|
1.
|
L SehulsterRY ChinnCDC; HICPACGuidelines
for environmental infection control in health-care facilities.
Recommendations of CDC and the Healthcare Infection Control
Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC)MMWR Recomm Rep521422003
|
|
2.
|
N RajapakseE SilvaA KortenkampCombining
xenoestrogens at levels below individual no-observed-effect
concentrations dramatically enhances steroid hormone actionEnviron
Health Perspect110917921200210.1289/ehp.02110917
|
|
3.
|
S JinF YangT LiaoY HuiS WenY XuEnhanced
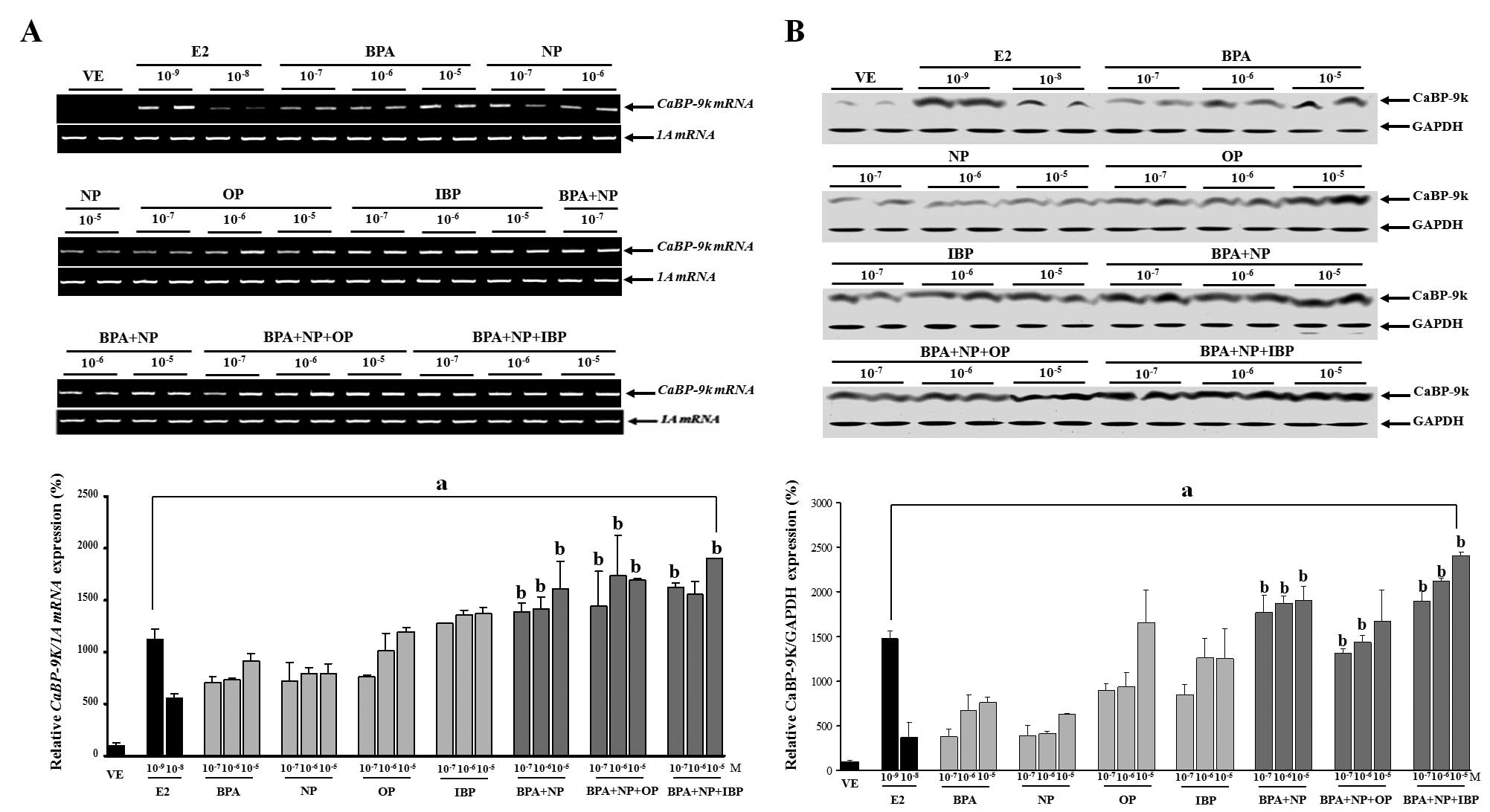
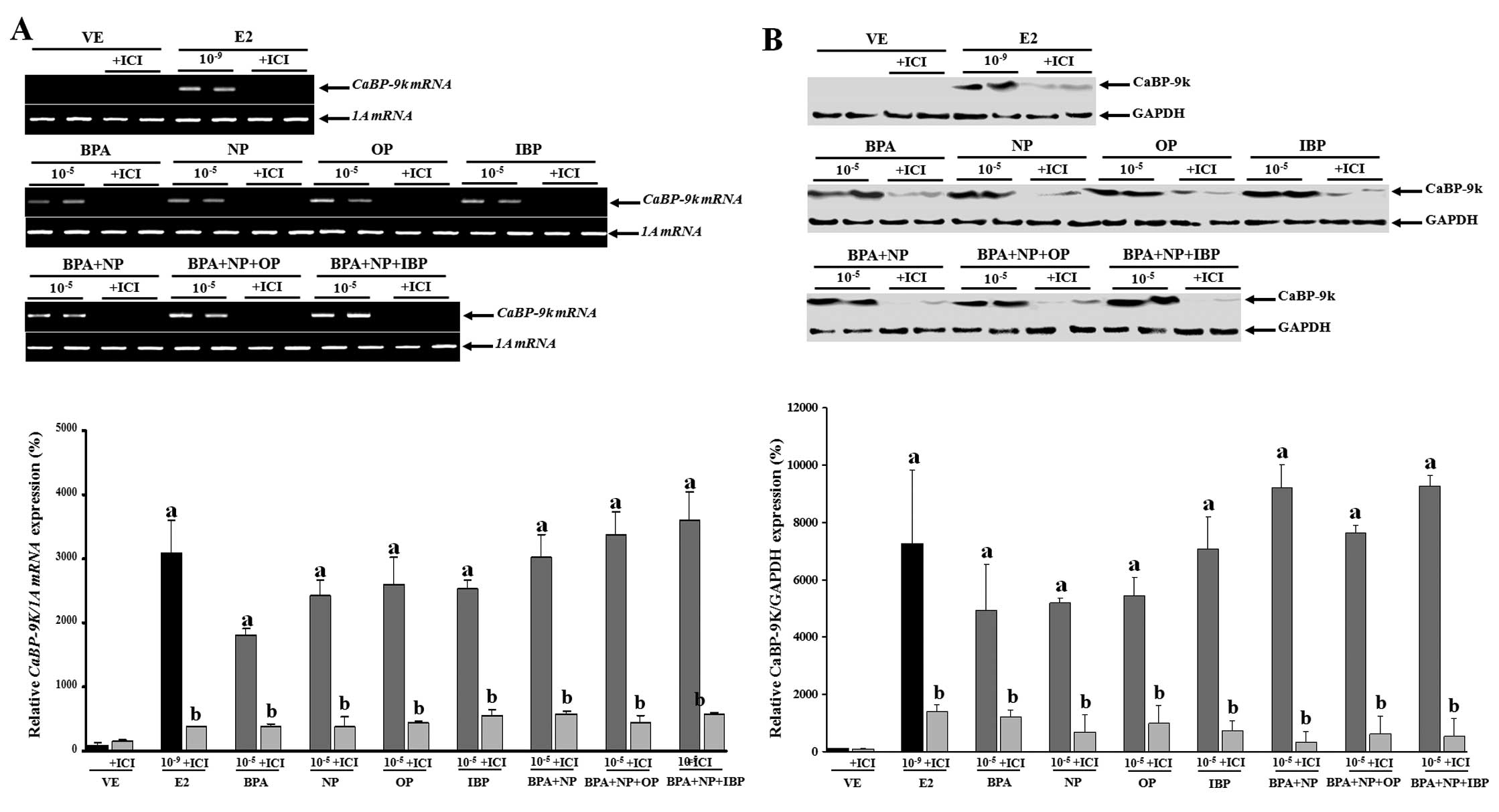
effects by mixtures of three estrogenic compounds at
environmentally relevant levels on development of Chinese rare
minnow (Gobiocypris rarus)Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol33277283201110.1016/j.etap.2011.12.01622240186
|
|
4.
|
JV BrianCA HarrisM ScholzeAccurate
prediction of the response of freshwater fish to a mixture of
estrogenic chemicalsEnviron Health
Perspect113721728200510.1289/ehp.759815929895
|
|
5.
|
S PoongothaiR RavikrishnanPB
MurthyEndocrine disruption and perspective human health
implications: a reviewInternet J Toxicol42200810.5580/263
|
|
6.
|
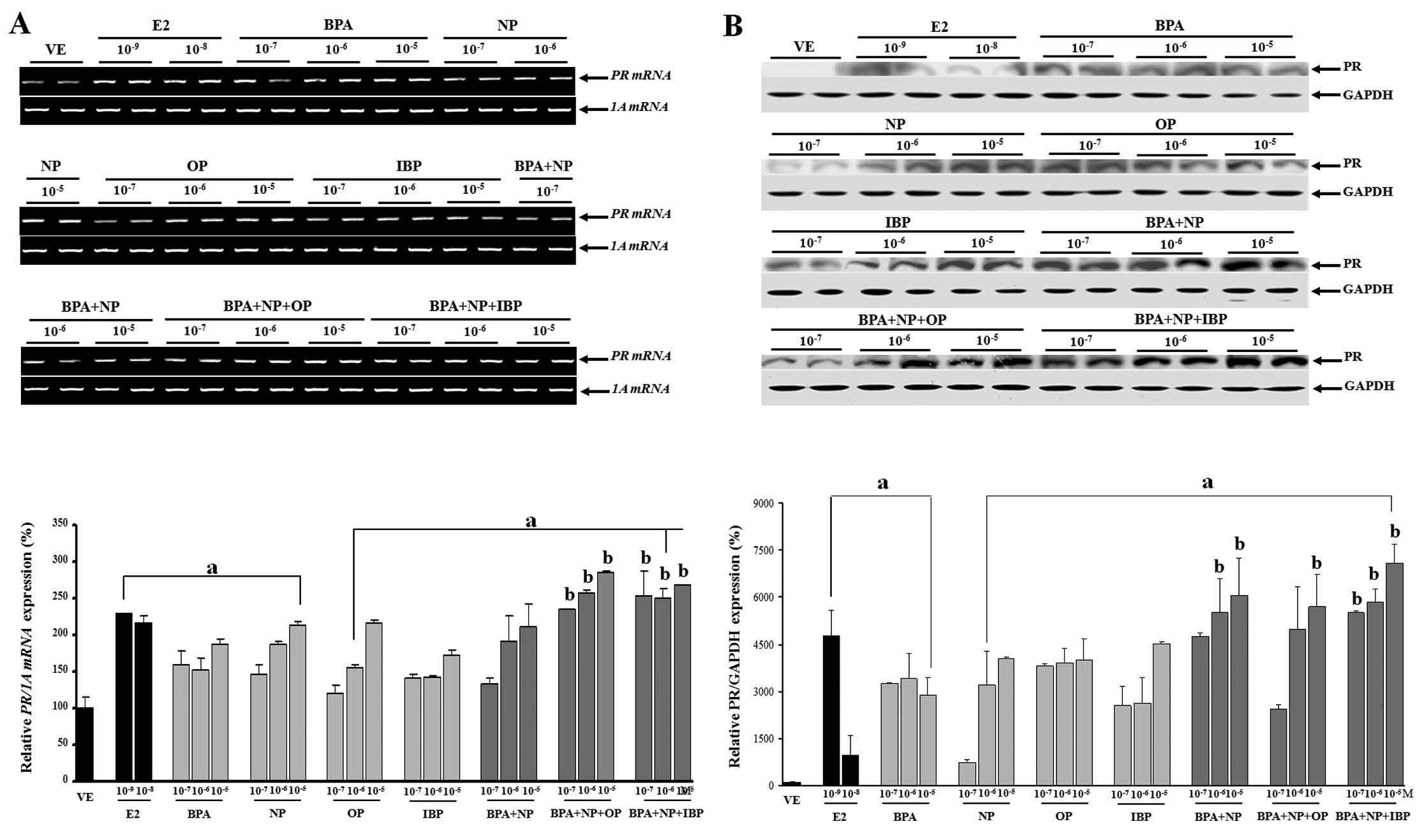
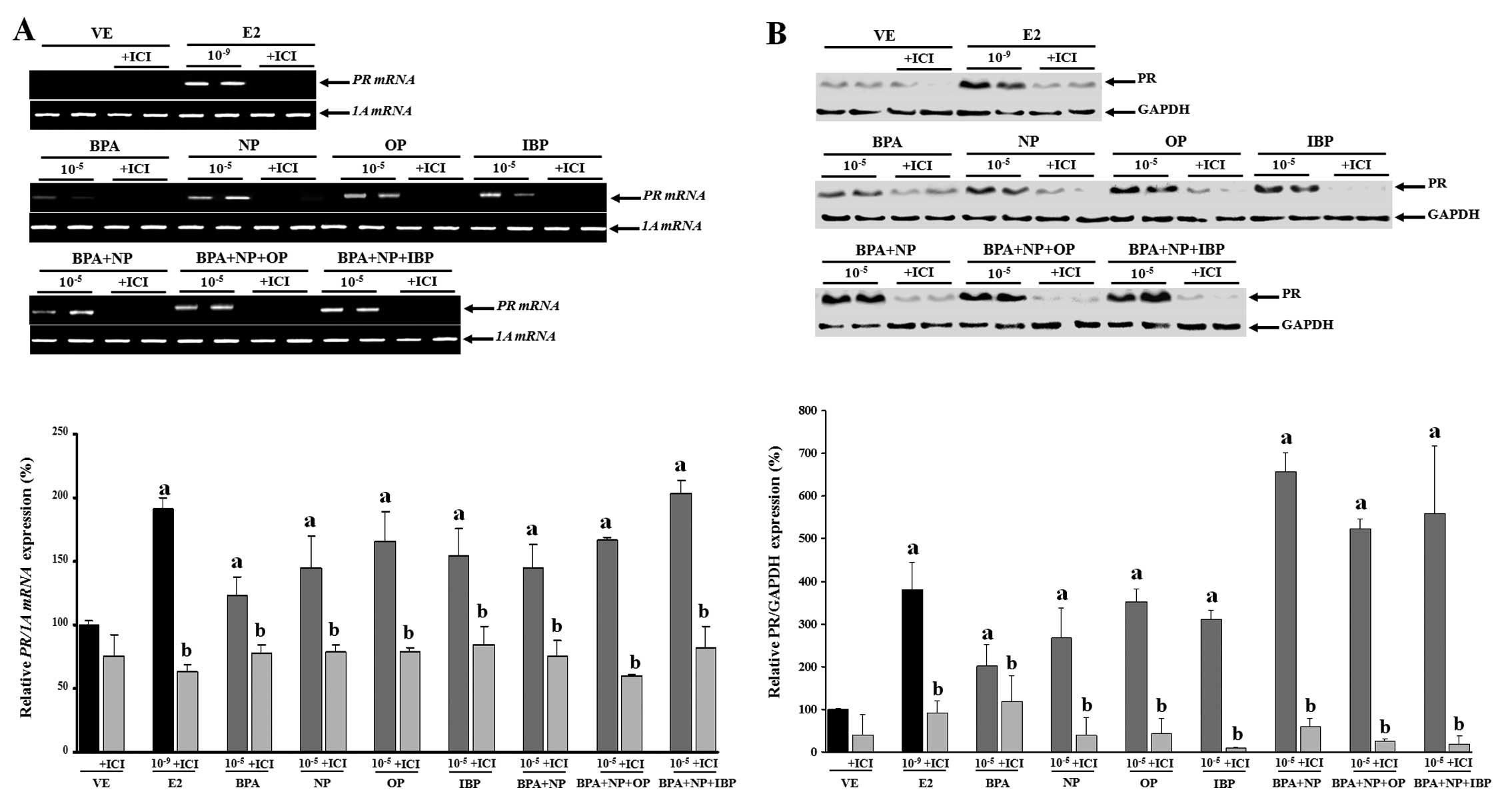
N OleaJP ArrebolaJ TaoufikiR
Fernández-ValadesR PradaN NaveaJM Molina-MolinaMF
FernandezAlkylphenols and bisphenol-A and its chlorinated
derivatives in adipose tissue of childrenEnviron
Toxicol1103692008
|
|
7.
|
MG SoniIG CarabinGA BurdockSafety
assessment of esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (parabens)Food Chem
Toxicol439851015200510.1016/j.fct.2005.01.02015833376
|
|
8.
|
D RoyJB ColerangleKP SinghIs exposure to
environmental or industrial endocrine disrupting estrogen-like
chemicals able to cause genomic instability?Front
Biosci3d913d92119989696883
|
|
9.
|
S TayamaY NakagawaK TayamaGenotoxic
effects of environmental estrogen-like compounds in CHO-K1
cellsMutat
Res649114125200810.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.08.00617913570
|
|
10.
|
JS RheeYM LeeS RaisuddinJS LeeExpression
of R-ras oncogenes in the hermaphroditic fish Kryptolebias
marmoratus, exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicalsComp
Biochem Physiol C Toxicol
Pharmacol149433439200910.1016/j.cbpc.2008.10.10219000778
|
|
11.
|
YM LeeS RaisuddinJS RheeJS KiIC KimJS
LeeModulatory effect of environmental endocrine disruptors on N-ras
oncogene expression in the hermaphroditic fish, Kryptolebias
marmoratusComp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol
Pharmacol147299305200810.1016/j.cbpc.2007.11.00618248853
|
|
12.
|
K BabaK OkadaT KinoshitaS ImaokaBisphenol
A disrupts Notch signaling by inhibiting gamma-secretase activity
and causes eye dysplasia of Xenopus laevisToxicol
Sci108344355200910.1093/toxsci/kfp02519218331
|
|
13.
|
C KudoK WadaT MasudaNonylphenol induces
the death of neural stem cells due to activation of the caspase
cascade and regulation of the cell cycleJ
Neurochem8814161423200410.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02270.x15009642
|
|
14.
|
K SatoN MatsukiY OhnoK NakazawaEffects of
17beta-estradiol and xenoestrogens on the neuronal survival in an
organotypic hippocampal
cultureNeuroendocrinology76223234200210.1159/00006594812411739
|
|
15.
|
RM BlairH FangWS BranhamThe estrogen
receptor relative binding affinities of 188 natural and
xenochemicals: structural diversity of ligandsToxicol
Sci54138153200010.1093/toxsci/54.1.13810746941
|
|
16.
|
PW HarveyParabens, oestrogenicity,
underarm cosmetics and breast cancer: a perspective on a
hypothesisJ Appl Toxicol23285288200310.1002/jat.94612975767
|
|
17.
|
PD DarbreJR ByfordLE ShawRA HortonGS
PopeMJ SauerOestrogenic activity of isobutylparaben in vitro and in
vivoJ Appl Toxicol22219226200210.1002/jat.86012210538
|
|
18.
|
X LvQ ZhouM SongG JiangJ ShaoVitellogenic
responses of 17beta-estradiol and bisphenol A in male Chinese loach
(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol24155159200710.1016/j.etap.2007.04.00721783804
|
|
19.
|
M KanekoR OkadaK YamamotoBisphenol A acts
differently from and independently of thyroid hormone in
suppressing thyrotropin release from the bullfrog pituitaryGen Comp
Endocrinol155574580200810.1016/j.ygcen.2007.09.00917959175
|
|
20.
|
YR KimEM JungKC ChoiEB JeungSynergistic
effects of octylphenol and isobutyl paraben on the expression of
calbindin-D9k in GH3 rat pituitary cellsInt J Mol
Med29294302201222076563
|
|
21.
|
H YangTT NguyenBS AnKC ChoiEB
JeungSynergistic effects of parabens on the induction of
calbindin-D9k gene expression act via a progesterone
receptor-mediated pathway in GH3 cellsHum Exp
Toxicol31134144201210.1177/096032711142240222027501
|
|
22.
|
HY ShenHL JiangHL MaoG PanL ZhouYF
CaoSimultaneous determination of seven phthalates and four parabens
in cosmetic products using HPLC-DAD and GC-MS methodsJ Sep
Sci304854200710.1002/jssc.20060021517313141
|
|
23.
|
KC ChoiEB JeungMolecular mechanism of
regulation of the calcium-binding protein calbindin-D9k,
and its physiological role(s) in mammals: a review of current
researchJ Cell Mol
Med12409420200810.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00209.x18182065
|
|
24.
|
BS AnSK KangJH ShinEB JeungStimulation of
calbindin-D(9k) mRNA expression in the rat uterus by octyl-phenol,
nonylphenol and bisphenolMol Cell
Endocrinol191177186200210.1016/S0303-7207(02)00042-412062901
|
|
25.
|
TT VoEB JeungAn evaluation of estrogenic
activity of parabens using uterine calbindin-d9k gene in an
immature rat modelToxicol
Sci1126877200910.1093/toxsci/kfp17619654335
|
|
26.
|
YK JiGS LeeKC ChoiEB
JeungAnti-progestogenic effect of flutamide on uterine expression
of calbindin-D9k mRNA and protein in immature miceReprod
Toxicol22694701200610.1016/j.reprotox.2006.04.01516777378
|
|
27.
|
JH ShinHJ MoonIH KangCalbindin-D9k mRNA
expression in the rat uterus following exposure to methoxychlor: a
comparison of oral and subcutaneous exposureJ Reprod
Dev53179188200710.1262/jrd.1805417077578
|
|
28.
|
GS LeeKC ChoiEB JeungGlucocorticoids
differentially regulate expression of duodenal and renal
calbindin-D9k through glucocorticoid receptor-mediated pathway in
mouse modelAm J Physiol Endocrinol Metab290E299E3072006
|
|
29.
|
GS LeeKC ChoiHJ KimEB JeungEffect of
genistein as a selective estrogen receptor beta agonist on the
expression of Calbindin-D9k in the uterus of immature ratsToxicol
Sci82451457200410.1093/toxsci/kfh29615456916
|
|
30.
|
TT VoEM JungKC ChoiFH YuEB JeungEstrogen
receptor alpha is involved in the induction of Calbindin-D(9k) and
progesterone receptor by parabens in GH3 cells: a biomarker gene
for screening
xenoestrogensSteroids76675681201110.1016/j.steroids.2011.03.00621473877
|
|
31.
|
VH DangTH NguyenKC ChoiEB JeungA
calcium-binding protein, calbindin-D9k, is regulated through an
estrogen-receptor mediated mechanism following xenoestrogen
exposure in the GH3 cell lineToxicol
Sci98408415200710.1093/toxsci/kfm120
|
|
32.
|
M SongY XuQ JiangMeasurement of estrogenic
activity in sediments from Haihe and Dagu River, ChinaEnviron
Int32676681200610.1016/j.envint.2006.03.00216624408
|
|
33.
|
S TakayanagiT TokunagaX LiuH OkadaA
MatsushimaY ShimohigashiEndocrine disruptor bisphenol A strongly
binds to human estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) with high
constitutive activityToxicol
Lett16795105200610.1016/j.toxlet.2006.08.012
|
|
34.
|
TT VoYM YooKC ChoiEB JeungPotential
estrogenic effect(s) of parabens at the prepubertal stage of a
postnatal female rat modelReprod
Toxicol29306316201010.1016/j.reprotox.2010.01.01320132880
|
|
35.
|
E SilvaN RajapakseA KortenkampSomething
from ‘nothing’ - eight weak estrogenic chemicals combined at
concentrations below NOECs produce significant mixture
effectsEnviron Sci Technol36175117562002
|
|
36.
|
A KortenkampLow dose mixture effects of
endocrine disrupters: implications for risk assessment and
epidemiologyInt J
Androl31233240200810.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00862.x18248400
|
|
37.
|
JM IbarluzeaMF FernándezL Santa-MarinaMF
Olea-SerranoAM RivasJJ AurrekoetxeaJ ExpósitoM LorenzoP TornéM
VillalobosV PedrazaAJ SascoN OleaBreast cancer risk and the
combined effect of environmental estrogensCancer Causes
Control15591600200410.1023/B:CACO.0000036167.51236.8615280638
|
|
38.
|
AG StewartJ CarterTowards the development
of a multidisciplinary understanding of the effects of toxic
chemical mixtures on healthEnviron Geochem
Health31239251200910.1007/s10653-008-9210-919023667
|
|
39.
|
BS AnKC ChoiSK KangWS HwangEB JeungNovel
Calbindin-D(9k) protein as a useful biomarker for environmental
estrogenic compounds in the uterus of immature ratsReprod
Toxicol17311319200310.1016/S0890-6238(03)00003-012759100
|
|
40.
|
P TinnanooruVH DangTH NguyenGS LeeKC
ChoiEB JeungEstrogen regulates the localization and expression of
calbindin-D9k in the pituitary gland of immature male rats via the
ERalpha–pathwayMol Cell Endocrinol2852633200818313836
|
|
41.
|
EC Bonefeld-JorgensenM LongMV HofmeisterAM
VinggaardEndocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A, bisphenol A
dimethacrylate, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in vitro: new
data and a brief reviewEnviron Health Perspect115Suppl
1S69S76200710.1289/ehp.936818174953
|
|
42.
|
M GhisariEC Bonefeld-JorgensenEffects of
plasticizers and their mixtures on estrogen receptor and thyroid
hormone functionsToxicol
Lett1896777200910.1016/j.toxlet.2009.05.00419463926
|
|
43.
|
T FunabashiTJ NakamuraF
Kimurap-Nonylphenol, 4-tert-octylphenol and bisphenol A increase
the expression of progesterone receptor mRNA in the frontal cortex
of adult ovariectomized ratsJ
Neuroendocrinol1699104200410.1111/j.0953-8194.2004.01136.x14763995
|
|
44.
|
CM MarkeyPR WadiaBS RubinC SonnenscheinAM
SotoLong-term effects of fetal exposure to low doses of the
xenoestrogen bisphenol-A in the female mouse genital tractBiol
Reprod7213441351200510.1095/biolreprod.104.03630115689538
|
|
45.
|
T OkuboY YokoyamaK KanoI KanoER-dependent
estrogenic activity of parabens assessed by proliferation of human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells and expression of ERalpha and PRFood Chem
Toxicol3912251232200110.1016/S0278-6915(01)00073-411696396
|
|
46.
|
GS LeeHJ KimYW JungKC ChoiEB JeungEstrogen
receptor alpha pathway is involved in the regulation of
Calbindin-D9k in the uterus of immature ratsToxicol
Sci84270277200510.1093/toxsci/kfi07215635152
|