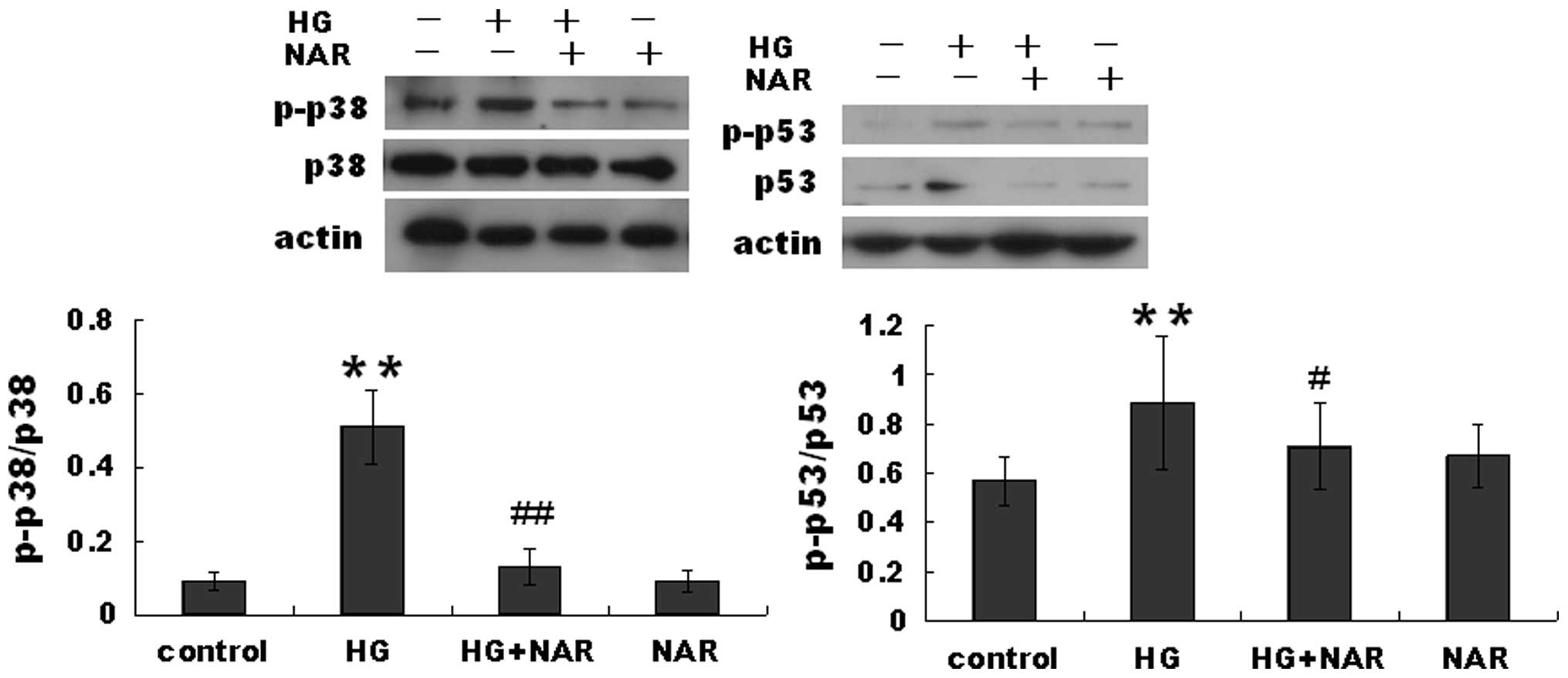
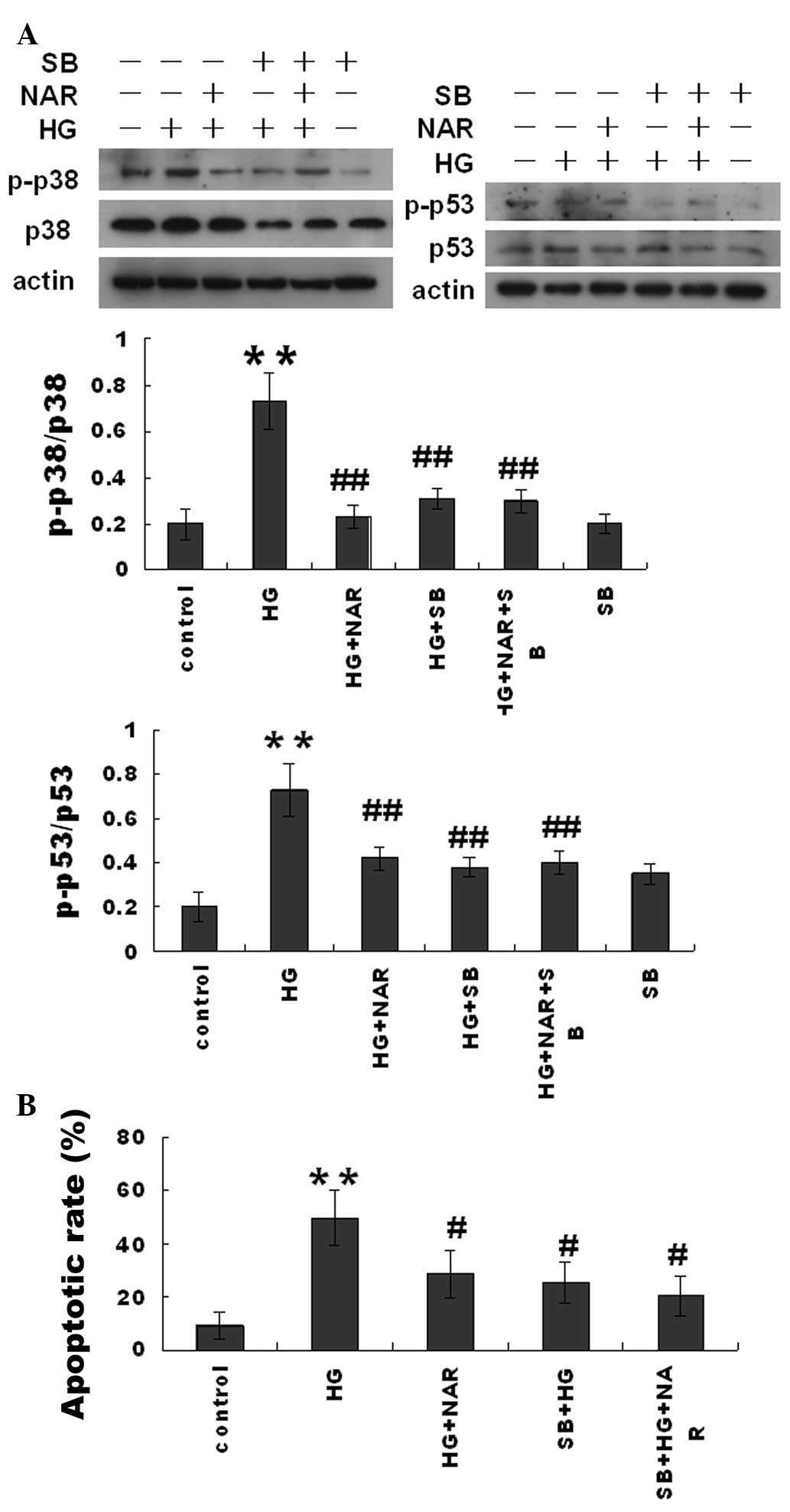
|
1
|
Cai L and Kang YJ: Cell death and diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 3:219–228. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Adeghate E: Molecular and cellular basis
of the aetiology and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy: a short
review. Mol Cell Biochem. 261:187–191. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lakshmanan AP, Harima M, Suzuki K, et al:
The hyperglycemia stimulated myocardial endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
stress contributes to diabetic cardiomyopathy in the transgenic
non-obese type 2 diabetic rats: a differential role of unfolded
protein response (UPR) signaling proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:438–447. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jankyova S, Kmecova J, Cernecka H, et al:
Glucose and blood pressure lowering effects of
Pycnogenol® are inefficient to prevent prolongation of
QT interval in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Pathol Res
Pract. 208:452–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai L: Diabetic cardiomyopathy and its
prevention by metallothionein: experimental evidence, possible
mechanisms and clinical implications. Curr Med Chem. 14:2193–2203.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miki T, Yuda S, Kouzu H and Miura T:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology and clinical features.
Heart Fail Rev. Mar 28–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Regan TJ, Ahmed S, Haider B, Moschos C and
Weisse A: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: experimental and clinical
observations. N J Med. 91:776–778. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C, et al:
Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res. 87:1123–1132.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cai L, Wang Y, Zhou G, et al: Attenuation
by metallothionein of early cardiac cell death via suppression of
mitochondrial oxidative stress results in a prevention of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:1688–1697. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Condorelli G, Morisco C, Stassi G, et al:
Increased cardiomyocyte apoptosis and changes in proapoptotic and
antiapoptotic genes bax and bcl-2 during left ventricular
adaptations to chronic pressure overload in the rat. Circulation.
99:3071–3078. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lv X, Yu X, Wang Y, et al: Berberine
inhibits doxorubicin-triggered cardiomyocyte apoptosis via
attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and increasing Bcl-2
expression. PLoS One. 7:e473512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ruffolo SC and Shore GC: BCL-2 selectively
interacts with the BID-induced open conformer of BAK, inhibiting
BAK auto-oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 278:25039–25045. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yi X, Yin XM and Dong Z: Inhibition of
Bid-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2. tBid insertion, Bax translocation,
and Bax/Bak oligomerization suppressed. J Biol Chem.
278:16992–16999. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SJ, Hwang SG, Shin DY, Kang SS and
Chun JS: p38 kinase regulates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of
articular chondrocytes by accumulating p53 via NFkappa B-dependent
transcription and stabilization by serine 15 phosphorylation. J
Biol Chem. 277:33501–33508. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jain M and Parmar HS: Evaluation of
antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potential of hesperidin and
naringin on the rat air pouch model of inflammation. Inflamm Res.
60:483–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kawaguchi K, Maruyama H, Hasunuma R and
Kumazawa Y: Suppression of inflammatory responses after onset of
collagen-induced arthritis in mice by oral administration of the
Citrus flavanone naringin. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
33:723–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cavia-Saiz M, Busto MD, Pilar-Izquierdo
MC, Ortega N, Perez-Mateos M and Muniz P: Antioxidant properties,
radical scavenging activity and biomolecule protection capacity of
flavonoid naringenin and its glycoside naringin: a comparative
study. J Sci Food Agric. 90:1238–1244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jagetia GC and Reddy TK: Alleviation of
iron induced oxidative stress by the grape fruit flavanone naringin
in vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 190:121–128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Camargo CA, Gomes-Marcondes MC, Wutzki NC
and Aoyama H: Naringin inhibits tumor growth and reduces
interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels in rats with
Walker 256 carcinosarcoma. Anticancer Res. 32:129–133.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Celiz G, Daz M and Audisio MC:
Antibacterial activity of naringin derivatives against pathogenic
strains. J Appl Microbiol. 111:731–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carino-Cortes R, Alvarez-Gonzalez I,
Martino-Roaro L and Madrigal-Bujaidar E: Effect of naringin on the
DNA damage induced by daunorubicin in mouse hepatocytes and
cardiocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:697–701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao S, Li P, Yang H, Fang S and Su W:
Antitussive effect of naringin on experimentally induced cough in
Guinea pigs. Planta Med. 77:16–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu M, Zou W, Yang C, Peng W and Su W:
Metabolism and excretion studies of oral administered naringin, a
putative antitussive, in rats and dogs. Biopharm Drug Dispos.
33:123–134. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gopinath K, Prakash D and Sudhandiran G:
Neuroprotective effect of naringin, a dietary flavonoid against
3-nitropropionic acid-induced neuronal apoptosis. Neurochem Int.
59:1066–1073. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gopinath K and Sudhandiran G: Naringin
modulates oxidative stress and inflammation in 3-nitropropionic
acid-induced neurodegeneration through the activation of nuclear
factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 signalling pathway.
Neuroscience. 227:134–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kandhare AD, Raygude KS, Ghosh P, Ghule AE
and Bodhankar SL: Neuroprotective effect of naringin by modulation
of endogenous biomarkers in streptozotocin induced painful diabetic
neuropathy. Fitoterapia. 83:650–659. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ikemura M, Sasaki Y, Giddings JC and
Yamamoto J: Preventive effects of hesperidin, glucosyl hesperidin
and naringin on hypertension and cerebral thrombosis in
stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytother Res.
26:1272–1277. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chanet A, Milenkovic D, Deval C, et al:
Naringin, the major grapefruit flavonoid, specifically affects
atherosclerosis development in diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in
mice. J Nutr Biochem. 23:469–477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kanno S, Shouji A, Asou K and Ishikawa M:
Effects of naringin on hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity and
apoptosis in P388 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 92:166–170. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim HJ, Song JY, Park HJ, Park HK, Yun DH
and Chung JH: Naringin protects against rotenone-induced apoptosis
in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
13:281–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mahmoud AM, Ashour MB, Abdel-Moneim A and
Ahmed OM: Hesperidin and naringin attenuate hyperglycemia-mediated
oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokine production in high
fat fed/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Diabetes
Complications. 26:483–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ramesh E and Alshatwi AA: Naringin induces
death receptor and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human
cervical cancer (SiHa) cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 51:97–105. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nie YC, Wu H, Li PB, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of naringin in chronic pulmonary
neutrophilic inflammation in cigarette smoke-exposed rats. J Med
Food. 15:894–900. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xulu S and Oroma Owira PM: Naringin
ameliorates atherogenic dyslipidemia but not hyperglycemia in rats
with type 1 diabetes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 59:133–141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rajadurai M and Prince PS: Naringin
ameliorates mitochondrial lipid peroxides, antioxidants and lipids
in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats.
Phytother Res. 23:358–362. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Punithavathi VR, Anuthama R and Prince PS:
Combined treatment with naringin and vitamin C ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male Wistar rats. J Appl
Toxicol. 28:806–813. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shore GC and Nguyen M: Bcl-2 proteins and
apoptosis: choose your partner. Cell. 135:1004–1006. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y and
Kang YJ: Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium:
mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway.
Diabetes. 51:1938–1948. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fiordaliso F, Leri A, Cesselli D, et al:
Hyperglycemia activates p53 and p53-regulated genes leading to
myocyte cell death. Diabetes. 50:2363–2375. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu W, Soonpaa MH, Chen H, et al: Acute
doxorubicin cardiotoxicity is associated with p53-induced
inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway.
Circulation. 119:99–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Childs AC, Phaneuf SL, Dirks AJ, Phillips
T and Leeuwenburgh C: Doxorubicin treatment in vivo causes
cytochrome C release and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, as well as
increased mitochondrial efficiency, superoxide dismutase activity,
and Bcl-2:Bax ratio. Cancer Res. 62:4592–4598. 2002.
|
|
45
|
Younce CW, Burmeister MA and Ayala JE:
Exendin-4 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of
SERCA2a. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 304:C508–C518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kuo WW, Wang WJ, Tsai CY, Way CL, Hsu HH
and Chen LM: Diallyl trisufide (DATS) suppresses high
glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting JNK/NFkappaB
signaling via attenuating ROS generation. Int J Cardiol. View Article : Google Scholar : 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yu XY, Geng YJ, Liang JL, et al: High
levels of glucose induce apoptosis in cardiomyocyte via epigenetic
regulation of the insulin-like growth factor receptor. Exp Cell
Res. 316:2903–2909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|