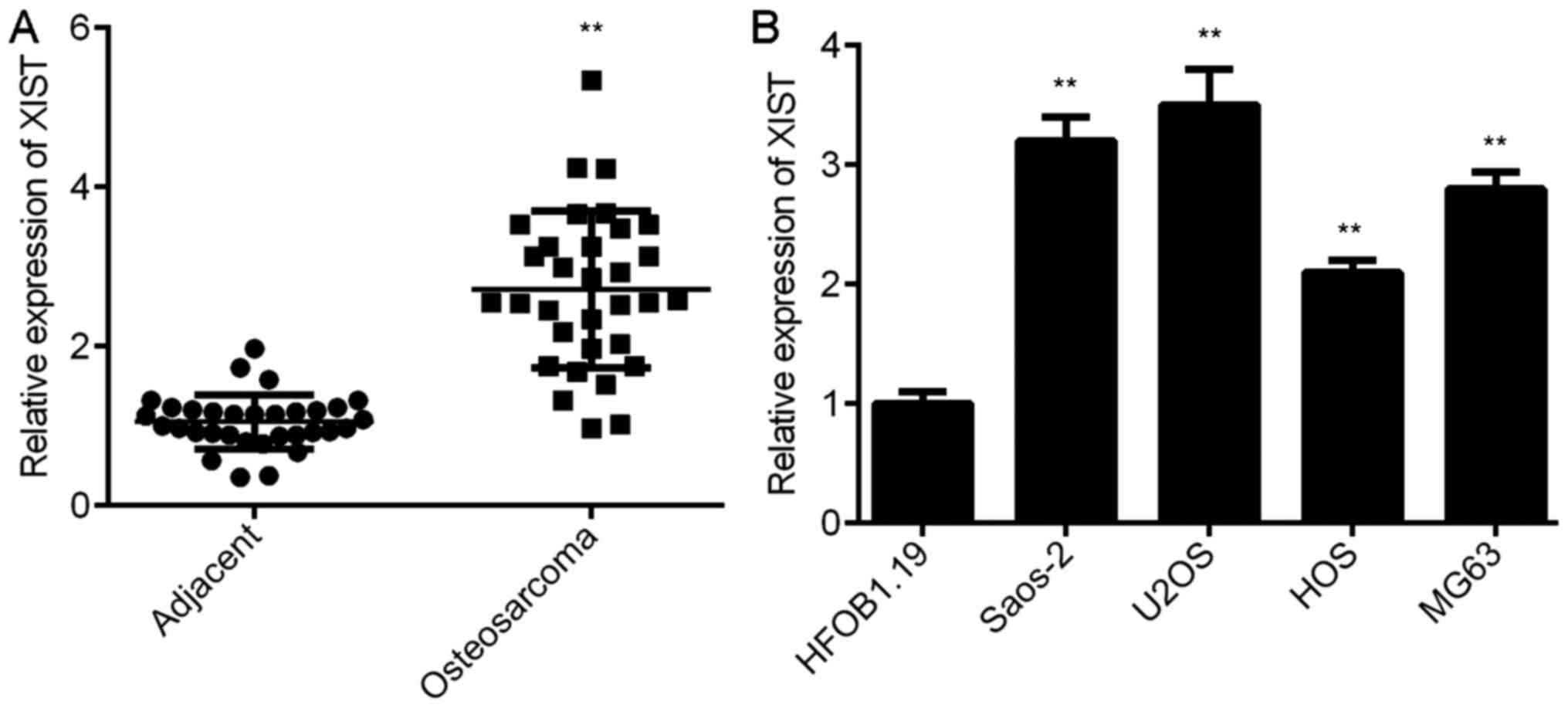
Li GL, Wu YX, Li YM and Li J: High
expression of long non-coding RNA XIST in osteosarcoma is
associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:2829–2834. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lv GY, Miao J and Zhang XL: Long
non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting
ras-related protein RAP2B via miR-320b. Oncol Res. 26:837–846.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu D, Nie X, Ma C, Liu X, Liang X, An Y,
Zhao B and Wu X: RSF1 functions as an oncogene in osteosarcoma and
is regulated by XIST/miR-193a-3p axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
95:207–214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang C, Wu K, Wang S and Wei G: Long
non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting
YAP via miR-195-5p. J Cell Biochem. 119:5646–5656. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang R and Xia T: Long non-coding RNA
XIST regulates PDCD4 expression by interacting with miR-21-5p and
inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis. Int J Oncol.
51:1460–1470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun Z, Zhang B and Cui T: Long non-coding
RNA XIST exerts oncogenic functions in pancreatic cancer via
miR-34a-5p. Oncol Rep. 39:1591–1600. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
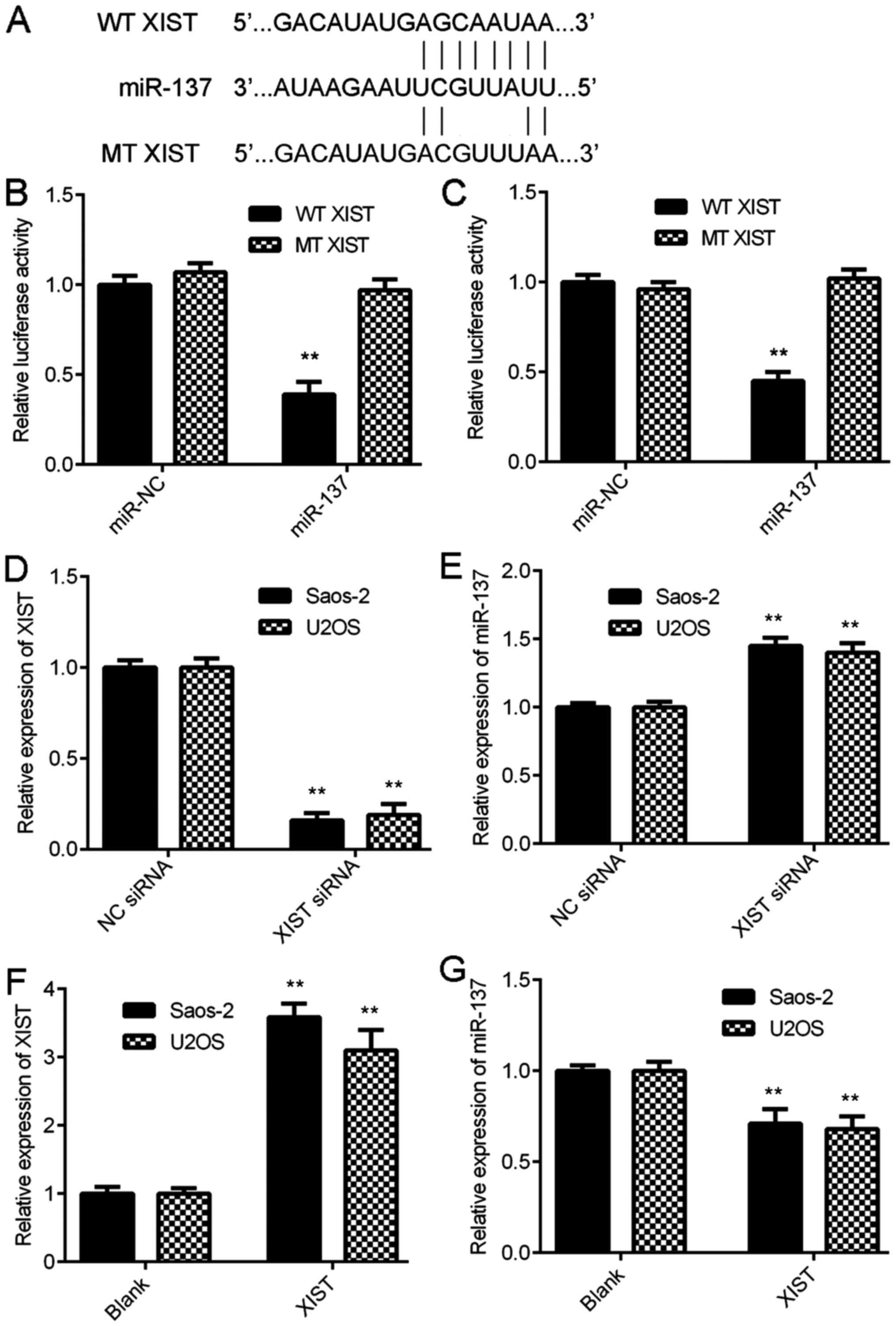
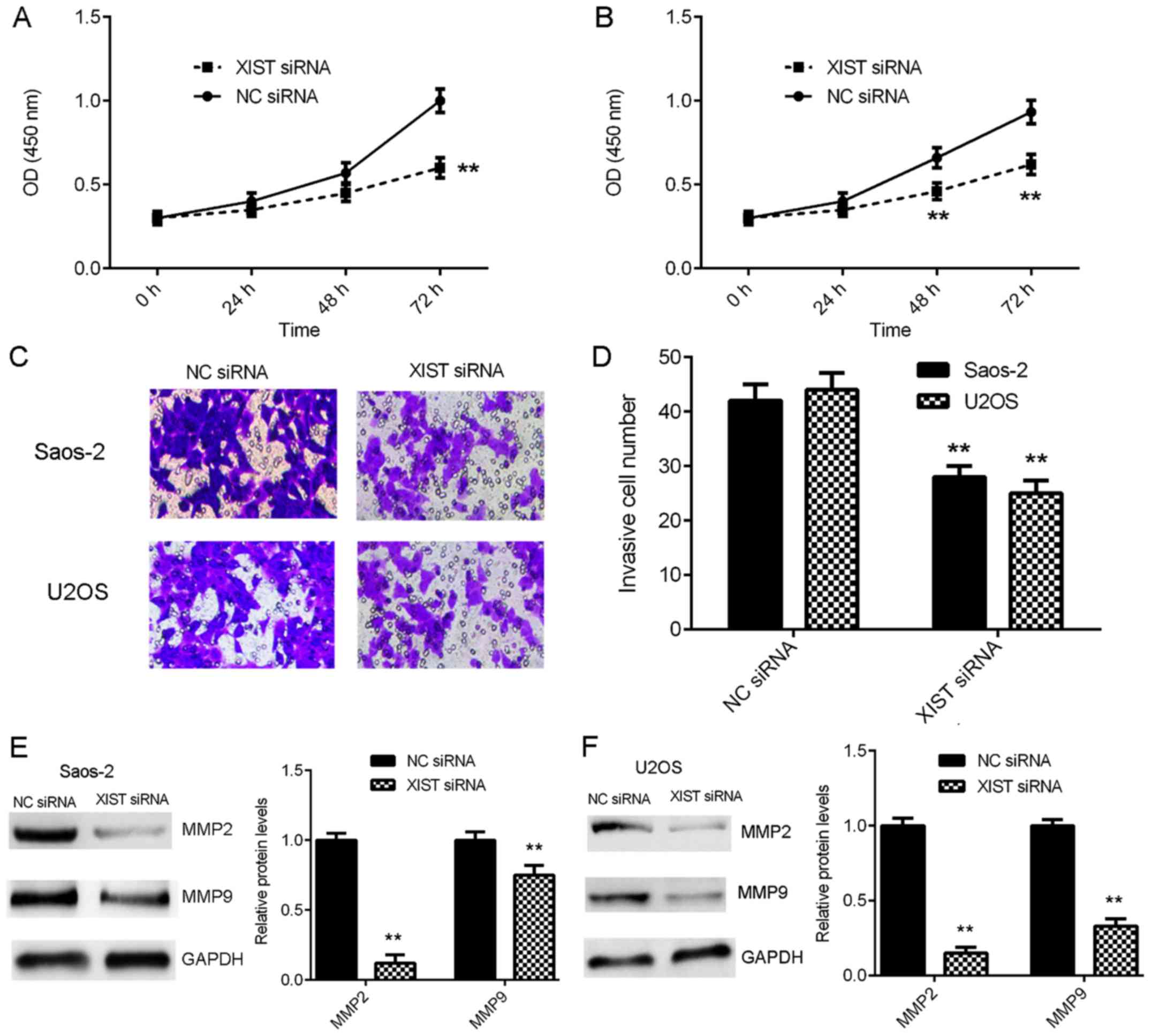
Jiang H, Zhang H, Hu X and Li W: Knockdown
of long non-coding RNA XIST inhibits cell viability and invasion by
regulating miR-137/PXN axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J
Biol Macromol. 111:623–631. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Chen B, Liu P and Yang J: XIST
promotes gastric cancer (GC) progression through TGF-beta1 via
targeting miR-185. J Cell Biochem. 119:2787–2796. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng Q, Xu X, Jiang H, Xu L and Li Q:
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA XIST suppresses nasopharyngeal
carcinoma progression by activating miR-491-5p. J Cell Biochem.
119:3936–3944. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng Q, Wu Q, Liu X, Xiong Y and Li H:
MicroRNA-137 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by
targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2. Exp Ther Med. 13:3167–3174.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
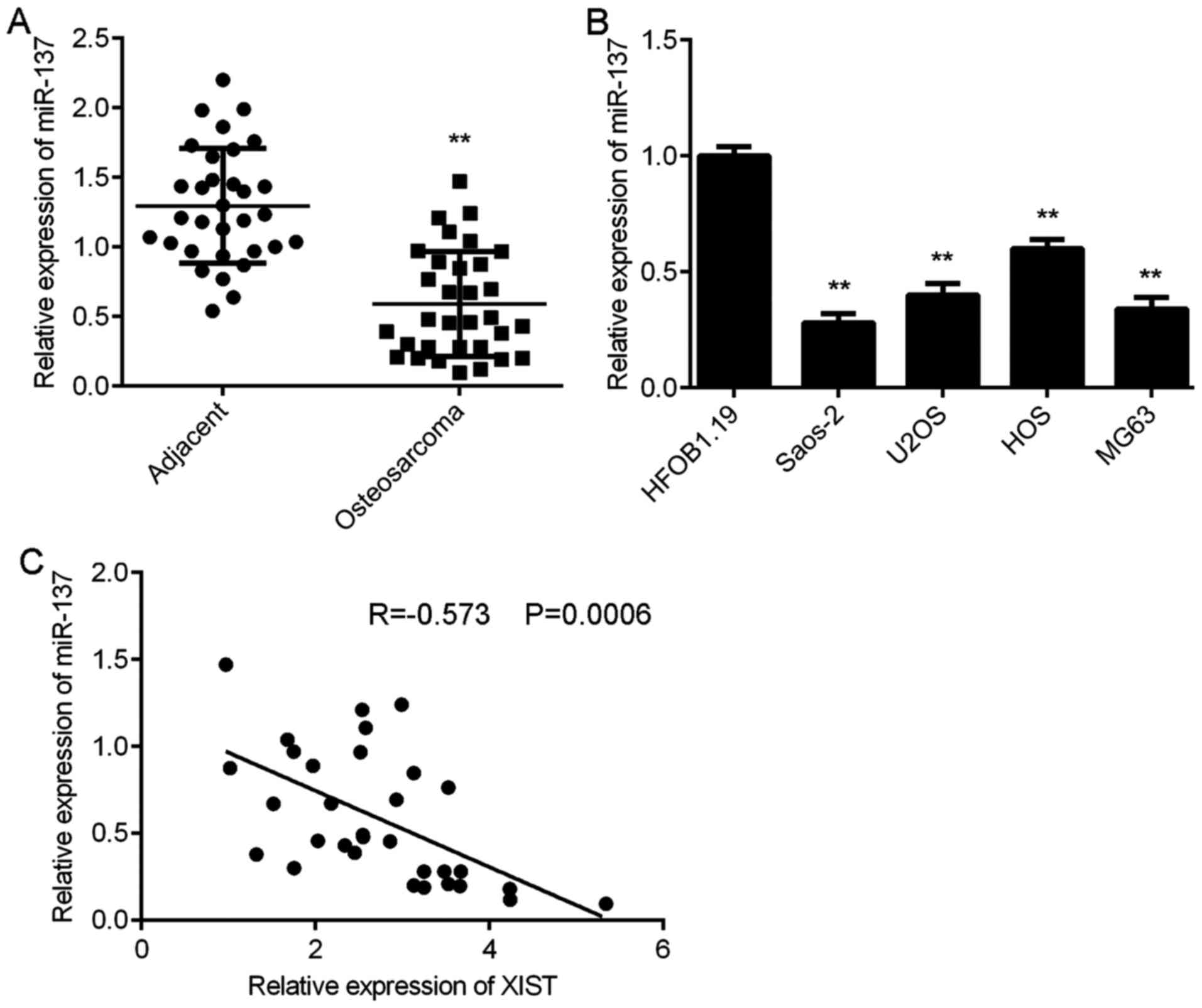
Li ZM, Zhang HY, Wang YX and Wang WB:
MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in human osteosarcoma and regulates
cell proliferation and migration through targeting FXYD6. J Drug
Target. 24:102–110. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|