Introduction
Retinal neovascularization is one of the
vision-threatening complications of ocular vascular diseases.
Recently, the incidence rate of these diseases, such as diabetic
retinopathy, central retinal vein occlusion, neovascular glaucoma
and retinopathy of prematurity has shown an increasing trend due to
the aging of society and the improvement of living conditions
(1). A series of events may be
involved in the mechanisms of these diseases, such as the
degradation of the extracellular matrix components, proliferation
and migration of endothelial cells and tube formation. There are a
number of angiogenic factors, such as insulin-like growth factor,
basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), erythropoietin and vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF), that may be involved in this
complex process (2–5). Intensive biochemical and
pharmacological studies have focused on anti-VEGF agents, which
have been widely used in clinical trials for blocking pathological
retinal neovascularization (6).
However, the inhibition of VEGF alone cannot completely suppress
pathological angiogenesis, as other angiogenic factors, such as
hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α (7), erythropoietin (8) and the recently described peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) (9,10)
may participate in this pathological process.
PGC-1α is a recently discovered transcriptional
coactivator; it belongs to gene families and has a variety of
nuclear hormone receptor binding sites, and is involved in cell
oxidation reaction and mitochondrial energy metabolism with height
adjustment (11). It is
abundantly expressed in human and rodent brown adipose tissue,
skeletal muscle, the heart, kidneys, liver, brain and vascular
endothelial cells (11–14). As is already known, the formation
of new blood vessels is closely associated with ischemia and
hypoxia. PGC-1α has been confirmed to be involved in the cellular
response to tissue hypoxia. As previously demonstrated, under
ischemic and hypoxic conditions, PGC-1α expression and
transcriptional regulation are significantly enhanced in rat
myocardial cells (15,16), the brain (17,18), rabbit renal tubular cells
(19) and human skeletal muscle
(20). Arany et al
(9) demonstrated that PGC-1α
upregulates the expression of angiogenic factors, including VEGF,
and promotes neovascularization. Thus, another important function
of PGC-1α in a hypoxic environment is to stimulate the formation of
new blood vessels. Hypoxia upregulates PGC-1α expression, then
stimulates the expression of VEGF, and this process does not
require the participation of HIF-1 (9,21).
Therefore, PGC-1α may be a novel therapeutic target in hypoxic or
ischemic disease (22).
In this study, we demonstrate the expression of
PGC-1α in the retina and the upregulation of PGC-1α under hypoxic
conditions in the retina. We hypothesized that PGC-1α is involved
in the regulation of pathological retinal neovascularization and
may play a role in promoting pathological retinal
neovascularization. Therefore, we aimed to determine whether PGC-1α
plays such a role and to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of the
regulation of pathological retinal neovascularization by PGC-1α. In
order to confirm our hypothesis, we investigated the effects of
small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting PGC-1α on PGC-1α and VEGF
mRNA and protein expression and retinal neovascularization in a
murine model of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR).
Materials and methods
siRNA design
The selection of siRNAs was based on the
characterization of siRNA by Elbashir et al (23). Three siRNAs targeting mouse PGC-1α
mRNA (PGC-1α siRNA1–3) were designed. The sense strand of PGC-1α
siRNA1 was 5′-CCAA GACUCUAGACAACUAdTdT-3′, and the antisense strand
was 3′-dTdTGGUUCUGAGAUCUGUUGAU-5′. The sense strand of PGC-1α
siRNA2 was 5′-GCAACAUGCUCAAG CCAAAdTdT-3′, and the antisense strand
was 3′-dTdTCGUU GUACGAGUUCGGUUU-5′. The sense strand of PGC-1α
siRNA3 was 5′-CUGCGAACAUUUUGAGAAdTdT-3′, and the antisense strand
was 3′-dTdTGACGCUUGUAUAAAC UCUU-5′. One negative control siRNA
which has limited homology to sequences in the human and mouse
genomes and 3 PGC-1α siRNAs were synthesized and purified by a
siRNA company (RiboBio, Guangzhou, China). In order to find the
most effective siRNA, we transfected these 3 siRNAs into vascular
endothelial cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad,
CA, USA). Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to
evaluate the efficacy of the siRNAs in downregulating PGC-1α
expression in the cells. The PGC-1α siRNA which had the best
inhibitory effect on PGC-1α mRNA expression would be the one used
in the following experiments.
Cell culture and transfection
Mouse retinal vascular endothelial cells
(MIC-CELL-0055; PriCells, Wuhan, China) were cultured in DMEM
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1%
penicillin-streptomycin in a humidified incubator containing 5%
CO2 at 37°C. The transfection reagent, Lipofectamine
2000 (Invitrogen), was used to transfect PGC-1α siRNA into the
retinal vascular endothelial cells according to the manufacturer’s
instructions (Invitrogen).
Animal model
All animal experiments were carried out in
accordance with the Association for Research in Vision and
Ophthalmology (ARVO) Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic
and Vision Research. The murine model of OIR was created as
previously described (24).
Briefly, C57BL/6J mice (purchased from Shanghai Laboratory Animal
Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) were exposed
to 75±2% oxygen for 5 days from day 7 after birth [post-natal day
(P)7] with nursing mothers. On P12, the mice were removed from the
hyperoxic environment and maintained under normal conditions until
P17. Age-matched C57BL/6J mice maintained under normal oxygen
conditions were used as the controls. The mice were randomly
divided into a normal group, an OIR group (murine model of OIR), a
negative control siRNA group and a PGC-1α siRNA group.
Assessment of PGC-1α expression in the
retinas of mice with OIR
Mice with OIR and normal (healthy) mice were
sacrificed on P12 (0, 3 and 6 h), P13, P14, P17 and P26. An equal
number of mice (n=5) was used at each time point; the eyes were
enucleated and the total RNA and protein from the retinas were
extracted. PGC-1α expression was detected by real-time PCR and
western blot analysis.
Intravitreal injection
On P12, the mice (n=5 per group) were anesthetized
by an intraperitoneal injection of 1% pentobarbital sodium (0.01
ml, 30 mg/kg body weight). The lid fissure was opened using a
scalpel blade. A 32-gauge Hamilton needle and syringe were used to
deliver 1 μl liposome-PGC-1α siRNA (2.5 μg) complex (PGC-1α siRNA
group) or 1 μl control complex (liposome-negative control siRNA;
negative control siRNA group) into the vitreous cavity. The eye was
then repositioned and the lids were approximated over the cornea.
Mice were returned to room air at P12.
Fluorescein angiography
On P17, mice (n=5/each group) from each group were
deeply anesthetized and then perfused through the left ventricle
with 1 ml of phosphate-buffered-saline (PBS) containing 50 mg
fluorescein-conjugated dextran (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). The
eyes were then enucleated and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 20
min. The retinas were dissected to remove the cornea, lens, sclera
and placed in 4% paraformaldehyde for a further 5 min. The retina
was cut in 4 places at the peripheral area and flat-mounted on the
microscope slides with antifade solution. We analyzed the retinal
size of the non-perfusion area by using the method of pixel
detection of teh non-perfusion area and the whole area of the
retina, as previously described (25,26). Images were analyzed using
Photoshop software (Adobe Systems, Mountain View, CA, USA). The
results are expressed as (non-perfusion area/total area) ×100%.
Real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted and 1 μg template was
reverse-transcribed using the RevertAid™ First-Strand cDNA
synthesis kit from MBI Biosystems (Fermentas, Copenhagen, Denmark).
Each RNA sample was obtained from 2 retinas. Real-time PCR was
performed on a 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System apparatus (Applied
Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) using SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ (Takara
Bio, Inc., Shiga, Japan). The sequences of the PGC-1α (mouse)
primers were: 5′-AGCAGAAAGCAATTGAAGAG-3′ (sense) and 5′-AGG
TGTAACGGTAGGTGATG-3′ (antisense) 171 bp. The sequences of the
β-actin (mouse) primers were: 5′-TTCCTTC TTGGGTATGGAAT-3′ (sense)
and 5′-GAGCAATGATCTT GATCTTC-3′ (antisense) 203 bp. The sequences
of the VEGF (mouse) primers were: 5′-CATCTTCAAGCCGTCCTGT-3′ (sense)
and 5′-GAG GAAAGGGAAAGGGTCA-3′ (antisense) 240 bp. Thermal cycling
conditions were as follows: 5′ at 95°C; 40 cycles of 20 sec at
94°C, 20 sec at 57–60°C, 20 sec at 72°C.
Western blot analysis
The murine retinas were collected and lysed in lysis
buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 2 mM EDTA and 1%
NP-40) (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) containing protease inhibitors
(Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany). Each protein sample was obtained
from 4 retinas. Total protein was resolved by SDS polyacrylamide
gel electrophoresis and was then transferred onto a nitrocellulose
membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membrane was
incubated with rabbit polyclonal anti-mouse PGC-1α antibody (1:500
dilution; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) or monoclonal anti-mouse VEGF
antibody (1:200 dilution; Abcam) and monoclonal anti-mouse β-actin
(1:10,000 dilution; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA,
USA). Peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:2,000 dilution;
Abcam) were used as secondary detection reagents with an enhanced
chemiluminescence kit (GE Healthcare, New York, NY, USA).
Chemiluminescent signals were visualized by exposure to X-ray film
(Kodar, Rochester, NY, USA). Band intensities were quantified using
BandScan software (version 5.0). The expression levels of β-actin
were used for standardization. The results are expressed as the
ratio of PGC-1α/β-actin or VEGF/β-actin.
Histological analysis of
neovascularization
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)
At P17, mice (n=5/each group) from each group were
sacrificed by an intraperitoneal injection of an overdose of sodium
pentobarbital. Their eyes were enucleated and fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde in PBS and embedded in paraffin. Serial sections
(5 μm) of whole eyes were cut sagittally through the cornea and
parallel to the optic nerve, then stained with CD31 antibody (1:50
dilution; Abcam) to mark the endothelial cells lining the blood
vessels and stained with H&E to visualize nuclei anterior to
the internal limiting membrane. Cross-sections including the optic
nerve were excluded. A total of 10 non-serial sections were
analyzed per eye. The nuclei above the internal limiting membrane
were counted in 400 sections.
Immunofluorescence
The frozen sections were incubated with
rabbit polyclonal anti-mouse PGC-1α antibody or monoclonal
anti-mouse VEGF antibody at 4°C overnight. Cy3 or Alexa Fluor 488
secondary antibody (1:20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) were used
to label the target protein, and microscopic evaluation and photo
documentations were performed on a Leica microscope (Leica DFC310
FX; Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany).
Statistical analysis
Experimental data are expressed as the means ±
standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way ANOVA followed by the LSD
t-test were used to evaluate significance. A P-value <0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
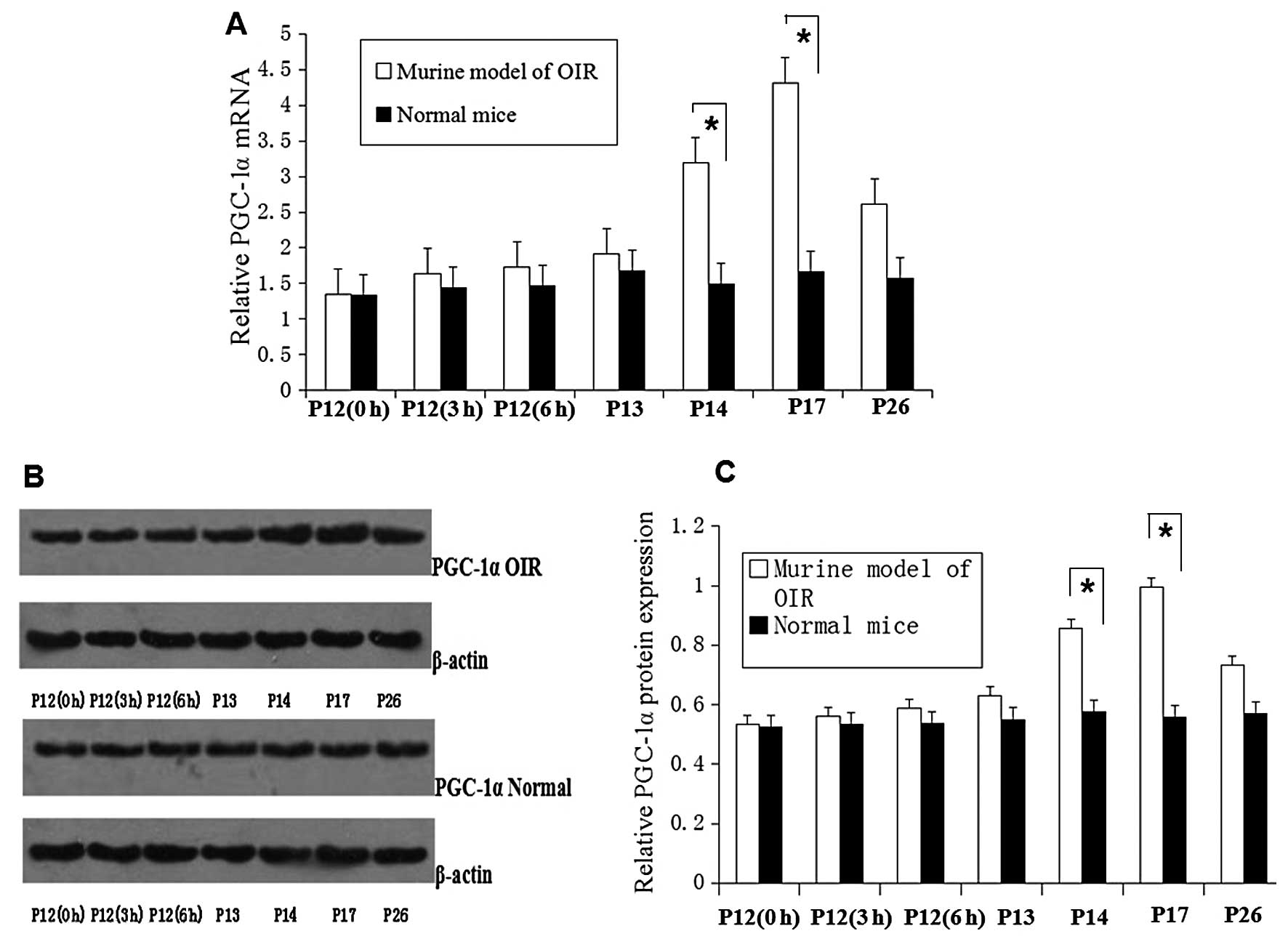
Upregulation of PGC-1α expression in the
retinas of mice with OIR
The mRNA and protein levels of PGC-1α in the retinas
of mice were evaluated. The mRNA and protein expression of PGC-1α
was significantly (P<0.05) upregulated in the retinas of mice
with OIR at P17 compared with the normal mice group ( Fig. 1). The mRNA and protein levels of
PGC-1α were upregulated at P14, reaching a peak at P17 and were
significantly increased by approximately 2-fold compared with the
normal (healthy) mice (P<0.05; Fig. 1A and C).
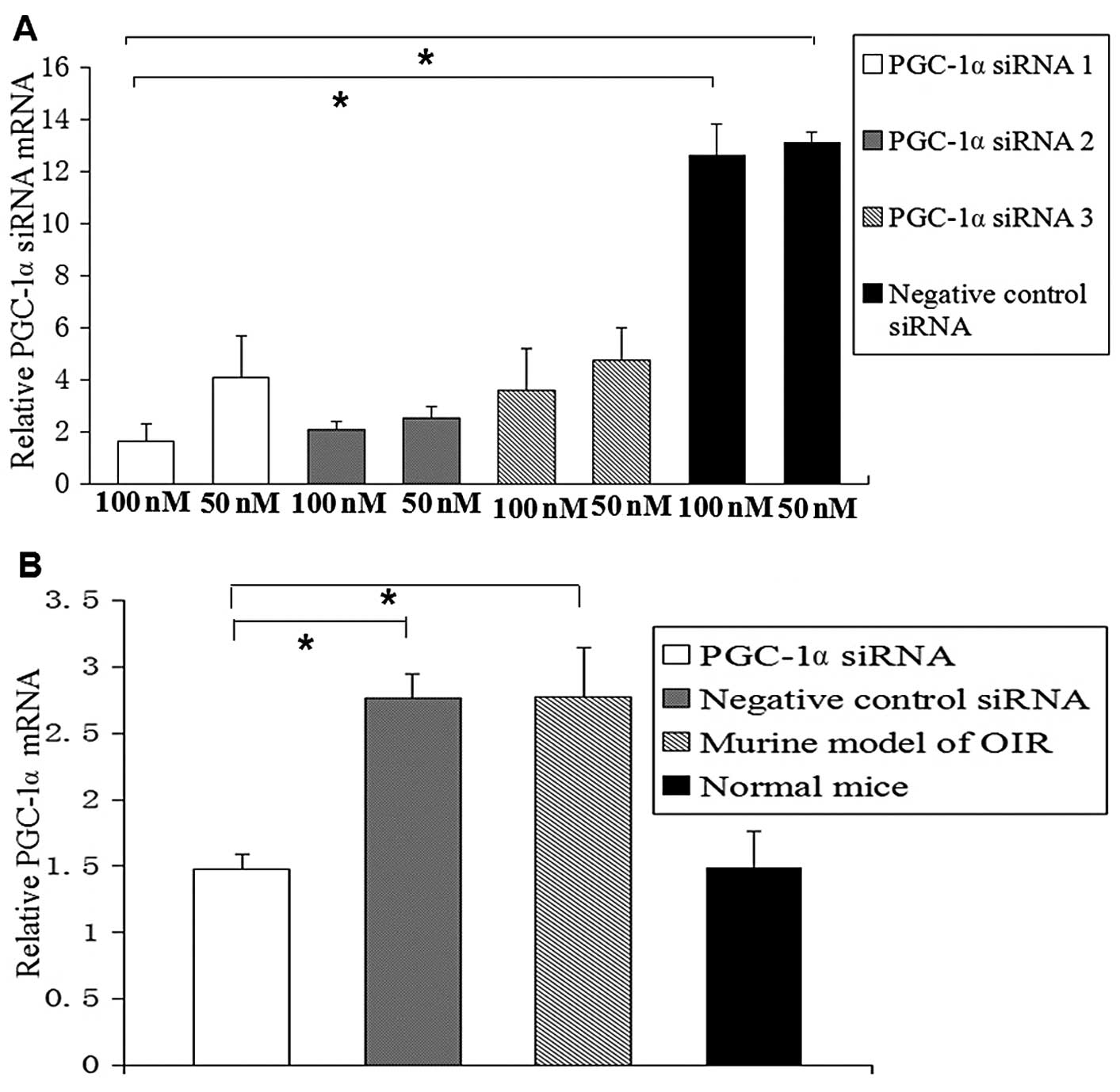
Suppression of PGC-1α expression in vitro
and in vivo by PGC-1α siRNA
We found that the 3 designed siRNAs suppressed
PGC-1α expression to a different extent. PGC-1α siRNA1 was found to
be the most efficient siRNA (Fig.
2A). Therefore, PGC-1α siRNA1 was used in the intravitreal
injection. The PGC-1α mRNA level in the PGC-1α siRNA1-transfected
cells was markedly decreased compared with the cells transfected
with the negative control siRNA (P<0.05). Real-time PCR and
western blot analysis were also used to detect PGC-1α mRNA and
protein levels in vivo. We found that the PGC-1α mRNA level
was significantly downregulated by 54%, and the protein level was
downregulated by 53% following the intravitreal injection of PGC-1α
siRNA1 compared with the murine model of OIR and the negative
control siRNA group (P<0.05; Fig.
2B–D).
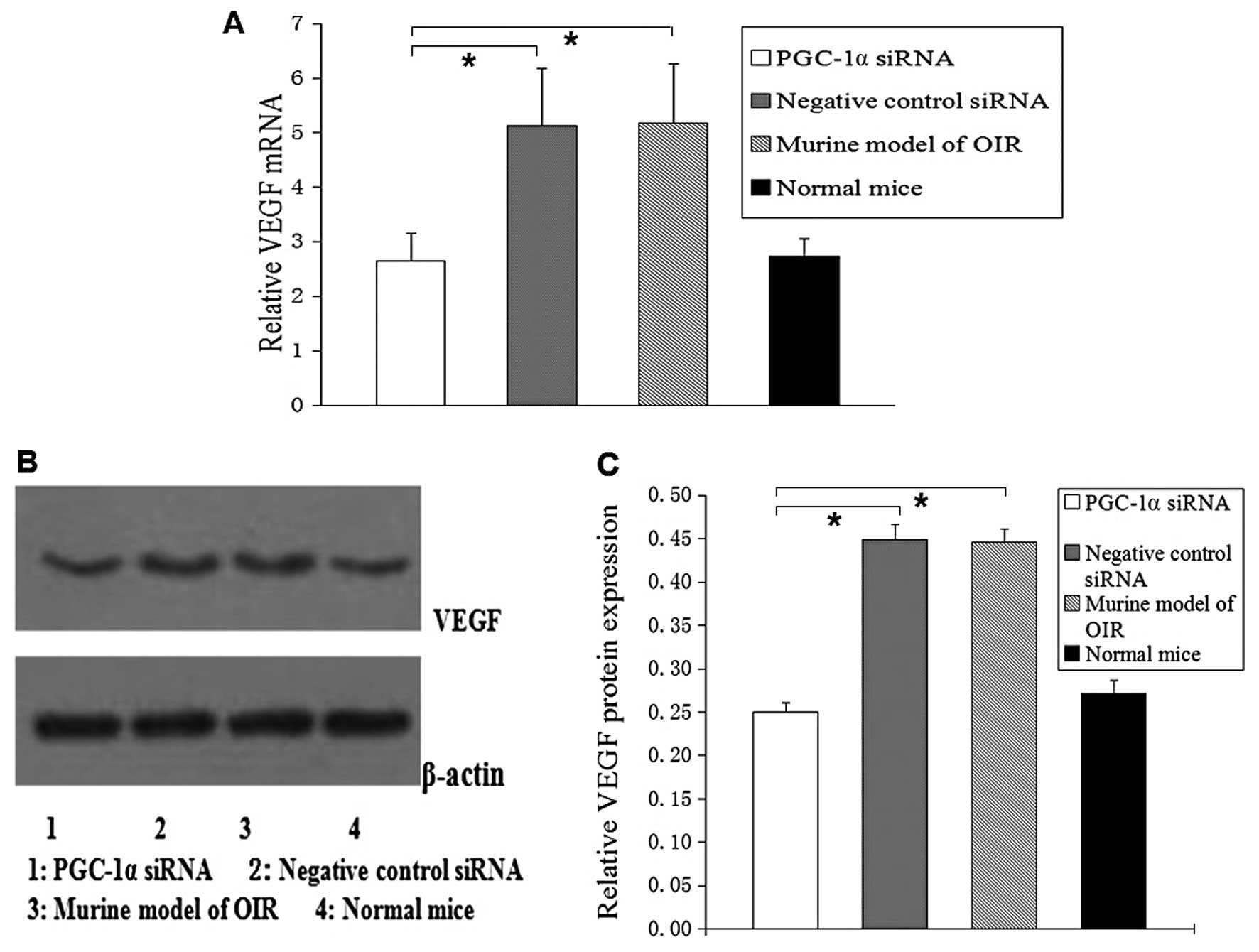
Concomitant downregulation of the VEGF
expression by PGC-1α siRNA
We analyzed the levels of VEGF mRNA and protein in
the retinas of mcie by real-time PCR and western blot analysis.
Following the intravitreal injection of PGC-1α siRNA1, we found
that the level of VEGF mRNA decreased by 48% (P<0.05; Fig. 3A) and the level of VEGF protein
decreased by 40% (P<0.05; Fig. 3B
and C), compared with the murine OIR model and the negative
control siRNA group.
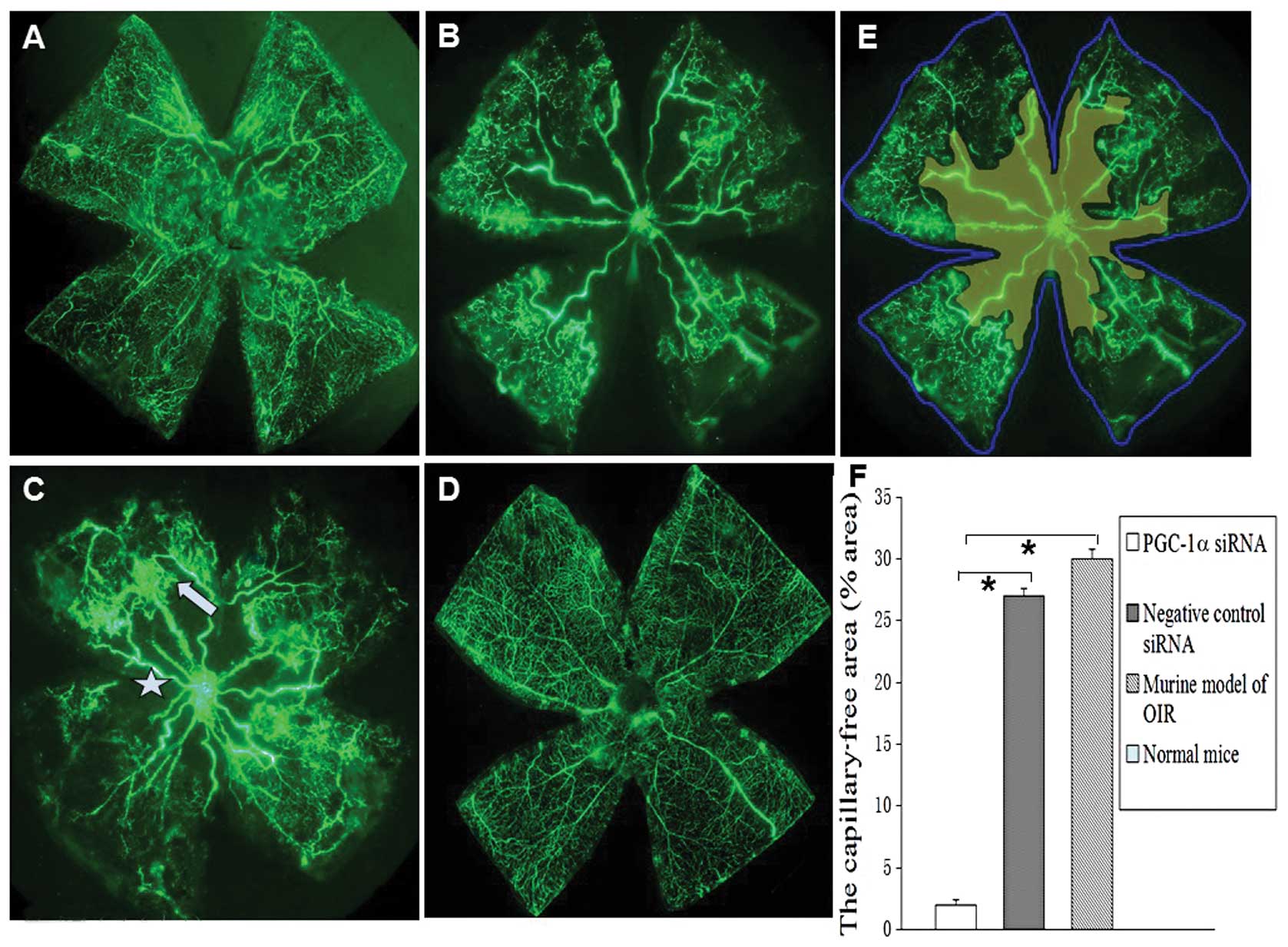
Angiographic evaluation of the effects of
PGC-1α siRNA on retinal neovascularization
To evaluate the angiostatic efficacy of PGC-1α siRNA
on oxygen-induced retinal neovascularization, the retinas were
examined by fluorescein-dextran perfusion and flat-mounted on P17.
No mice used in this study developed signs of infection and retinal
detachment. The retinas of the room-air-raised mice revealed
superficial and deep vascular layers that extended from the optic
nerve to the periphery. Fewer neovascular complexes were observed
in the retinas of the eyes of mice injected with PGC-1α siRNA1
(Fig. 4A). However, retinas from
the hyperoxia-exposed mice injected with the negative control siRNA
or from the mice not injected with siRNA contained multiple
neovascular tufts and a central non-perfusion area (Fig. 4B and C). By contrast, the vessels
formed a fine radial branching pattern in the superficial retinal
layer and a polygonal reticular pattern in the deep retinal layer,
without neovascular tufts (Fig.
4D). Areas of non-perfusion (yellow), as well as the total
retinal area (blue line) were measured (Fig. 4E). The area ratio of the retinal
non-perfusion area and total area of the murine model of OIR was
30±0.6%, in the negative control siRNA group it was 27.1±0.8%,
while in the PGC-1α siRNA group (2.4±0.4%) it decreased
significantly compared with mice with OIR and the negative control
siRNA group (*P<0.05). No obvious non-perfusion area
was observed in the normal group (Fig. 4F).
Histological analysis of retinal
neovascularization
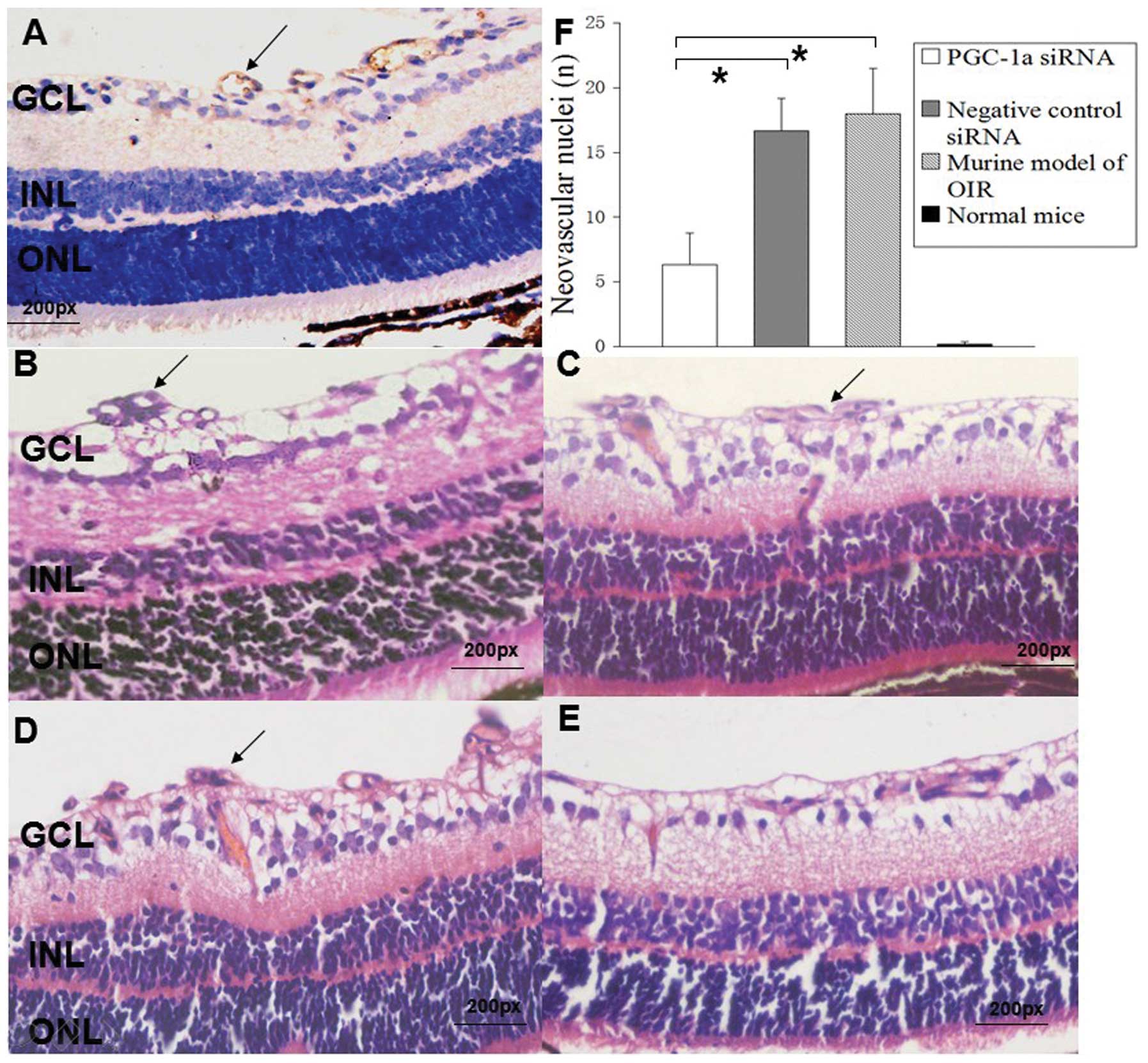
As shown in (Fig.
5B–F), there were no neovascular nuclei in the normal group
(n=100 slices); however, the average number of neovascular nuclei
were 18.0±3.5 in the non-injected eyes exposed to hyperoxic
conditions (n=100 slices), 16.7±2.5 in the eyes injected with the
negative control siRNA (n=100 slices) and 6.3±2.5 in the eyes
injected with PGC-1α siRNA1 (n=100 slices). There was a significant
reduction in retinal neovascularization in the PGC-1α siRNA group,
approximately 65% (P<0.05).
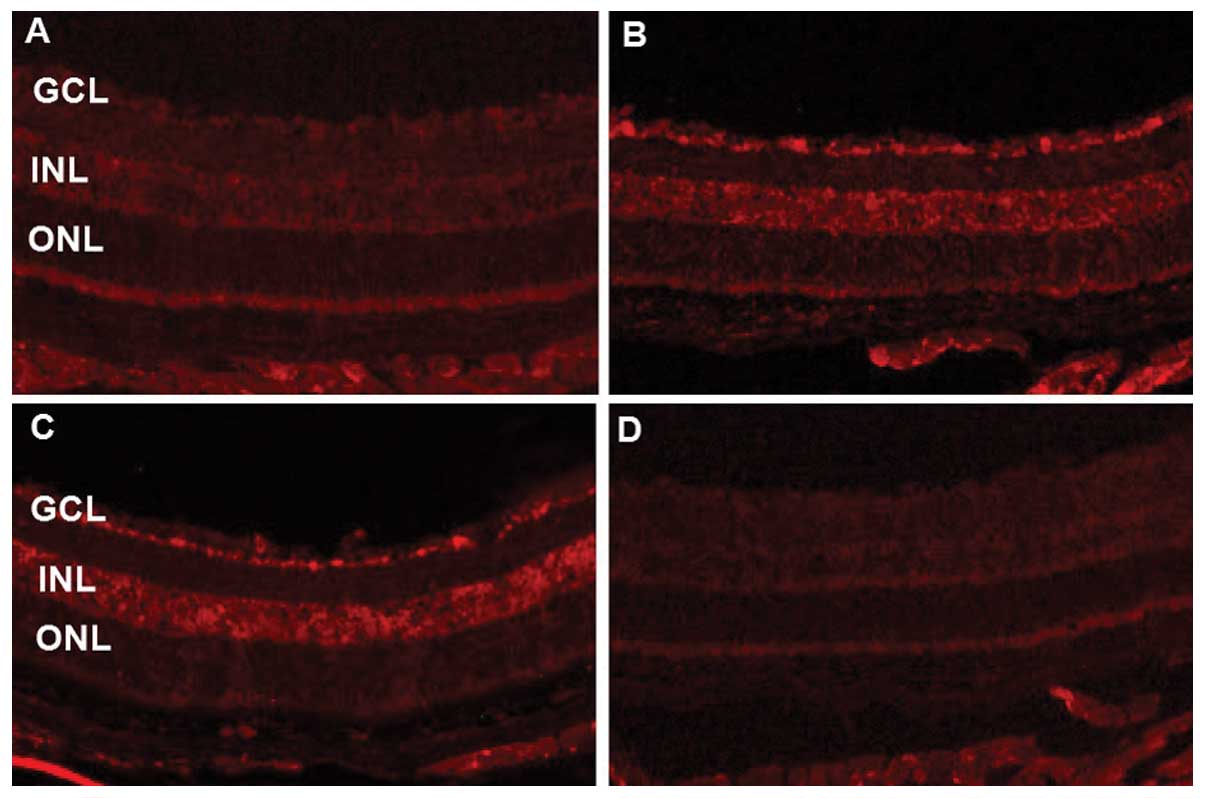
To further confirm the inhibitory effects of PGC-1α
siRNA on angiogenesis, immunofluorescence analysis was performed
and the results indicated that PGC-1α and VEGF expression was were
downregulated by PGC-1α siRNA1 compared with the mice with OIR
(Fig. 6A–D and E–H). PGC-1α and
VEGF expression was mainly observed in the ganglion cell layer and
inner nuclear layer and was reduced mainly in the ganglion cell
layer following the local administration of PGC-1α siRNA compared
with the mice with OIR (murine model of OIR).
Discussion
Retinal neovascularization, the abnormal formation
of new vessels from pre-existing capillaries in the retina, is a
common complication of many ocular diseases, such as advanced
diabetic retinopathy or retinopathy of prematurity.
Neovascularization can lead to fibrosis and the disruption of
delicate tissues required for vision (24). Although some orthodox treatments
are effective in the suppression of angiogenesis in short term,
they are also destructive to the retinal tissue, which lead to
immediate and sometimes significant loss of vision. Therefore,
therapy based on the molecular mechanisms of retinal
neovascularization provides a potential for a more effective
treatment.
In this study, in the mouse model of OIR, the
retinal vasculature initially underwent reversible central
vasoconstriction followed by non-perfusion on P7 when exposed to
hyperoxia, then more peripheral vessels were spared, a small
avascular zone appeared at the ora serrata, larger central radial
vessels became tortuous and engorged on P14, and retinal
neovascularization occurred extensively during P17 and P21
(8). In this study, the mRNA and
protein expression of PGC-1α was highly upregulated in the retinas
of the mice with OIR on P17 compared with the controls. The strong
expression of PGC-1α was detected in the retinas of mice with OIR
by immunofluorescence, which was mainly localized in the ganglion
cell layer and inner nuclear layer. Furthermore, PGC-1α expression
was observed in the areas of where neovascular vessels had broken
through the inner limiting membrane. Therefore, PGC-1α is involved
in retinal neovascularization and its upregulation may promote
angiogenesis.
RNA interference (RNAi) is a sequence-specific RNA
degradation process that is conserved in eukaryotes and mediates
target-specific RNA sequence degradation through a double-stranded
RNA-induced silencing complex (27). Recently, the RNAi pathway has
become the predominant means of assessing loss of gene function in
many organisms (28,29). The remarkable utility of siRNA in
modulating gene expression has resulted in an explosion of interest
in deciphering the molecular mechanisms that control this pathway
and imaginative ideas of ways to apply it to research and clinical
settings (30,31). In our stuty, in order to determine
the most prominent inhibitory effect of PGC-1α siRNA, 3 sequences
(PGC-1α siRNA1-3) were designed and synthesized. The results
revealed that all 3 siRNAs suppressed PGC-1α expression to a
different extent. The most significant inhibitory effect was
observed with PGC-1α siRNA1, which inhibited the expression of
PGC-1α by 80% in the cultured cells.
In this study, we found that retinal
neovascularization was inhibited by 65% by counting the number of
endothelial cell nuclei protruding into the vitreous cavity in the
murine model of OIR following the injection of PGC-1α siRNA1 (2.5
μg). Retinal neovascularization and non-perfused areas were
markedly reduced by PGC-1α siRNA transfection in the model of OIR.
Moreover, the number of new vessels and endothelial cells
protruding into the inner limiting membrane in the retinas treated
with PGC-1α siRNA was also significantly reduced. PGC-1α mRNA and
protein levels in the retinas were also significantly downregulated
by PGC-1α siRNA. We speculated that PGC-1α exerts its functions in
pathological angiogenesis through two possible mechanisms. Firstly,
the localization where PGC-1α siRNA was distributed in the retina
was close to the site of hypoxia-induced PGC-1α generation; it
increased gene expression in a particular layer of the retina
(either the ganglion cell layer or inner nuclear layer). We
demonstrated that intravitreally injected siRNA rapidly accessed
the internal limiting membrane and entered the inner retinal cells,
which was consistent with the results of a previous study (32). Therefore, intravitreally injected
PGC-1α siRNA can be carried successfully into retinal cells, which
are responsible for producing hypoxia-induced PGC-1α. Secondly, the
catalytic nature of RNAi was another reason. PGC-1α siRNA which was
absorbed by the retinal cells can bind to the RNA-induced silencing
complex (RISC), which in turn becomes activated. The activated RISC
complex seeks the PGC-1α mRNA and then splices the mRNA at the site
of the homologous sequence (33).
Furthermore, in a multiple turnover kinetic manner, the activated
RISC can seek another PGC-1α mRNA to bind and destroy. One
activated RISC complex can bind and destroy hundreds of PGC-1α
mRNA. Therefore, the local administration of a small amount of
PGC-1α siRNA is an effective approach for suppressing retinal
neovascularization.
VEGF is considered the primary factor that leads to
angiogenesis in the retina. VEGF promotes the recruitment of
endothelial precursor cells into the circulation during local
hypoxia and the proliferation of resident retinal vasculature to
respond to ischemic injury (34,35). During the past decade, relevant
clinical trials emphasizing on inhibitors of the VEGF signaling
pathway, have achieved successful attenuation of pathological
angiogenesis and have improved the vision of patients (6). However, the regrowth of new vessels
often occurs within a few months of the regression of
neovascularization after the application of these agents (35). The inhibition of VEGF alone cannot
completely suppress pathological angiogenesis, as other angiogenic
factors may participate in this pathological process. PGC-1α
induces the expression of VEGFA in numerous retinal cells, and
PGC-1α expression is strongly induced during post-natal retinal
development, coincident with VEGFA expression and angiogenesis
(10). In this study, the mRNA
and protein expression of VEGF were both downregulated following
the administration of PGC-1α siRNA in the mouse model of OIR. VEGF
expression was mainly observed in the ganglion cell layer and inner
nuclear layer and was reduced mainly in the ganglion cell layer
following the local administration of PGC-1α siRNA. The data
presented in this study demonstrate that PGC-1α siRNA downregulates
the expression of PGC-1α, which then reduces the expression of VEGF
through the PGC-1α-VEGF signaling pathway, finally inhibiting
neovascularization. Therefore, PGC-1α regulates the expression of
VEGF in the retina, particularly in ganglion cells. Under hypoxic
conditions, VEGF can be regulated by not only PGC-1α, but also by
HIF-1α (36). The regulation of
VEGF by PGC-1α is HIF-independent (9). In additoin, there are other
angiogenic factors, such as platelet-derived growth factor-B
(PDGF-B), angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) and bFGF regulated by PGC-1α
(9,37). Therefore, we hypothesized that the
suppression of PGC-1α may enhance other signaling pathways to
promote the regrowth of vessels into the central avascular zone
from P12 to P17, and reduce non-perfused areas in the model of
OIR.
In conclusion, the data presented in this study
demonstrate the expression of PGC-1α in the retina and the
upregulation of PGC-1α under hypoxic conditions in a certain time
period. The local administration of PGC-1α siRNA decreases both
PGC-1α and VEGF expression, leading to a reduction in retinal
neovascularization in the mouse model of OIR. The results of our
study demonstrate that the local administration of PGC-1α siRNA
holds great potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for ocular
neovascular diseases.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural
Science Fundation of China (grant no. 81000387).
References
|
1
|
Al-Latayfeh M, Silva PS, Sun JK and Aiello
LP: Antiangiogenic therapy for ischemic retinopathies. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0064112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Watanabe D, Suzuma K, Matsui S, Kurimoto
M, Kiryu J, Kita M, Suzuma I, Ohashi H, Ojima T, Murakami T,
Kobayashi T, Masuda S, Nagao M, Yoshimura N and Takagi H:
Erythropoietin as a retinal angiogenic factor in proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 353:782–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pe’er J, Shweiki D, Itin A, Hemo I,
Gnessin H and Keshet E: Hypoxia-induced expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor by retinal cells is a common factor in
neovascularizing ocular diseases. Lab Invest. 72:638–645.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aiello LP, Northrup JM, Keyt BA, Takagi H
and Iwamoto MA: Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor in retinal cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 113:1538–1544. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sondell M, Sundler F and Kanje M: Vascular
endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates
axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci.
12:4243–4254. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rosenfeld PJ, Rich RM and Lalwani GA:
Ranibizumab: Phase III clinical trial results. Ophthalmol Clin
North Am. 19:361–372. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xia XB, Xiong SQ, Xu HZ, Jiang J and Li Y:
Suppression of retinal neovascularization by shRNA targeting
HIF-1alpha. Curr Eye Res. 33:892–902. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiong SQ, Xia XB, Xu HZ and Jiang J:
Suppression of retinal neovascularization by small-interference RNA
targeting erythropoietin. Ophthalmologica. 223:306–312. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arany Z, Foo SY, Ma Y, Ruas JL,
Bommi-Reddy A, Girnun G, Cooper M, Laznik D, Chinsomboon J,
Rangwala SM, Baek KH, Rosenzweig A and Spiegelman BM:
HIF-independent regulation of VEGF and angiogenesis by the
transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. Nature. 451:1008–1012.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saint-Geniez M, Jiang A, Abend S, Liu L,
Sweigard H, Connor KM and Arany Z: PGC-1α regulates normal and
pathological angiogenesis in the retina. Am J Pathol. 182:255–265.
2013.
|
|
11
|
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R,
Wright M and Spiegelman BM: A cold-Iducible coactivator of nuclear
receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 92:829–839. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Larrouy D, Vidal H, Andreelli F, Laville M
and Langin D: Cloning and mRNA tissue distribution of human
PPARgamma coactivator-1. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord.
23:1327–1332. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valle I, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Arza E,
Lamas S and Monsalve M: PGC-1alpha regulates the mitochondrial
antioxidant defense system in vascular endothelial cells.
Cardiovasc Res. 66:562–573. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Borniquel S, Valle I, Cadenas S, Lamas S
and Monsalve M: Nitric oxide regulates mitochondrial oxidative
stress protection via the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha.
FASEB J. 20:1889–1991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barger PM, Browning AC, Garner AN and
Kelly DP: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activates peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor alpha: a potential role in the
cardiac metabolic stress response. J Biol Chem. 276:44495–44501.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mascareno E, Manukyan I, Das DK and
Siddiqui MA: Down-regulation of cardiac lineage protein (CLP-1)
expression in CLP-1 +/− mice affords. J Cell Mol Med. 13:2744–2753.
2009.
|
|
17
|
Gutsaeva DR, Carraway MS, Suliman HB,
Demchenko IT, Shitara H, Yonekawa H and Piantadosi CA: Transient
hypoxia stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in brain subcortex by a
neuronal nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci.
28:2015–2024. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen SD, Lin TK, Yang DI, Lee SY, Shaw FZ,
Liou CW and Chuang YC: Protective effects of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors gamma coactivator-1alpha against
neuronal cell death in the hippocampal CA1 subfield after transient
global ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 88:605–613. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Rasbach KA and Schnellmann RG: Signaling
of mitochondrial biogenesis following oxidant injury. J Biol Chem.
282:2355–2362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Norrbom J, Sunderg CJ, Ameln H, Kraus WE,
Jansson E and Gustafsson T: PGC-1alpha mRNA expression is
influenced by metabolic perturbation in exercising human skeletal
muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 96:189–194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stein RA, Gallard S and McDonnell DP:
Estrogen-related receptor alpha induces the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor in breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem
Mol Biol. 114:106–112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carmeliet P and Baes M: Metabolism and
therapeutic angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 358:2511–2512. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W and Tuschl T: RNA
interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev.
15:188–200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk
SK, D’Amato R, Sullivan R and D’Amore PA: Oxygen-induced
retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 35:101–111.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Banin E, Dorrell MI, Aguilar E, Ritter MR,
Aderman CM, Smith AC, Friedlander J and Friedlander M: T2-TrpRS
inhibits preretinal neovascularization and enhances physiological
vascular regrowth in OIR as assessed by a new method of
quantification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:2125–2134. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gebarowska D, Stitt AW, Gardiner TA,
Harriott P, Greer B and Nelson J: Synthetic peptides interacting
with the 67-kd laminin receptor can reduce retinal ischemia and
inhibit hypoxia-induced retinal neovascularization. Am J Pathol.
160:307–313. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Abbas-Terki, Blanco-Bose W, Déglon N,
Pralong W and Aebischer P: Lentiviral- mediated RNA interference.
Hum Gene Ther. 13:2197–2201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chin L, Hahn WC, Getz G and Meyerson M:
Making sense of cancer genomic data. Genes Dev. 25:534–555. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang T, Zhou Q and Pignoni F: Yki/YAP,
Sd/TEAD and Hth/MEIS control tissue specification in the
Drosophila eye disc epithelium. PLoS One. 6:e222782011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cooper TA, Wan L and Dreyfuss G: RNA and
disease. Cell. 136:777–793. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Olejniczak M, Galka P and Krzyzosiak WJ:
Sequence-non-specific effects of RNA interference triggers and
microRNA regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:1–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen J, Samul R, Silva RL, et al:
Suppression of ocular neovascularization with siRNA targeting VEGF
receptor 1. Gene Ther. 13:225–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lipardi C, Wei Q and Paterson BM: RNAi as
random degradative PCR: siRNA primers convert mRNA into dsRNAs that
are degraded to generate new siRNAs. Cell. 107:297–307. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arjamaa O and Nikinmaa M: Oxygen-dependent
diseases in the retina: Role of hypoxia- inducible factors. Exp Eye
Res. 83:473–483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Afzal A, Shaw LC, Ljubimov AV, Boulton ME,
Segal MS and Grant MB: Retinal and choroidal microangiopathies:
therapeutic opportunities. Microvasc Res. 74:131–144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F,
Leung SW, Koos RD and Semenza GL: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible
factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4604–4613. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fraisl P, Baes M and Carmeliet P: Hungry
for blood vessels: linking metabolism and angiogenesis. Dev Cell.
14:313–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|