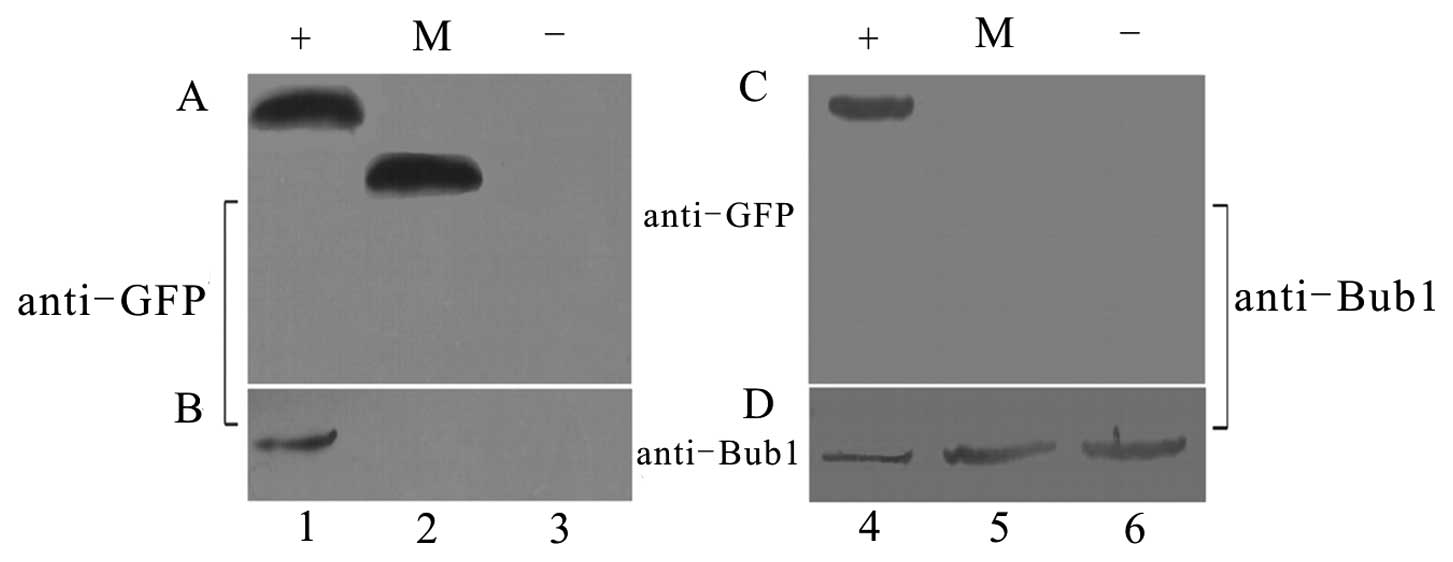
Spandidos Publications style
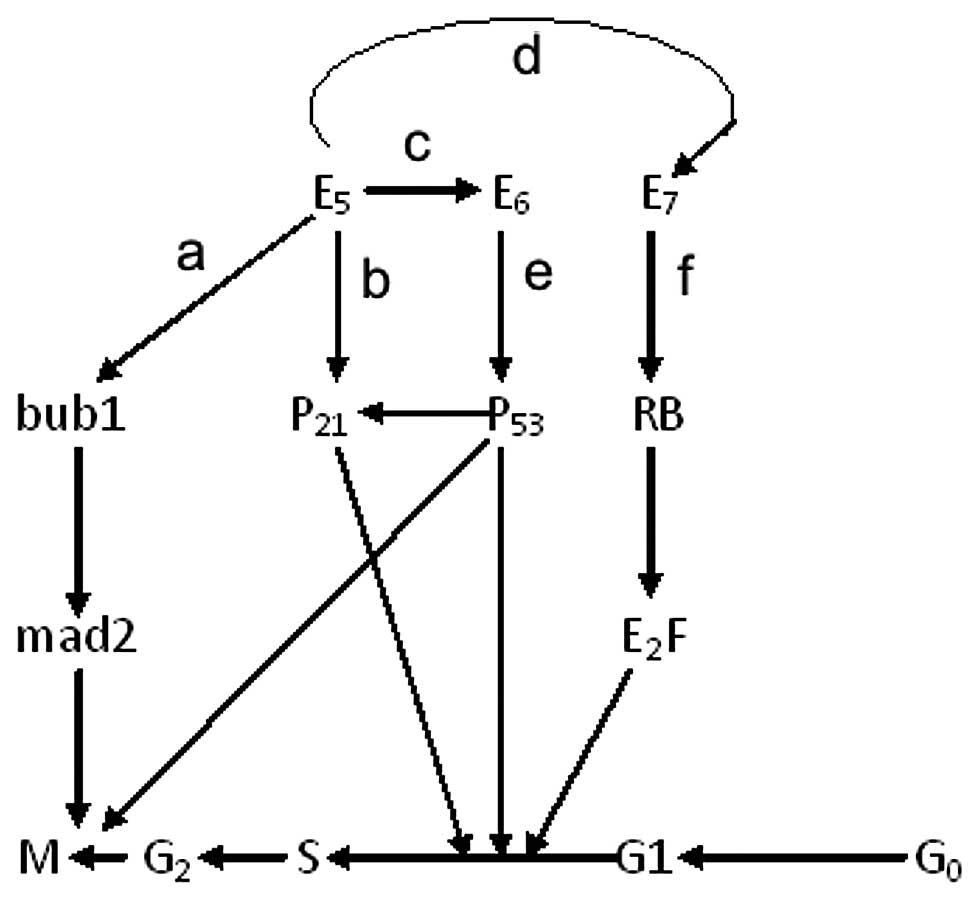
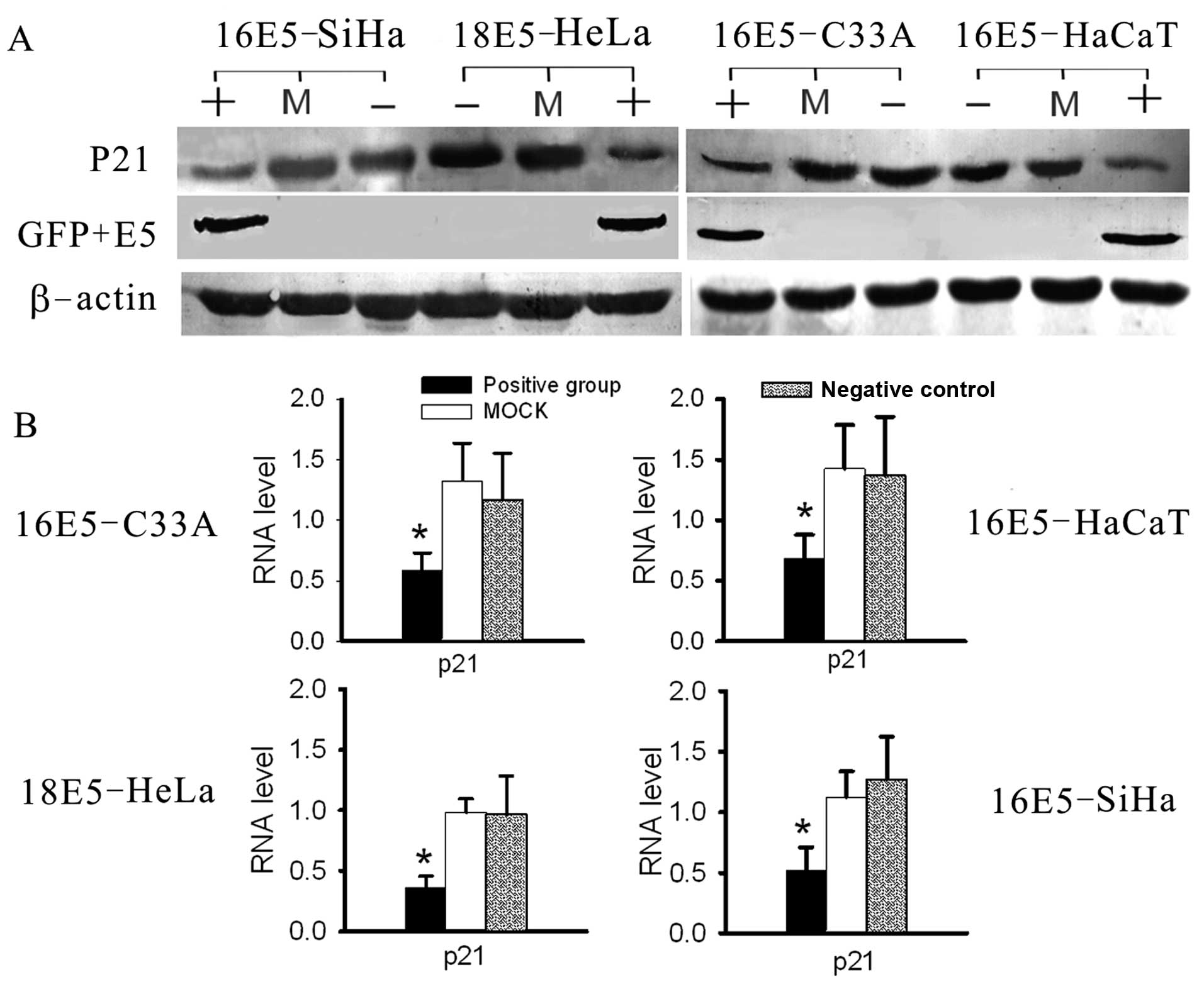
Liao S, Deng D, Hu X, Wang W, Li L, Li W, Zhou J, Xu G, Meng L, Wang S, Wang S, et al: HPV16/18 E5, a promising candidate for cervical cancer vaccines, affects SCPs, cell proliferation and cell cycle, and forms a potential network with E6 and E7. Int J Mol Med 31: 120-128, 2013.
APA
Liao, S., Deng, D., Hu, X., Wang, W., Li, L., Li, W. ... Ma, D. (2013). HPV16/18 E5, a promising candidate for cervical cancer vaccines, affects SCPs, cell proliferation and cell cycle, and forms a potential network with E6 and E7. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 31, 120-128. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1168
MLA
Liao, S., Deng, D., Hu, X., Wang, W., Li, L., Li, W., Zhou, J., Xu, G., Meng, L., Wang, S., Ma, D."HPV16/18 E5, a promising candidate for cervical cancer vaccines, affects SCPs, cell proliferation and cell cycle, and forms a potential network with E6 and E7". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 31.1 (2013): 120-128.
Chicago
Liao, S., Deng, D., Hu, X., Wang, W., Li, L., Li, W., Zhou, J., Xu, G., Meng, L., Wang, S., Ma, D."HPV16/18 E5, a promising candidate for cervical cancer vaccines, affects SCPs, cell proliferation and cell cycle, and forms a potential network with E6 and E7". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 31, no. 1 (2013): 120-128. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.1168