Introduction
Human keratinocytes compose the outermost layer of
the skin, and are the predominant cells found in the epidermis. Due
to their localization in the human body, keratinocytes are
continuously exposed to endogenous and environmental pro-oxidant
agents. Therefore, the levels of intracellular hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2) increase in response to a variety of
pro-oxidant agents (e.g., UV radiation and sunlight), free ions
liberated from storage and heme-containing proteins (1,2).
Epidermal cells and keratinocytes of normal skin are the primary
targets of pro-oxidant agents, and thus express high levels of
cellular proteins related to the detoxification of reactive oxygen
species (ROS) (1). These
increased levels are implicated in certain inflammatory skin
diseases, such as psoriasis, and are mediated by oxidative stress
(3). Therefore, increased ROS
production and defects in the antioxidant system may be involved in
the pathogenesis of keratinocyte-related diseases (4).
Recently, a number of studies have reported that
microRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in the regulation of
functions of keratinocytes. Biswas et al (5) first reported the association between
miRNAs and keratinocyte proliferation by demonstrating that miR-210
attenuates keratinocyte proliferation by downregulating the cell
cycle regulatory gene, E2F3. Moreover, Yu et al
(6) revealed that miR-205
promotes keratinocyte migration through the downregulation of
SH2-containing phosphoinositide 5′-phosphatase 2 (SHIP2), a lipid
phosphatase that dephosphorylates a critical cell survival factor,
termed phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP3). Furthermore,
Hildebrand et al (7)
identified an association between miRNAs and keratinocyte
differentiation by profiling miRNA expression during human
keratinocyte differentiation. miRNAs have also been linked to
psoriasis, a disease characterized by abnormal keratinocyte
proliferation. More specifically, miR-125a and miR-424 are
downregulated in the skin of patients with psoriasis. These miRNAs
modulate keratinocyte proliferation by targeting fibroblast growth
factor receptor 2 (FGFR2), and putatively target mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and cyclin E1 (8,9).
We recently reported that the titrated extract of Centella
asiatica protects HaCaT keratinocytes from UVB-induced
cytotoxicity by altering miRNA expression (10). Despite these studies demonstrating
that miRNAs are key regulators in diverse biological processes in
human keratinocytes, the association between ROS and miRNAs in
these cells remains unclear.
Oridonin, a diterpenoid isolated from Rabdosia
rubescens, has been shown to exhibit anticancer,
anti-microbial, and anti-inflammatory properties (11). Although increased ROS production
has been implicated in the anticancer effects of oridonin (12,13), studies have revealed that this
effect does not occur in normal cells (14). In fact, oridonin has been shown to
exert protective effects against arsenic(III)-induced oxidative
stress (15). These data indicate
that the oridonin-mediated regulation of ROS production varies by
cell type. In the present study, we demonstrate that oridonin
reduces ROS production and exerts protective effects against
H2O2-induced damage in HaCaT keratinocytes.
Furthermore, we used miRNA microarray and bioinformatics tools to
elucidate the molecular mechanisms that mediate these protective
effects against oxidative stress.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and chemical treatment
Normal human HaCaT keratinocytes were grown in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Gibco®, Life
Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine
serum (FBS; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and antibiotics.
Oridonin and H2O2 were purchased from
Sigma-Aldrich and Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), respectively. For
toxicity and cell viability assays, 4×104 HaCaT cells
per well were seeded into 96-well plates and 7×105 cells
were seeded into 60-mm culture plates, respectively. Oridonin and
H2O2 were diluted into DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich)
and deionized water, respectively. The cells were treated with
various doses of oridonin and a fixed dose (800 μM) of
H2O2 for 3–24 h. Propidium iodide (PI) and
Triton X-100 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Cell viability assay
The effects of oridonin on the growth of HaCaT cells
treated with or without H2O2 were assessed
using water-soluble tetrazolium salt (WST-1) assays. After
treatment, the HaCaT cells were mixed with 100 μl of WST-1 solution
followed by incubation at 37°C for 1 h. Cell viability was
determined after measuring the absorbance at 450 nm using an iMark
microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). All
results are expressed as the mean percentage ± standard deviation
(SD) of 3 independent experiments. When comparing treated and
untreated cells, p-values <0.05 as determined by the Student’s
t-test were considered to indicate statistically significant
differences.
ROS scavenging assay
Intracellular ROS scavenging assays were performed
by measuring the fluorescence intensity of the
2′7′-dichlorofluroescein diacetate (DCF-DA) probe, which was
proportional to the amount of ROS formed. The cells pre-treated
with and without oridonin were incubated with
H2O2 for 3 h prior to harvest. The cells were
then mixed with DCF-DA solution and incubated at 37°C for 1 h.
Fluorescence intensity was measured using a BD FACSCalibur flow
cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA).
Analysis of cell death by flow
cytometry
Cell cycle and death were estimated by assessing the
incorporation of the fluorescent dye, PI. Cells treated with and
without oridonin and/or H2O2 were harvested,
resuspended, and then incubated with PI staining solution (50 μg/ml
PI, 0.5% Triton X-100, and 100 μg/ml RNase) at 37°C for 1 h.
Fluorescence intensity was detected using a BD FACSCalibur flow
cytometer.
miRNA-based microarray analysis
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent
(Invitrogen, Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. RNA integrity, concentration and purity were
estimated using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies,
Santa Clara, CA, USA) and MaestroNano (Maestrogen, Las Vegas, NV,
USA). RNA samples that exhibited A260/280 and
A260/A230 values >1.8, as well as an RNA integrity
number (RIN) >8.0, were subjected to microarray analysis, which
was performed using SurePrint G3 Human V16 miRNA 8×60 K arrays
(Agilent Technologies) according to a previously described protocol
(16). Derived data were analyzed
using GeneSpring GX software, version 11.5 (Agilent Technologies).
The raw data were filtered using Flag and t-tests. miRNA expression
was evaluated by assessing the fluorescence ratio between 2
samples. Those displaying >1.5-fold increase or decrease were
selected for further bioinformatics analysis.
Computational analysis of miRNAs
To investigate the biological functions of miRNAs
that exhibited significant changes in expression, we identified
their putative target genes using MicroCosm Targets, version 5
(www.ebi.ac.uk/enright-srv/microcosm/htdocs/targets/v5/).
The cellular functions of the target genes were then determined
using AmiGO, a Gene Ontology (GO)-based analysis and categorization
tool (amigo.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/browse.cgi).
Results
Oridonin reduces
H2O2-induced cytotoxicity in HaCaT cells
Prior to investigating the protective effects of
oridonin on H2O2-induced cellular stress, we
first determined the dose range of oridonin that causes
cytotoxicity in HaCaT cells. The HaCaT cells were treated with
various concentrations of oridonin (1–20 μM) for 24 h, and
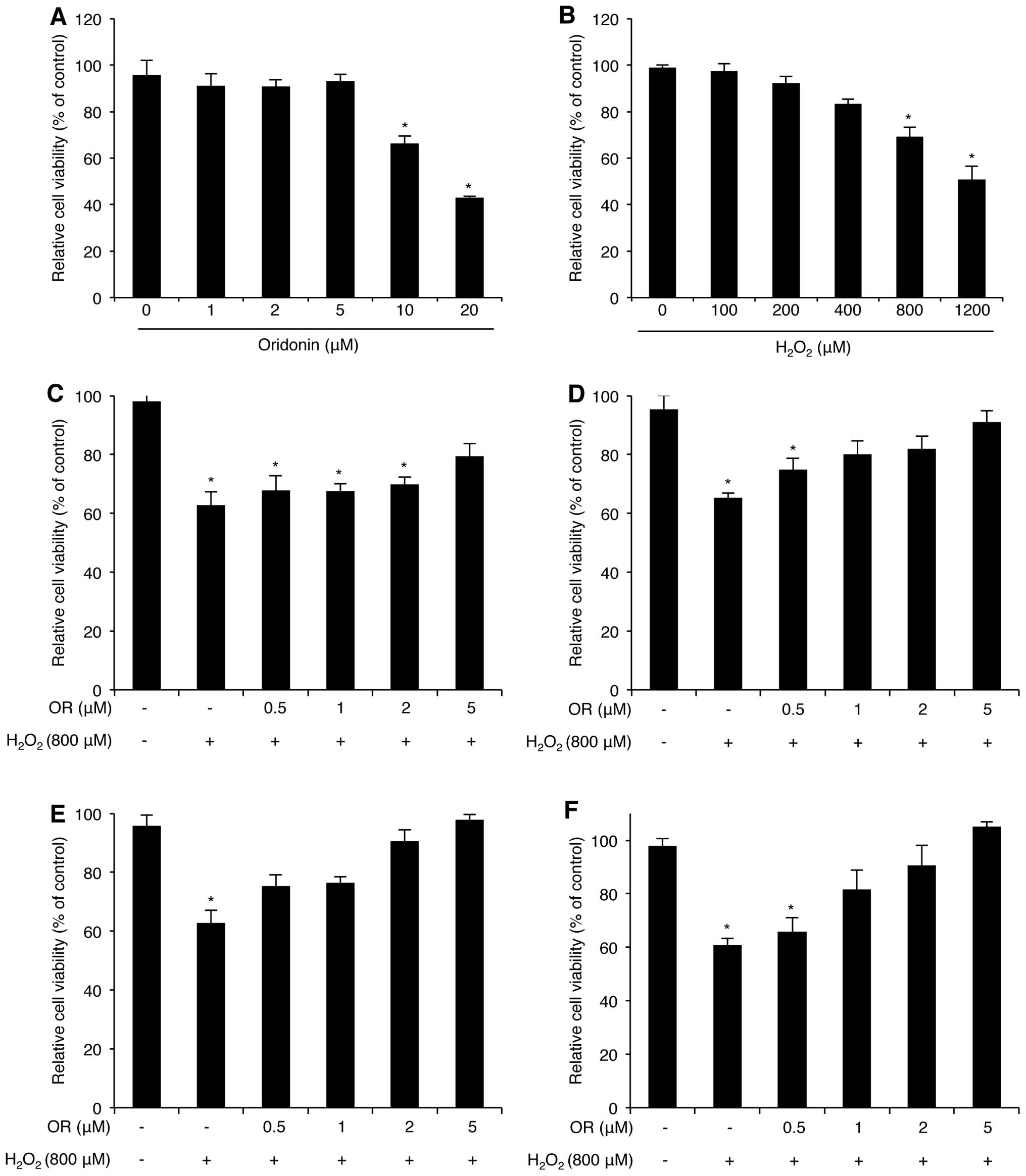
cytotoxicity was estimated using the WST-1 assay (Fig. 1A). Cell viability was maintained
at doses between 1 to 5 μM; however, higher concentrations of
oridonin (10 and 20 μM) decreased HaCaT cell viability. We also
determined that HaCaT cell viability decreased following treatment
with H2O2 in a dose-dependent manner
(Fig. 1B). As we were concerned
about the combined effects of H2O2 and
oridonin on HaCaT cytotoxicity, the cells were pre-treated with
various doses of oridonin for different periods of time prior to
the induction of oxidative stress with H2O2.
Cell viability was analyzed using the WST-1 assay. Surprisingly,
the oridonin-pre-treated HaCaT cells exhibited a marked resistance
to H2O2-mediated cytotoxicity (Fig. 1C–F). In fact, this effect
increased in a concentration and time-dependent manner, suggesting
that oridonin exerts a protective effect against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HaCaT
cells.
H2O2-induced HaCaT
cell death is reduced following treatment with oridonin
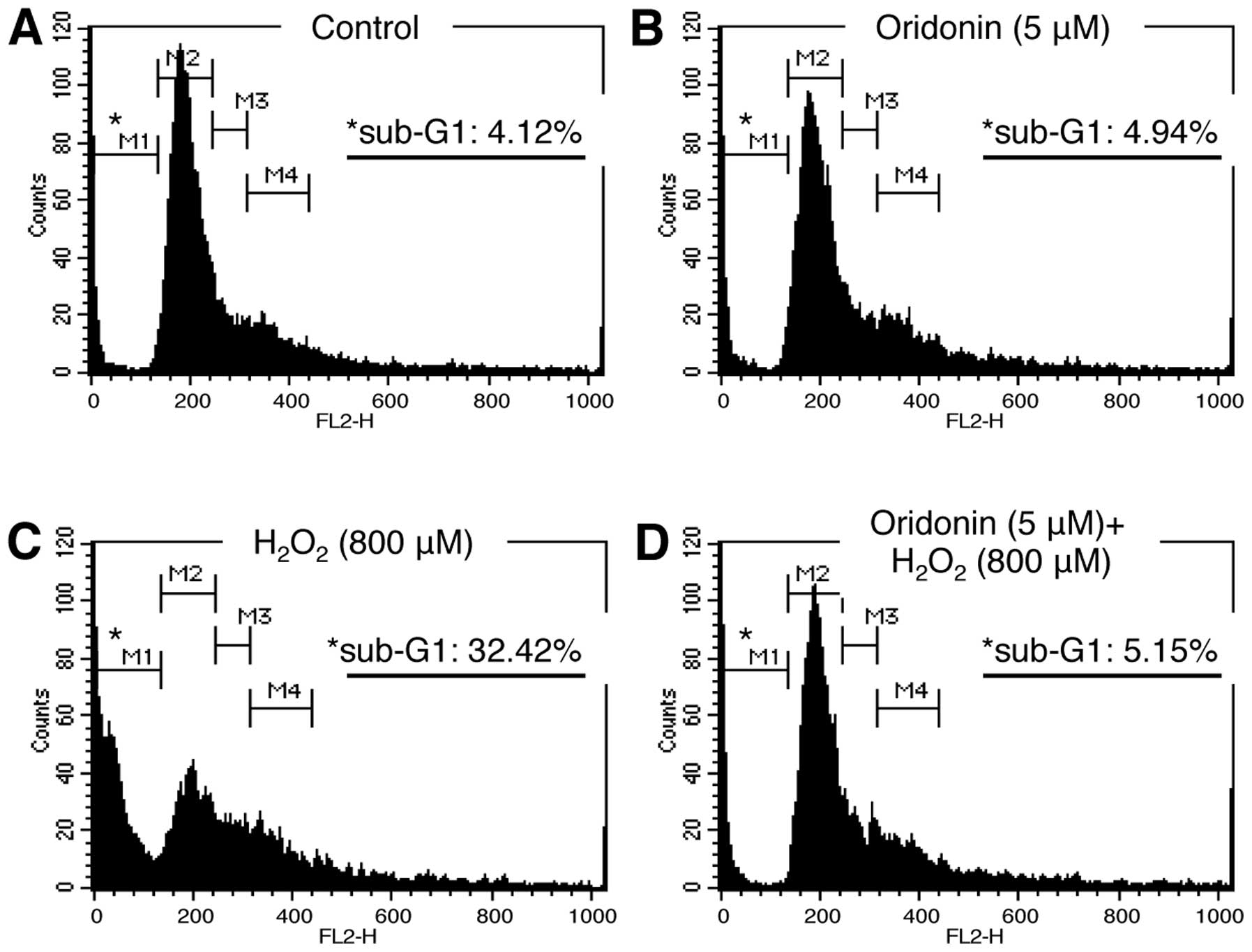
We subsequently investigated the biological
mechanisms involved in the protective effects of oridonin against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Changes in
cell viability can be physiologically related to cell cycle arrest
and cell death. Therefore, we examined cell cycle progression by PI
staining and flow cytometry. The HaCaT cells treated as indicated
in Fig. 2 were collected, fixed,
stained with PI solution, and subsequently analyzed by flow
cytometry. Our data demonstrated that the distribution of cells
across the various stages of the cell cycle was similar between the
oridonin-treated and the control (DMSO-treated) cells, confirming
that treatment with 5 μM oridonin was non-cytotoxic (Fig. 2A and B). By contrast, the
percentage of cells in the sub-G1 phase was much higher in the
H2O2-treated HaCaT cells compared with the
untreated and oridonin-treated cells (Fig. 2C). Nevertheless, this increase was
not observed in the HaCaT cells pre-treated with oridonin prior to
the induction of oxidative stress (Fig. 2D). These results suggest that
treatment with oridonin maintains cell viability by reducing HaCaT
cell death in H2O2-induced oxidative
stress.
Treatment with oridonin decreases
H2O2-induced ROS production
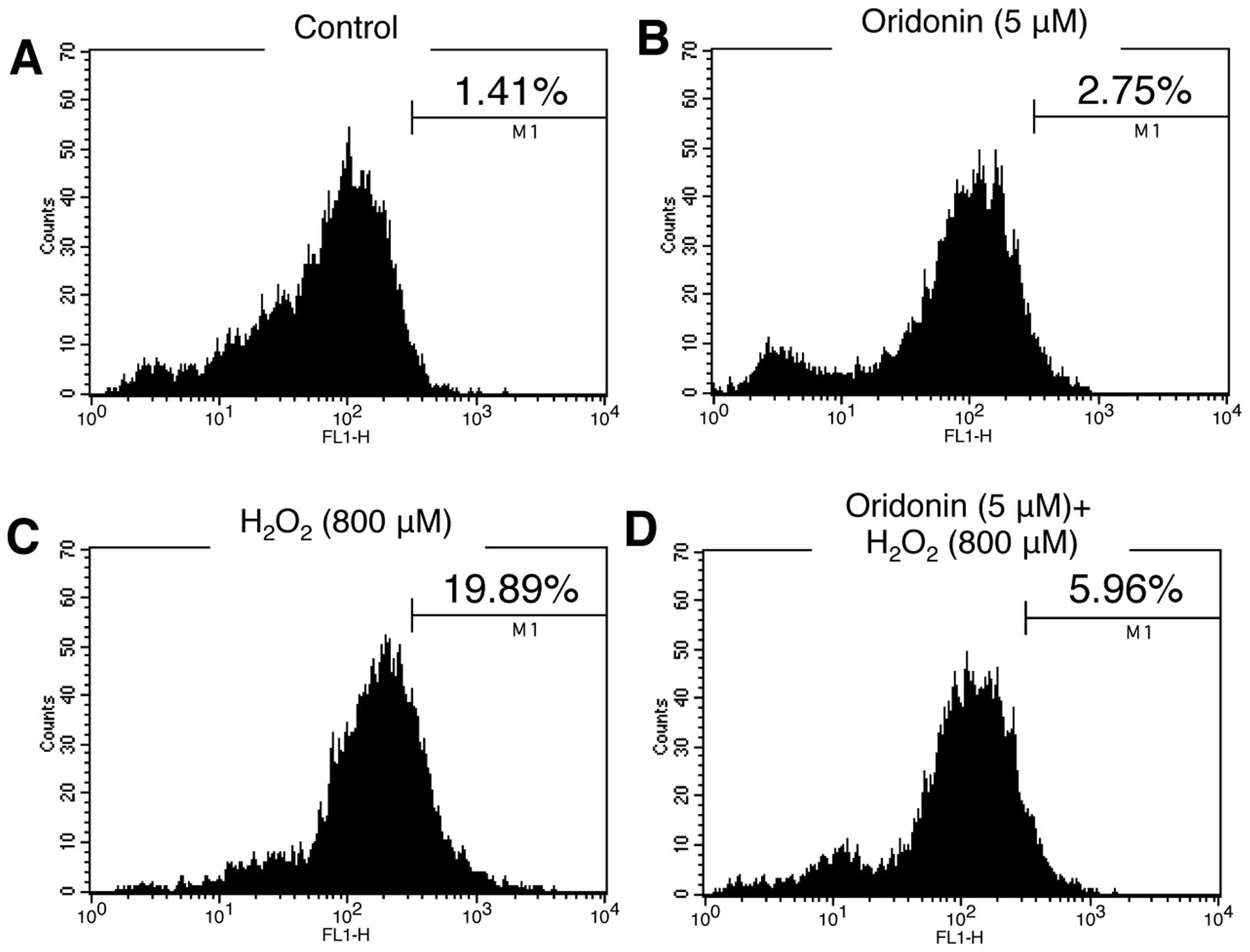
H2O2 is well established as a
strong inducer of ROS, which, if present at high levels, promote
cell death. Since oridonin is a diterpenoid compound, and some
diterpenoid compounds have been shown to have antioxidant
properties, we examined the possibility that oridonin acts as a ROS
scavenger. HaCaT cells grown in oridonin-containing medium were
treated with H2O2 for 3 h. Following exposure
to H2O2, the cells were stained with DCF-DA
solution and the levels of ROS were then analyzed by flow
cytometry. Unlike treatment with H2O2,
oridonin alone did not induce significant ROS production in the
HaCaT cells (Fig. 3A and C). Of
note, our results demonstrated that the increased ROS production
induced by H2O2 was reduced to the levels of
the controls following treatment with oridonin (Fig. 3D), indicating that oridonin has a
scavenging effect on ROS produced in response to
H2O2 in HaCaT cells.
Oridonin alters miRNA expression profiles
in H2O2-treated HaCaT cells
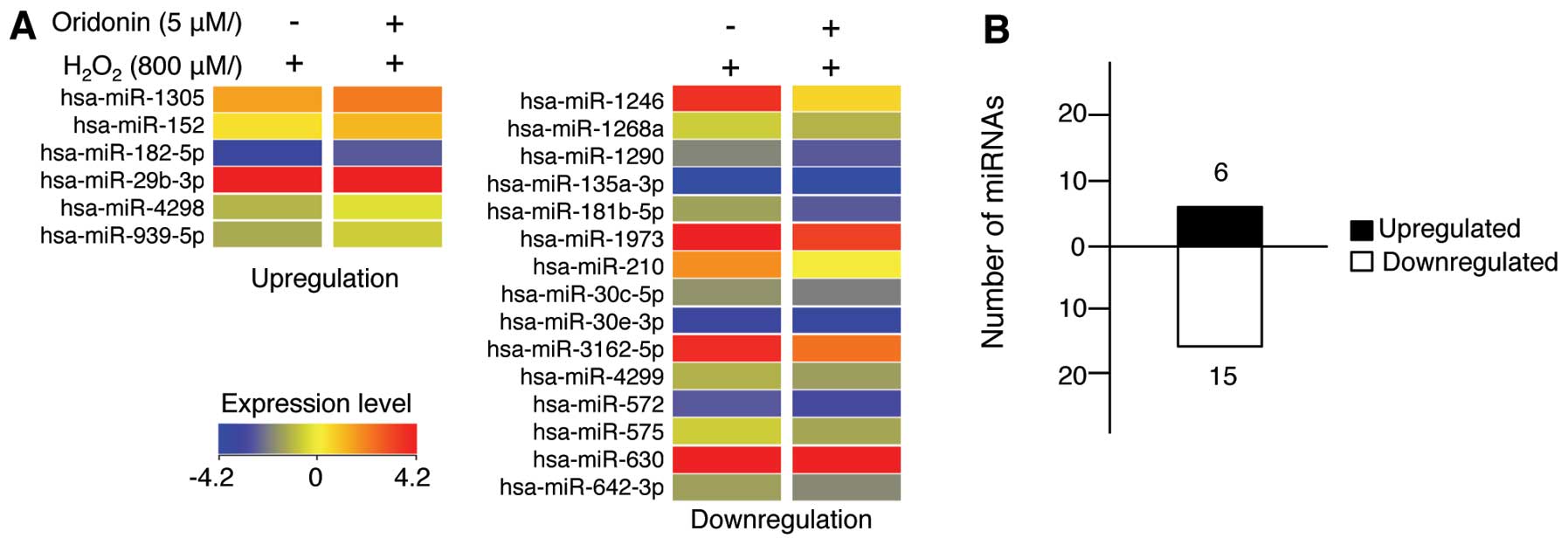
Since miRNAs have been reported to regulate almost
every biological process, including development, differentiation,
proliferation and apoptosis (17–19), we sought to determine the effects
of oridonin on miRNA expression in HaCaT cells treated with
H2O2 for 24 h. A total of 21 miRNAs were
differentially expressed following treatment with oridonin
(Fig. 4 and Table I). More specifically, 6 miRNAs
were upregulated while 15 miRNAs were downregulated. These results
indicate that, although the majority of miRNAs did not exhibit
significant changes in expression, treatment with oridonin still
affected the miRNA expression levels in the HaCaT cells exposed to
H2O2.
 | Table ImiRNAs whose expression was altered
following treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells. |
Table I
miRNAs whose expression was altered
following treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells.
| miRNAa | FC | Chromosome | miRNA | FC | Chromosome |
|---|
| hsa-miR-1246 | −3.58 | Chr2 | hsa-miR-572 | −1.90 | Chr4 |
| hsa-miR-1268 | −1.58 | Chr15 | hsa-miR-575 | −2.01 | Chr4 |
| hsa-miR-1290 | −2.49 | Chr1 | hsa-miR-630 | −2.29 | Chr15 |
|
hsa-miR-135a-3p | −1.87 | Chr3 |
hsa-miR-642b-3p | −1.68 | Chr19 |
|
hsa-miR-181b-5p | −2.96 | Chr1 | hsa-miR-1305 | 1.59 | Chr4 |
| hsa-miR-1973 | −1.51 | Chr4 | hsa-miR-152 | 2.13 | Chr17 |
| hsa-miR-210 | −4.30 | Chr11 | hsa-miR-182-5p | 2.87 | Chr7 |
| hsa-miR-30c-5p | −2.76 | Chr1 | hsa-miR-29b-3p | 1.65 | Chr1 |
| hsa-miR-30e-5p | −1.53 | Chr1 | hsa-miR-4298 | 1.51 | Chr11 |
|
hsa-miR-3162-5p | −1.57 | Chr11 | hsa-miR-939-5p | 1.94 | Chr8 |
| hsa-miR-4299 | −1.55 | Chr11 | | | |
Bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs
affected by treatment with oridonin
The miRNAs that exhibited altered expression levels
following treatment with oridonin are likely involved in the the
cellular mechanisms responsible for the protective effects of
oridonin against H2O2-induced oxidative
stress in HaCaT cells. Therefore, we used the miRbase Target
Database tool, MicroCosm, to identify the putative target genes of
these miRNAs. We then determined the biological functions
associated with the target genes by GO analysis using AmiGO.
Finally, the target genes were grouped according to biological
processes. Our data demonstrated that the target genes of the
differentially expressed miRNAs could be categorized into 4 groups,
namely aging, skin development, apoptosis and cell proliferation
(Tables II and III).
 | Table IIPredicted targets of miRNAs which
were upregulated in response to treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells. |
Table II
Predicted targets of miRNAs which
were upregulated in response to treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells.
| Target genes and
functions |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| miRNA | Aging | Skin
development | Apoptosis | Cell
proliferation |
|---|
| hsa-miR-29b-3p | AURKB, FOS, CNR1,
BAK1, LOXL2, NUAK1, ATP5G3 | ABCB6, FRAS1,
COL5A1, COL1A1, COL5A3 | AURKB, BIRC2,
NOTCH1, AKAP13, HMGB1, DIABLO, MAP2K4, TIAM1, ZNF336, BAK1, CNR1,
MCL1, ISL1 | AURKB, BIRC2,
NOTCH1, ABI1, GAB1, ARNT, NASP, RXRB, STAT3, CDC7, CO80, AKT2,
VEGFA |
| hsa-miR-182-5p | BCL2, RTN4, TWIST1,
MET, NOX4, AQP2, NUAK1 | APC, TFAP2B | BCL2, TWIST1, APC,
RARG, TOPORS, HDAC2, ARHGEF2, BAG1, CASP9, MLL, ROCK1, PDCD7,
CREB1, RASSF6, MAPK9, SORT1, MEF2C, GLI2, AQP2 | BCL2, TWIST1, NOX4,
RBM5, BIRC5, RARG, WNT5A, ADK, CDK3, SMAD1, FIGF, NUM, NRAS |
| hsa-miR-152 | MNT, BRCA2, TP53,
WNT1, MAP2K1, SCAP, CNR1 | PTGES3, ERRFI1 | MNT, TP53, WNT1,
BRCA2, JAG2, ADAM17, BCL2L11, RTN3, SEMA3A, DEDD2, C1D, PDIA3,
SIX4, TRIM39, USP7, BAG3, E2F1, CNR1 | CDK1B, E2F1, ERBB3,
JAG2, FGF1, FOXF1, IRS1, CDON |
| hsa-miR-939-5p | CDKN1A, HRAS, RARA,
SIN3A, TBX2, ICAM1, GRB2, HTT, BAK1 | SRF, NGFR, EDA,
TCF7L1, JUP, SUFU, COL1A1 | CDKN1A, HRAS, CALR,
CLU, SAMD3, MSX1, TCF7, TNF, CUL1, HDAC6, DFFA, IF16, DUSP2, E2F2,
MCF2L, RHOB, SPDEF, IRAK1, USP47, AXL, ZMAT, BNIP2, TRAF1,
PAX8 | HRAS, RXRA, CLU,
ERBB4, VDR, CDKN1A, SRF, TCF7, CREB3, VAX1, WDR6, OSR2, EDN2, IGF2,
FOXO4, BAI1, TSC1, OSMR, IGF1R |
| hsa-miR-1305 | CTGF, JUN, NEK6,
MSH2, ACAN, FAS, SERP1, CAT, FADS1, EDN1, MAPKAPK5, SIRT1, ATM,
NR3C1, PTEN, CDK6 | ITGA2, CDSN, ATP7A,
STS, LEF1, PSEN1, COL1A2, TCF7L2, COL3A1, COL5A2, TFAP2C,
BCL11B | JUN, FOXC1, FOXO1,
HIF1A, NEK6, MSH2, YAP1, DICER1, BMI1, CD24, PDCD6IP, NET1, PSMD5,
SIRT1, PTEN, ATM, IL6R, MDM4, SGK6, MAGI3, GLO1, LEF1, RB1, HOXA13,
NF1, PAK2, DNAJC10, PECR, MAP2K, IFG1, ROBO1, SGK3, MITF, EDN1 | JUN, WNT16, LEF1,
FGFR2, HIF1A, MDM4, USP28, RB1, BMI1, STA1, CDK7, JAG1, ERG, FKTN,
ATF3, CCNB1, BIRC6, LIFR, BCL6, PI3KR1, DICER1, IGF1, ID4, ROBO1,
SGK3, MITF, KRAS |
 | Table IIIPredicted targets of miRNAs which
were downregulated in response to treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells. |
Table III
Predicted targets of miRNAs which
were downregulated in response to treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells.
| Functions of target
genes |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| miRNA | Aging | Skin
development | Apoptosis | Cell
proliferation |
|---|
| hsa-miR-30c-5p | EDNRA, CAT, LIMS1,
CISD2, MNT, SIRT1, TIMP3, UCP3, SLC6A3 | BCL11B, PDGFA,
OVOL1 | EDNRA, CAT, BCL11B,
VAV3, TRIM32, FRZB, GCG, AR, JAG2, BCL6, HIP1, SON, TIA1, CARD14,
ARHGEF6, SIRT1, TCTN3, ITSN1, BEX2, MNT, MLL | EDNRA, CAT, BCL11B,
IRS1, VAV3, TRIM32, FRZB, GCG, CDCA7, LRRK2, BIRC6, ERG, AR, JAG2,
BCL6, PRG4, VIP, NOX1, MTBP, AREG, PELO, BNC1, TSC1, ERG, PDGFA,
RUNX1, NFIB, LIFR, MAGI2 |
|
hsa-miR-181b-5p | AGT, NR3C1, CNR1,
MET, HCN2, SMC6, PDCD4, VCAM1 | STS | CTNNA1, TGFBR1,
PDCD4, HEY2, SGK3, GATA6, IFNG TNF, SOX7, KRIT1, DUSP6, AKT2,
MAGI3, ARF6, PDCD2, RAD21, SORT1, MAP2K4 | AGT, NR3C1, TGFBR1,
STS, MORC3, MET, WNT16, ID4, VACM1, HEY2, SGK3, NBN, TNF, SOX7,
CDKN3, CREB3, EREG, FGF7, MMP7, PKD2, APPL2, TGFBI, CDC73,
ARTN |
| hsa-miR-210 | INPP5D, SIN3A,
TFRC | - | INPP5D, SIN3A,
RUNX3, CCKBR, AIFM3, DLX1, BTK | INPP5D, ASCL1,
RUNX3, CCKBR, TRIB1, DEAF1, CSF1, NPPC, FGFRL1, PROK1 |
| hsa-miR-572 | NOX4, FZR1,
ATM | - | PIK3R1, BFAR, UACA,
BAG1, ATM | NOX4, PIK3R1,
CCNB1, CTH, BMPER, FZR1, ATM, CDH13 |
| hsa-miR-575 | IL6, VDR, MAPK14,
FAS, IL15, PTEN, TP63, EDN1 | COL5A2, ITGA2,
TP63 | IL6, VDR, MAPK14,
HDAC2, HIF1A, JAK3, MDM2, BID, AKAKP13, BCL2L1, VEGFB, CD40, DAPK3,
MCL1, FXR1, CASP3, PTEN, TP63, EDN1 | IL6, VDR, DLC1,
HGF, HIF1A, PURA, OVOL2, WARS, PTEN, JAK3, MDM2, HDAC2, TP63,
USP28, CD40, VSIG4, COMT, BCL2L1, DBN1, FGF1, NKX2-8, FOXA3, MMP14,
PDFGB EVI5, DISC1, BRCA1, FGFR2, VEGFB |
| hsa-miR-630 | SOD2, SOCS, HMGCR,
CANX, SLC1A2, MME | - | SOD2, YAP1, FOXO1,
PAX3, CYLD, DOCK1, GHR, MPO, MKNK2, APAF1, TGFBR2, MEF2D, RAC1,
PAK7, DDIT4, ETS1, XIAP, IL7, NOTCH2 | SOD2, YAP1, FOXO1,
TOB2, TDGF1, SMAD2, PID1, KLF5, FZD6, PAWR, XIAP, TGFBR2 CDON,
MMP12, FYN, SAV1 SOCS2, NOTCH2, RASGRF1, FRS2 |
| hsa-miR-1290 | NUP62, DLD, TGFB3,
CDK6, TWIST1, GSN, SOCS3, BCL2, NUAK1, FADS1, MAP2K1 | DHCR24, COL5A1,
JUP, SUFU, DSP, ERRFI1 | NUP62, FOXC1, EGFR,
LRP6, SMAD3, NUAK2, NOTCH1, MEF2C, BMP4, RNF144B, RRN3, CUL4A,
PTK2, RALB, ATG5, MAP3K5, MAP2K7, SOX9, ACTC1, TCHP, GDNF SIX4,
STK24, BTG2, SOCS3, MAP3K1, BCL2, IGF1R | NUP62, TWIST,
HTR2A, IGF1, DHCR24, TGFB3, TNFRSF9, SMAD3, MAP2K1, EGFR, F3,
MEF2C, PRNP, PTK2, NRAS, TRIM24, CHUK, DLG3, DPT, EMP2, ANG, INSR,
NOTCH3, IRF2, ATF3, IRAK4, FBXW7, TIPIN, NR2F2, CER1, ERBB4, BECN1,
MAFG, CUL5, KRAS, MDM4, IRS2, ROBO1, CDK6 |
| hsa-miR-1246 | PRKCQ, CTSC,
PRELP | EDA | PRKCQ, CTSC, ESR2,
HIPK2, CAV1, DIDO1, PEG3, SART1 | PRKCQ, ESR2, PRKCA,
BTC, WT1, CAV1, CGRRF1, DKC1, MYO16, SESN1, ING1, PCM1, PRL, ACE2,
WNT2B, POLA1 |
| hsa-miR-1268 | DBH, TERF1,
CDKN2A | DDR1, TGM3 | DBH, TERF1, E2F1,
CARD10, PAX2, MAPK1, SFRP4, PAX8, TBX5, TRIO, TNS4, BCL2L15, E2F2,
CARD8, NOL3 | DBH, NES, E2F1,
TBX5, FTO, ICMT, RASGRP4, PGR, EGR4, CXCL10, TRIM27, TGFB1I1, MITF,
BNIPL, PAX2, MAPK1, CDKN2A, IGFBR3, EIF5A2 |
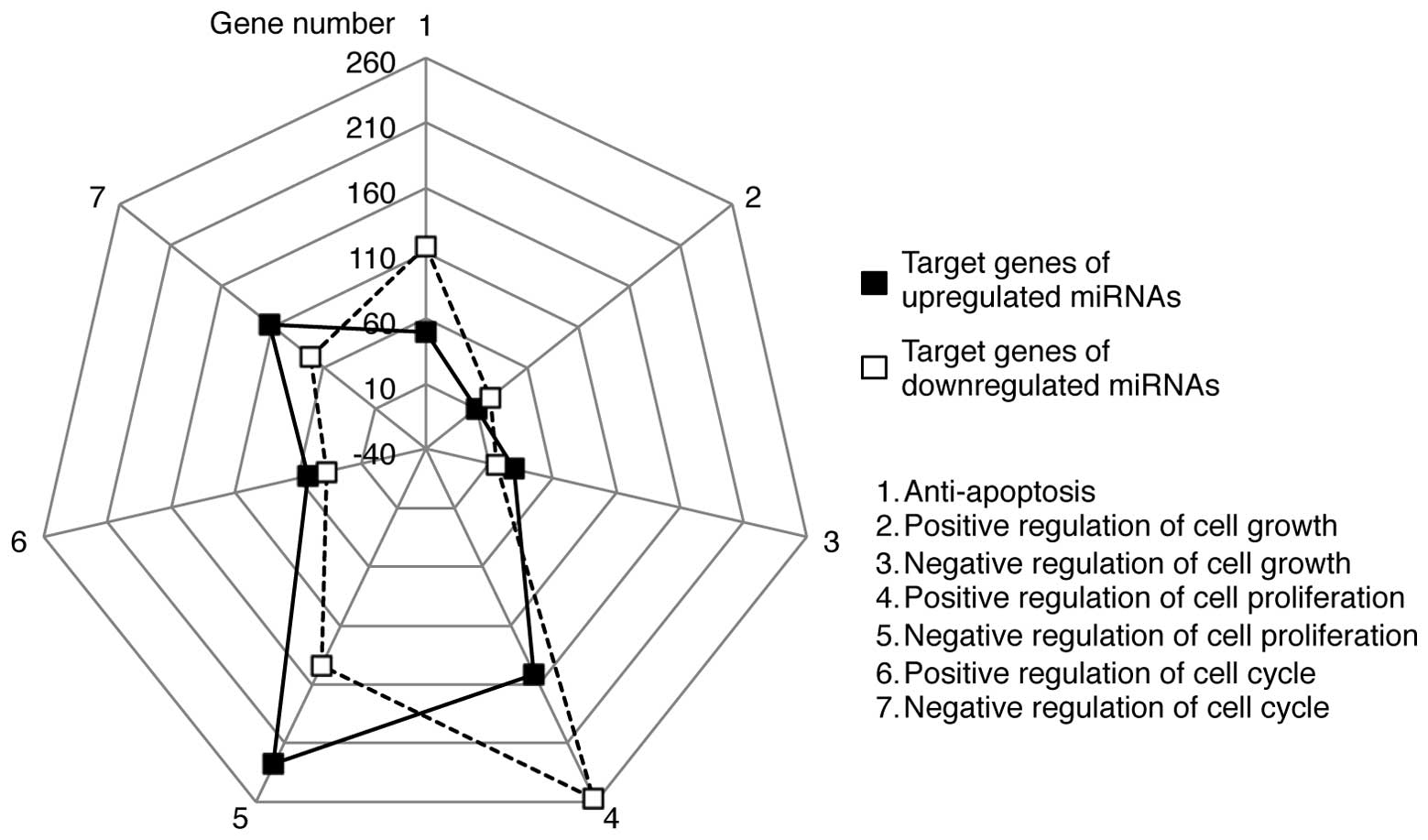
The GO terms contained bi-directional processes for
each term. For example, ‘apoptosis’ included both anti-apoptotic
and pro-apoptotic processes. Therefore, we further categorized the
target genes into subsets of GO terms, such as anti-apoptosis and
positive or negative regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth and
cell proliferation (Fig. 5). A
greater number of target genes of the upregulated miRNAs was
associated with the negative regulation of the cell cycle, growth
and proliferation than with the positive regulation of these
processes. Conversely, the target genes of the downregulated miRNAs
were more biased towards anti-apoptosis and positive regulation of
the cell cycle, growth and proliferation. These results suggest
that the upregulated miRNAs may potentially target genes involved
in cell death, whereas the downregulated miRNAs may regulate genes
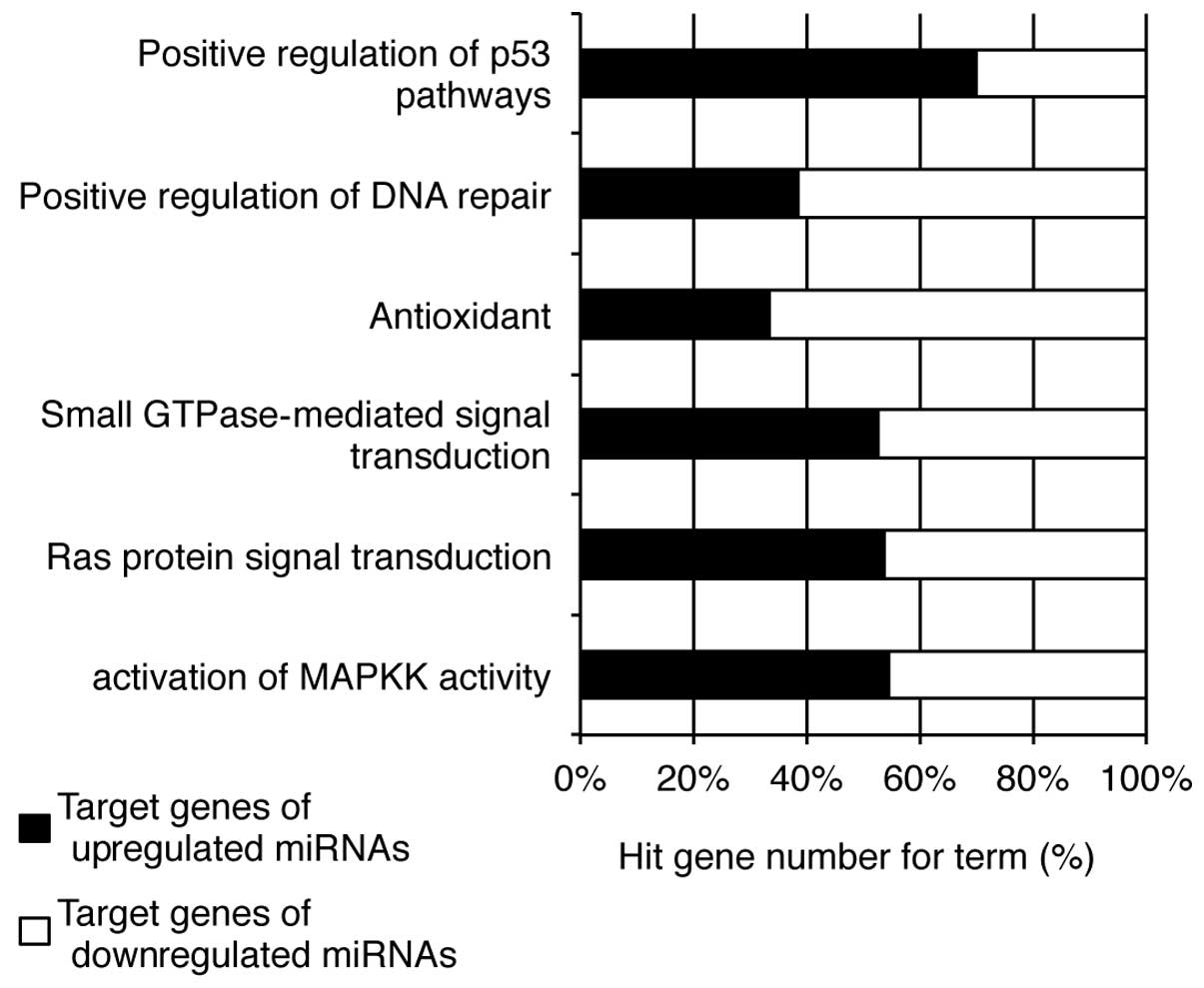
critical for cell survival. Further categorization of the target
genes demonstrated that the upregulated miRNAs may be linked to the
positive regulation of p53 pathways and the activation of MAPKK
activity, while those targeted by the downregulated miRNAs are
associated with antioxidant activity and the positive regulation of
DNA repair (Fig. 6).
Collectively, these results suggest that the oridonin-mediated
protective effects against H2O2-induced
damage in HaCaT cells involve changes in the expression of specific
miRNAs that regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Discussion
In this study, we demonstrate that the protective
effects of oridonin against H2O2-induced
damage in HaCaT human keratinocytes occurs through the regulation
of miRNA expression. Oridonin, a diterpenoid isolated from
Rabdosia rubescens, reportedly exhibits anticancer effects
(11). Although some terpenoid
compounds are used as antioxidants (20), this property has yet to be
confirmed for oridonin. Depending on the dosage, this compound
induces bifunctional effects. As previoiusly demonstrated, high
doses (≥10 μM) induce apoptosis in several cancer cell types
(11,13,21), while low doses (≤5 μM) protect
against arsenic(III)-induced cytotoxicity in UROtsa cells (15). Consistent with these studies, we
found that cytotoxicity due to treatment with oridonin only occurs
at high concentrations (>5 μM). Notably, at non-cytotoxic
concentrations, oridonin induced a protective effect on
H2O2-induced cell death in HaCaT cells. In
addition, DCF-based fluorimetric assay revealed that low doses of
oridonin act as a scavenger of ROS during
H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Our data
suggest that oridonin exerts these effects by altering miRNA
expression profiles. Bioinformatics analysis of the putative target
genes of the miRNAs revealed that the differentially expressed
miRNAs may potentially be involved in the anti-apoptotic and
antioxidant effects induced by oridonin in HaCaT cells.
Our miRNA microarray and bioinformatics analysis
indicated that the putative target genes of the downregulated
miRNAs may be involved in antioxidant processes and the negative
regulation of cell proliferation. Of note, miR-210 expression was
markedly decreased by oridonin in the
H2O2-treated HaCaT cells (Table I). This miRNA has been reported to
increase ROS formation in response to hypoxia and to target the
iron-sulfur cluster protein, ISCU, in MCF-7 and HCT116 cancer cells
(22,23). Moreover, miR-210 is the
predominant miRNA activated under hypoxic conditions in various
cancer types, and its expression is upregulated by
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α (24). Hypoxia-induced miR-210 expression
has been shown to attenuate keratinocyte proliferation by
downregulating the cell cycle regulatory protein, E2F3 (5). Taken together, these data strongly
suggest that miR-210 is an important miRNA in ROS-mediated cellular
processes; thus, the regulation of its expression is a major
strategy in antioxidative defense mechanisms in keratinocytes.
Our investigation also revealed that miR-1246 and
miR-181b-5p (also known as miR-181b) expression was downregulated
following treatment with oridonin in
H2O2-treated HaCaT cells. Recent studies
identified miR-1246 as a novel target of p53, p63 and p73 (25), of which p53 and p63 are important
regulators of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation
(26,27). miR-181b expression is induced
during human keratinocyte differentiation (7). Another study demonstrated that the
overexpression of miR-181b induces cisplatin-mediated apoptosis by
targeting B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) mRNA (28). Moreover, miR-181 expression has
been found to be upregulated in the brain tissue of patients with
Alzheimer’s disease, which has been linked to ROS-mediated
oxidative stress (29,30). Collectively, these data, as well
as ours indicate that miR-1246 and miR-181 are important targets
involved in the regulation of ROS-mediated oxidative stress in
keratinocytes.
The treatment of HaCaT cells exposed to
H2O2 with oridonin also induced an increase
in miRNA expression. The expression of miR-182-5p (also known as
miR-182) was significantly upregulated in our system, and was
predicted to function in anti-apoptotic processes. Indeed,
previously published studies have demonstrated a role of miR-182-5p
in anti-apoptosis. miR-182-5p enhances melanoma oncogenic behavior
and reduces apoptosis by targeting the tumor suppressor genes,
forkhead factor O3 (FOXO3) and microphthalmia-associated
transcription factor-M (MITF-M) (31). In addition, the overexpression of
miR-182-5p has been shown to induce prostate cancer progression by
targeting the tumor suppressor genes forkhead box F2
(FOXF2), reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal
motifs (RECK) and metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1)
(32). Furthermore, miR-182-5p
overexpression has been shown to markedly induce tumorigenesis and
to reduce ionizing radiation (IR)-mediated apoptosis in ovarian
cancer cells (33). Similar to
these studies, we observed that miR-182-5p expression was
significantly higher in the oridonin-pre-treated
H2O2-exposed HaCaT cells compared with the
control cells treated only with H2O2.
Therefore, our results indicate that the oridonin-mediated
upregulation of miR-182-5p expression enhances cell growth- and
anti-apoptosis-related functions, thus exerting protective effects
against oxidative stress and cell death induced by
H2O2 in HaCaT cells.
In this study, we provide evidence of the potential
role of miRNAs in oridonin-mediated anti-apoptosis in response to
H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HaCaT human
keratinocytes. Although further research is required to verify the
biological significance of these changes in miRNA expression, as
well as the target genes of these miRNAs, our study provides a
meaningful link between oridonin-induced antioxidative defense
mechanims and the regulation of miRNA expression in human
keratinocytes.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all members of our research group
for their support and advice regarding this study. This study was
supported by the KU Research Professor Program of Konkuk University
and a grant from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning
(Grant 20110028646) of the Republic of Korea.
References
|
1
|
Wojas-Pelc A and Marcinkiewicz J: What is
a role of haeme oxygenase-1 in psoriasis? Current concepts of
pathogenesis. Int J Exp Pathol. 88:95–102. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Applegate LA, Scaletta C, Panizzon R and
Frenk E: Evidence that ferritin is UV inducible in human skin: part
of a putative defense mechanism. J Invest Dermatol. 111:159–163.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bickers DR and Athar M: Oxidative stress
in the pathogenesis of skin disease. J Invest Dermatol.
126:2565–2575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Briganti S and Picardo M: Antioxidant
activity, lipid peroxidation and skin diseases. What’s new. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 17:663–669. 2003.
|
|
5
|
Biswas S, Roy S, Banerjee J, et al:
Hypoxia inducible microRNA 210 attenuates keratinocyte
proliferation and impairs closure in a murine model of ischemic
wounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:6976–6981. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu J, Peng H, Ruan Q, Fatima A, Getsios S
and Lavker RM: microRNA-205 promotes keratinocyte migration via the
lipid phosphatase SHIP2. FASEB J. 24:3950–3959. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hildebrand J, Rutze M, Walz N, et al: A
comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression during human
keratinocyte differentiation in vitro and in vivo. J Invest
Dermatol. 131:20–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu N, Brodin P, Wei T, et al: MiR-125b, a
microRNA downregulated in psoriasis, modulates keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting FGFR2. J Invest Dermatol. 131:1521–1529.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ichihara A, Jinnin M, Yamane K, et al:
microRNA-mediated keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis
vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 165:1003–1010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
An IS, An S, Choe TB, et al: Centella
asiatica protects against UVB-induced HaCaT keratinocyte damage
through microRNA expression changes. Int J Mol Med. 30:1349–1356.
2012.
|
|
11
|
Tian W and Chen SY: Recent advances in the
molecular basis of anti-neoplastic mechanisms of oridonin. Chin J
Integr Med. 19:315–320. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Ye Y, Chui JH, et al: Oridonin
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through MAPK and p53
signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. Oncol Rep. 24:647–651.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Zhong Z, Wan J, et al: Oridonin
induces apoptosis, inhibits migration and invasion on
highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells. Am J Chin Med.
41:177–196. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Gao J, Halicka HD, Huang X,
Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z: The cytostatic and cytotoxic
effects of oridonin (Rubescenin), a diterpenoid from Rabdosia
rubescens, on tumor cells of different lineage. Int J Oncol.
26:579–588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du Y, Villeneuve NF, Wang XJ, et al:
Oridonin confers protection against arsenic-induced toxicity
through activation of the Nrf2-mediated defensive response. Environ
Health Perspect. 116:1154–1161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An IS, An S, Kang SM, et al: Titrated
extract of Centella asiatica provides a UVB protective
effect by altering microRNA expression profiles in human dermal
fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 30:1194–1202. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Ambros V and Lee RC: Identification of
microRNAs and other tiny noncoding RNAs by cDNA cloning. Methods
Mol Biol. 265:131–158. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, et al: The
role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle
proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet. 38:228–233. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grassmann J: Terpenoids as plant
antioxidants. Vitam Horm. 72:505–535. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao FH, Liu F, Wei W, et al: Oridonin
induces apoptosis and senescence by increasing hydrogen peroxide
and glutathione depletion in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Mol
Med. 29:649–655. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Favaro E, Ramachandran A, McCormick R, et
al: microRNA-210 regulates mitochondrial free radical response to
hypoxia and krebs cycle in cancer cells by targeting iron sulfur
cluster protein ISCU. PLoS One. 5:e103452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim JH, Park SG, Song SY, Kim JK and Sung
JH: Reactive oxygen species-responsive miR-210 regulates
proliferation and migration of adipose-derived stem cells via
PTPN2. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression
involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell. 35:856–867. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liao JM, Zhou X, Zhang Y and Lu H:
MiR-1246: a new link of the p53 family with cancer and Down
syndrome. Cell Cycle. 11:2624–2630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Woodworth CD, Wang H, Simpson S,
Alvarez-Salas LM and Notario V: Overexpression of wild-type p53
alters growth and differentiation of normal human keratinocytes but
not human papillomavirus-expressing cell lines. Cell Growth Differ.
4:367–376. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Truong AB and Khavari PA: Control of
keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation by p63. Cell Cycle.
6:295–299. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu W, Shan X, Wang T, Shu Y and Liu P:
miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human
cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 127:2520–2529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dumont M and Beal MF: Neuroprotective
strategies involving ROS in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med.
51:1014–1026. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schipper HM, Maes OC, Chertkow HM and Wang
E: microRNA expression in Alzheimer blood mononuclear cells. Gene
Regul Syst Bio. 1:263–274. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Segura MF, Hanniford D, Menendez S, et al:
Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by
repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription
factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:1814–1819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirata H, Ueno K, Shahryari V, et al:
microRNA-182-5p promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down
regulating FOXF2, RECK and MTSS1 genes in human prostate cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e555022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Z, Liu J, Segura MF, et al: MiR-182
overexpression in tumourigenesis of high-grade serous ovarian
carcinoma. J Pathol. 228:204–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|