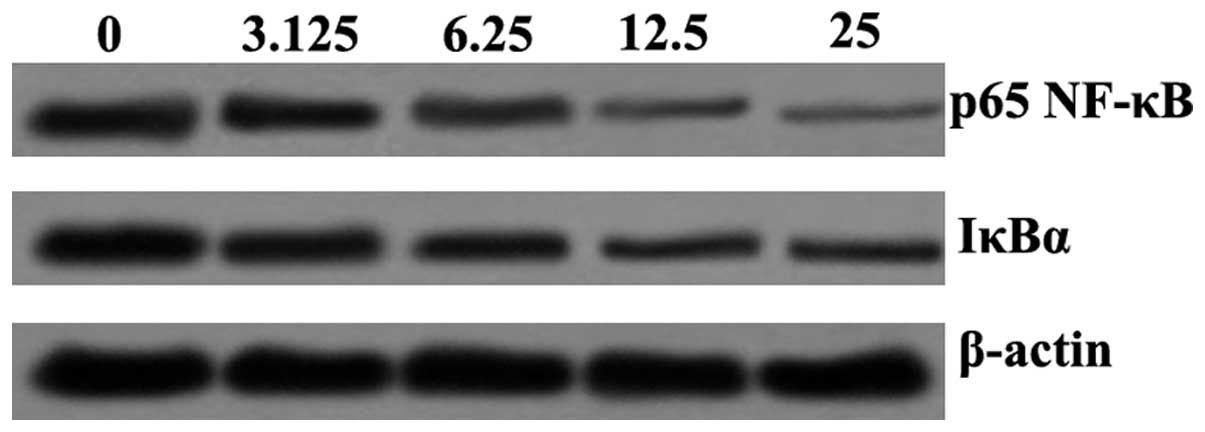
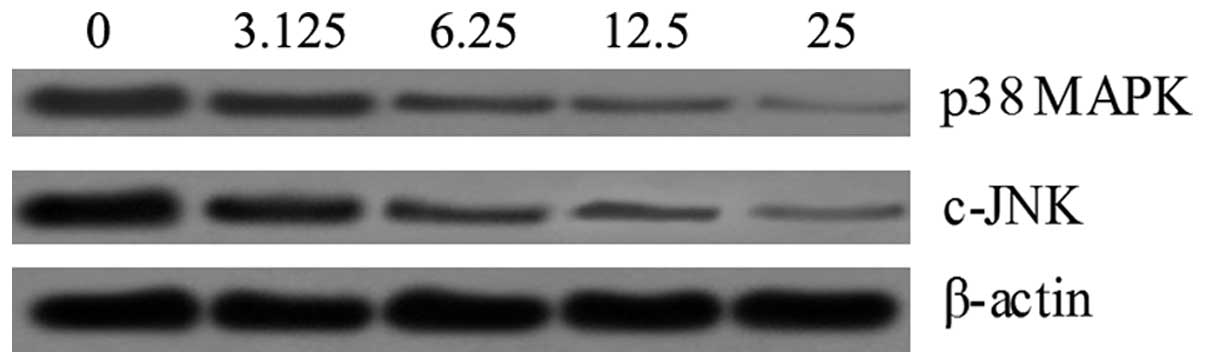
|
1.
|
Ashour ML and Wink M: Genus
Bupleurum: a review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology and
modes of action. J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:305–321. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Kong XY, Hao Y, Wu TX and Xie YM: Adverse
drug reactions or adverse events of Chaihu Injection: a systematic
review. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 8:1124–1132. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
3.
|
Wu GC, Wu H, Fan LY and Pan HF:
Saikosaponins: a potential treatment option for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Ir J Med Sci. 180:259–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Sui C, Zhang J, Wei J, et al:
Transcriptome analysis of Bupleurum chinense focusing on
genes involved in the biosynthesis of saikosaponins. BMC Genomics.
12:5392011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lu CN, Yuan ZG, Zhang XL, et al:
Saikosaponin a and its epimer saikosaponin d exhibit
anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing activation of NF-kappaB
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:121–126. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Philippou A, Maridaki M, Theos A and
Koutsilieris M: Cytokines in muscle damage. Adv Clin Chem.
58:49–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Lee IT and Yang CM: Role of NADPH
oxidase/ROS in pro-inflammatory mediators-induced airway and
pulmonary diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:581–590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Romeo GR, Lee J and Shoelson SE: Metabolic
syndrome, insulin resistance and roles of inflammation - mechanisms
and therapeutic targets. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:1771–1776. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Wang Y, Yu C, Pan Y, et al: A novel
compound C12 inhibits inflammatory cytokine production and protects
from inflammatory injury in vivo. PLoS One. 6:e243772011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Borges MC, Vinolo MA, Crisma AR, et al:
High-fat diet blunts activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB
signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peritoneal
macrophages of Wistar rats. Nutrition. Oct 19–2012.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
11.
|
Paulsen G, Mikkelsen UR, Raastad T and
Peake JM: Leucocytes, cytokines and satellite cells: what role do
they play in muscle damage and regeneration following eccentric
exercise? Exerc Immunol Rev. 18:42–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ren G, Zhao X, Zhang L, et al:
Inflammatory cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in mesenchymal stem cells are
critical for immunosuppression. J Immunol. 184:2321–2328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Wu YH, Chuang SY, Hong WC, Lai YJ, Chang
GJ and Pang JH: Berberine reduces leukocyte adhesion to
LPS-stimulated endothelial cells and VCAM-1 expression both in vivo
and in vitro. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 25:741–750.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Shao J, Liu T, Xie QR, et al: Adjudin
attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- and ischemia-induced
microglial activation. J Neuroimmunol. 254:83–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Sohn KH, Jo MJ, Cho WJ, et al:
Bojesodok-eum, a herbal prescription, ameliorates acute
inflammation in association with the inhibition of
NF-kappaB-mediated nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokine
production. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012 Oct
8–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
16.
|
Cortez M, Carmo LS, Rogero MM, Borelli P
and Fock RA: A high-fat diet increases IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-alpha
production by increasing NF-kappaB and attenuating PPAR-gamma
expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Inflammation. Oct
19–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
17.
|
Xie GC and Duan ZJ: Signal transduction of
innate immunity to virus infection. Bing Du Xue Bao. 28:303–310.
2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
18.
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian MAPK
signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation:
a 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 92:689–737. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Gyorfy Z, Duda E and Vizler C:
Interactions between LPS moieties and macrophage pattern
recognition receptors. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. Sep 26–2012.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
20.
|
Liu Z, Li W, Wang F, et al: Enhancement of
lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide and interleukin-6
production by PEGylated gold nanoparticles in RAW264.7 cells.
Nanoscale. Oct 16–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
21.
|
Tacchi L, Casadei E, Bickerdike R,
Secombes CJ and Martin SA: MULAN related gene (MRG): A potential
novel ubiquitin ligase activator of NF-kB involved in immune
response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Dev Comp Immunol.
38:545–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M:
NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol
Rev. 246:379–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Iwai K: Diverse ubiquitin signaling in
NF-kappaB activation. Trends Cell Biol. 22:355–364. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Dyson HJ and Komives EA: Role of disorder
in IkappaB-NFkappaB interaction. IUBMB Life. 64:499–505. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Tang X and Zhu Y: TLR4 signaling promotes
immune escape of human colon cancer cells by inducing
immunosuppressive cytokines and apoptosis resistance. Oncol Res.
20:15–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Wang Z, Jiang W, Zhang Z, Qian M and Du B:
Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines
production via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 144:145–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Cheng W, Chen L, Yang S, et al: Puerarin
suppresses proliferation of endometriotic stromal cells partly via
the MAPK signaling pathway induced by 17ss-estradiol-BSA. PLoS One.
7:e455292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ihara H, Yamamoto H, Ida T, et al:
Inhibition of nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide
synthase expression by a polymethoxyflavone from young fruits of
Citrus unshiu in rat primary astrocytes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
76:1843–1848. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|