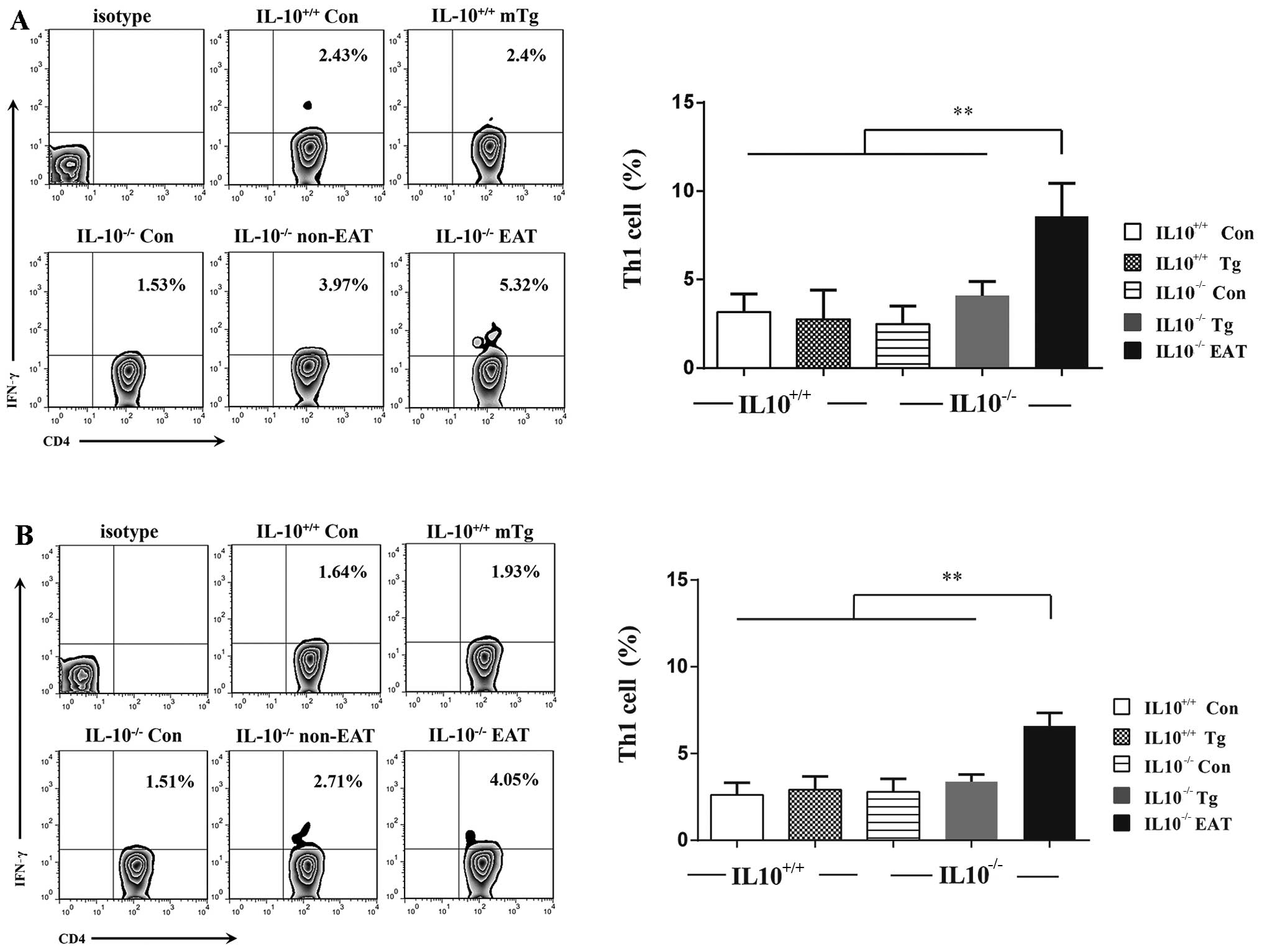
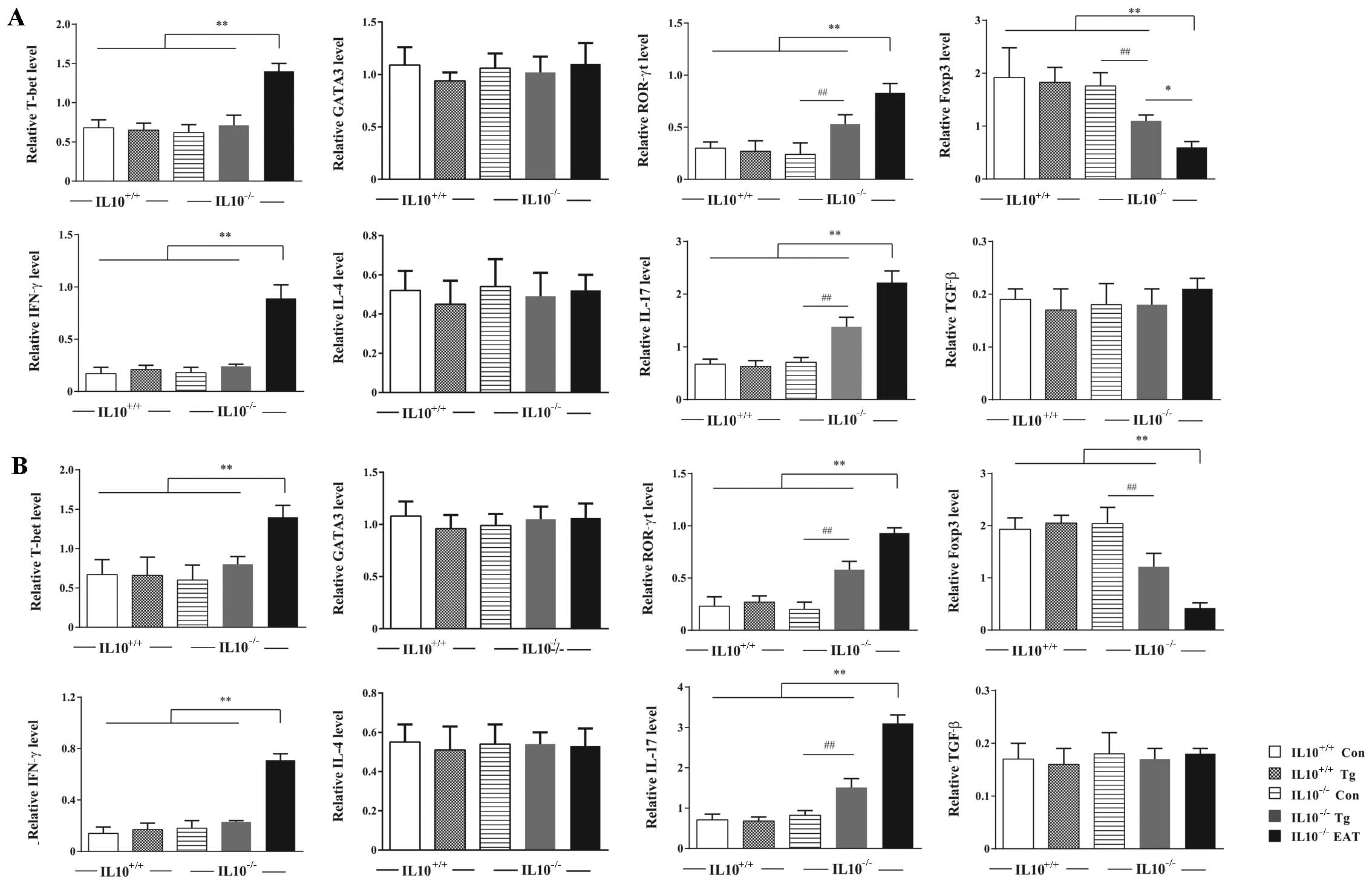
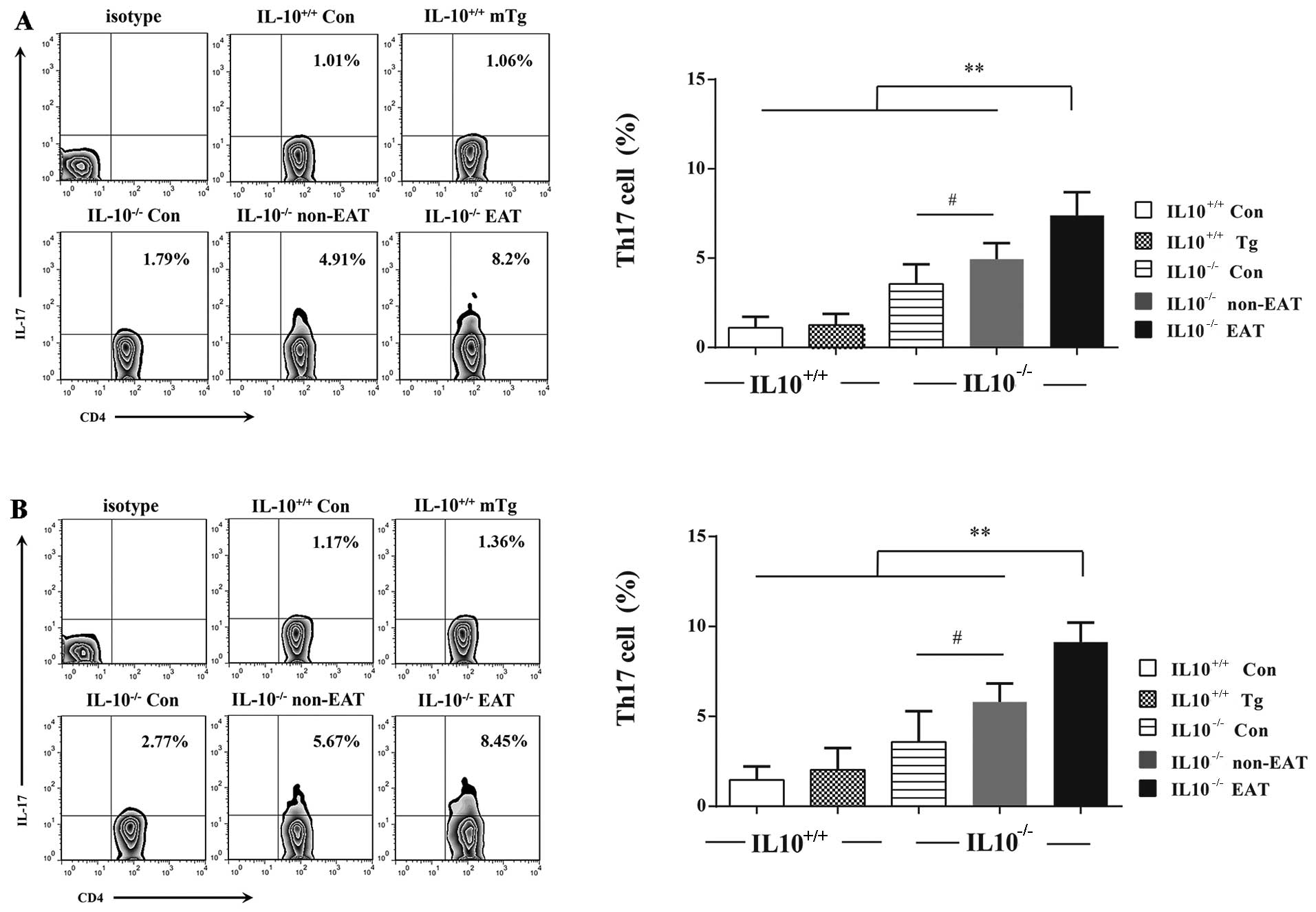
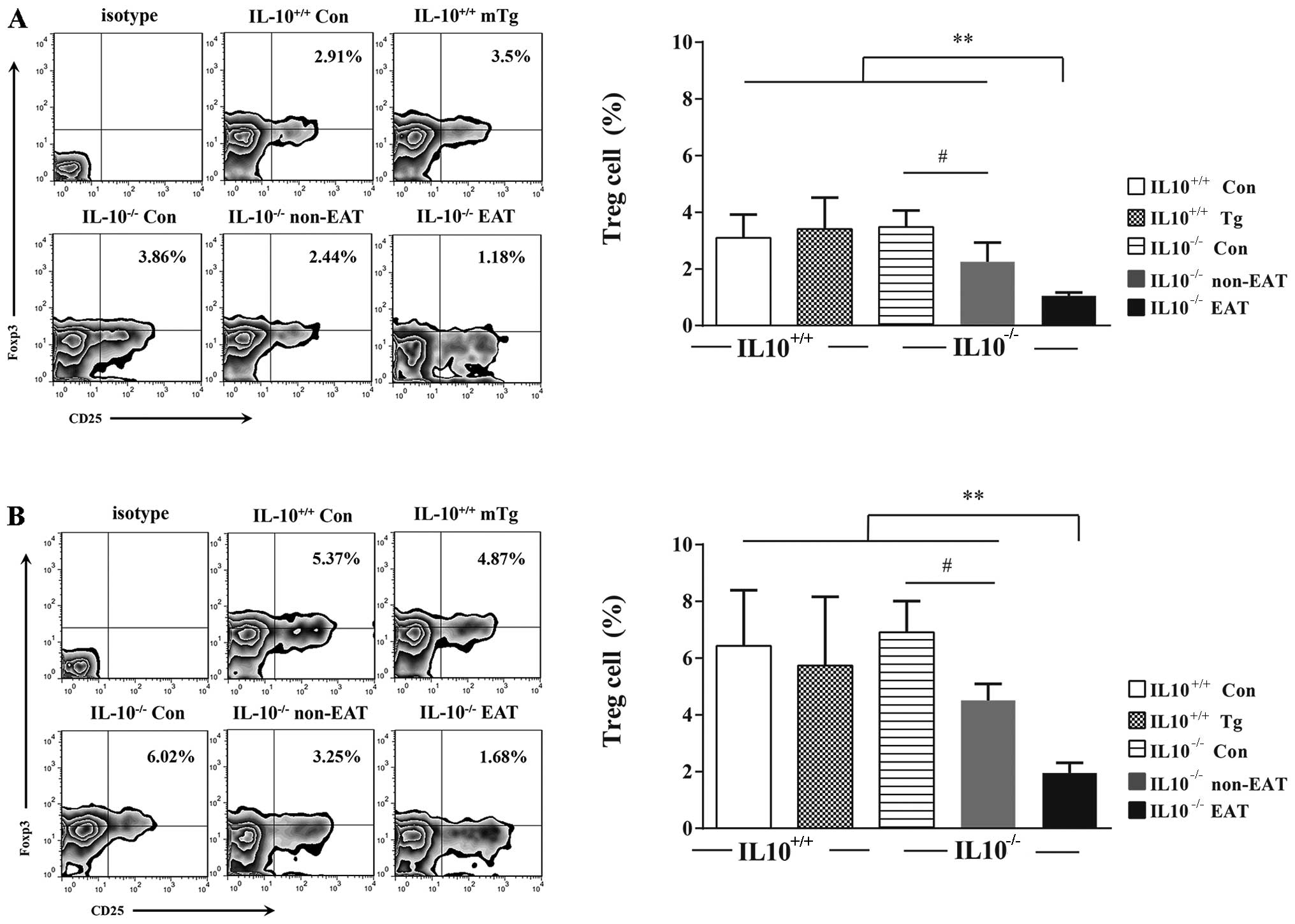
|
1
|
Rose NR, Twarog FJ and Crowle AJ: Murine
thyroiditis: importance of adjuvant and mouse strain for the
induction of thyroid lesions. J Immunol. 3:698–704. 1971.
|
|
2
|
Braley-Mullen H, Johnson M, Sharp GC and
Kyriakos M: Induction of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis in
mice with in vitro activated splenic T cells. Cell Immunol.
1:132–143. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ganesh BB, Bhattacharya P, Gopisetty A and
Prabhakar BS: Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis and suppression
of thyroid autoimmunity. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 10:721–731.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kong YC: Experimental autoimmune
thyroiditis in the mouse. Curr Protoc Immunol. Chapter 15: Unit
15.7. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vladutiu AO and Rose NR: Autoimmune murine
thyroiditis relation to histocompatibility (H-2) type. Science.
4014:1137–1139. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Beisel KW, Kong YM, Babu KS, David CS and
Rose NR: Regulation of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis:
influence of non-H-2 genes. J Immunogenet. 4:257–265. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL
and O’Garra A: Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu
Rev Immunol. 19:683–765. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Saraiva M and O’Garra A: The regulation of
IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:170–181. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kühn R, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K
and Müller W: Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic
enterocolitis. Cell. 2:263–274. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Batteux F, Trebeden H, Charreire J and
Chiocchia G: Curative treatment of experimental autoimmune
thyroiditis by in vivo administration of plasmid DNA coding for
interleukin-10. Eur J Immunol. 3:958–963. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fang Y, Sharp GC and Braley-Mullen H:
Interleukin-10 promotes resolution of granulomatous experimental
autoimmune thyroiditis. Am J Patho. l72:1591–1602. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Teng XC, Jia XK, Fan CL, Wang H, Guo R and
Teng WP: Extraction, purification and identification thyroglobulin
of mouse. Chin J Med Med. 12:1467–1469. 2007.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Gangi E, Vasu C, Cheatem D and Prabhakar
BS: IL-10-producing CD4+CD25+ regulatory T
cells play a critical role in granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor-induced suppression of experimental
autoimmune thyroiditis. J Immunol. 11:7006–7013. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xue H, Wang W, Shan Z, Li Y, Teng X, Gao
Y, Fan C and Teng W: Dynamic changes of
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in NOD
H-2h4 mice with iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis.
Biol Trace Elem Res. 1:292–301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gangi E, Vasu C, Cheatem D and Prabhakar
BS: IL-10-producing CD4+CD25+ regulatory T
cells play a critical role in granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor-induced suppression of experimental
autoimmune thyroiditis. J Immunol. 11:7006–7013. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Vasu C, Dogan RN, Holterman MJ and
Prabhakar BS: Selective induction of dendritic cells using
granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor, but not fms-like
tyrosine kinase receptor 3-ligand, activates thyroglobulin-specific
CD4+/CD25+ T cells and suppresses
experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. J Immunol. 11:5511–5522. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
El Fassi D, Banga JP, Gilbert JA, Padoa C,
Hegedüs L and Nielsen CH: Treatment of Graves’ disease with
rituximab specifically reduces the production of thyroid
stimulating auto-antibodies. Clin Immunol. 130:252–258. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tang H, Mignon-Godefroy K, Meroni PL,
Garotta G, Charreire J and Nicoletti F: The effects of a monoclonal
antibody to interferon-gamma on experimental autoimmune thyroiditis
(EAT): prevention of disease and decrease of EAT-specific T cells.
Eur J Immunol. 1:275–278. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shi L, Bi M, Yang R, Zhou J, Zhao s, Fan
C, Shan Z, Li Y and Teng W: Defective expression of regulatory B
cells in iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in non-obese
diabetic H-2(h4) mice. J Endocrinol Invest. 37:43–50. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Verginis P, Li HS and Carayanniotis G:
Tolerogenic semimature dendritic cells suppress experimental
autoimmune thyroiditis by activation of thyroglobulin-specific
CD4+CD25+ T cells. J Immunol. 174:7433–7439.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tomazic V, Rose NR and Shreffler DC:
Autoimmune murine thyroiditis. IV. Localization of genetic control
of the immune response. J Immunol. 3:965–969. 1974.
|
|
22
|
Kalampokis I, Yoshizaki A and Tedder TF:
IL-10-producing regulatory B cells (B10 cells) in autoimmune
disease. Arthritis Res Ther. Feb 11–2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang SH, Bretz JD, Phelps E, Mezosi E,
Arscott PL, Utsugi S and Baker JR Jr: A unique combination of
inflammatory cytokines enhances apoptosis of thyroid follicular
cells and transforms nondestructive to destructive thyroiditis in
experimental auto-immune thyroiditis. J Immunol. 5:2470–2474. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kennedy MK, Torrance DS, Picha KS and
Mohler KM: Analysis of cytokine mRNA expression in the central
nervous system of mice with experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis reveals that IL-10 mRNA expression correlates
with recovery. J Immunol. 149:2496–2505. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Vieira P,
Mosmann TR, Howard M, Moore KW and O’Garra A: IL-10 acts on the
antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1
cells. J Immunol. 10:3444–3451. 1991.
|
|
26
|
Todd I, Pujol-Borrell R, Hammond LJ,
Bottazzo GF and Feldmann M: Interferon-gamma induces HLA-DR
expression by thyroid epithelium. Clin Exp Immunol. 2:265–273.
1985.
|
|
27
|
Maddur MS, Miossec P, Kaveri SV and Bayry
J: Th17 cells: biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory
diseases, and therapeutic strategies. Am J Pathol. 1:8–18. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Figueroa-Vega N, Alfonso-Perez M,
Benedicto I, Sanchez-Madrid F, Gonzalez-Amaro R and Marazuela M:
Increased circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and Th17
lymphocytes in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
95:953–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li D, Cai W, Gu R, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Tang
K, Xu P, Katirai F, Shi W, Wang L, Huang T and Huang B: Th17 cell
plays a role in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in
patients. Clin Immunol. 149:411–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Horie I, Abiru N, Nagayama Y, Kuriya G,
Saitoh O, Ichikawa T, Iwakura Y and Eguchi K: T helper type 17
immune response plays an indispensable role for development of
iodine-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in nonobese diabetic-H2h4
mice. Endocrinology. 11:5135–5142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huber S, Gagliani N, Esplugues E, O’Connor
W Jr, Huber FJ, Chaudhry A, Kamanaka M, Kobayashi Y, Booth CJ,
Rudensky AY, Roncarolo MG, Battaglia M and Flavell RA: Th17 cells
express interleukin-10 receptor and are controlled by
Foxp3− and Foxp3+ regulatory CD4+
T cells in an interleukin-10-dependent manner. Immunity. 4:554–565.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 5:775–787. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA and Rudensky AY:
Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4(+)CD25(+)
regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 4:330–336. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Murai M, Turovskaya O, Kim G, Madan R,
Karp CL, Cheroutre H and Kronenberg M: Interleukin 10 acts on
regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription
factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat
Immunol. 11:1178–1184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|