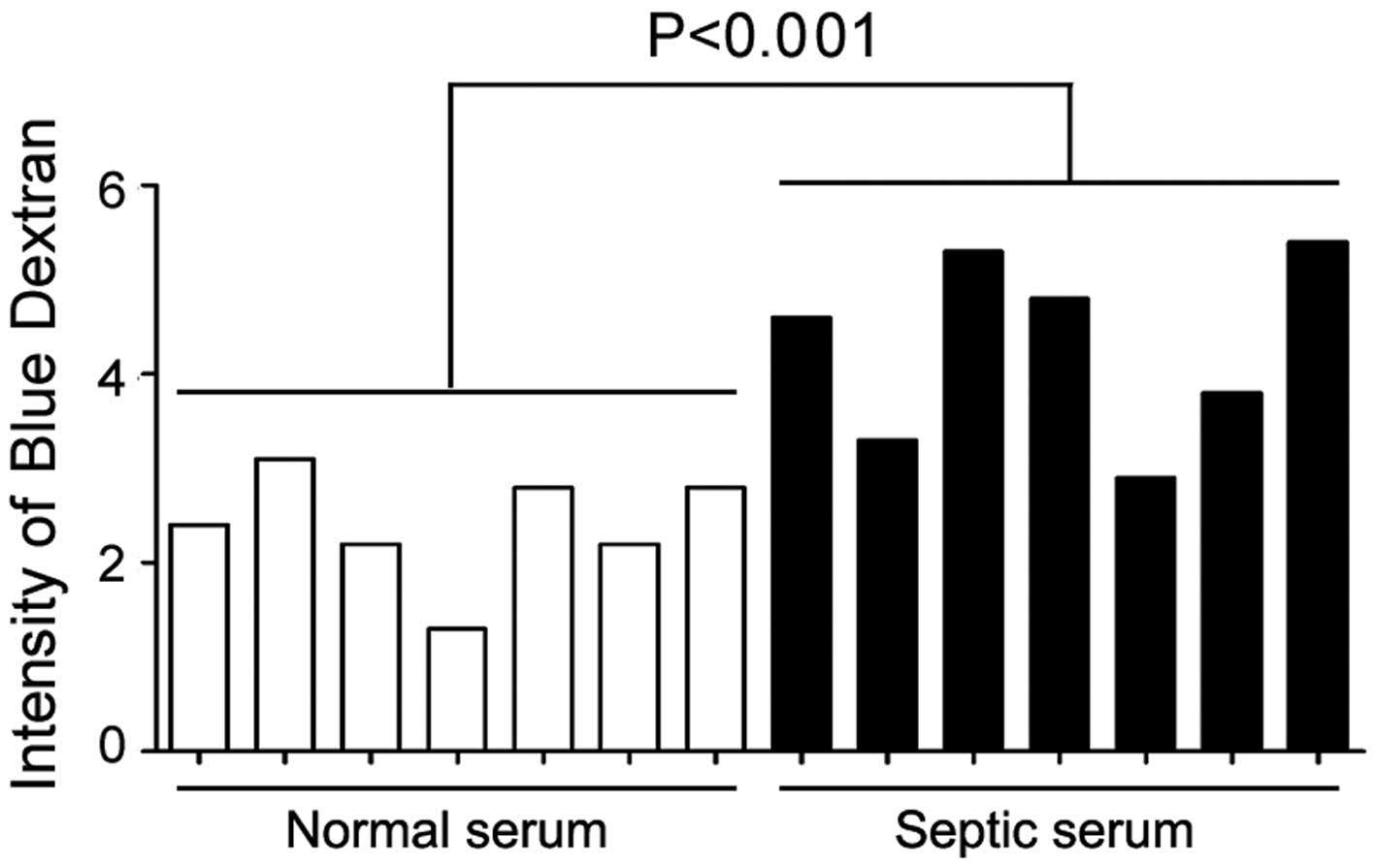
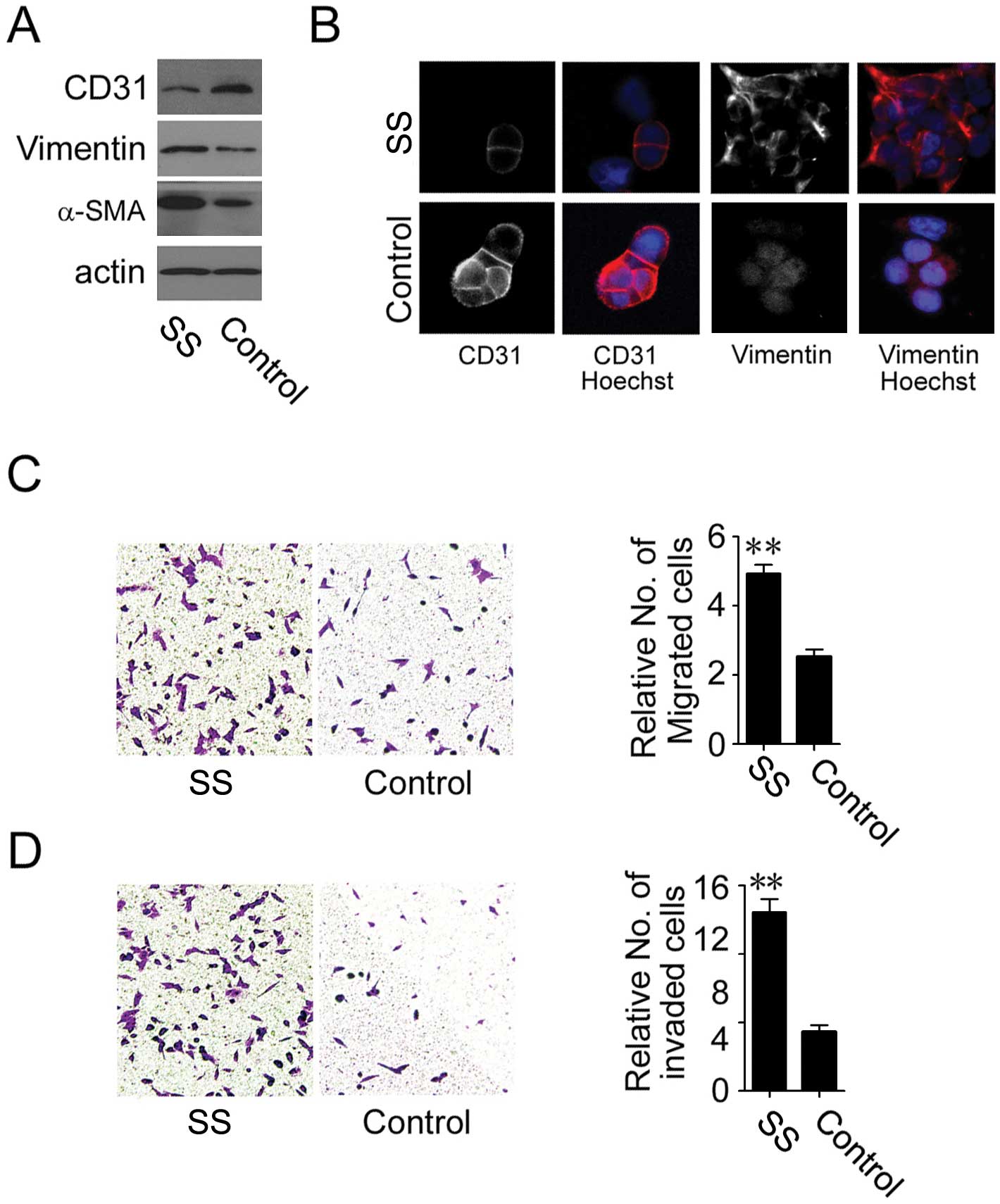
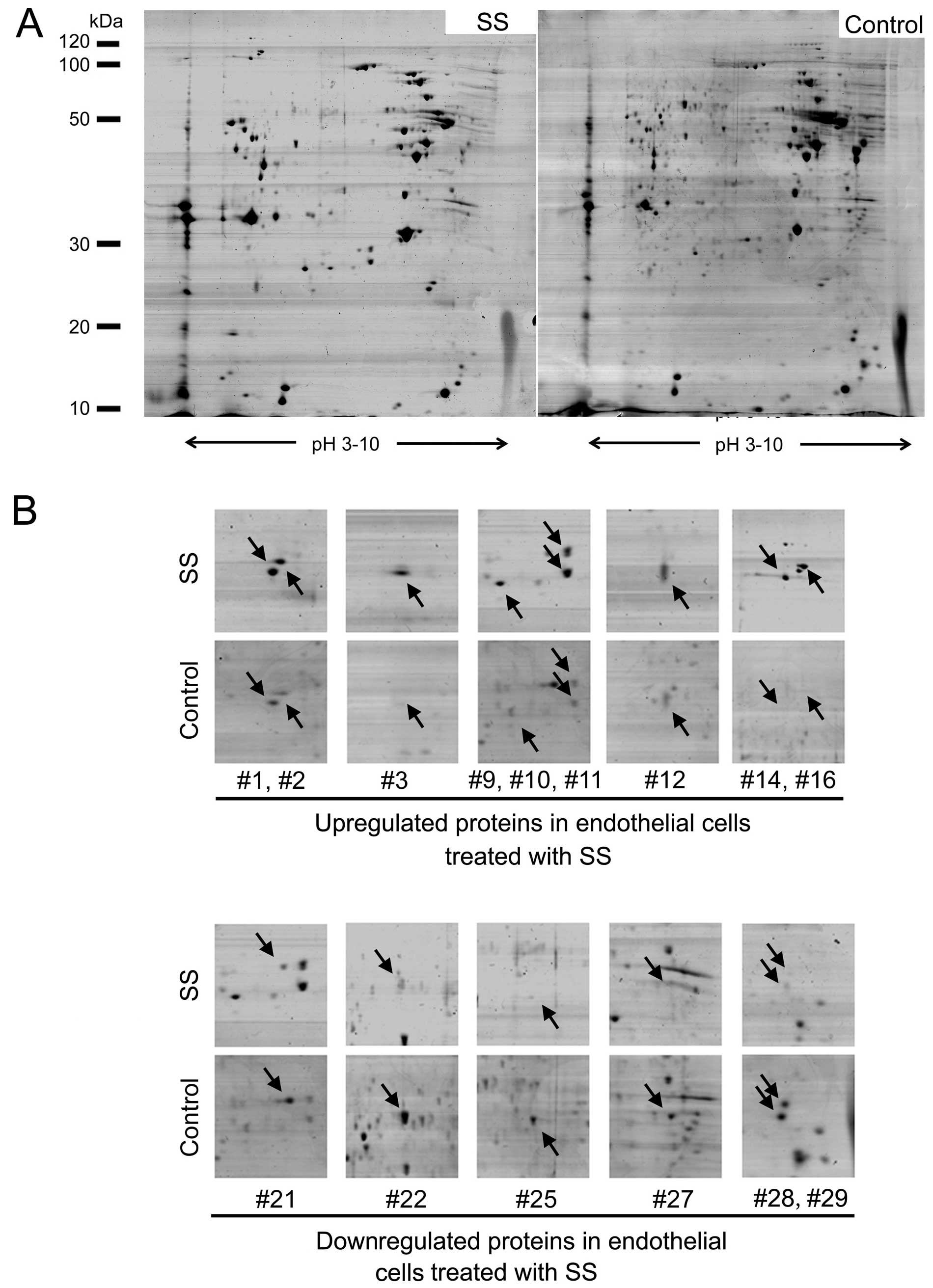
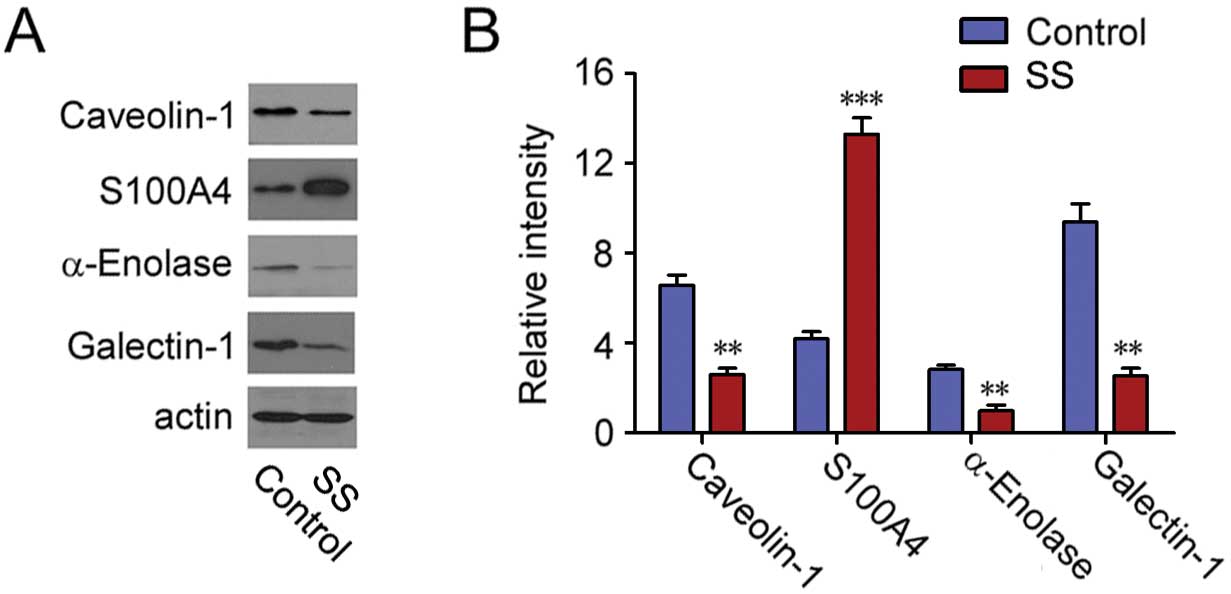
|
1
|
Cornell TT, Rodenhouse P, Cai Q, Sun L and
Shanley TP: Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 2
regulates the inflammatory response in sepsis. Infect Immun.
78:2868–2876. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akrout N, Sharshar T and Annane D:
Mechanisms of brain signaling during sepsis. Curr Neuropharmacol.
7:296–301. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu SF and Malik AB: NF-kappa B activation
as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L622–L645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shapiro NI, Schuetz P, Yano K, et al: The
association of endothelial cell signaling, severity of illness, and
organ dysfunction in sepsis. Crit Care. 14:R1822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aird WC: The role of the endothelium in
severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood.
101:3765–3777. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee WL and Slutsky AS: Sepsis and
endothelial permeability. N Engl J Med. 363:689–691. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garcia J, Sandi MJ, Cordelier P, et al:
Tie1 deficiency induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO
Rep. 13:431–439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoshimatsu Y and Watabe T: Roles of TGF-β
signals in endothelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac
fibrosis. Int J Inflam. 2011:7240802011.
|
|
9
|
van Meeteren LA and ten Dijke P:
Regulation of endothelial cell plasticity by TGF-β. Cell Tissue
Res. 347:177–186. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Nagasawa K, Chiba H, Fujita H, et al:
Possible involvement of gap junctions in the barrier function of
tight junctions of brain and lung endothelial cells. J Cell
Physiol. 208:123–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H,
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Am Soc Nephrol.
19:2282–2287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tanjore H, Xu XC, Polosukhin VV, et al:
Contribution of epithelial-derived fibroblasts to bleomycin-induced
lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 180:657–665. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu CC and Yates JR III: The application of
mass spectrometry to membrane proteomics. Nat Biotechnol.
21:262–267. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiong P, Li Y, Tang Y and Chen H:
Proteomic analyses of Sirt1-mediated cisplatin resistance in OSCC
cell line. Protein J. 30:499–508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsao N, Hsu HP, Wu CM, Liu CC and Lei HY:
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha causes an increase in blood-brain
barrier permeability during sepsis. J Med Microbiol. 50:812–821.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu Z, Ghosh S, Wang Z and Hunter T:
Downregulation of caveolin-1 function by EGF leads to the loss of
E-cadherin, increased transcriptional activity of β-catenin, and
enhanced tumor cell invasion. Cancer Cell. 4:499–515.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salem AF, Bonuccelli G, Bevilacqua G, et
al: Caveolin-1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell differentiation and
restores membranous E-cadherin via suppression of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Cycle. 10:3692–3700. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bailey KM and Liu J: Caveolin-1
up-regulation during epithelial to mesenchymal transition is
mediated by focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 283:13714–13724.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schuetz P, Jones AE, Aird WC and Shapiro
NI: Endothelial cell activation in emergency department patients
with sepsis-related and non-sepsis-related hypotension. Shock.
36:104–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kokudo T, Suzuki Y, Yoshimatsu Y, Yamazaki
T, Watabe T and Miyazono K: Snail is required for TGFbeta-induced
endothelial-mesenchymal transition of embryonic stem cell-derived
endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 121:3317–3324. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Qu X, Yao J, et al: Blockade of
endothelial-mesenchymal transition by a Smad3 inhibitor delays the
early development of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 59:2612–2624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Widyantoro B, Emoto N, Nakayama K, et al:
Endothelial cell-derived endothelin-1 promotes cardiac fibrosis in
diabetic hearts through stimulation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Circulation. 121:2407–2418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu Y, Liao HL, Wang N, et al: Lipoprotein
promotes caveolin-1 and ras translocation to caveolae: role of
cholesterol in endothelial signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 20:2465–2470. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Potenta S, Zeisberg E and Kalluri R: The
role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Br J Cancer. 99:1375–1379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, et al:
Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use
of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus
Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society
of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 101:1644–1655. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|