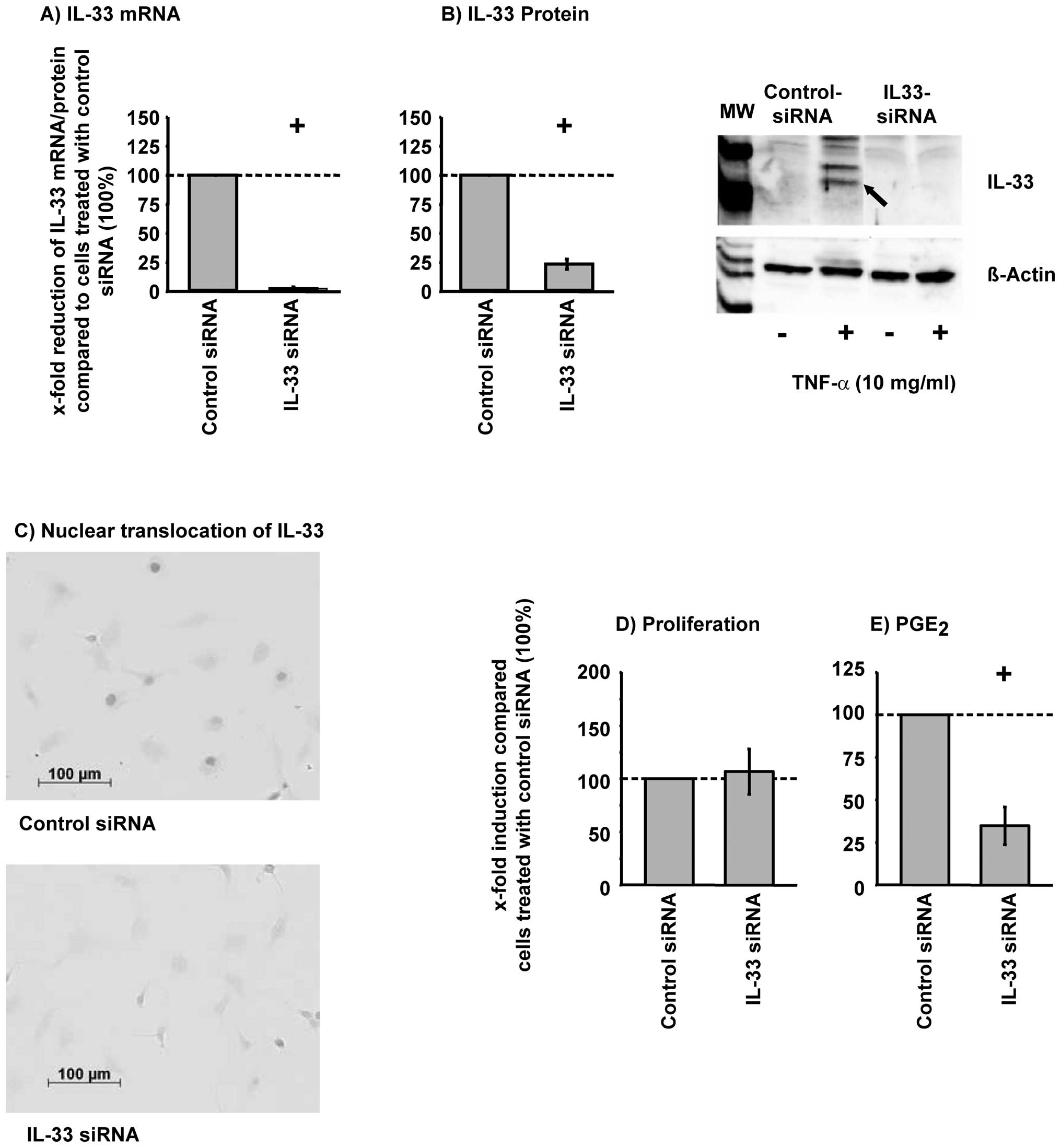
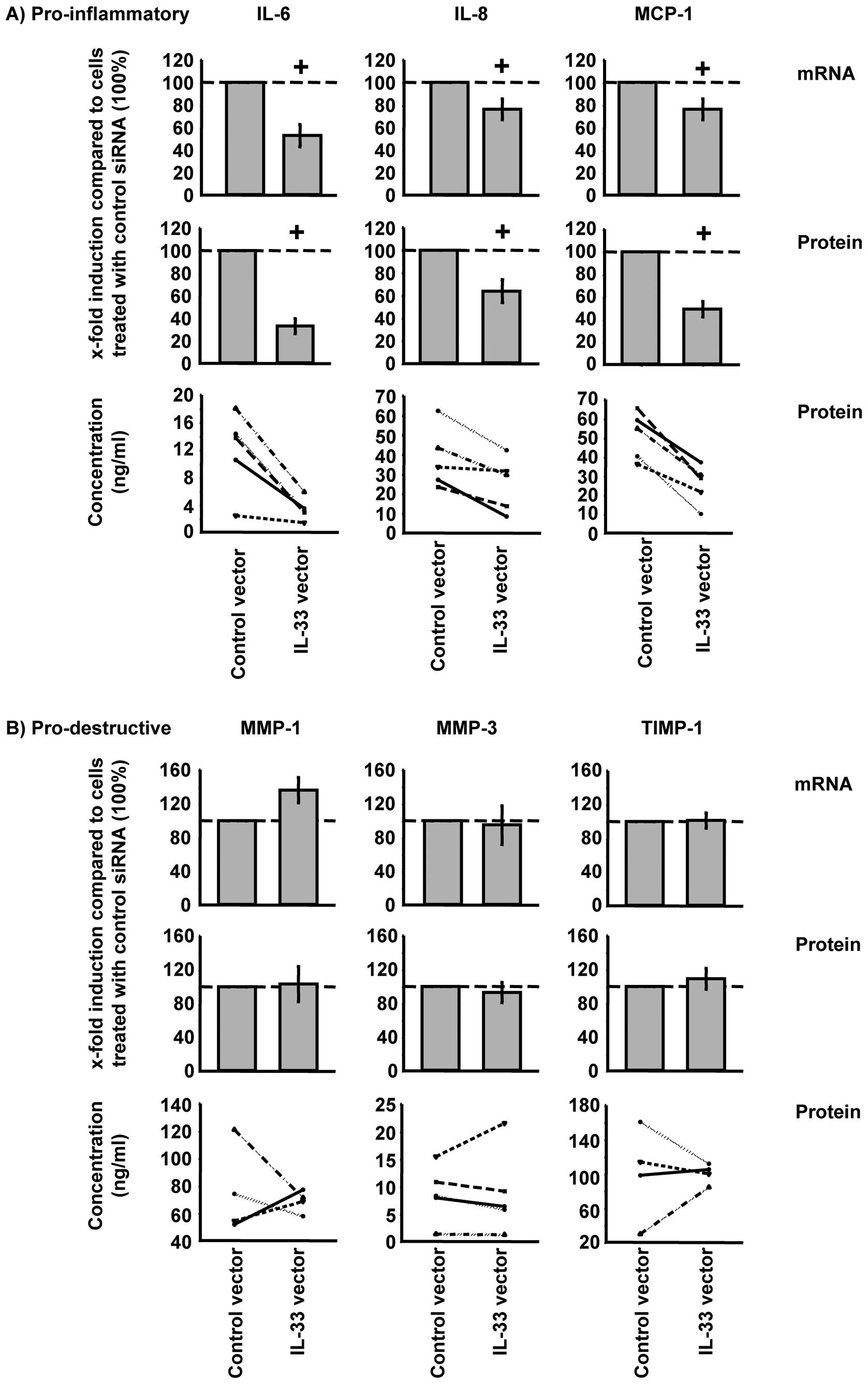
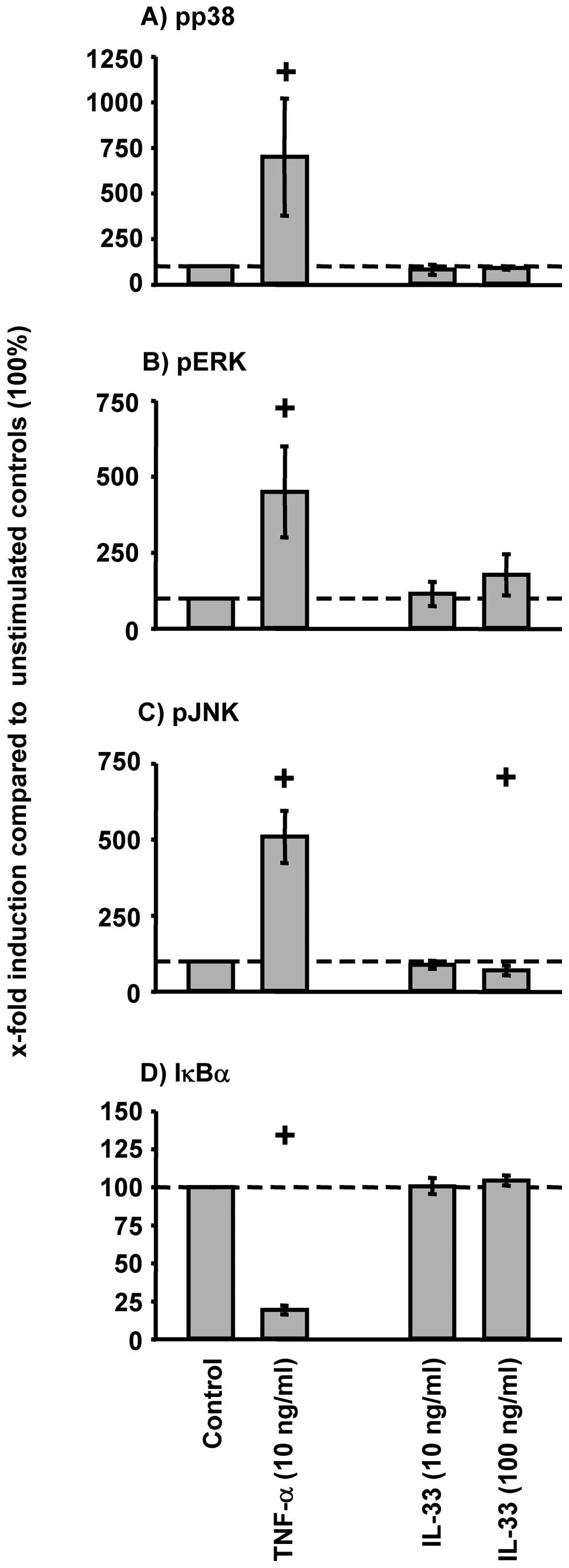
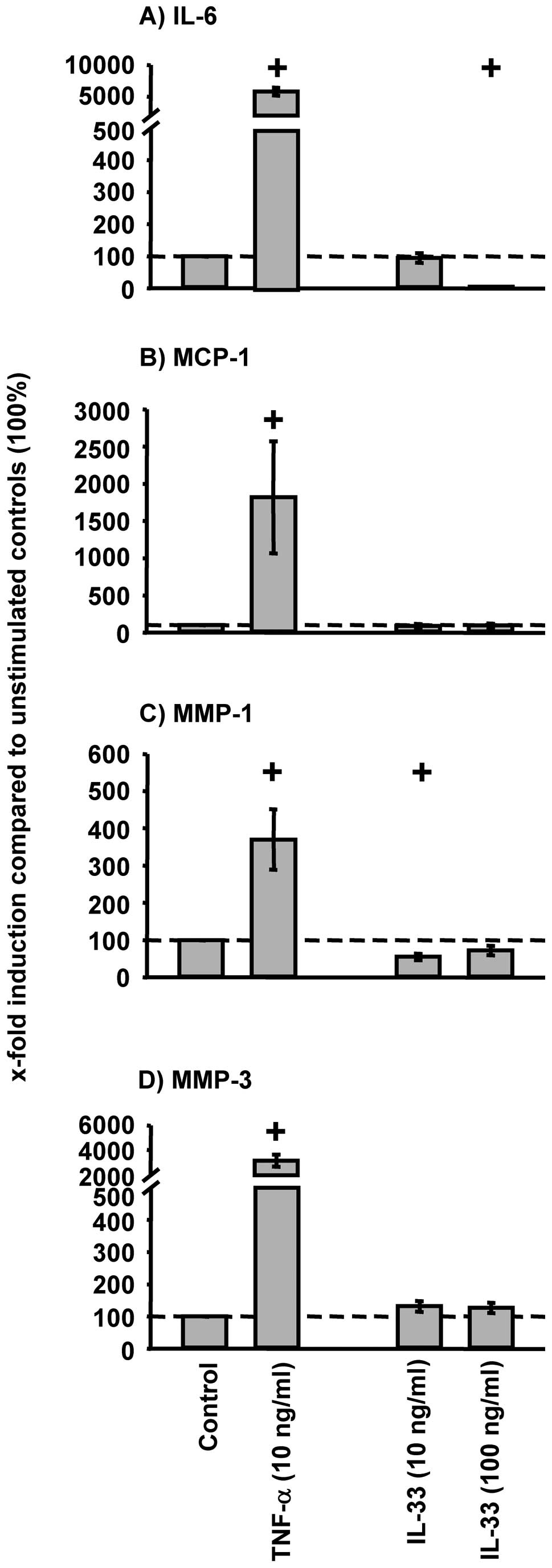
|
1
|
J SchmitzA OwyangE OldhamIL-33, an
interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated
cytokinesImmunity23479490200510.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.01516286016
|
|
2
|
ES BaekkevoldM RoussigneT
YamanakaMolecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor
preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venulesAm J
Pathol1636979200310.1016/S0002-9440(10)63631-012819012
|
|
3
|
V CarriereL RousselN OrtegaIL-33, the
IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a
chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivoProc Natl Acad Sci
USA104282287200710.1073/pnas.060685410417185418
|
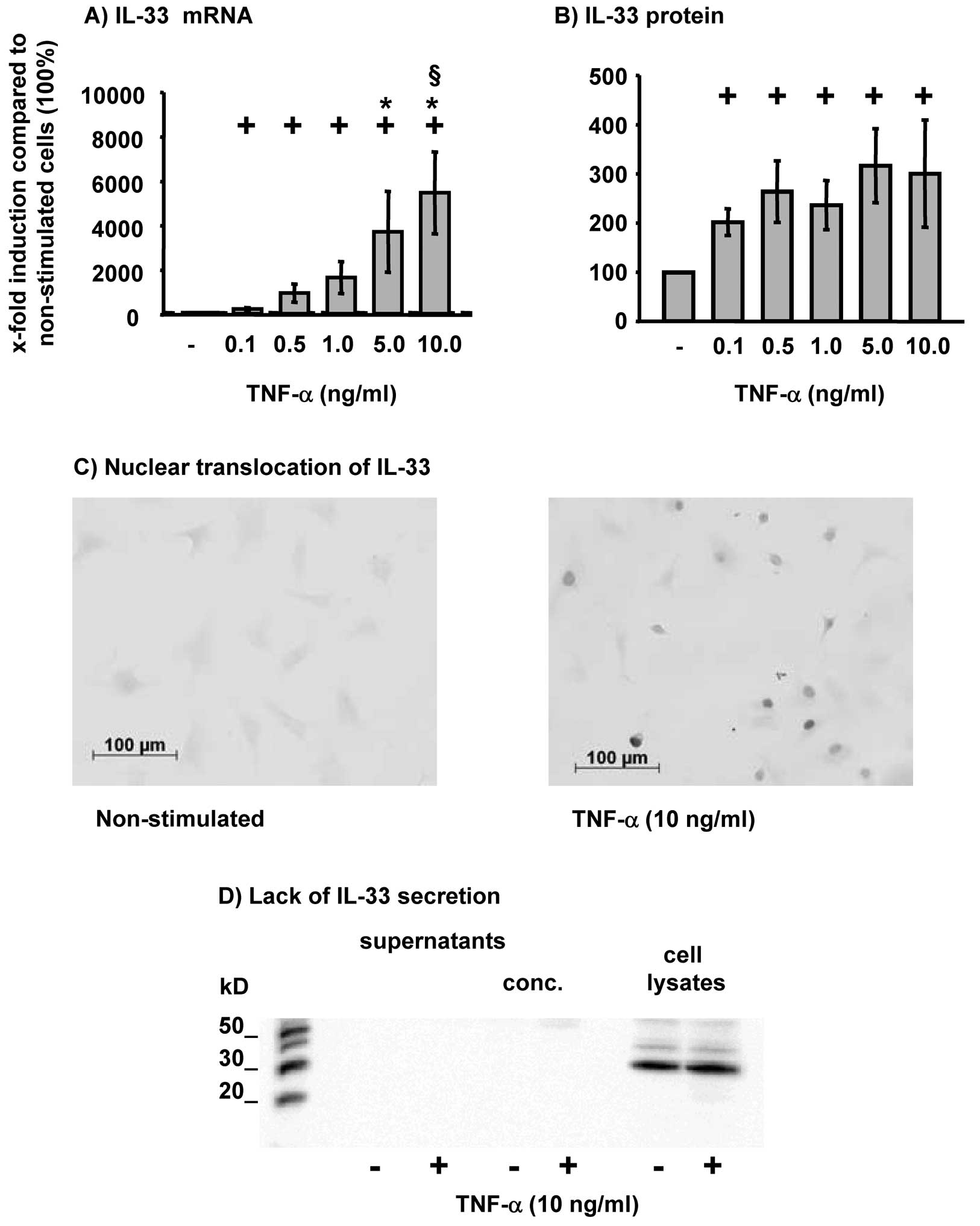
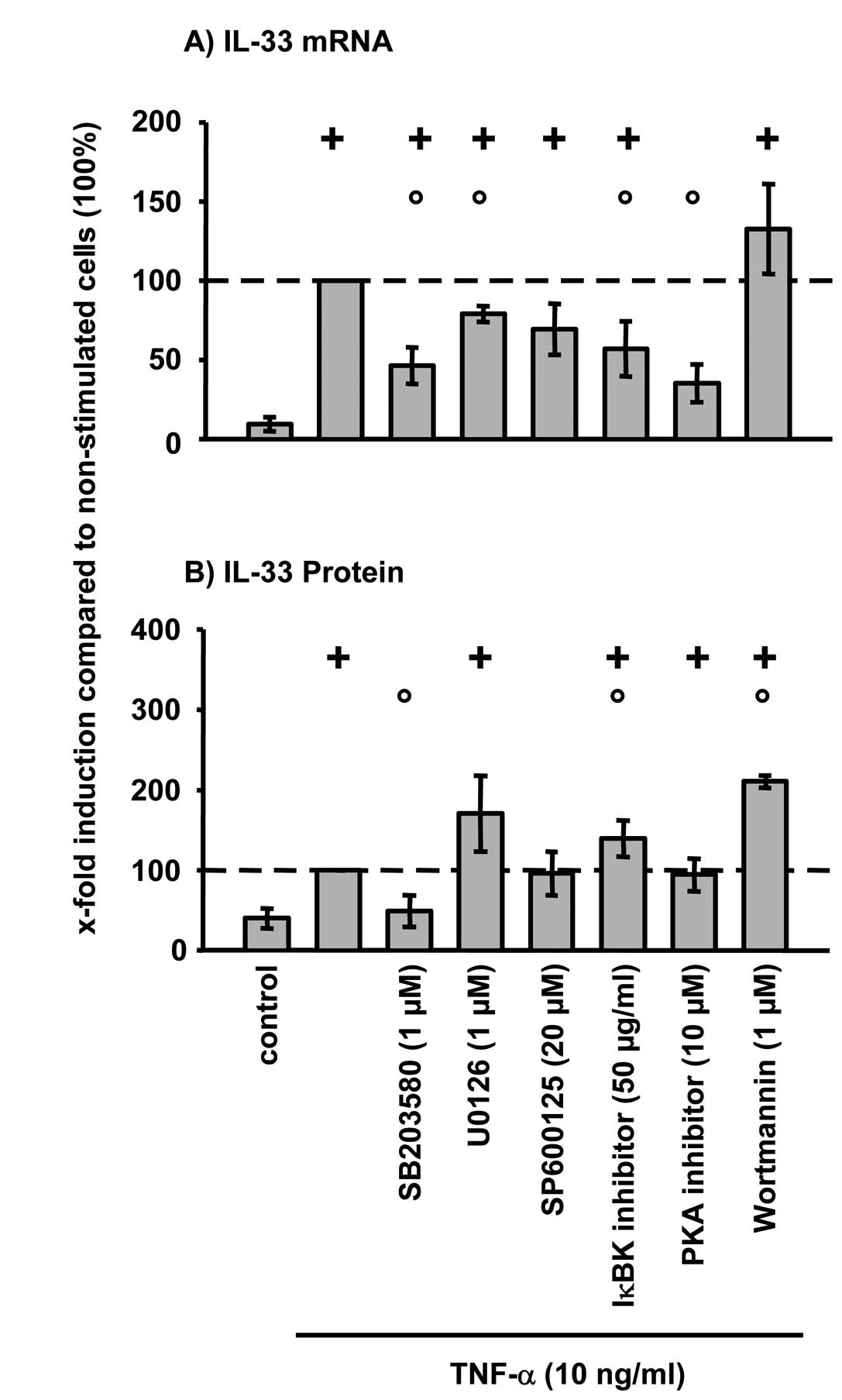
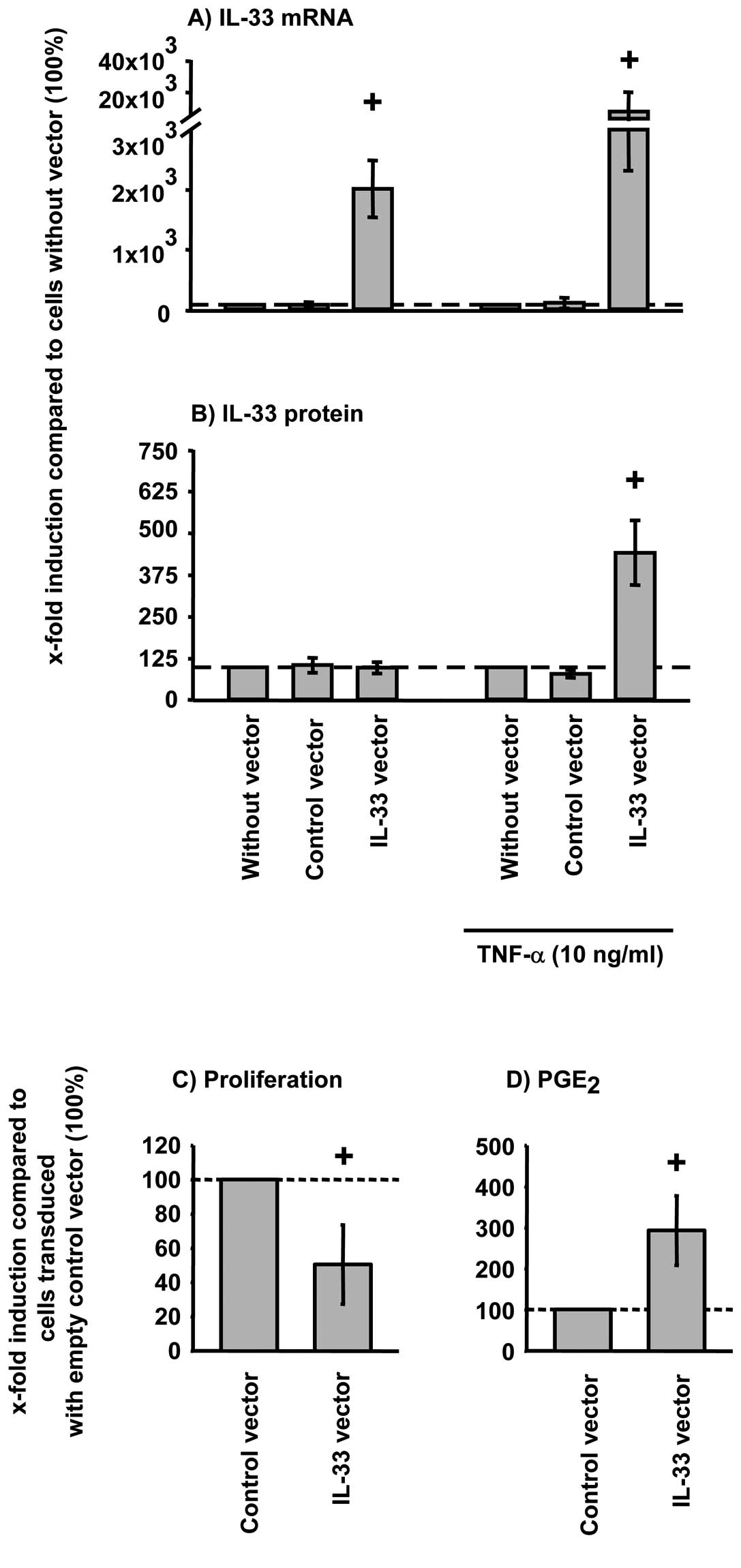
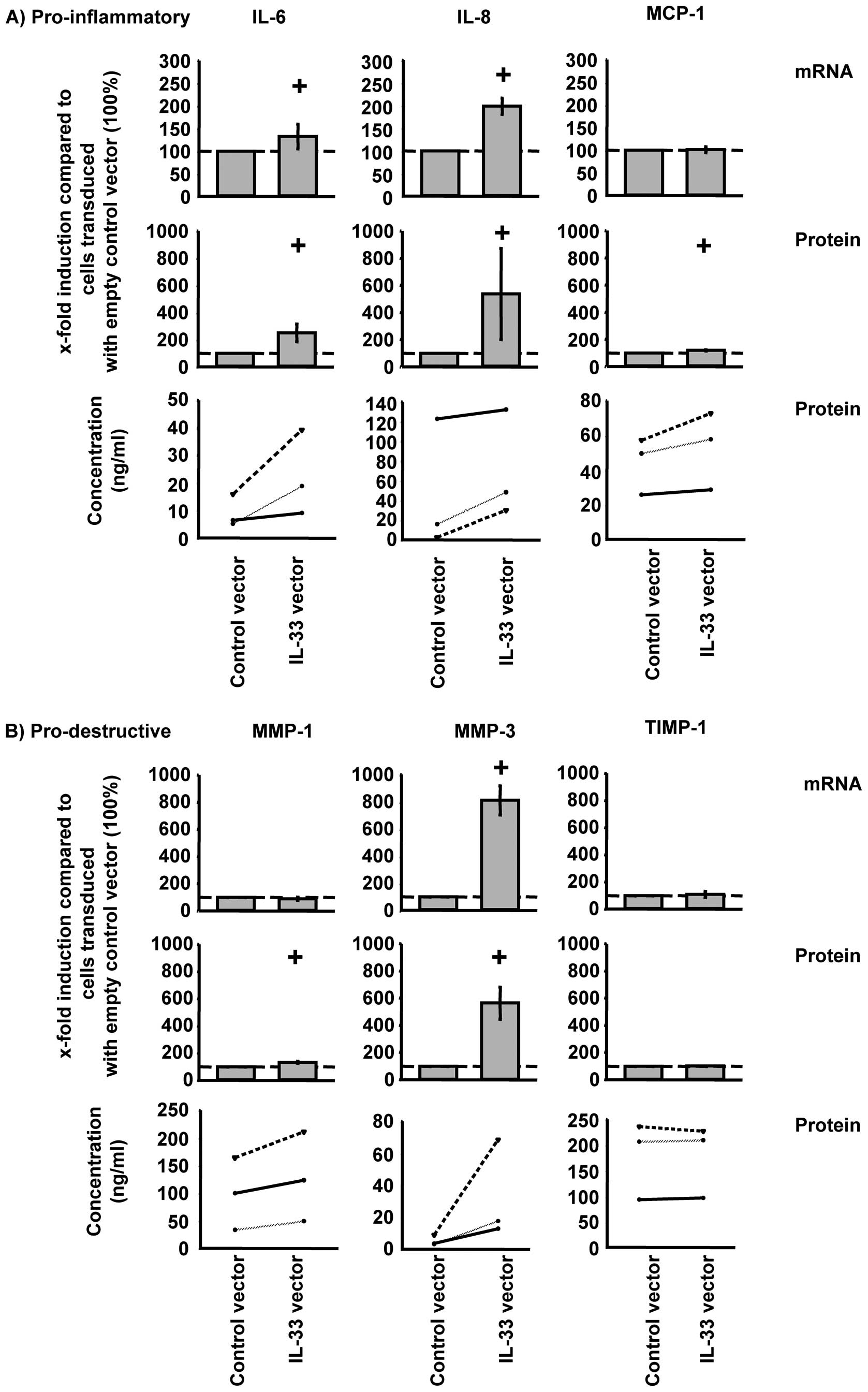
|
4
|
CA HudsonGP ChristophiRC GruberJR
WilmoreDA LawrencePT MassaInduction of IL-33 expression and
activity in central nervous system gliaJ Leukoc
Biol84631643200810.1189/jlb.120783018552204
|
|
5
|
AM KuchlerJ PollheimerJ BaloghNuclear
interleukin-33 is generally expressed in resting endothelium but
rapidly lost upon angiogenic or proinflammatory activationAm J
Pathol17312291242200810.2353/ajpath.2008.08001418787100
|
|
6
|
M IikuraH SutoN KajiwaraIL-33 can promote
survival, adhesion and cytokine production in human mast cellsLab
Invest87971978200710.1038/labinvest.370066317700564
|
|
7
|
D MoulinO DonzeD Talabot-AyerF MezinG
PalmerC GabayInterleukin (IL)-33 induces the release of
pro-inflammatory mediators by mast
cellsCytokine40216225200710.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.01318023358
|
|
8
|
R KakkarRT LeeThe IL-33/ST2 pathway:
therapeutic target and novel biomarkerNat Rev Drug
Discov7827840200810.1038/nrd266018827826
|
|
9
|
C CayrolJP GirardThe IL-1-like cytokine
IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA10690219026200910.1073/pnas.081269010619439663
|
|
10
|
C MoussionN OrtegaJP GirardThe IL-1-like
cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of
endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel
‘alarmin’?PLoS One3e3331200818836528
|
|
11
|
BP LeungD XuS CulshawIB McInnesFY LiewA
novel therapy of murine collagen-induced arthritis with soluble
T1/ST2J Immunol173145150200410.4049/jimmunol.173.1.14515210768
|
|
12
|
D XuHR JiangP KewinIL-33 exacerbates
antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cellsProc Natl Acad
Sci USA1051091310918200810.1073/pnas.080189810518667700
|
|
13
|
G PalmerD Talabot-AyerC
LamacchiaInhibition of interleukin-33 signaling attenuates the
severity of experimental arthritisArthritis
Rheum60738749200910.1002/art.2430519248109
|
|
14
|
WA Verri JrFO SoutoSM VieiraIL-33 induces
neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of
anti-TNF therapyAnn Rheum
Dis6916971703201010.1136/ard.2009.12265520472598
|
|
15
|
Y MatsuyamaH OkazakiH TamemotoIncreased
levels of interleukin 33 in sera and synovial fluid from patients
with active rheumatoid arthritisJ
Rheumatol371825201010.3899/jrheum.09049219918048
|
|
16
|
S KaiedaK ShinPA NigrovicSynovial
fibroblasts promote the expression and granule accumulation of
tryptase via interleukin-33 and its receptor ST-2 (IL1RL1)J Biol
Chem2852147821486201010.1074/jbc.M110.11499120427273
|
|
17
|
G PalmerS TrollietD Talabot-AyerF MezinD
MagneC GabayPre-interleukin-1alpha expression reduces cell growth
and increases interleukin-6 production in SaOS-2 osteosarcoma
cells: differential inhibitory effect of interleukin-1 receptor
antagonist
(icIL-1Ra1)Cytokine31153160200510.1016/j.cyto.2005.03.007
|
|
18
|
S SharmaN KulkMF NoldThe IL-1 family
member 7b translocates to the nucleus and down-regulates
proinflammatory cytokinesJ
Immunol18054775482200810.4049/jimmunol.180.8.547718390730
|
|
19
|
FC ArnettSM EdworthyDA BlochThe American
Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification
of rheumatoid arthritisArthritis
Rheum31315324198810.1002/art.17803103023358796
|
|
20
|
T ZimmermannE KunischR PfeifferIsolation
and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts
from primary culture - primary culture cells markedly differ from
fourth-passage cellsArthritis Res37276200110.1186/ar142
|
|
21
|
A HirthA SkapenkoRW KinneF EmmrichH
Schulze-KoopsU SackCytokine mRNA and protein expression in
primary-culture and repeated-passage synovial fibroblasts from
patients with rheumatoid arthritisArthritis
Res4117125200210.1186/ar39111879547
|
|
22
|
N SwaroopF ChenL WangS DokkaD ToledoY
RojanasakulInhibition of nuclear transcription factor-kappaB by
specific IkappaB kinase peptide inhibitorPharm
Res1816311633200110.1023/A:101305101909811758774
|
|
23
|
DB GlassHC ChengL Mende-MuellerJ ReedDA
WalshPrimary structural determinants essential for potent
inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by inhibitory peptides
corresponding to the active portion of the heat-stable inhibitor
proteinJ Biol Chem264880288101989
|
|
24
|
S AlsalamehRJ AminE KunischHE JasinRW
KinnePreferential induction of prodestructive matrix
metalloproteinase-1 and proinflammatory interleukin 6 and
prostaglandin E2 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via
tumor necrosis factor receptor-55J Rheumatol30168016902003
|
|
25
|
E KunischM GandesiriR FuhrmannA RothR
WinterRW KinnePredominant activation of MAP kinases and
pro-destructive/pro-inflammatory features by TNF alpha in
early-passage synovial fibroblasts via TNF receptor-1: failure of
p38 inhibition to suppress matrix metalloproteinase-1 in rheumatoid
arthritisAnn Rheum Dis6610431051200710.1136/ard.2006.062521
|
|
26
|
D PohlersA BeyerD KoczanT WilhelmHJ
ThiesenRW KinneConstitutive upregulation of the transforming growth
factor-beta pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial
fibroblastsArthritis Res Ther9R59200710.1186/ar221717594488
|
|
27
|
D PretzelD PohlersS WeinertRW KinneIn
vitro model for the analysis of synovial fibroblast-mediated
degradation of intact cartilageArthritis Res
Ther11R25200910.1186/ar261819226472
|
|
28
|
LM CarruthS DemczukSB MizelInvolvement of
a calpain-like protease in the processing of the murine interleukin
1 alpha precursorJ Biol Chem266121621216719912061304
|
|
29
|
WM SidersJC KlimovitzSB
MizelCharacterization of the structural requirements and cell type
specificity of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta secretionJ Biol
Chem268221702217419938408078
|
|
30
|
FM BrennanIB McInnesEvidence that
cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritisJ Clin
Invest11835373545200810.1172/JCI3638918982160
|
|
31
|
B GrimbacherWK AicherHH PeterH
EibelTNF-alpha induces the transcription factor Egr-1,
pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell proliferation in human skin
fibroblasts and synovial lining cellsRheumatol
Int17185192199810.1007/s0029600500329542779
|
|
32
|
H KitasatoM NodaT AkahoshiActivated Ras
modifies the proliferative response of rheumatoid synovial cells to
TNF-alpha and TGF-alphaInflamm
Res50592597200110.1007/PL0000023911822784
|
|
33
|
K AupperleB BennettZ HanD BoyleA ManningG
FiresteinNF-kappa B regulation by I kappa B kinase-2 in rheumatoid
arthritis synoviocytesJ
Immunol16627052711200110.4049/jimmunol.166.4.270511160335
|
|
34
|
Y TakadaH IchikawaA PataerS SwisherBB
AggarwalGenetic deletion of PKR abrogates TNF-induced activation of
IkappaBalpha kinase, JNK, Akt and cell proliferation but
potentiates p44/p42 MAPK and p38 MAPK
activationOncogene2612011212200710.1038/sj.onc.120990616924232
|
|
35
|
L RousselM ErardC CayrolJP GirardMolecular
mimicry between IL-33 and KSHV for attachment to chromatin through
the H2A-H2B acidic pocketEMBO
Rep910061012200810.1038/embor.2008.14518688256
|
|
36
|
M Funakoshi-TagoK TagoM HayakawaTRAF6 is a
critical signal transducer in IL-33 signaling pathwayCell
Signal2016791686200810.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.01318603409
|
|
37
|
T Pecaric-PetkovicSA DidichenkoS KaempferN
SpieglCA DahindenHuman basophils and eosinophils are the direct
target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member
IL-33Blood11315261534200910.1182/blood-2008-05-15781818955562
|
|
38
|
M SuzukawaM IikuraR KoketsuAn IL-1
cytokine member, IL-33, induces human basophil activation via its
ST2 receptorJ
Immunol18159815989200810.4049/jimmunol.181.9.598118941187
|
|
39
|
P BuflerF Gamboni-RobertsonT AzamSH KimCA
DinarelloInterleukin-1 homologues IL-1F7b and IL-18 contain
functional mRNA instability elements within the coding region
responsive to lipopolysaccharideBiochem
J381503510200410.1042/BJ2004021715046617
|