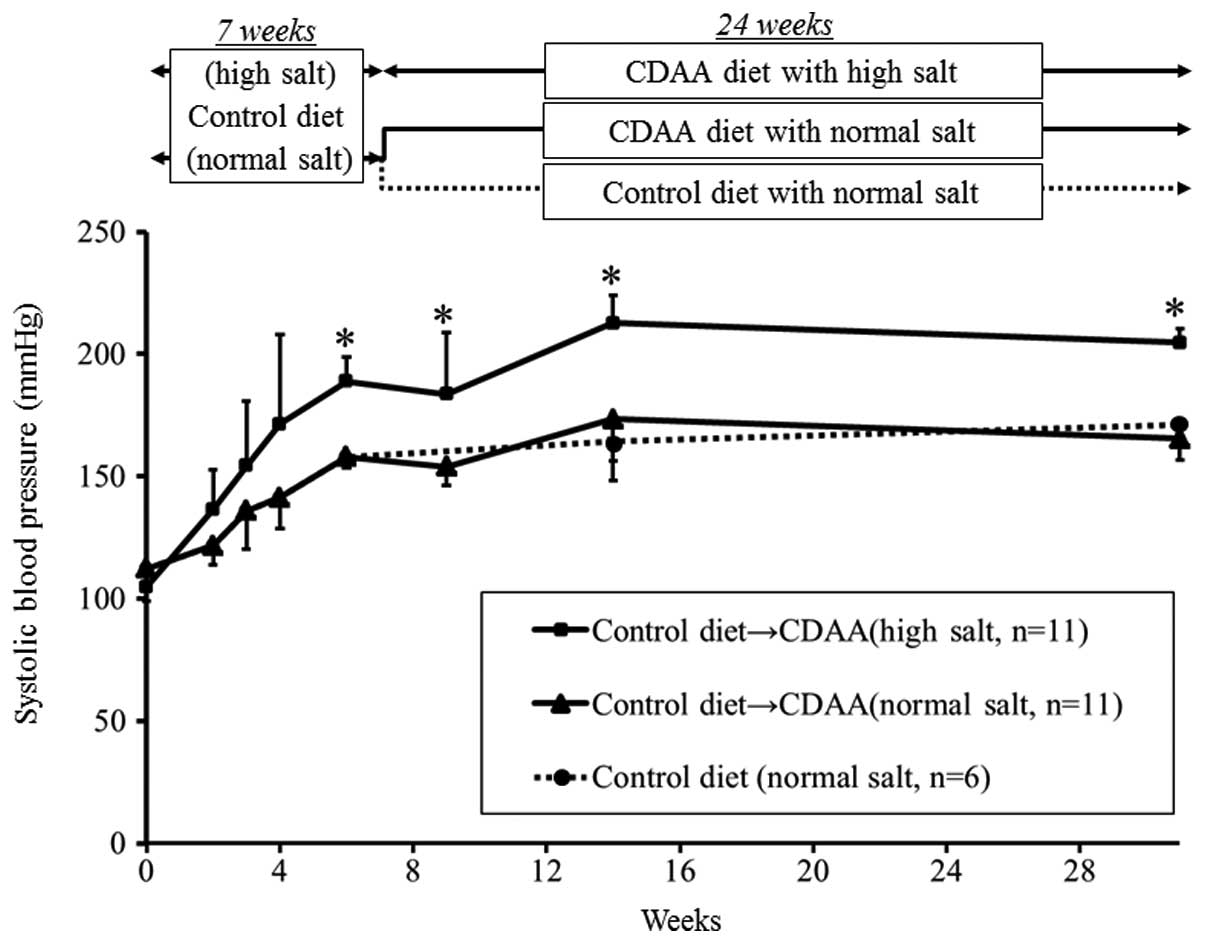
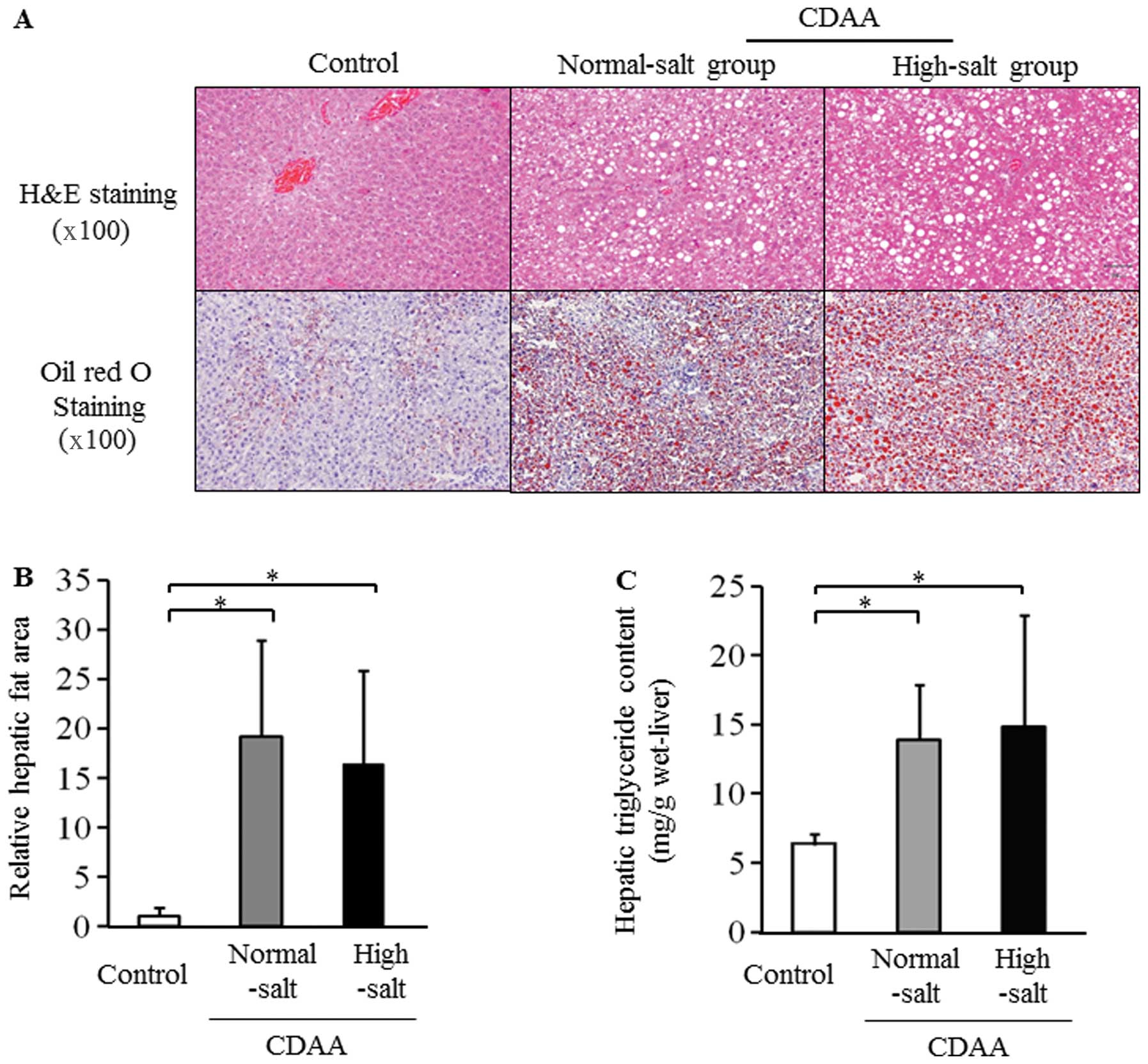
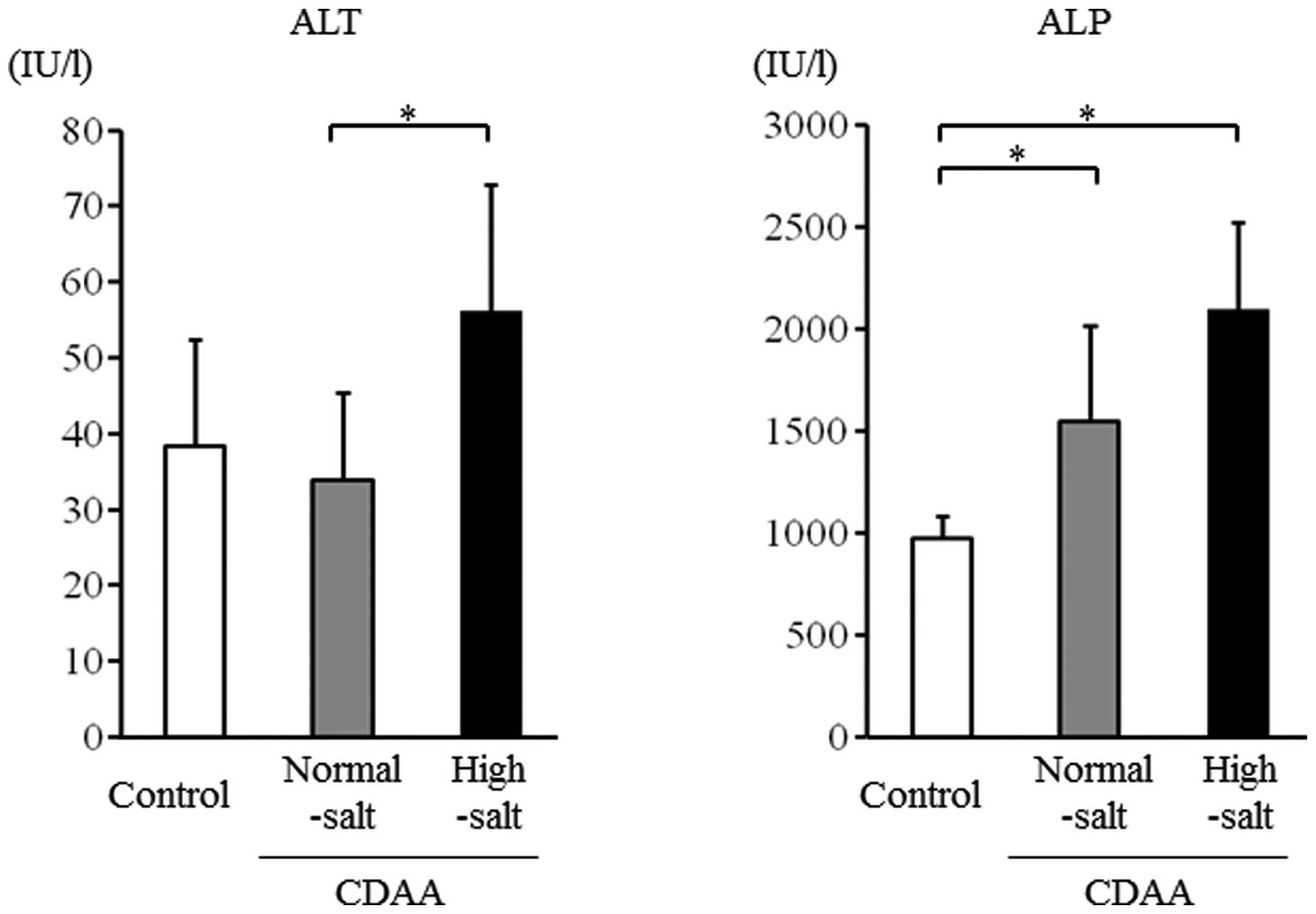
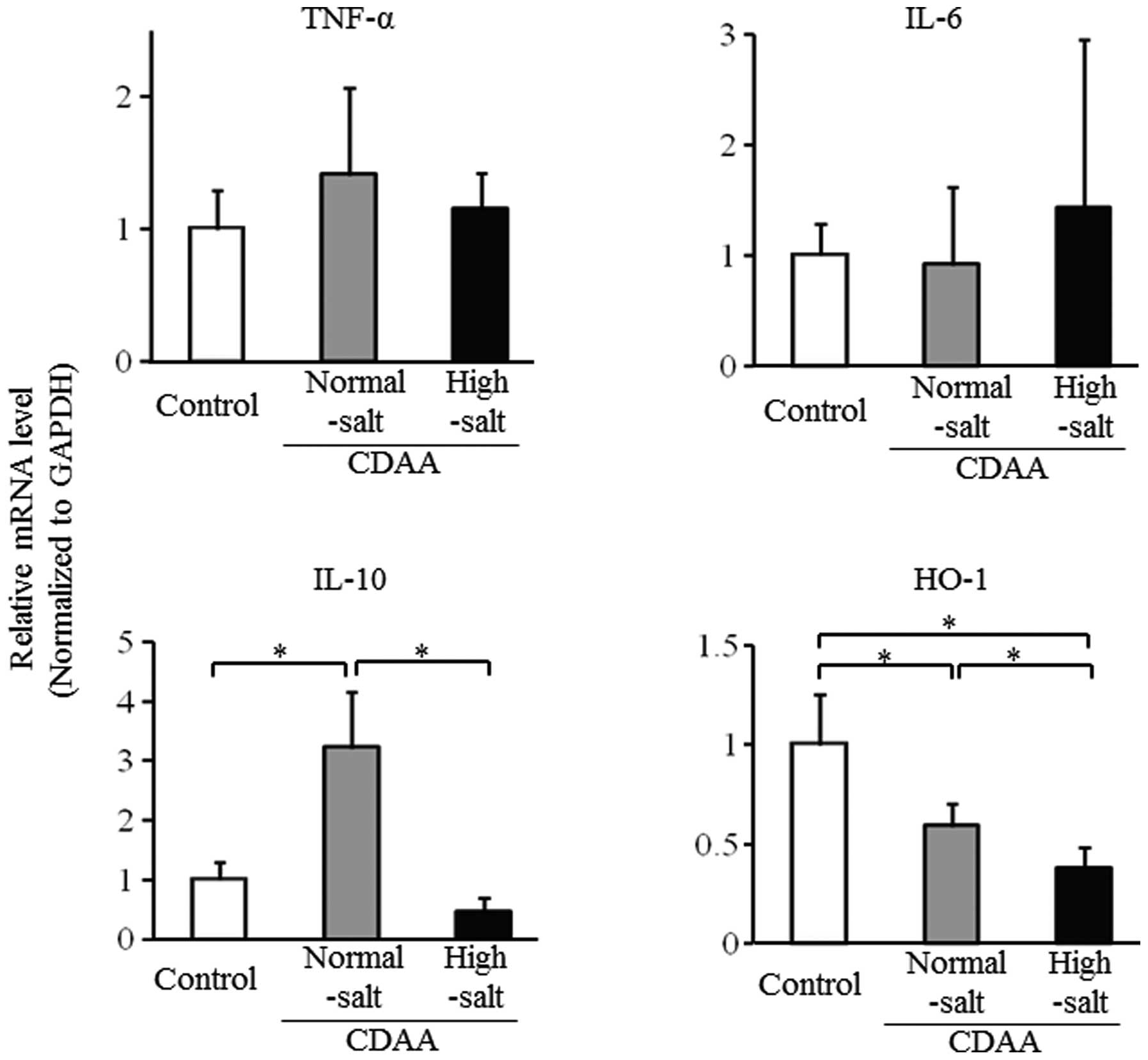
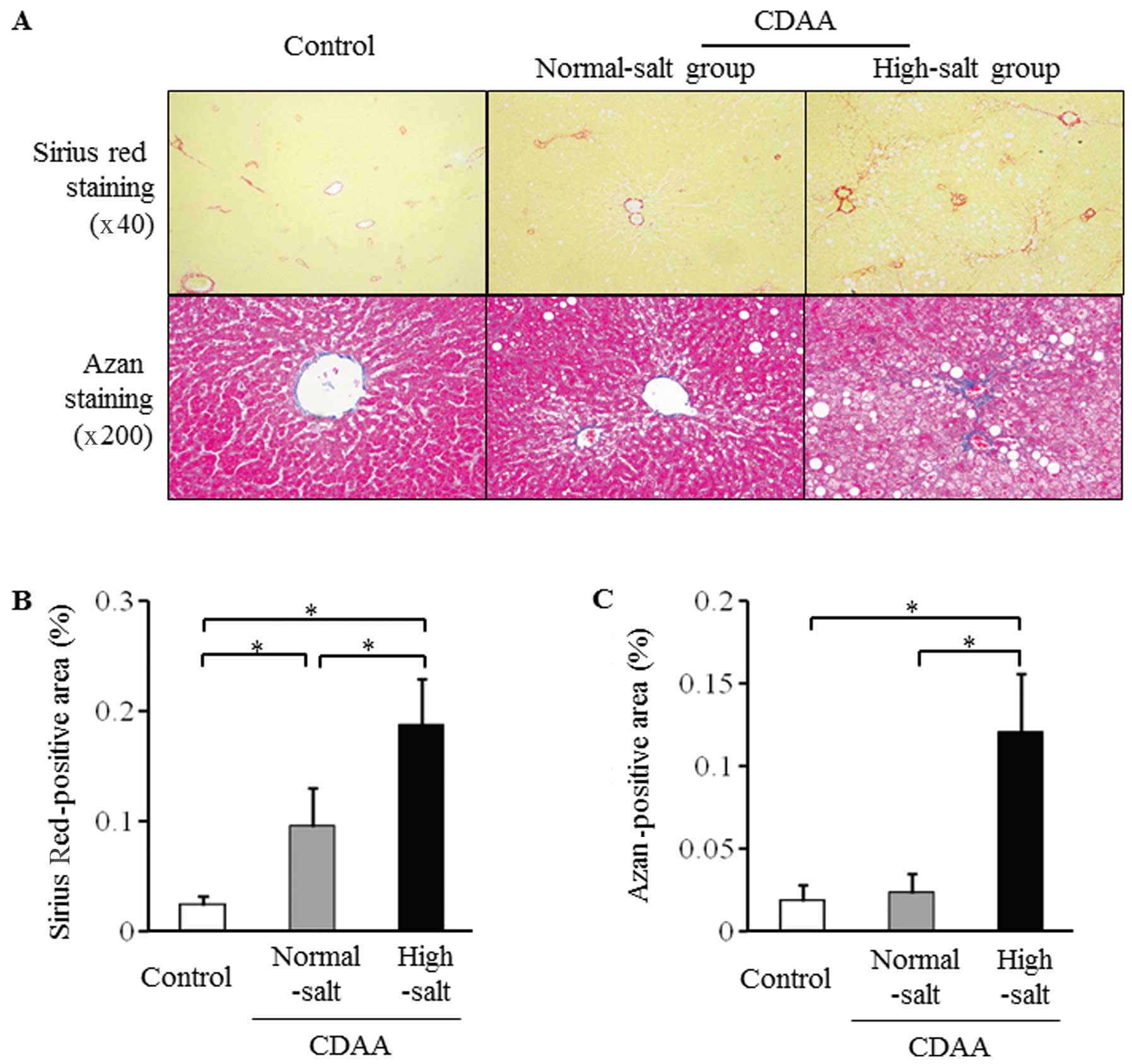
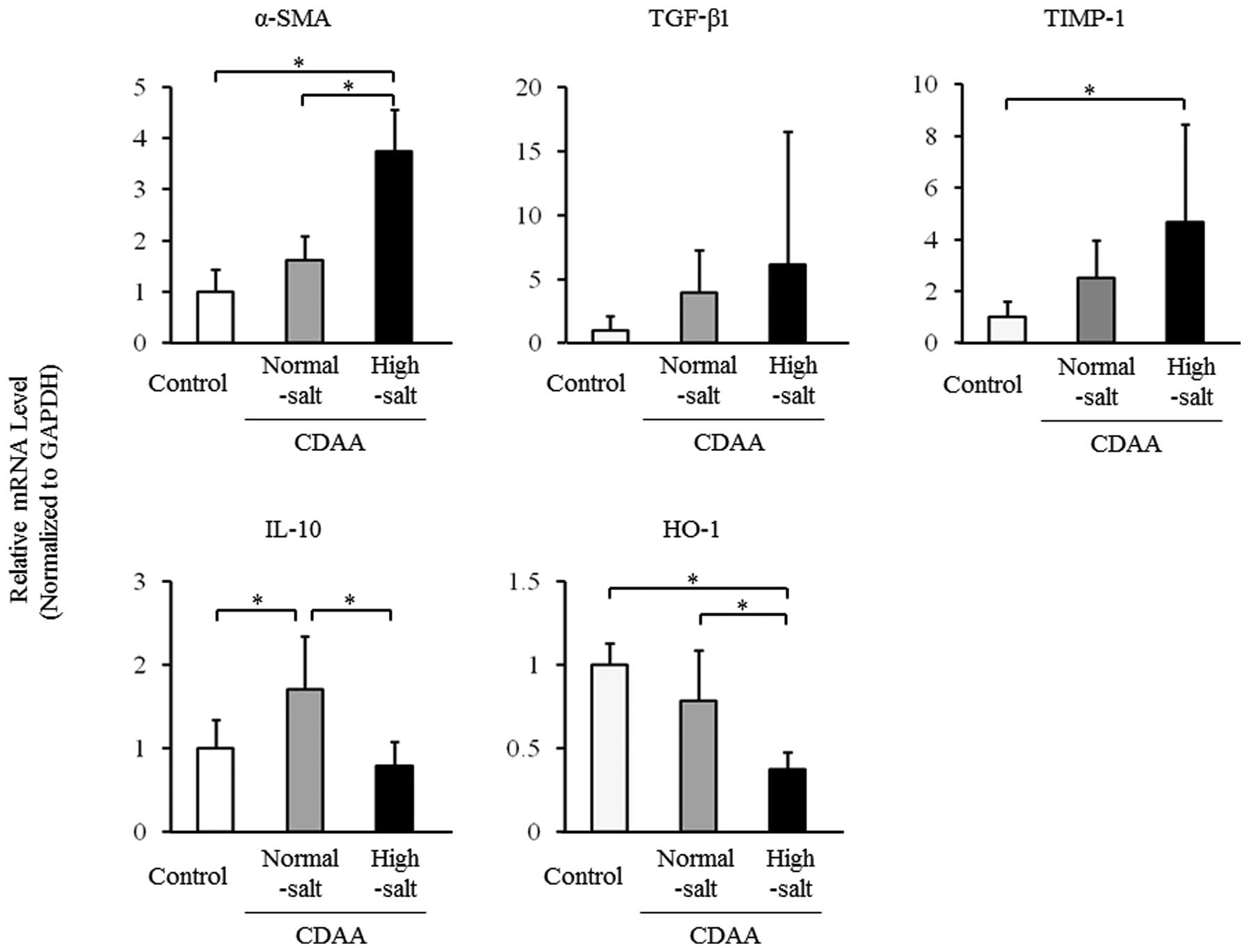
|
1
|
Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, Tamimi TA,
Feldstein AF and Zein NN: The incidence and risk factors of
hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 51:1972–1978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yasui K, Hashimoto E, Tokushige K, et al:
Clinical and pathological progression of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res.
42:767–773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, et al: The
natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a
population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 129:113–121. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hamaguchi M, Kojima T, Takeda N, et al:
The metabolic syndrome as a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. Ann Intern Med. 143:722–728. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
López-Suárez A, Guerrero JM,
Elvira-González J, Beltrán-Robles M, Cañas-Hormigo F and
Bascuñana-Quirell A: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated
with blood pressure in hypertensive and nonhypertensive individuals
from the general population with normal levels of alanine
aminotransferase. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1011–1017.
2011.
|
|
6
|
Dixon JB, Bhathal PS and O’Brien PE:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese.
Gastroenterology. 121:91–100. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakae D, Yoshiji H, Mizumoto Y, et al:
High incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas induced by a choline
deficient L-amino acid defined diet in rats. Cancer Res.
52:5042–5045. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsui H, Ando K, Kawarazaki H, et al:
Salt excess causes left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in rats
with metabolic disorder. Hypertension. 52:287–294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu CT: Ultrastructural changes in liver
damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in spontaneously
hypertensive rats and Wistar-Kyoto rats. J Auton Nerv Syst.
70:79–83. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ikuta T, Kanno K, Arihiro K, et al:
Spontaneously hypertensive rats develop pronounced hepatic
steatosis induced by choline-deficient diet: Evidence for
hypertension as a potential enhancer in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Hepatol Res. 42:310–320. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Svoboda DS and Kawaja MD: Changes in
hepatic protein expression in spontaneously hypertensive rats
suggest early stages of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J
Proteomics. 75:1752–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Amarapurkar DN, Hashimoto E, Laurentius
LA, et al: Howcommon is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the
Asia-Pacific region and are there local differences? J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:788–793. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lewis JR and Mohanty SR: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: a review and update. Dig Dis Sci. 55:560–578.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kojima S, Watanabe N, Numata M, Ogawa T
and Matsuzaki S: Increase in the prevalence of fatty liver in Japan
over the past 12 years: analysis of clinical background. J
Gastroenterol. 38:954–961. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Radu C, Grigorescu M, Crisan D, Lupsor M,
Constantin D and Dina L: Prevalence and associated risk factors of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in hospitalized patients. J
Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 17:255–260. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jimba S, Nakagami T, Takahashi M, et al:
Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its association
with impaired glucose metabolism in Japanese adults. Diabet Med.
22:1141–1145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matrougui K, Abd Elmageed Z, Kassan M, et
al: Natural regulatory T cells control coronary arteriolar
endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive mice. Am J Pathol.
178:434–441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kassan M, Galan M, Partyka M, Trebak M and
Matrougui K: Interleukin-10 released by CD4(+)CD25(+) natural
regulatory T cells improves microvascular endothelial function
through inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity in hypertensive mice.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2534–2542. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Cintra DE, Pauli JR, Araújo EP, et al:
Interleukin-10 is a protective factor against diet-induced insulin
resistance in liver. J Hepatol. 48:628–637. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen XD, Ke B, Zhai Y, et al: Toll-like
receptor and heme oxygenase-1 signaling in hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J Transplant. 5:1793–1800. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu HP, Choudhry MA, Shimizu T, et al:
Mechanism of the salutary effects of flutamide on intestinal
myeloperoxidase activity following trauma-hemorrhage: up-regulation
of estrogen receptor-β-dependent HO-1. J Leukoc Biol. 79:277–284.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu FC, Hwang TL, Lau YT and Yu HP:
Mechanism of salutary effects of astringinin on rodent hepatic
injury following trauma-hemorrhage: Akt-dependent hemeoxygenase-1
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 6:e259072011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Devey L, Mohr E, Bellamy C, et al: c-Jun
terminal kinase-2 gene deleted mice overexpress hemeoxygenase-1 and
are protected from hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury.
Transplantation. 88:308–316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu HP, Yang SC, Lau YT and Hwang TL: Role
of Akt-dependent up-regulation of hemeoxygenase-1 in
resveratrol-mediated attenuation of hepatic injury after trauma
hemorrhage. Surgery. 148:103–109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elmarakby AA, Faulkner J, Baban B and
Sullivan JC: Induction of hemeoxygenase-1 reduces renal oxidative
stress and inflammation in diabetic spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Int J Hypertens. 2012:9572352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hou HS, Liao CL, Sytwu HK, et al:
Deficiency of interleukin-15 enhances susceptibility to
acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. PLoS One. 7:e448802012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou YC, Chen S, Cao JJ, Chen SY, Xie YF
and Niu QX: Adenovirus-mediated viral interleukin-10 gene transfer
prevents concanavalin A-induced liver injury. Dig Liver Dis.
44:398–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang LJ, Zheng WD, Shi MN and Wang XZ:
Effects of interleukin-10 on activation and apoptosis of hepatic
stellate cells in fibrotic rat liver. World J Gastroenterol.
12:1918–1923. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee TS and Chau LY: Heme oxygenase-1
mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 in mice.
Nat Med. 8:240–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gunnett CA, Heistad DD and Faraci FM:
Interleukin-10 protects nitric oxide-dependent relaxation during
diabetes: role of superoxide. Diabetes. 51:1931–1937. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang LJ, Zheng WD, Chen YX, et al:
Antifibrotic effects of interleukin-10 on experimental hepatic
fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 54:2092–2098. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hamaguchi M, Kojima T, Takeda N, et al:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a novel predictor of
cardiovascular disease. World J Gastroenterol. 13:1579–1584. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bedogni G, Miglioli L, Masutti F,
Tiribelli C, Marchesini G and Bellentani S: Prevalence of and risk
factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the Dionysos
nutrition and liver study. Hepatology. 42:44–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Donati G, Stagni B, Piscaglia F, et al:
Increased prevalence of fatty liver in arterial hypertensive
patients with normal liver enzymes: role of insulin resistance.
Gut. 53:1020–1023. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pollare T, Lithell H and Berne C: Insulin
resistance is a characteristic feature of primary hypertension
independent of obesity. Metabolism. 39:167–174. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Raitakari OT, Porkka KV, Rönnemaa T, et
al: The role of insulin in clustering of serum lipids and blood
pressure in children and adolescents. The cardiovascular risk in
young finns study. Diabetologia. 38:1042–1050. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Allemann Y, Horber FF, Colombo M, et al:
Insulin sensitivity and body fat distribution in normotensive
offspring of hypertensive parents. Lancet. 341:327–331. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ogihara T, Asano T, Ando K, et al:
High-salt diet enhances insulin signaling and induces insulin
resistance in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension. 40:83–89.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ogihara T, Asano T and Fujita T:
Contribution of salt intake to insulin resistance associated with
hypertension. Life Sci. 73:509–523. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Petta S, Macaluso FS, Barcellona MR, et
al: Serum γ-glutamyl transferase levels, insulin resistance and
liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver diseases. PLoS One.
7:e511652012.
|
|
41
|
Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, et al:
Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic
subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology.
135:1176–1184. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cohen JC, Horton JD and Hobbs HH: Human
fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science.
332:1519–1523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Day CP and James OF: Steatohepatitis: a
tale of two ‘hits’? Gastroenterology. 114:842–845. 1998.
|