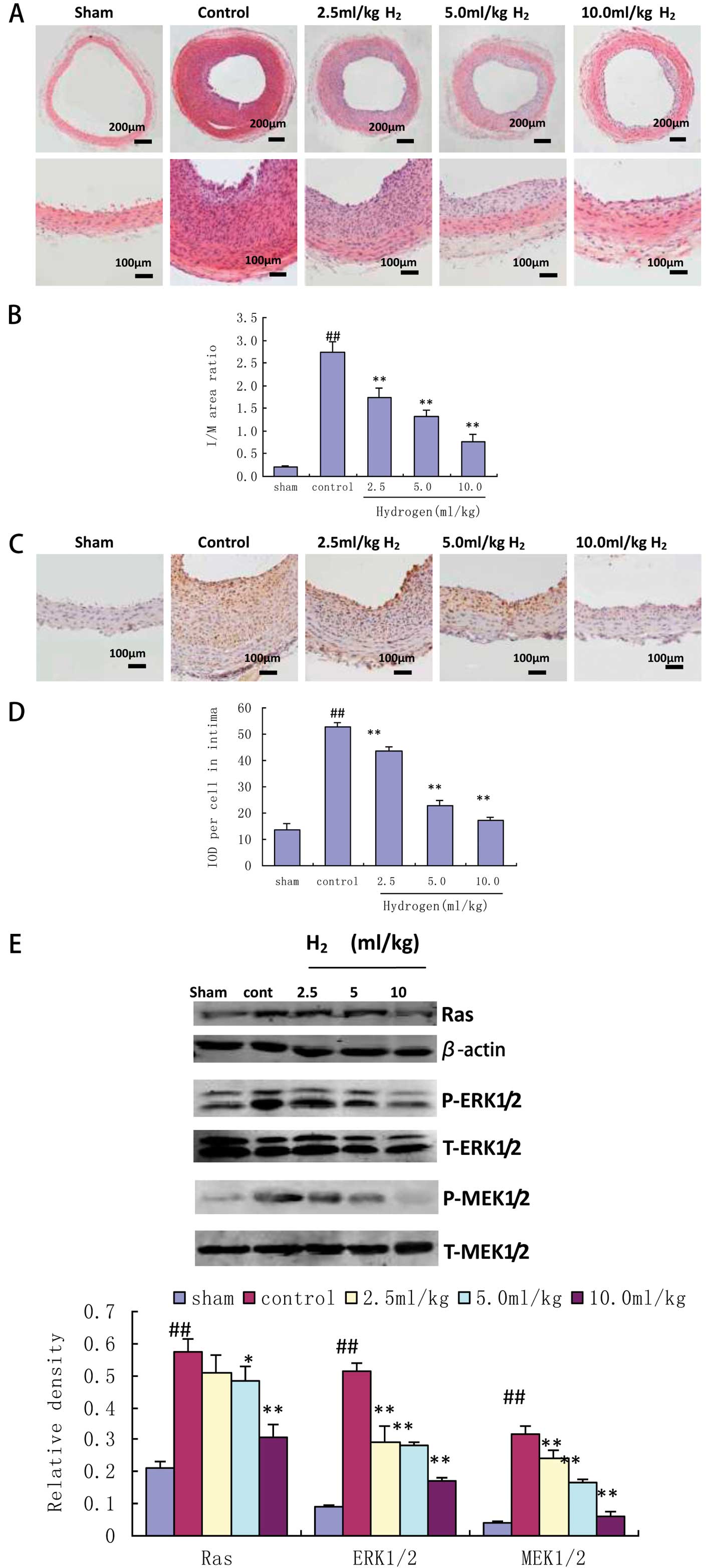
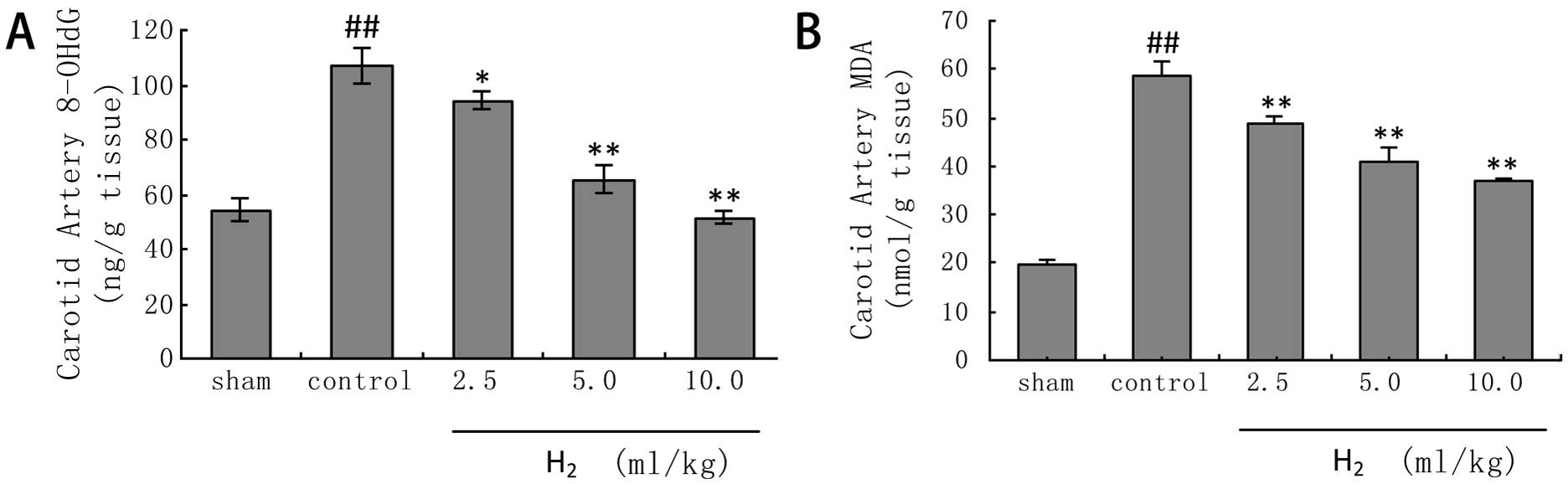
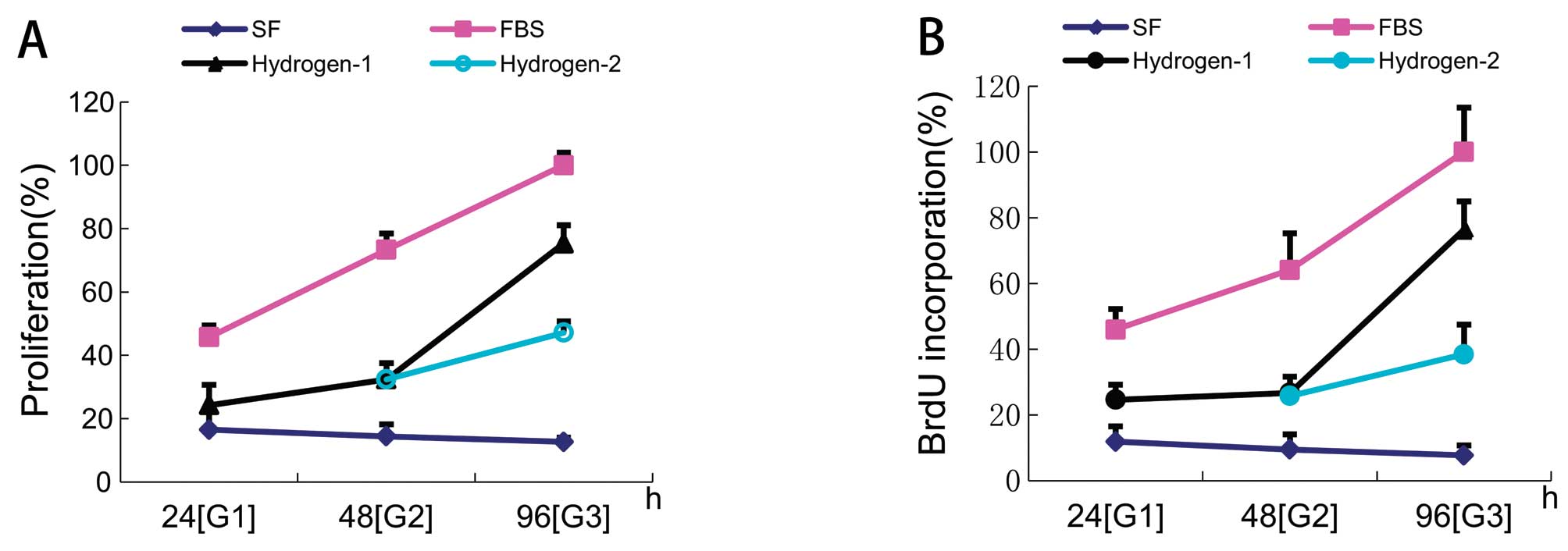
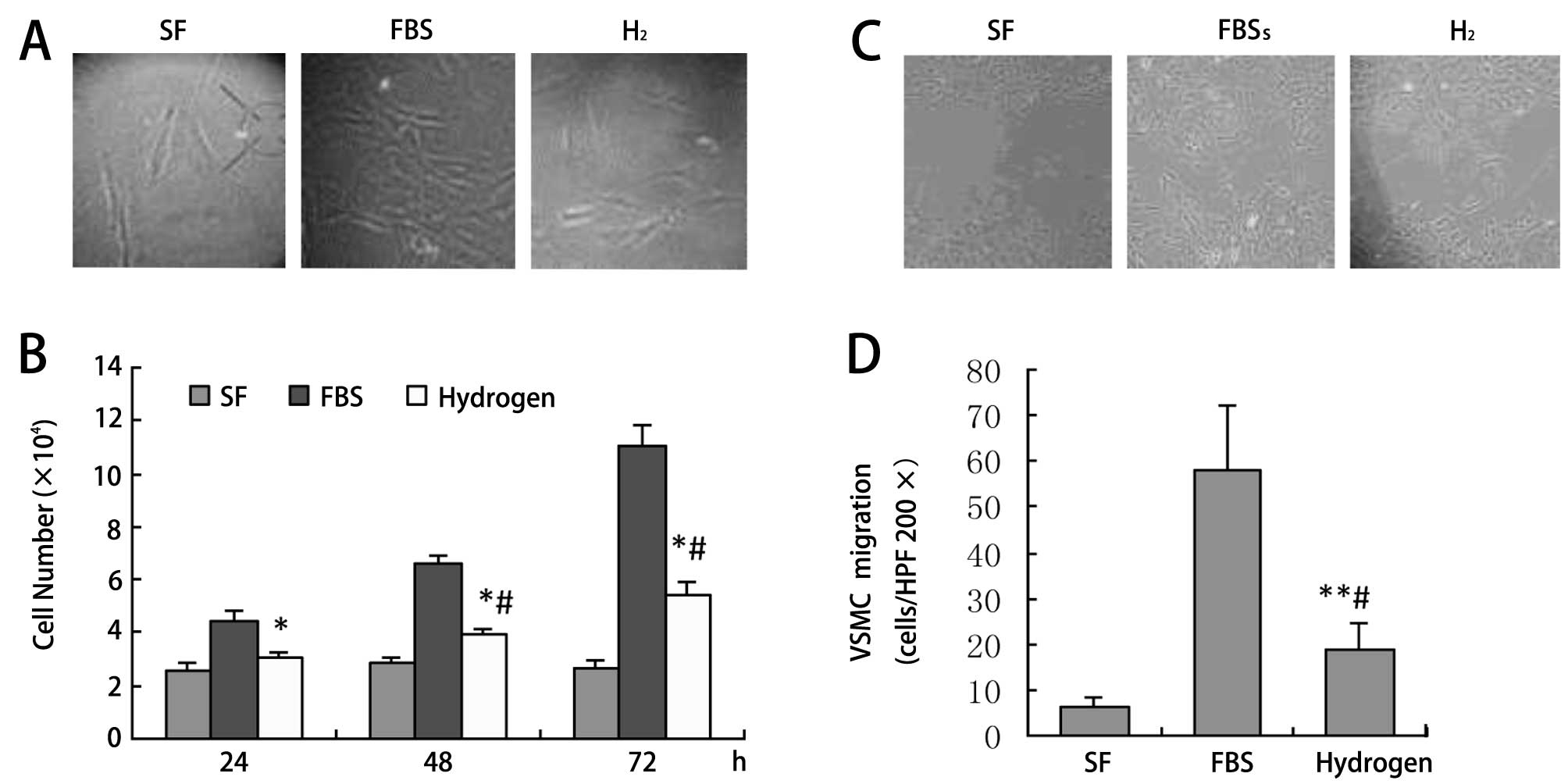
|
1
|
Landau C, Lange RA and Hillis LD:
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. N Engl J Med.
330:981–993. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Domburg RT, Foley DP, Breeman A, van
Herwerden LA and Serruys PW: Coronary artery bypass graft surgery
and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Twenty-year
clinical outcome. Eur Heart J. 23:543–549. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sturek M and Reddy HK: New tools for
prevention of restenosis could decrease the ‘oculo-stento’ reflex.
Cardiovasc Res. 53:292–293. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sasaki T, Maruyama H, Kase Y, Takeda S and
Aburada M: Antianginal effects of lercanidipine on the vasopressin
or methacholine induced anginal model in rats. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:811–816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Park J, Ha H, Seo J, et al: Mycophenolic
acid inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced reactive
oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in
rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Transplant. 4:1982–1990.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al:
Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing
cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 13:688–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hong Y, Chen S and Zhang JM: Hydrogen as a
selective antioxidant: a review of clinical and experimental
studies. J Int Med Res. 38:1893–1903. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang C, Li J, Liu Q, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline reduces oxidative stress and inflammation by inhibit of JNK
and NF-kappaB activation in a rat model of amyloid-beta-induced
Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 491:127–132. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun H, Chen L, Zhou W, et al: The
protective role of hydrogen-rich saline in experimental liver
injury in mice. J Hepatol. 54:471–480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. Exp Biol Med. 234:1212–1219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kajiya M, Silva MJ, Sato K, Ouhara K and
Kawai T: Hydrogen mediates suppression of colon inflammation
induced by dextran sodium sulfate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
386:11–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakao A, Kaczorowski DJ, Wang Y, et al:
Amelioration of rat cardiac cold ischemia/reperfusion injury with
inhaled hydrogen or carbon monoxide, or both. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 29:544–553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hayashida K, Sano M, Ohsawa I, et al:
Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat model of
myocardial ischemiareperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
373:30–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qin ZX, Yu P, Qian DH, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline prevents neointima formation after carotid
balloon injury by suppressing ROS and the TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB
pathway. Atherosclerosis. 220:343–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Yu G, Liu SY, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.
J Surg Res. 167:e339–e344. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shingu C, Koga H, Hagiwara S, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline solution attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion
injury. J Anesth. 24:569–574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Q, Cai J, Zhou J, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline reduces delayed neurologic sequelae in experimental carbon
monoxide toxicity. Crit Care Med. 39:765–769. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohsawa I, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K,
Ishikawa M and Ohta S: Consumption of hydrogen water prevents
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 377:1195–1198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Itoh T, Fujita Y, Ito M, et al: Molecular
hydrogen suppresses FcepsilonRI-mediated signal transduction and
prevents degranulation of mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
389:651–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng X, Mao Y, Cai J, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline protects against intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Free Radic Res. 43:478–484.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Clowes AW, Reidy MA and Clowes MM:
Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I Smooth
muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest.
49:327–333. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei GL, Krasinski K, Kearney M, Isner JM,
Walsh K and Andres V: Temporally and spatially coordinated
expression of cell cycle regulatory factors after angioplasty. Circ
Res. 80:418–426. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yeh JL, Liou SF, Chang YP, et al:
Isoeugenodilol inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation and
neointimal thickening after balloon injury via inactivation of
ERK1/2 pathway. J Biomed Sci. 15:375–389. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liou SF, Yeh JL, Liang JC, Chiu CC, Lin YT
and Chen IJ: Inhibition of mitogen-mediated proliferation of rat
vascular smooth muscle cells by labedipinedilol-A through PKC and
ERK 1/2 pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 44:539–551. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Parenti A, Bellik L, Brogelli L, Filippi S
and Ledda F: Endogenous VEGF-A is responsible for mitogenic effects
of MCP-1 on vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 286:H1978–H1984. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Berridge MV, Herst PM and Tan AS:
Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: new insights into their
cellular reduction. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 11:127–152. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Muir D, Varon S and Manthorpe M: An
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bromodeoxyuridine
incorporation using fixed microcultures. Anal Biochem. 185:377–382.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li JJ, Han M, Wen JK and Li AY:
Osteopontin stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell migration by
inducing FAK phosphorylation and ILK dephosphorylation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 356:13–19. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fishbein MC, Wang T, Matijasevic M, Hong L
and Apple FS: Myocardial tissue troponins T and I. An
immunohistochemical study in experimental models of myocardial
ischemia. Cardiovasc Pathol. 12:65–71. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salvemini D, Riley DP and Cuzzocrea S: SOD
mimetics are coming of age. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 1:367–374. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schwartz RS and Henry TD: Pathophysiology
of coronary artery restenosis. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 3(Suppl 5):
S4–S9. 2002.
|
|
32
|
Braun-Dullaeus RC, Mann MJ and Dzau VJ:
Cell cycle progression: new therapeutic target for vascular
proliferative disease. Circulation. 98:82–89. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Z, Lee FY, Bhalla KN and Wu J: Potent
inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-induced responses in
vascular smooth muscle cells by BMS-354825 (dasatinib). Mol
Pharmacol. 69:1527–1533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stettler C, Wandel S, Allemann S, et al:
Outcomes associated with drug-eluting and bare-metal stents: a
collaborative network meta-analysis. Lancet. 370:937–948. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lemos PA, Saia F, Ligthart JM, et al:
Coronary restenosis after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation:
morphological description and mechanistic analysis from a
consecutive series of cases. Circulation. 108:257–260. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fujii K, Mintz GS, Kobayashi Y, et al:
Contribution of stent underexpansion to recurrence after
sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for in-stent restenosis.
Circulation. 109:1085–1088. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Takebayashi H, Kobayashi Y, Mintz GS, et
al: Intravascular ultrasound assessment of lesions with target
vessel failure after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Am J
Cardiol. 95:498–502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Griendling KK and Ushio-Fukai M: Redox
control of vascular smooth muscle proliferation. J Lab Clin Med.
132:9–15. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kunsch C and Medford RM: Oxidative stress
as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ Res.
85:753–766. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boullier A, Bird DA, Chang MK, et al:
Scavenger receptors, oxidized LDL, and atherosclerosis. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 947:214–223. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF and Mason RP:
Inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 18:351–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Szocs K, Lassegue B, Sorescu D, et al:
Upregulation of Nox-based NAD(P)H oxidases in restenosis after
carotid injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:21–27. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shi Y, Niculescu R, Wang D, Patel S,
Davenpeck KL and Zalewski A: Increased NAD(P)H oxidase and reactive
oxygen species in coronary arteries after balloon injury.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:739–745. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kasai H: Analysis of a form of oxidative
DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, as a marker of cellular
oxidative stress during carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 387:147–163.
1997.
|
|
45
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lewis TS, Shapiro PS and Ahn NG: Signal
transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv Cancer Res.
74:49–139. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee JH, Johnson PR, Roth M, Hunt NH and
Black JL: ERK activation and mitogenesis in human airway smooth
muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 280:L1019–L1029.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Koyama H, Olson NE, Dastvan FF and Reidy
MA: Cell replication in the arterial wall: activation of signaling
pathway following in vivo injury. Circ Res. 82:713–721. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Roovers K, Davey G, Zhu X, Bottazzi ME and
Assoian RK: Alpha5beta1 integrin controls cyclin D1 expression by
sustaining mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in growth
factor-treated cells. Mol Biol Cell. 10:3197–3204. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hirata A, Igarashi M, Yamaguchi H, et al:
Nifedipine suppresses neointimal thickening by its inhibitory
effect on vascular smooth muscle cell growth via a MEK-ERK pathway
coupling with Pyk2. Br J Pharmacol. 131:1521–1530. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu JR, Liou SF, Lin SW, et al:
Lercanidipine inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
and neointimal formation via reducing intracellular reactive oxygen
species and inactivating Ras-ERK1/2 signaling. Pharmacol Res.
59:48–56. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lawlor MA and Alessi DR: PKB/Akt: a key
mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J
Cell Sci. 114:2903–2910. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ranganna K, Yatsu FM, Hayes BE, Milton SG
and Jayakumar A: Butyrate inhibits proliferation-induced
proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression (PCNA) in rat
vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 205:149–161. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wu CH, Lin CS, Hung JS, et al: Inhibition
of neointimal formation in porcine coronary artery by a Ras mutant.
J Surg Res. 99:100–106. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Grube E, Gerckens U, Muller R and
Bullesfeld L: Drug eluting stents: initial experiences. Z Kardiol.
91(Suppl 3): S44–S48. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Donovan M and Cotter TG: Control of
mitochondrial integrity by Bcl-2 family members and
caspase-independent cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:133–147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|