|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Atkin WS, Edwards R, Kralj-Hans I, et al:
Once-only flexible sigmoidoscopy screening in prevention of
colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 375:1624–1633. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grady WM and Carethers JM: Genomic and
epigenetic instability in colorectal cancer pathogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 135:1079–1099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leggett B and Whitehall V: Role of the
serrated pathway in colorectal cancer pathogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 138:2088–2100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stratton MR, Campbell PJ and Futreal PA:
The cancer genome. Nature. 458:719–724. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lanza G, Ferracin M, Gafa R, et al:
mRNA/microRNA gene expression profile in microsatellite unstable
colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 6:542007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, et al: Core
signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global
genomic analyses. Science. 321:1801–1806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lustig B and Behrens J: The Wnt signaling
pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
129:199–221. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maxwell PH, Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ:
Activation of the HIF pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
11:293–299. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sankpal UT, Goodison S, Abdelrahim M and
Basha R: Targeting SP1 transcription factor in prostate cancer
therapy. Med Chem. 7:518–525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, et al:
Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in
prostate cancer. Science. 310:644–648. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Goldstein BG, Chao HH and Katz JP:
KLF4 and KLF5 regulate proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in
esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:1216–1221. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J and
Matias-Guiu X: NF-κB in development and progression of human
cancer. Virchows Arch. 446:475–482. 2005.
|
|
14
|
Sabates-Bellver J, Van Der Flier LG, De
Palo M, et al: Transcriptome profile of human colorectal adenomas.
Mol Cancer Res. 5:1263–1275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bresalier RS, Mazurek N, Sternberg LR, et
al: Metastasis of human colon cancer is altered by modifying
expression of the β-galactoside-binding protein galectin 3.
Gastroenterology. 115:287–296. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
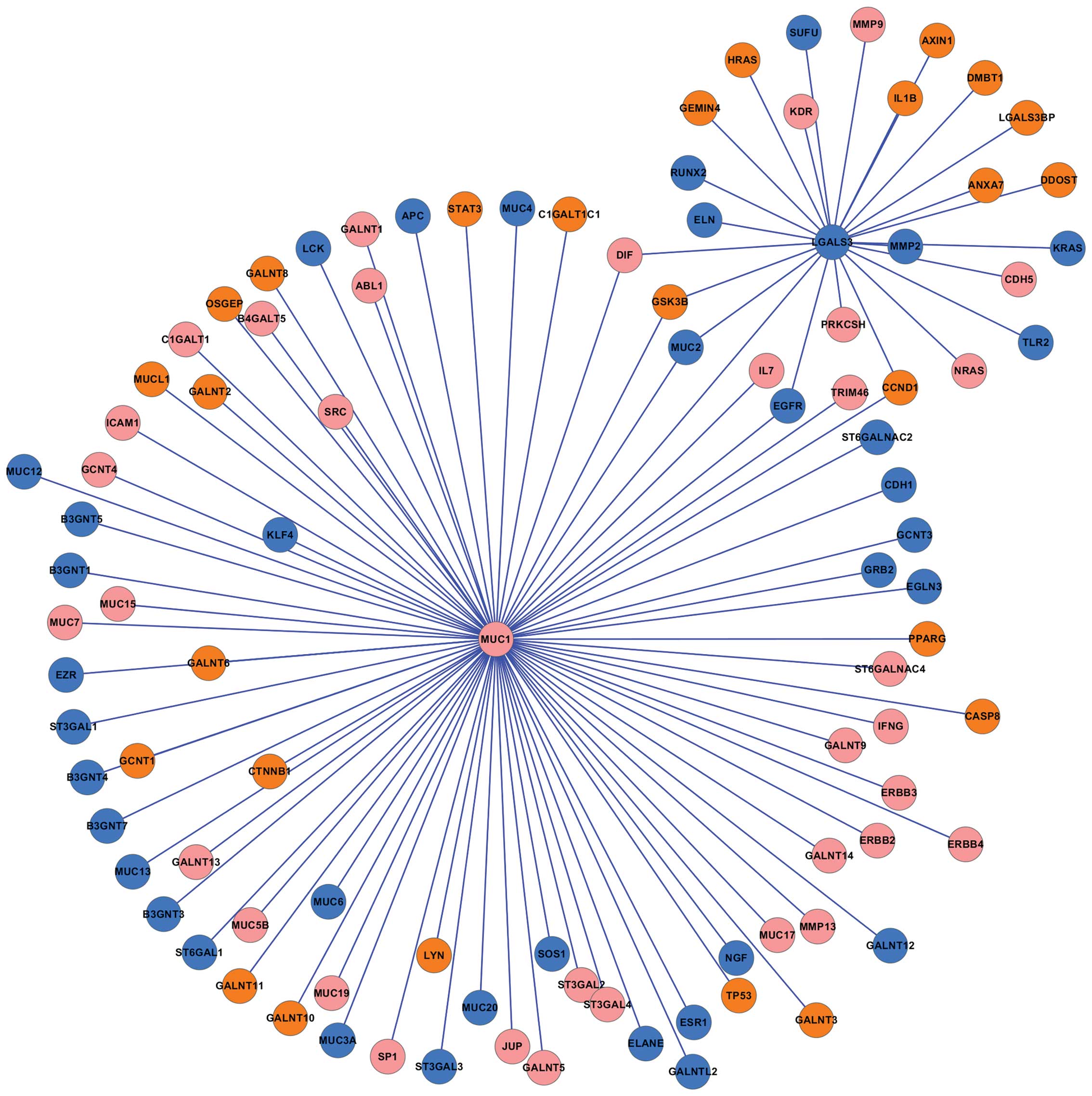
Zhao Q, Guo X, Nash GB, et al: Circulating
galectin-3 promotes metastasis by modifying MUC1 localization on
cancer cell surface. Cancer Res. 69:6799–6806. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao Q, Barclay M, Hilkens J, et al:
Research interaction between circulating galectin-3 and
cancer-associated MUC1 enhances tumour cell homotypic aggregation
and prevents anoikis. Mol Cancer. 9:1542010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, et al:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R and Chu G:
Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing
radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:5116–5121. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harris M, Clark J, Ireland A, et al: The
gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids
Res. 32:D258–D261. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tarca AL, Draghici S, Khatri P, et al: A
novel signaling pathway impact analysis. Bioinformatics. 25:75–82.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Essaghir A, Toffalini F, Knoops L, Kallin
A, van Helden J and Demoulin JB: Transcription factor regulation
can be accurately predicted from the presence of target gene
signatures in microarray gene expression data. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:e1202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: a database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Data Mining in Proteomics. Hamacher M, Eisenacher M and
Stephan C: Humana Press; pp. 291–303. 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cox DG, Hankinson SE and Hunter DJ:
Polymorphisms of the AURKA (STK15/Aurora Kinase) gene and breast
cancer risk (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 17:81–83. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Couch FJ, Sinilnikova O, Vierkant RA, et
al: AURKA F31I polymorphism and breast cancer risk in BRCA1 and
BRCA2 mutation carriers: a consortium of investigators of modifiers
of BRCA1/2 study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:1416–1421.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu X, Mao Z, Na Y, Guo Y, Wang X and Xin
D: Significance of pituitary tumor transforming gene 1 (PTTG1) in
prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 26:1253–1259. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gorynia S, Bandeiras TM, Pinho FG, et al:
Structural and functional insights into a dodecameric molecular
machine - the RuvBL1/RuvBL2 complex. J Struct Biol. 176:279–291.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Carattino MD, Prakasam HS, Ruiz WG, et al:
Bladder filling and voiding affect umbrella cell tight junction
organization and function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. Jul
24–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
32
|
Osunkoya AO, Cohen C, Lawson D, Picken MM,
Amin MB and Young AN: Claudin-7 and claudin-8: immunohistochemical
markers for the differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell
carcinoma and renal oncocytoma. Hum Pathol. 40:206–210. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: CLDN23 gene,
frequently down-regulated in intestinal-type gastric cancer, is a
novel member of CLAUDIN gene family. Int J Mol Med. 11:683–689.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
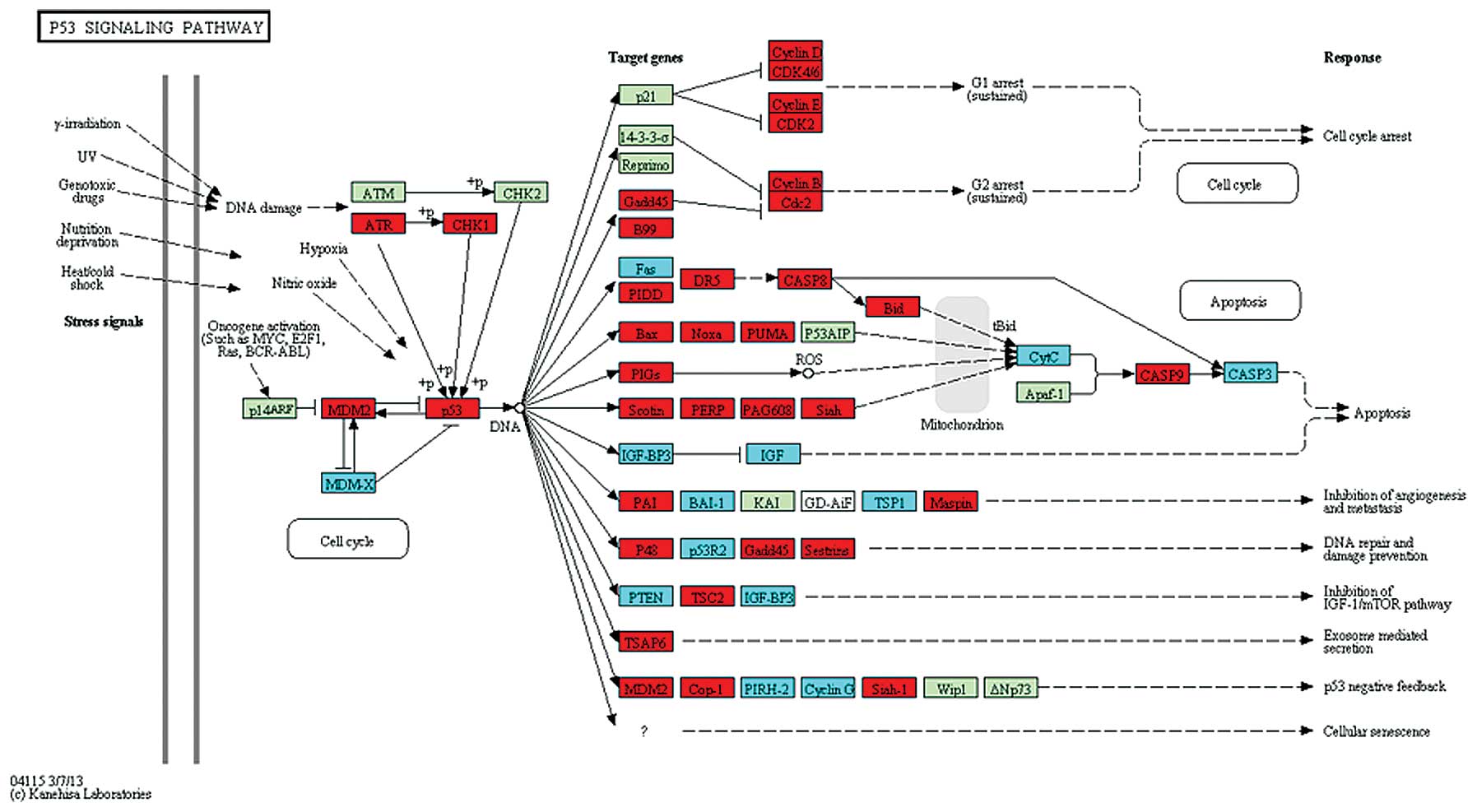
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Cancer genes
and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 10:789–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
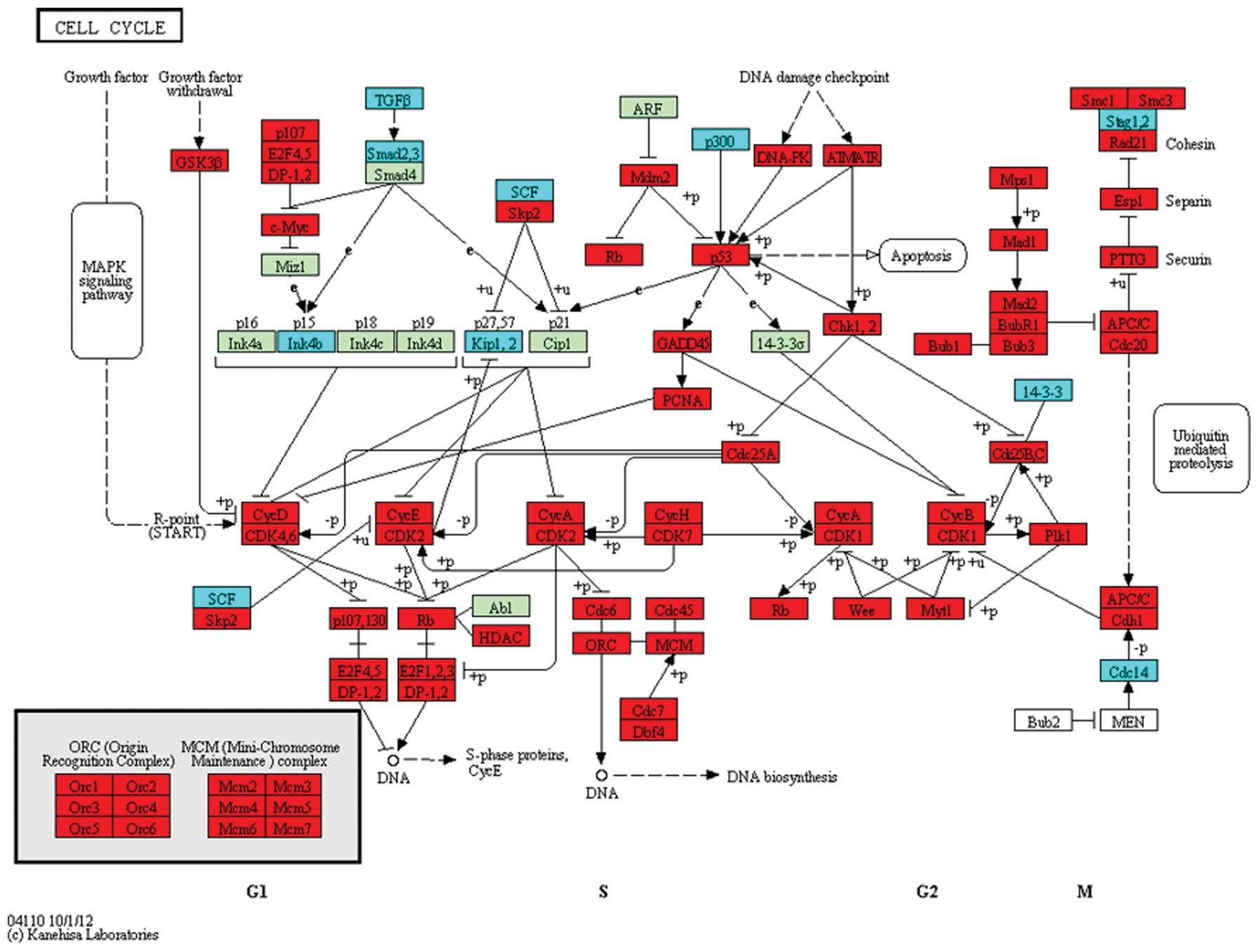
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maruyama K, Kawagoe T, Kondo T, Akira S
and Takeuchi O: TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator
(TANK) is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis and bone
formation. J Biol Chem. 287:29114–29124. 2012.
|
|
38
|
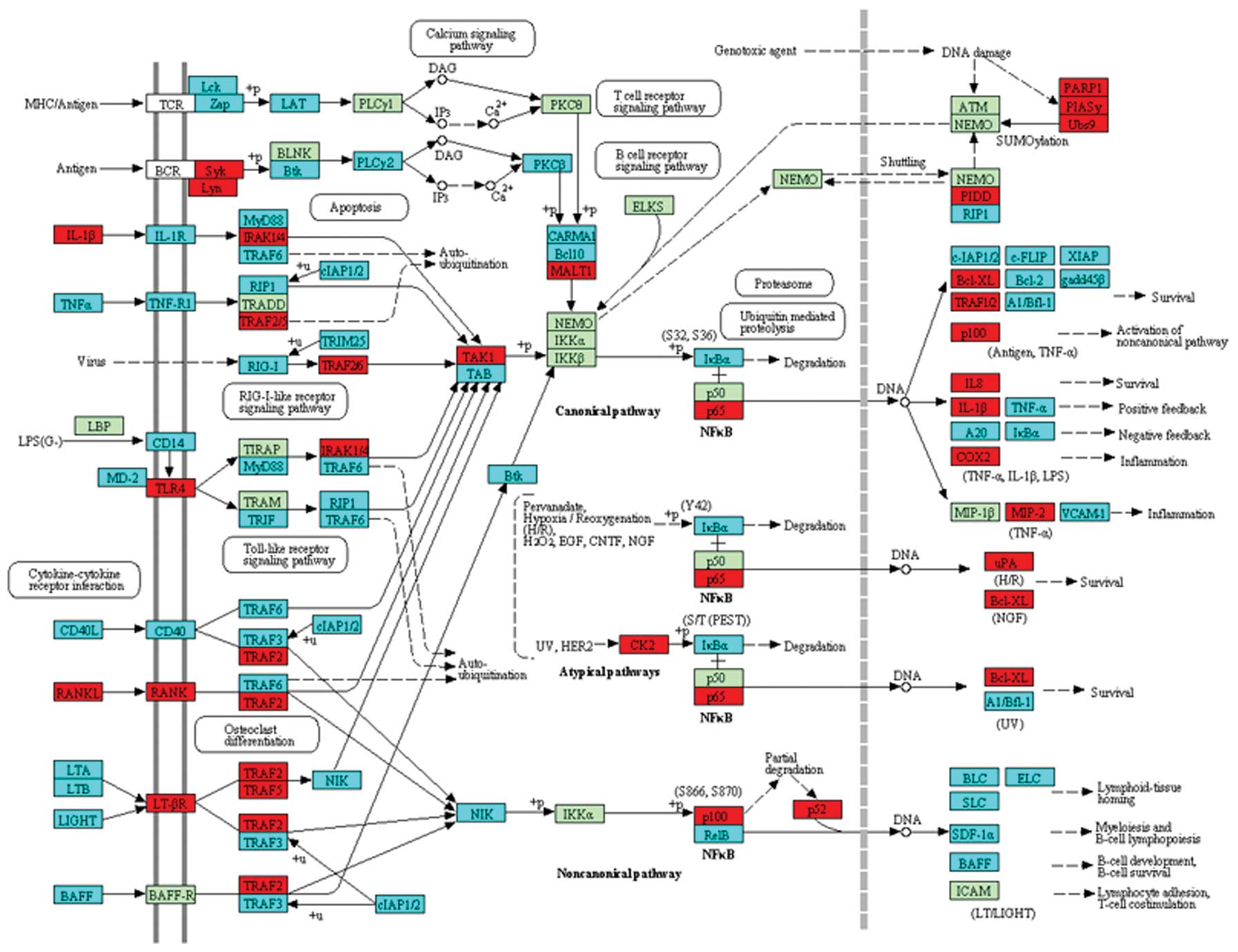
O’neill LA and Kaltschmidt C: NF-κB: a
crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function.
Trends Neurosci. 20:252–258. 1997.
|
|
39
|
Barnes PJ: Nuclear factor-κB. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 29:867–870. 1997.
|
|
40
|
Scartozzi M, Bearzi I, Pierantoni C, et
al: Nuclear factor-κB tumor expression predicts response and
survival in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer
treated with cetuximab-irinotecan therapy. J Clin Oncol.
25:3930–3935. 2007.
|
|
41
|
Darnell JE Jr: Transcription factors as
targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:740–749. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bièche I, Laurendeau I, Tozlu S, et al:
Quantitation of MYC gene expression in sporadic breast tumors with
a real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay. Cancer Res.
59:2759–2765. 1999.
|
|
43
|
Le Floch N, Rivat C, De Wever O, et al:
The proinvasive activity of Wnt-2 is mediated through a
noncanonical Wnt pathway coupled to GSK-3β and c-Jun/AP-1
signaling. FASEB J. 19:144–146. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kojima T, Shimazui T, Horie R, et al:
FOXO1 and TCF7L2 genes involved in metastasis and poor prognosis in
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
49:379–389. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Arden KC: Multiple roles of FOXO
transcription factors in mammalian cells point to multiple roles in
cancer. Exp Gerontol. 41:709–717. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Roy S, Srivastava R and Shankar S:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of
FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal. 5:102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
John A and Tuszynski G: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis.
Pathol Oncol Res. 7:14–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|