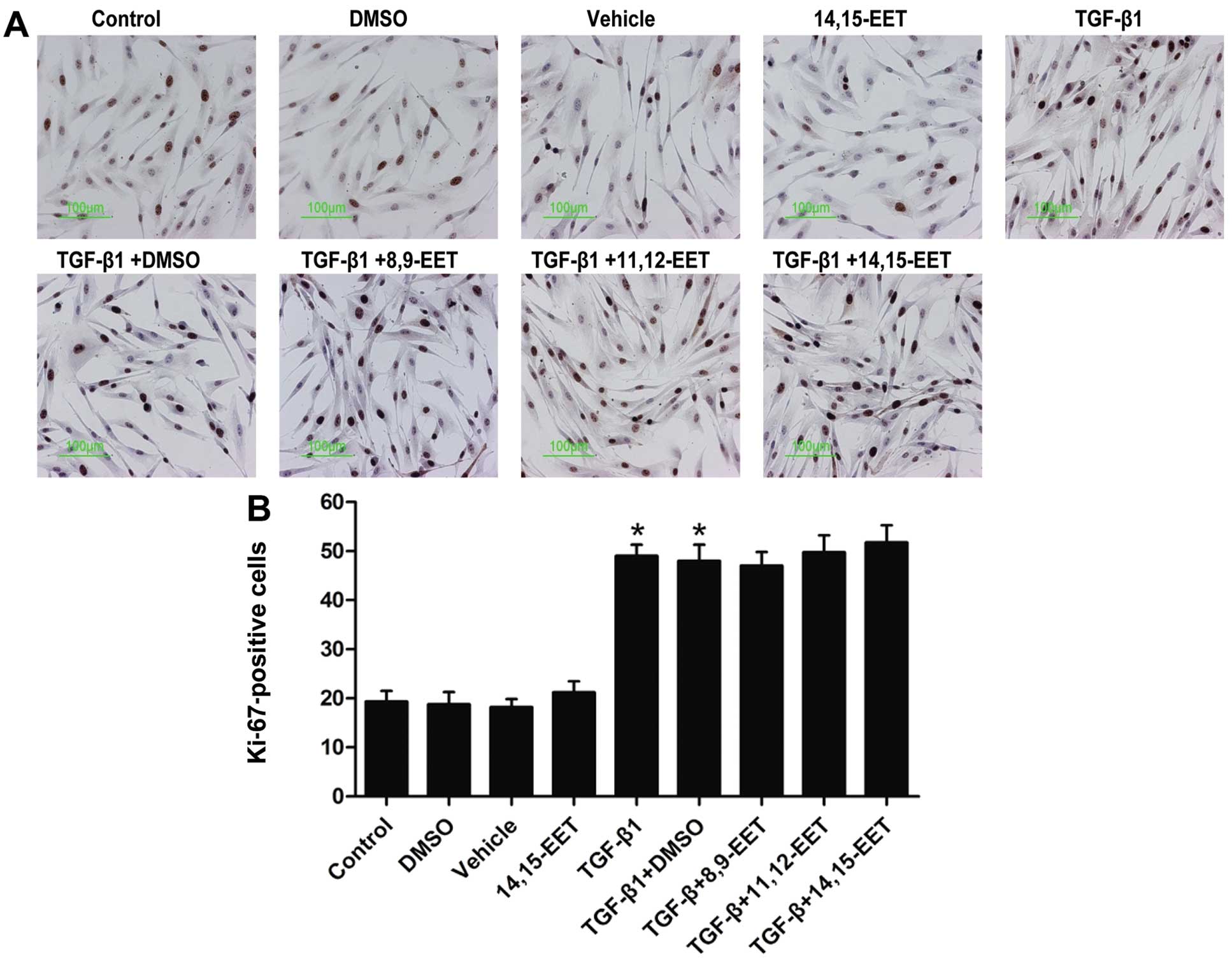
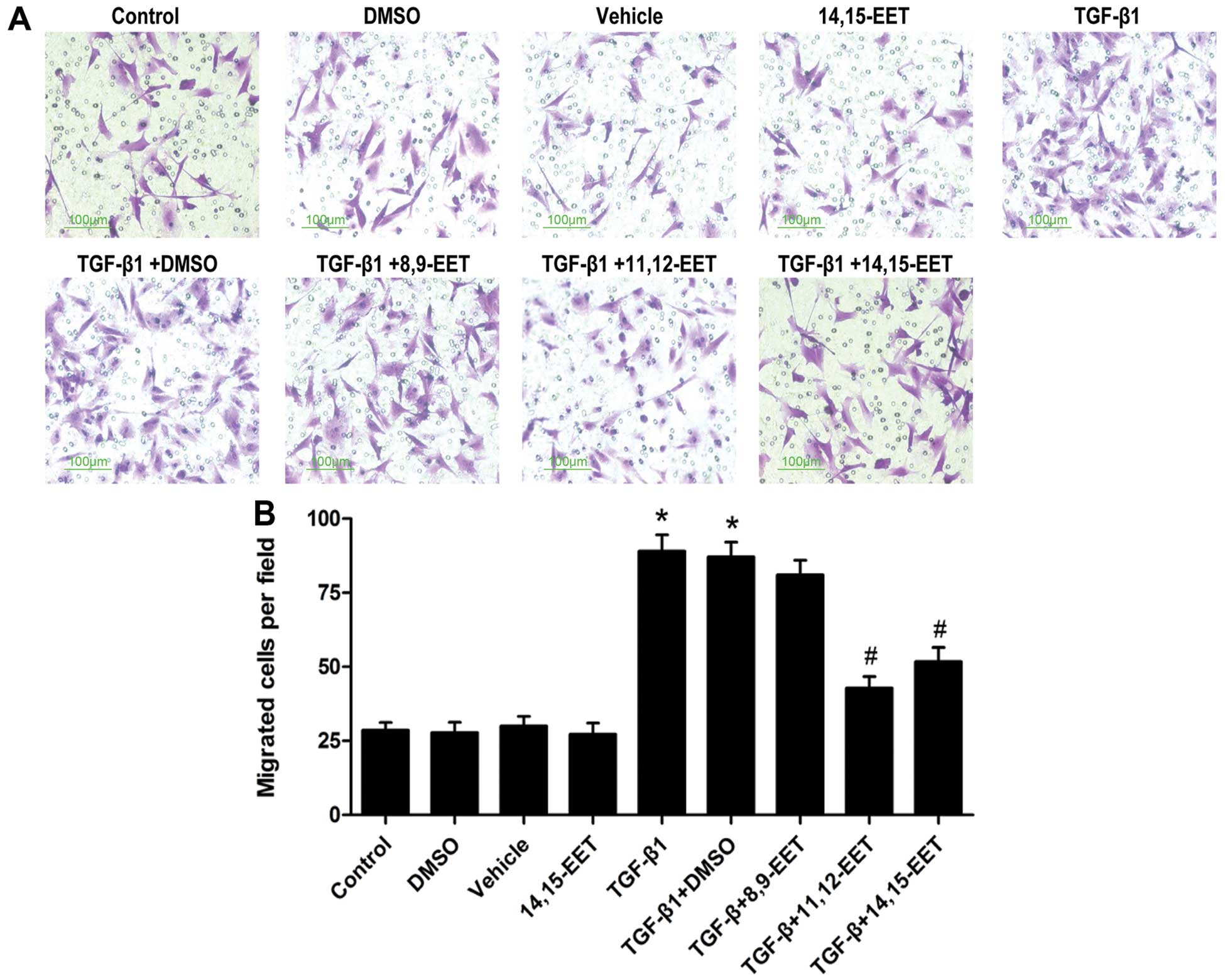
|
1
|
Stefanec T: Endothelial apoptosis: could
it have a role in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease? Chest.
117:841–854. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang X, Long L, Reynolds PN and Morrell
NW: Expression of mutant BMPR-II in pulmonary endothelial cells
promotes apoptosis and a release of factors that stimulate
proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Pulm Circ.
1:103–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wort SJ, Ito M, Chou PC, et al:
Synergistic induction of endothelin-1 by tumor necrosis factor
alpha and interferon gamma is due to enhanced NF-kappaB binding and
histone acetylation at specific kappaB sites. J Biol Chem.
284:24297–24305. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Soon E, Holmes AM, Treacy CM, et al:
Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines predict survival in
idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Circulation. 122:920–927. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antonelli-Orlidge A, Saunders KB, Smith SR
and D'Amore PA: An activated form of transforming growth factor
beta is produced by cocultures of endothelial cells and pericytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:4544–4548. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sakao S, Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Wood K,
Cool CD and Voelkel NF: Apoptosis of pulmonary microvascular
endothelial cells stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 291:L362–L368. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sturrock A, Cahill B, Norman K, et al:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces Nox4 NAD(P)H oxidase and
reactive oxygen species-dependent proliferation in human pulmonary
artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
290:L661–L673. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma W, Han W, Greer PA, et al: Calpain
mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of
pulmonary hypertension, and its inhibition attenuates pathologic
features of disease. J Clin Invest. 121:4548–4566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu S, Moomaw CR, Tomer KB, Falck JR and
Zeldin DC: Molecular cloning and expression of CYP2J2, a human
cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase highly expressed in
heart. J Biol Chem. 271:3460–3468. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeldin DC: Epoxygenase pathways of
arachidonic acid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 276:36059–36062. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, et al:
Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived
eicosanoids. Science. 285:1276–1279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pasceri V, Wu HD, Willerson JT and Yeh ET:
Modulation of vascular inflammation in vitro and in vivo by
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activators.
Circulation. 101:235–238. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang N, Verna L, Chen NG, et al:
Constitutive activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma suppresses pro-inflammatory adhesion molecules in
human vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 277:34176–34181.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Feige JN, Gelman L, Michalik L, Desvergne
B and Wahli W: From molecular action to physiological outputs:
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors
at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog Lipid Res.
45:120–159. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sacerdoti D, Colombrita C, Di Pascoli M,
et al: 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid stimulates heme-oxygenase-1
in endothelial cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
82:155–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Lin L, Jiang J, et al:
Up-regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by
endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor involves
mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C signaling
pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 307:753–764. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wei X, Xiao X, et al: Arachidonic
acid epoxygenase metabolites stimulate endothelial cell growth and
angiogenesis via mitogen-activated protein kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 314:522–532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang S, Lin L, Chen JX, et al: Cytochrome
P-450 epoxygenases protect endothelial cells from apoptosis induced
by tumor necrosis factor-alpha via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H142–H151. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun J, Sui X, Bradbury JA, Zeldin DC,
Conte MS and Liao JK: Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell
migration by cytochrome p450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Circ
Res. 90:1020–1027. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng C, Wang L, Li R, et al: Gene
delivery of cytochrome p450 epoxygenase ameliorates
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in rats. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:740–749. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian X, Vroom C, Ghofrani HA, et al:
Phosphodiesterase 10A upregulation contributes to pulmonary
vascular remodeling. PLoS One. 6:e181362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dhanasekaran A, Al-Saghir R, Lopez B, et
al: Protective effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on human
endothelial cells from the pulmonary and coronary vasculature. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H517–H531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang B, Graham L, Dikalov S, et al:
Overexpression of cytochrome P450 CYP2J2 protects against
hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in cultured bovine aortic endothelial
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 60:310–320. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan P, Salvadore G, Li X, et al:
Valproate activates the Notch3/c-FLIP signaling cascade: a strategy
to attenuate white matter hyperintensities in bipolar disorder in
late life? Bipolar Disord. 11:256–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim HY, Hwang JY, Kim SW, et al: The CXCR4
antagonist AMD3100 has dual effects on survival and proliferation
of myeloma cells in vitro. Cancer Res Treat. 42:225–234. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clark PE, Polosukhina DA, Gyabaah K, Moses
HL, Thorburn A and Zent R: TRAIL and interferon-alpha act
synergistically to induce renal cell carcinoma apoptosis. J Urol.
184:1166–1174. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang M, He Z, Wen L, et al: Cadmium
suppresses the proliferation of piglet Sertoli cells and causes
their DNA damage, cell apoptosis and aberrant ultrastructure.
Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 8:972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He J and Bazan HE: Epidermal growth factor
synergism with TGF-beta1 via PI-3 kinase activity in corneal
keratocyte differentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
49:2936–2945. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Merlo S, Frasca G, Canonico PL and Sortino
MA: Differential involvement of estrogen receptor alpha and
estrogen receptor beta in the healing promoting effect of estrogen
in human keratinocytes. J Endocrinol. 200:189–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu C, Gui Q, Chen W, et al: Small
interference RNA targeting tissue factor inhibits human lung
adenocarcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30:632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cool CD, Stewart JS, Werahera P, et al:
Three-dimensional reconstruction of pulmonary arteries in plexiform
pulmonary hypertension using cell-specific markers. Evidence for a
dynamic and heterogeneous process of pulmonary endothelial cell
growth. Am J Pathol. 155:411–419. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yi ES, Kim H, Ahn H, et al: Distribution
of obstructive intimal lesions and their cellular phenotypes in
chronic pulmonary hypertension. A morphometric and
immunohistochemical study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
162:1577–1586. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Zuo XR, Wang YY, Xie WP, Wang H
and Zhang M: Monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension
is attenuated by TNF-α antagonists via the suppression of TNF-α
expression and NF-κB pathway in rats. Vascul Pharmacol. 58:71–77.
2013.
|
|
34
|
Fujita M, Shannon JM, Irvin CG, et al:
Overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha produces an increase
in lung volumes and pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 280:L39–L49. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao YD, Courtman DW, Deng Y, Kugathasan
L, Zhang Q and Stewart DJ: Rescue of monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary arterial hypertension using bone marrow-derived
endothelial-like progenitor cells: efficacy of combined cell and
eNOS gene therapy in established disease. Circ Res. 96:442–450.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sage E, Mercier O, Van den Eyden F, et al:
Endothelial cell apoptosis in chronically obstructed and reperfused
pulmonary artery. Respir Res. 9:192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Taraseviciene-Stewart L, Kasahara Y, Alger
L, et al: Inhibition of the VEGF receptor 2 combined with chronic
hypoxia causes cell death-dependent pulmonary endothelial cell
proliferation and severe pulmonary hypertension. FASEB J.
15:427–438. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Kutryk MJ,
Kuliszewski MA, et al: Bone morphogenetic protein receptor-2
signaling promotes pulmonary arterial endothelial cell survival:
implications for loss-of-function mutations in the pathogenesis of
pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 98:209–217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sun CK, Lee FY, Sheu JJ, et al: Early
combined treatment with cilostazol and bone marrow-derived
endothelial progenitor cells markedly attenuates pulmonary arterial
hypertension in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 330:718–726. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Ma C, Zhang Q, et al: The key role
of transforming growth factor-beta receptor I and 15-lipoxygenase
in hypoxia-induced proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle
cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1184–1202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ismail S, Sturrock A, Wu P, et al: NOX4
mediates hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells: the role of autocrine production of
transforming growth factor-{beta}1 and insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L489–L499. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Revermann M, Barbosa-Sicard E, Dony E, et
al: Inhibition of the soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. J Hypertens.
27:322–331. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|