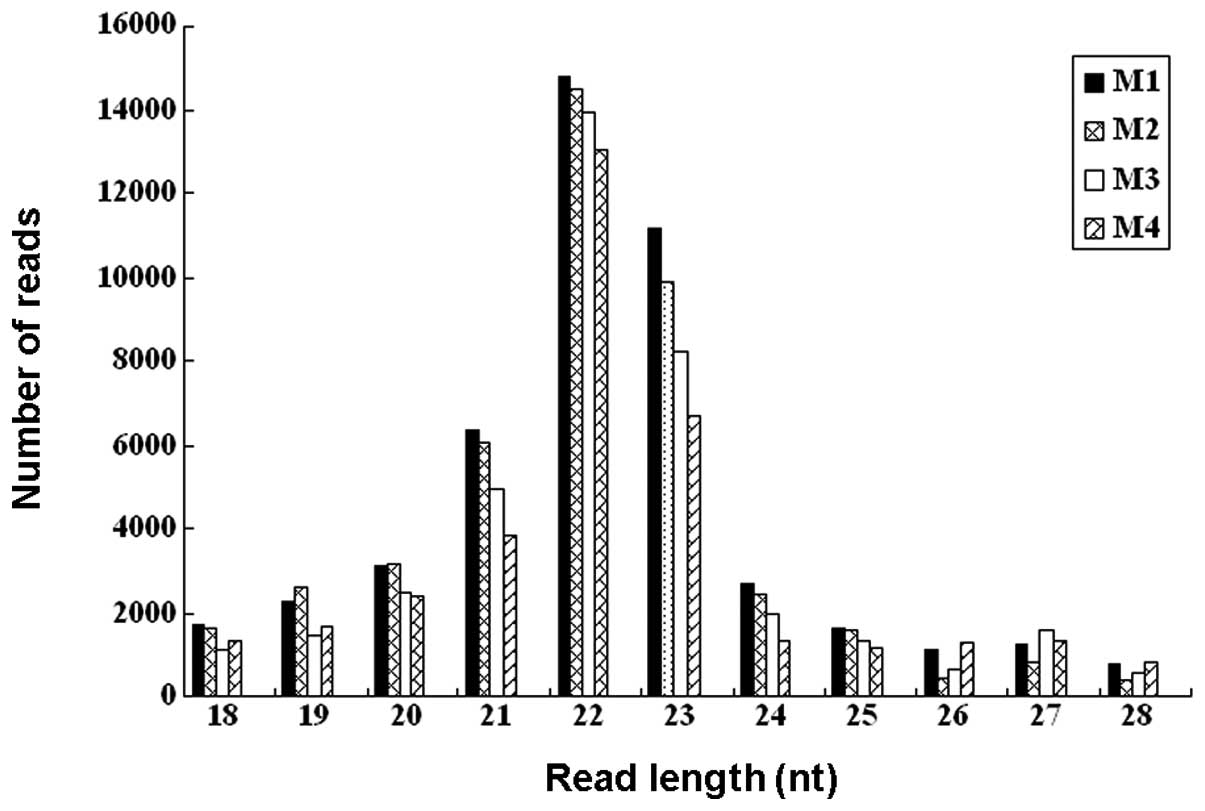
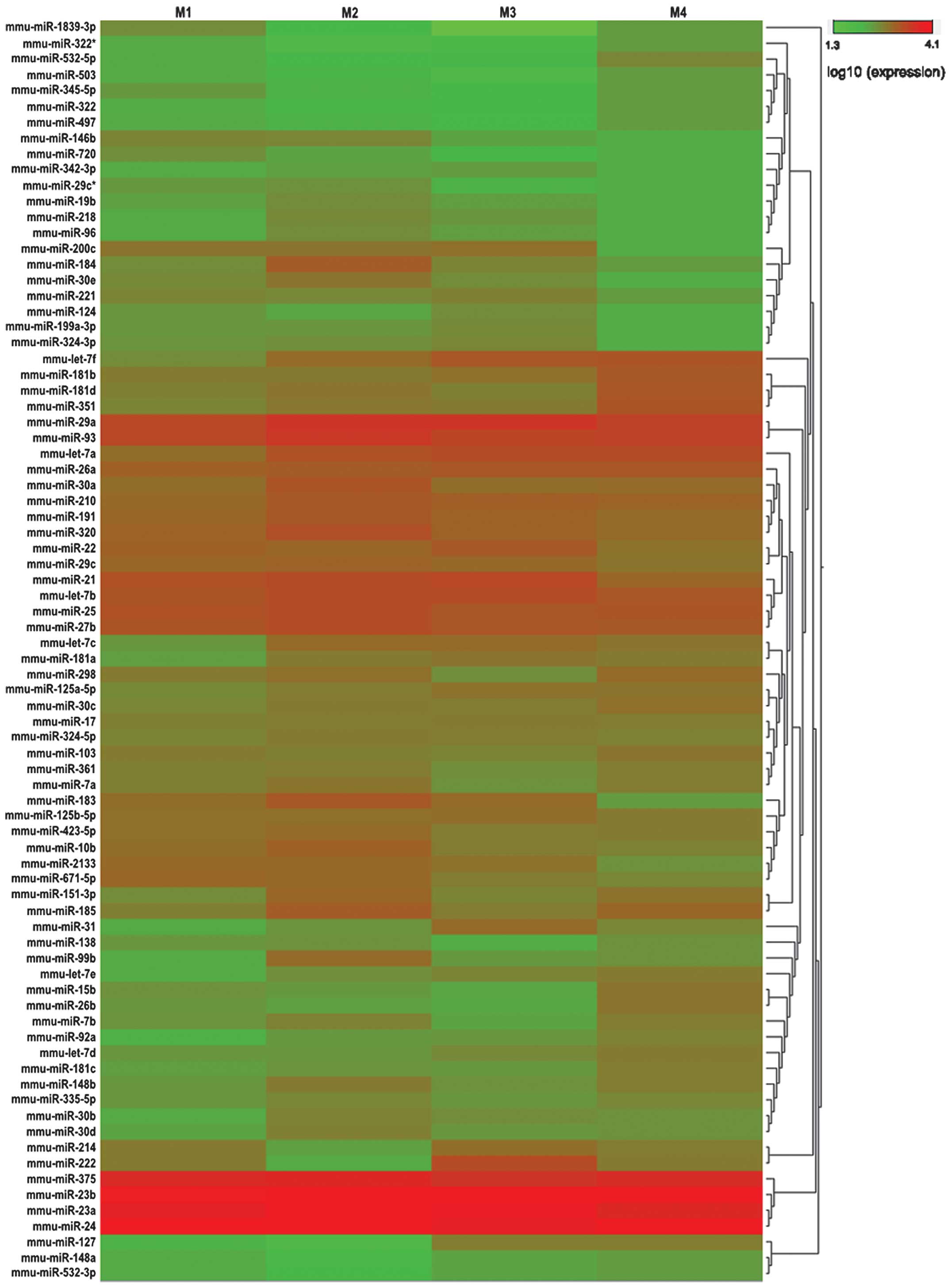
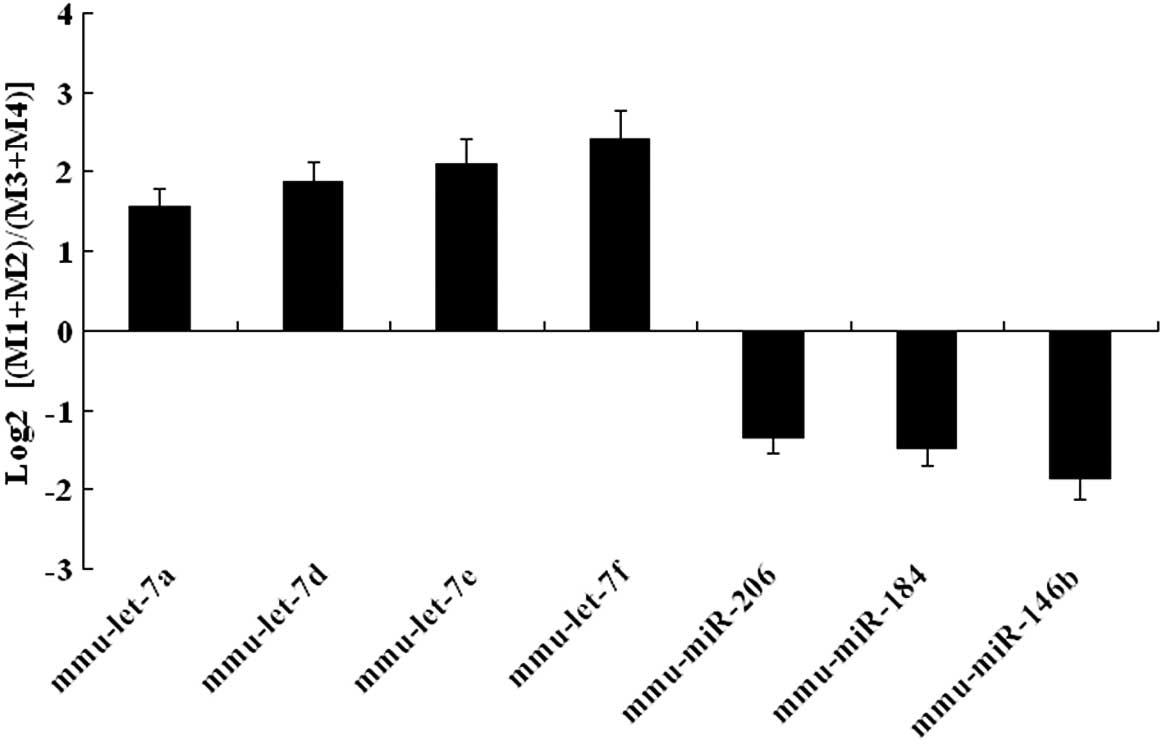
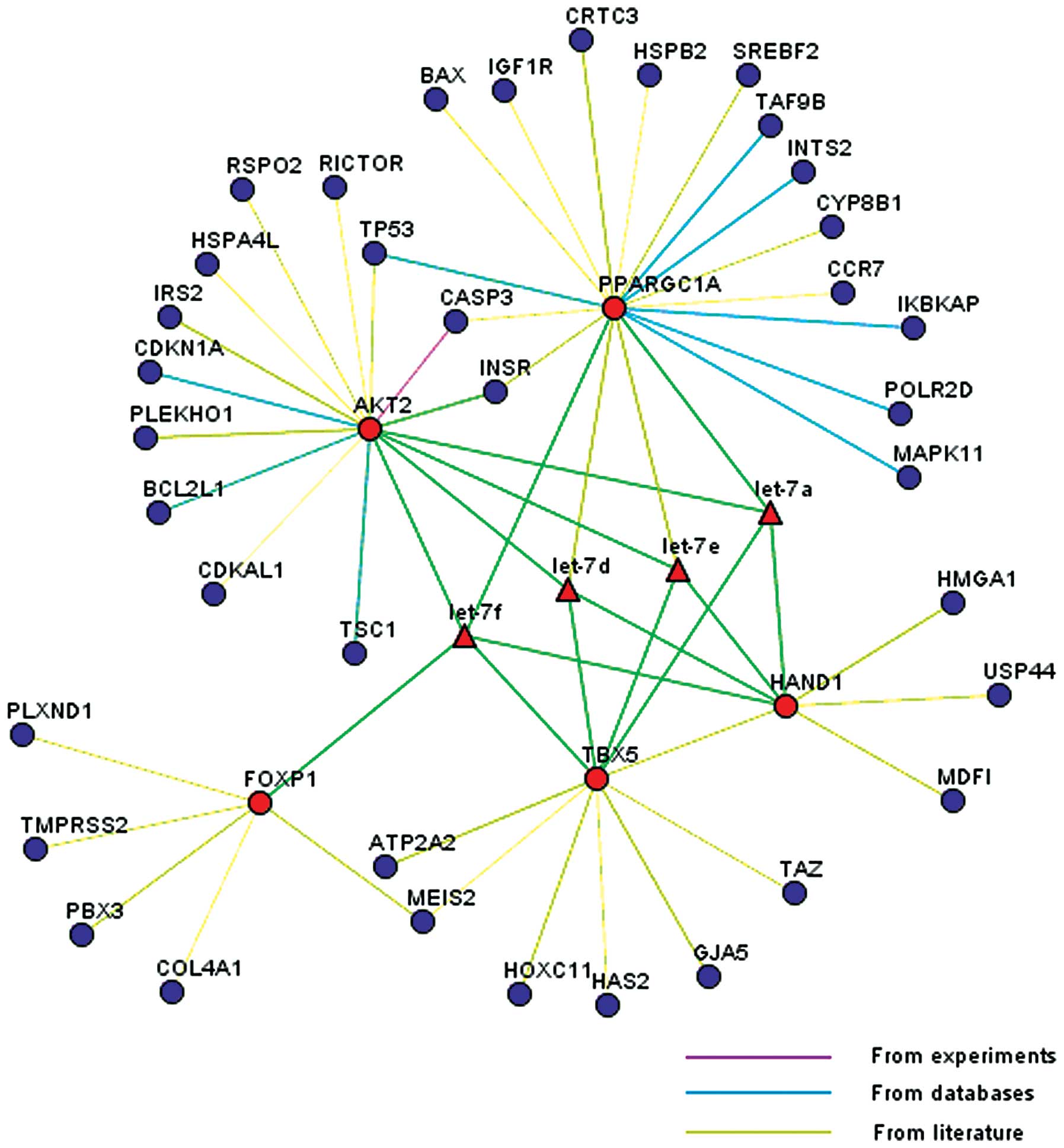
|
1.
|
DP BartelMicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis,
mechanism, and
functionCell116281297200410.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-514744438
|
|
2.
|
BP LewisCB BurgeDP BartelConserved seed
pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of
human genes are microRNA
targetsCell1201520200510.1016/j.cell.2004.12.03515652477
|
|
3.
|
Y LiangD RidzonL WongC
ChenCharacterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal
human tissuesBMC
Genomics8166200710.1186/1471-2164-8-16617565689
|
|
4.
|
E WienholdsWP KloostermanE MiskaE
Alvarez-SaavedraE BerezikovE de BruijnHR HorvitzS KauppinenRH
PlasterkMicroRNA expression in zebrafish embryonic
developmentScience309310311200510.1126/science.1114519
|
|
5.
|
M Lagos-QuintanaR RauhutA YalcinJ MeyerW
LendeckelT TuschlIdentification of tissue-specific microRNAs from
mouseCurr Biol12735739200210.1016/S0960-9822(02)00809-612007417
|
|
6.
|
L Hackler JrJ WanA SwaroopJ QianDJ
ZackMicroRNA profile of the developing mouse retinaInvest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci5118231831201010.1167/iovs.09-465719933188
|
|
7.
|
KH LingPJ BrautiganCN HahnT DaishJR
RaynerPS CheahJM RaisonS PiltzJR MannDM MattiskeDeep sequencing
analysis of the developing mouse brain reveals a novel microRNABMC
Genomics12176201110.1186/1471-2164-12-17621466694
|
|
8.
|
B LiuGR CunhaLS BaskinDifferential
expression of microRNAs in mouse embryonic bladderBiochem Biophys
Res Commun385528533200910.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.08819470377
|
|
9.
|
T ThumD CatalucciJ BauersachsMicroRNAs:
novel regulators in cardiac development and diseaseCardiovasc
Res79562570200810.1093/cvr/cvn13718511432
|
|
10.
|
D SayedC HongIY ChenJ LypowyM
AbdellatifMicroRNAs play an essential role in the development of
cardiac hypertrophyCirc
Res100416424200710.1161/01.RES.0000257913.42552.2317234972
|
|
11.
|
C SucharovMR BristowJD PortmiRNA
expression in the failing human heart: functional correlatesJ Mol
Cell Cardiol45185192200810.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.04.01418582896
|
|
12.
|
RE vanLB SutherlandJE ThatcherJM DiMaioRH
NaseemWS MarshallJA HillEN OlsonDysregulation of microRNAs after
myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac
fibrosisProc Natl Acad Sci
USA1051302713032200810.1073/pnas.080503810518723672
|
|
13.
|
A CareD CatalucciF FelicettiD BonciA
AddarioP GalloML BangP SegnaliniY GuND DaltonMicroRNA-133 controls
cardiac hypertrophyNat Med13613618200710.1038/nm158217468766
|
|
14.
|
RE vanLB SutherlandX QiJA RichardsonJ
HillEN OlsonControl of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene
expression by a
microRNAScience316575579200710.1126/science.113908917379774
|
|
15.
|
Y ZhaoJF RansomA LiV VedanthamM von
DrehleAN MuthT TsuchihashiMT McManusRJ SchwartzD
SrivastavaDysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and
cell cycle in mice lacking
miRNA-1-2Cell129303317200710.1016/j.cell.2007.03.03017397913
|
|
16.
|
N LiuEN OlsonMicroRNA regulatory networks
in cardiovascular developmentDev
Cell18510525201010.1016/j.devcel.2010.03.01020412767
|
|
17.
|
A StarkJ BrenneckeN BushatiRB RussellSM
CohenAnimal MicroRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have
a significant impact on 3′UTR
evolutionCell12311331146200516337999
|
|
18.
|
A ChinchillaE LozanoH DaimiFJ EstebanC
CristAE AranegaD FrancoMicroRNA profiling during mouse ventricular
maturation: a role for miR-27 modulating Mef2c expressionCardiovasc
Res8998108201110.1093/cvr/cvq26420736237
|
|
19.
|
A WesselsD SedmeraDevelopmental anatomy of
the heart: a tale of mice and manPhysiol
Genomics15165176200310.1152/physiolgenomics.00033.200314612588
|
|
20.
|
SM SavolainenJF FoleySA ElmoreHistology
atlas of the developing mouse heart with emphasis on E11.5 to
E18.5Toxicol Pathol37395414200910.1177/019262330933506019359541
|
|
21.
|
ZB YuSP HanYF BaiC ZhuY PanXR GuomicroRNA
expression profiling in fetal single ventricle malformation
identified by deep sequencingInt J Mol Med295360201221935567
|
|
22.
|
X WangX WangSystematic identification of
microRNA functions by combining target prediction and expression
profilingNucleic Acids
Res3416461652200610.1093/nar/gkl06816549876
|
|
23.
|
P LandgrafM RusuR SheridanA SewerN IovinoA
AravinS PfefferA RiceAO KamphorstM LandthalerA mammalian microRNA
expression atlas based on small RNA library
sequencingCell12914011414200710.1016/j.cell.2007.04.04017604727
|
|
24.
|
PK RaoY ToyamaHR ChiangS GuptaM BauerR
MedvidF ReinhardtR LiaoM KriegerR JaenischLoss of cardiac
microRNA-mediated regulation leads to dilated cardiomyopathy and
heart failureCirc
Res105585594200910.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.20045119679836
|
|
25.
|
S TakadaE BerezikovY YamashitaM
Lagos-QuintanaWP KloostermanM EnomotoH HatanakaS FujiwaraH
WatanabeM SodaMouse microRNA profiles determined with a new and
sensitive cloning methodNucleic Acids
Res34e115200610.1093/nar/gkl65316973894
|
|
26.
|
J WangY SongY ZhangH XiaoQ SunN HouS GuoY
WangK FanD ZhanCardiomyocyte overexpression of miR-27b induces
cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction in miceCell
Res22516527201210.1038/cr.2011.13221844895
|
|
27.
|
K WangZQ LinB LongJH LiJ ZhouPF LiCardiac
hypertrophy is positively regulated by MicroRNA miR-23aJ Biol
Chem287589599201210.1074/jbc.M111.26694022084234
|
|
28.
|
RE vanLB SutherlandN LiuAH WilliamsJ
McAnallyRD GerardJA RichardsonEN OlsonA signature pattern of
stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and
heart failureProc Natl Acad Sci
USA1031825518260200610.1073/pnas.060879110317108080
|
|
29.
|
MR SuhY LeeJY KimSK KimSH MoonJY LeeKY
ChaHM ChungHS YoonSY MoonHuman embryonic stem cells express a
unique set of microRNAsDev
Biol270488498200410.1016/j.ydbio.2004.02.01915183728
|
|
30.
|
D SayedM HeC HongS GaoS RaneZ YangM
AbdellatifMicroRNA-21 is a downstream effector of AKT that mediates
its antiapoptotic effects via suppression of Fas ligandJ Biol
Chem2852028120290201010.1074/jbc.M110.10920720404348
|
|
31.
|
V DivakaranJ AdrogueM IshiyamaML EntmanS
HaudekN SivasubramanianDL MannAdaptive and maladptive effects of
SMAD3 signaling in the adult heart after hemodynamic pressure
overloadingCirc Heart
Fail2633642200910.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.82307019919989
|
|
32.
|
PA Da Costa MartinsLJ De WindtMicroRNAs in
control of cardiac hypertrophyCardiovasc
Res93563572201222266752
|
|
33.
|
Y D’AlessandraP DevannaF LimanaS StrainoCA
DiPG BrambillaM RubinoMC CarenaL SpazzafumoM De SimoneCirculating
microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial
infarctionEur Heart J3127652773201020534597
|
|
34.
|
V DivakaranDL MannThe emerging role of
microRNAs in cardiac remodeling and heart failureCirc
Res10310721083200810.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.18308718988904
|
|
35.
|
S WangAB AuroraBA JohnsonX QiJ McAnallyJA
HillJA RichardsonR Bassel-DubyEN OlsonThe endothelial-specific
microRNA miR-126 governs vascular integrity and angiogenesisDev
Cell15261271200810.1016/j.devcel.2008.07.00218694565
|
|
36.
|
F FaziC NerviMicroRNA: basic mechanisms
and transcriptional regulatory networks for cell fate
determinationCardiovasc
Res79553561200810.1093/cvr/cvn15118539629
|
|
37.
|
X LiuY ChengS ZhangY LinJ YangC ZhangA
necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasiaCirc
Res104476487200910.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.18536319150885
|
|
38.
|
P GurhaC Abreu-GoodgerT WangMO RamirezAL
DrumondS van DongenY ChenN BartonicekAJ EnrightB LeeTargeted
deletion of microRNA-22 promotes stress induced cardiac dilation
and contractile
dysfunctionCirculation12527512761201210.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.04435422570371
|
|
39.
|
M HanZ YangD SayedM HeS GaoL LinS YoonM
AbdellatifGATA4 expression is primarily regulated via a
miR-26b-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism during cardiac
hypertrophyCardiovasc Res93645654201210.1093/cvr/cvs00122219180
|
|
40.
|
VK KhodiyarDP HillD HoweTZ BerardiniS
TweediePJ TalmudR BreckenridgeS BhattarcharyaP RileyP ScamblerRC
LoveringThe representation of heart development in the gene
ontologyDev Biol354917201110.1016/j.ydbio.2011.03.01121419760
|