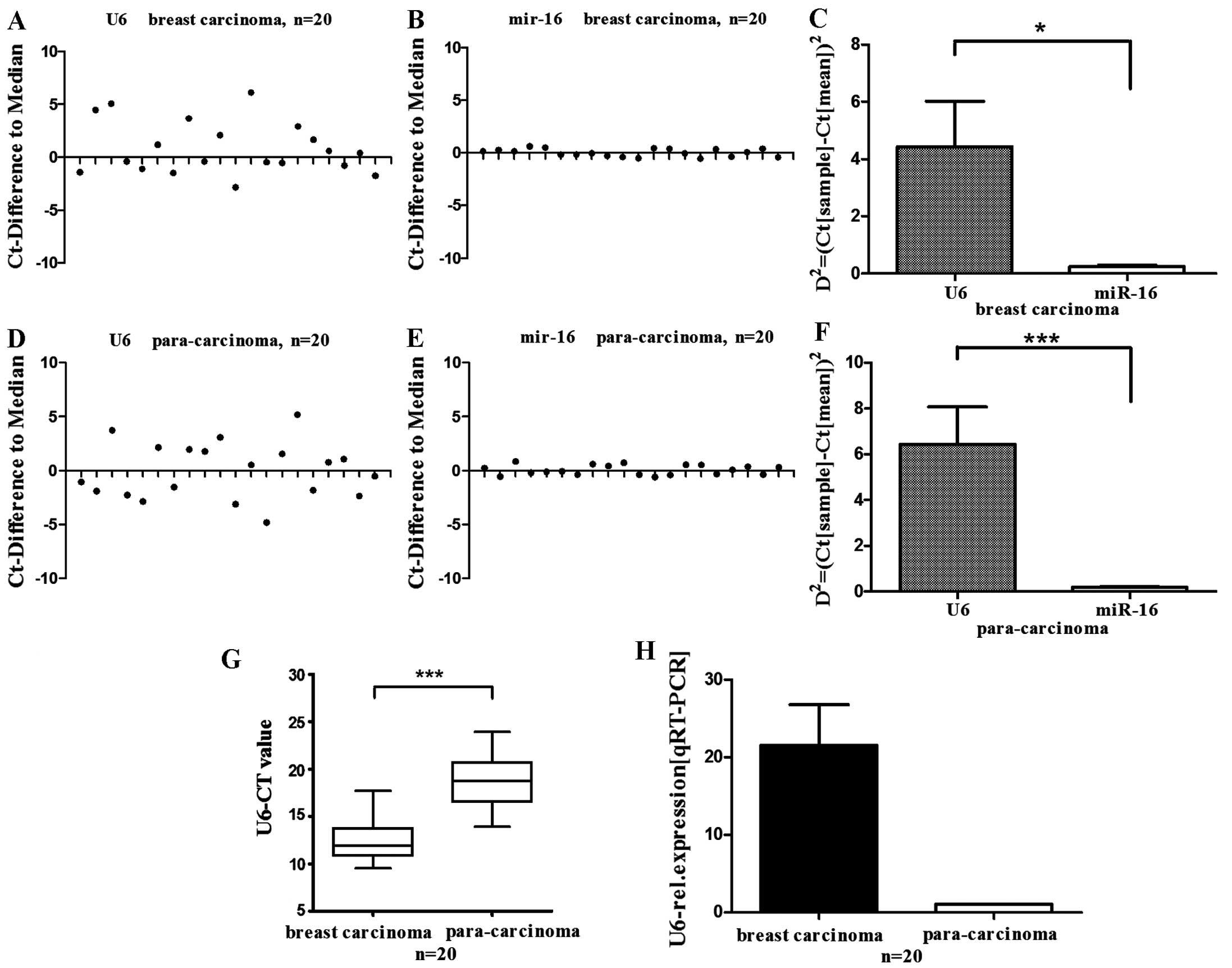
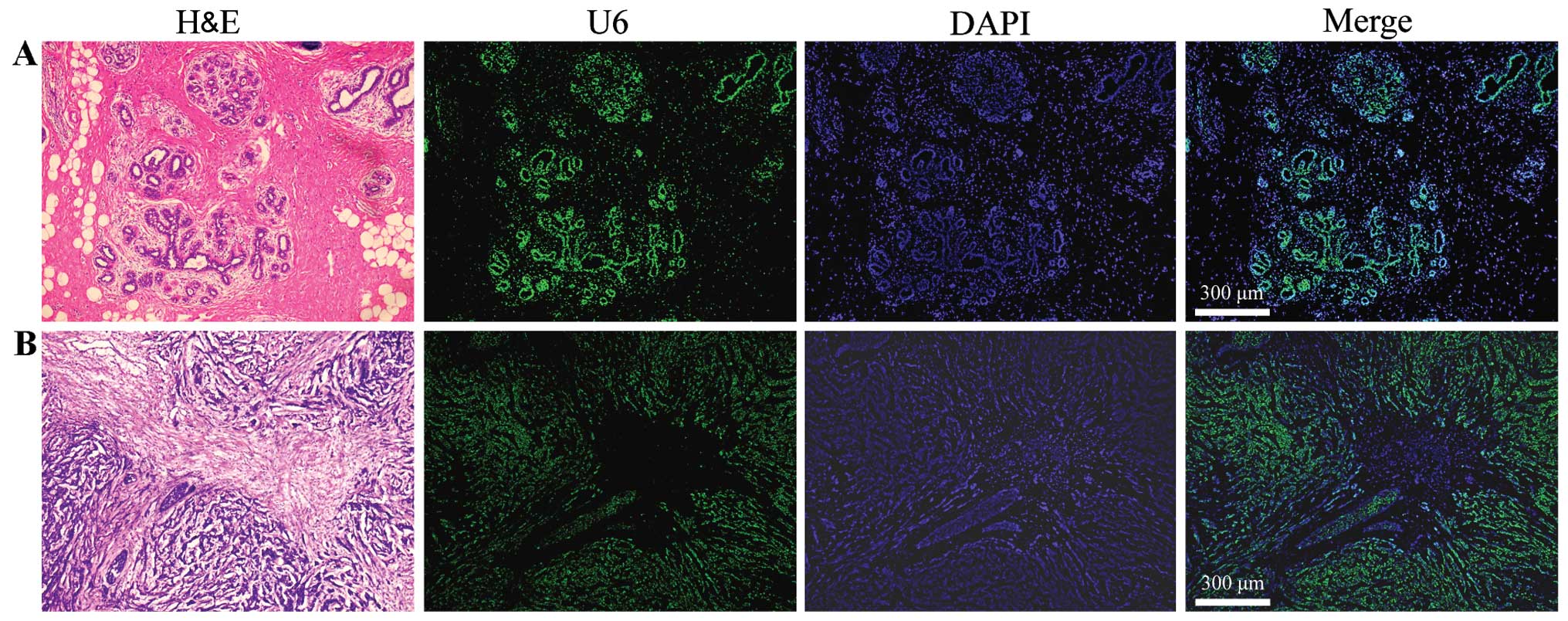
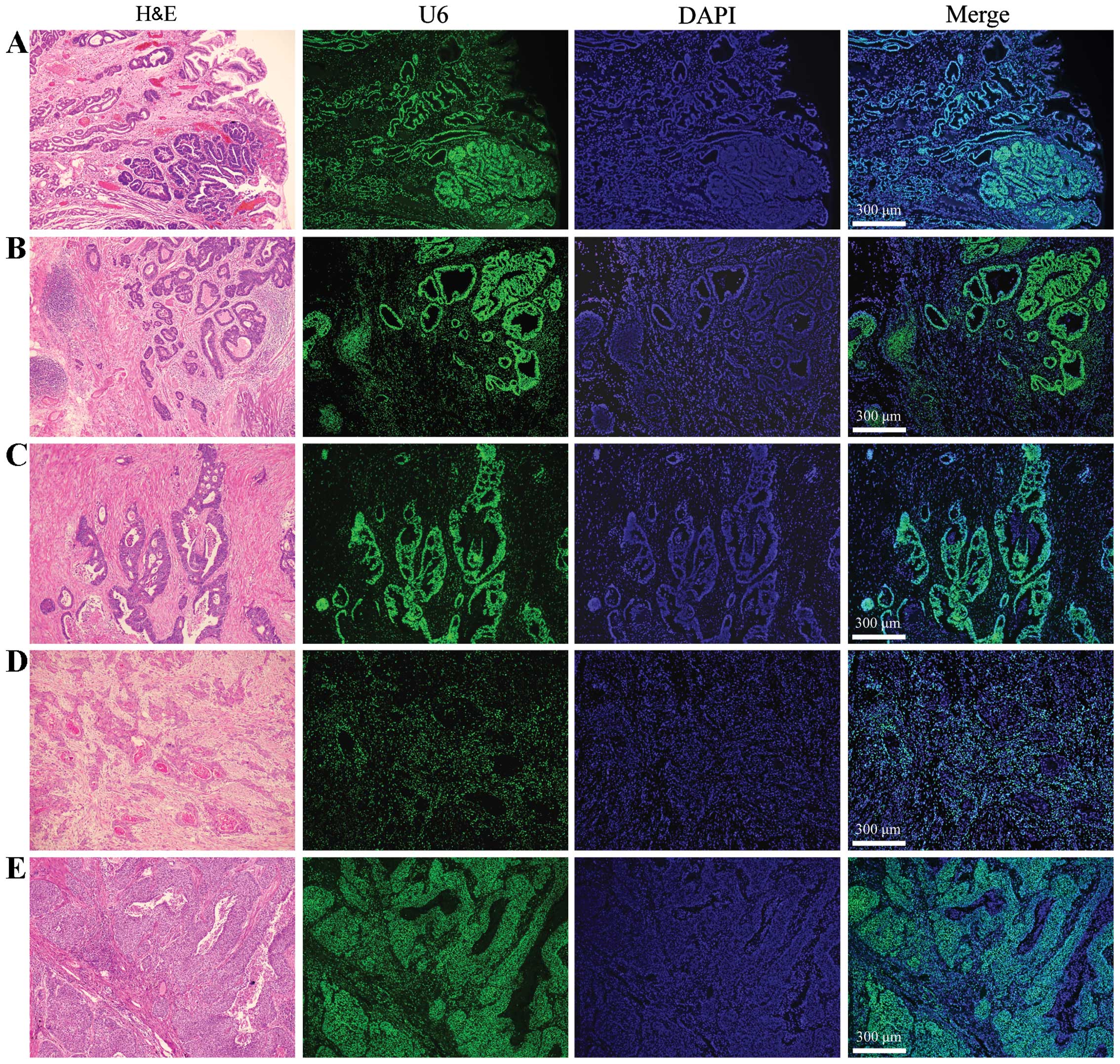
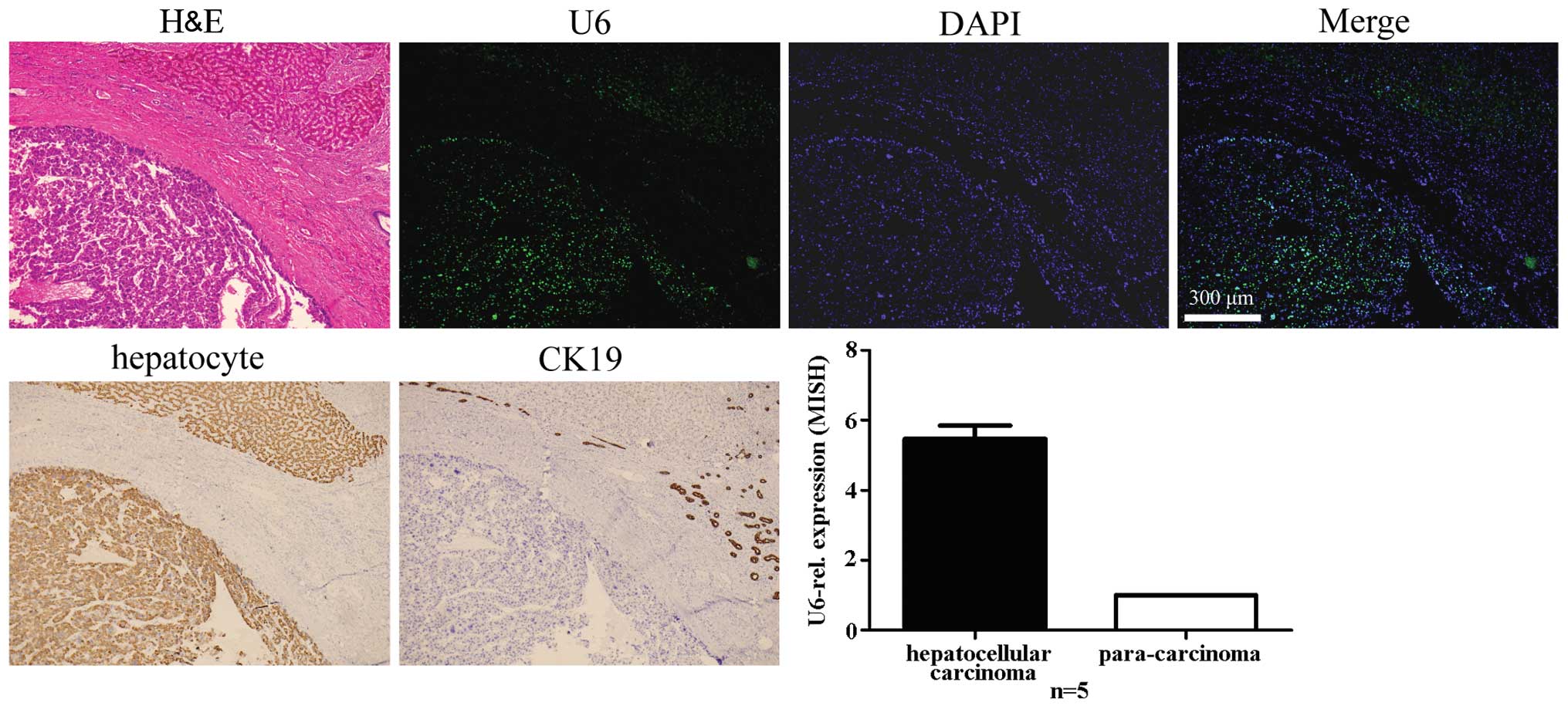
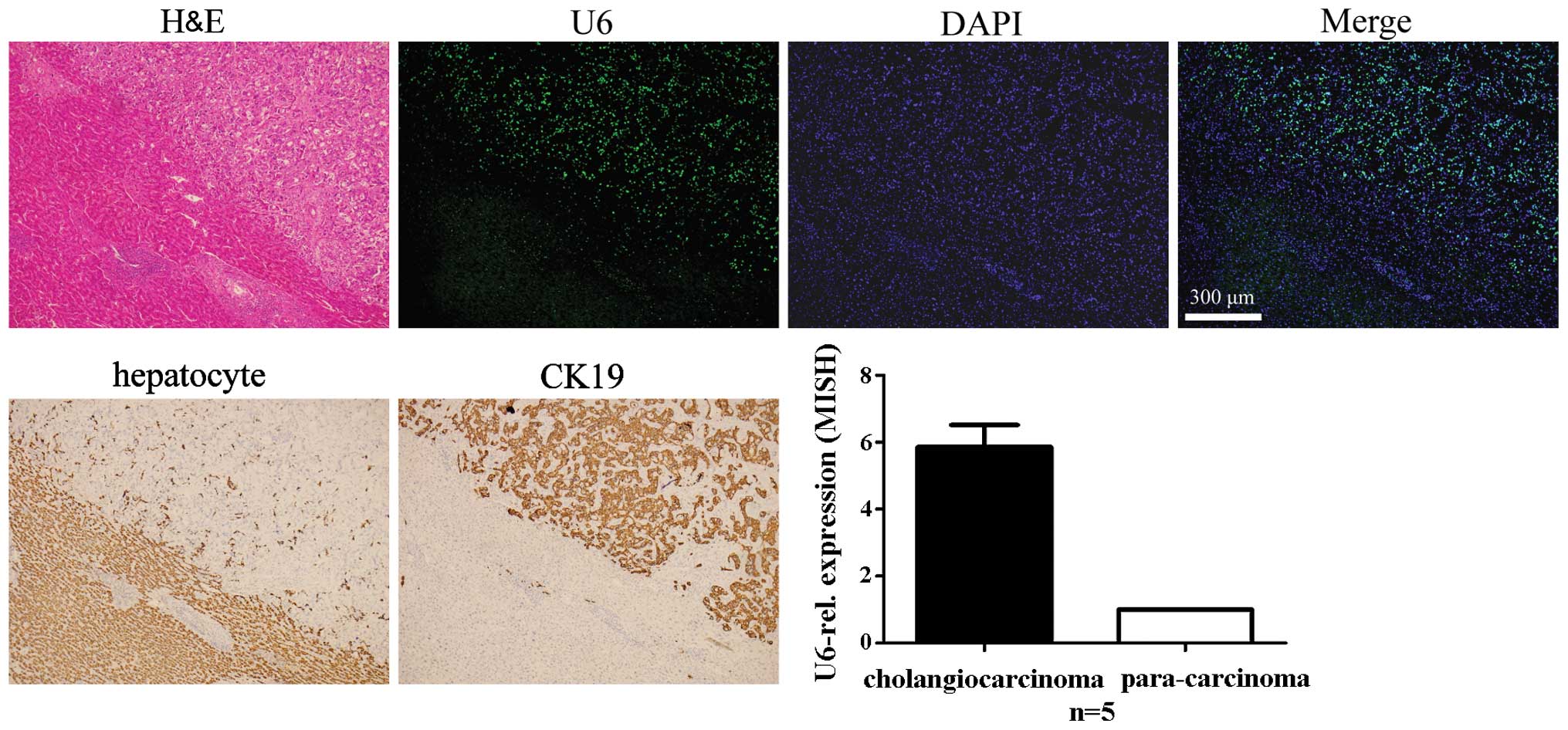
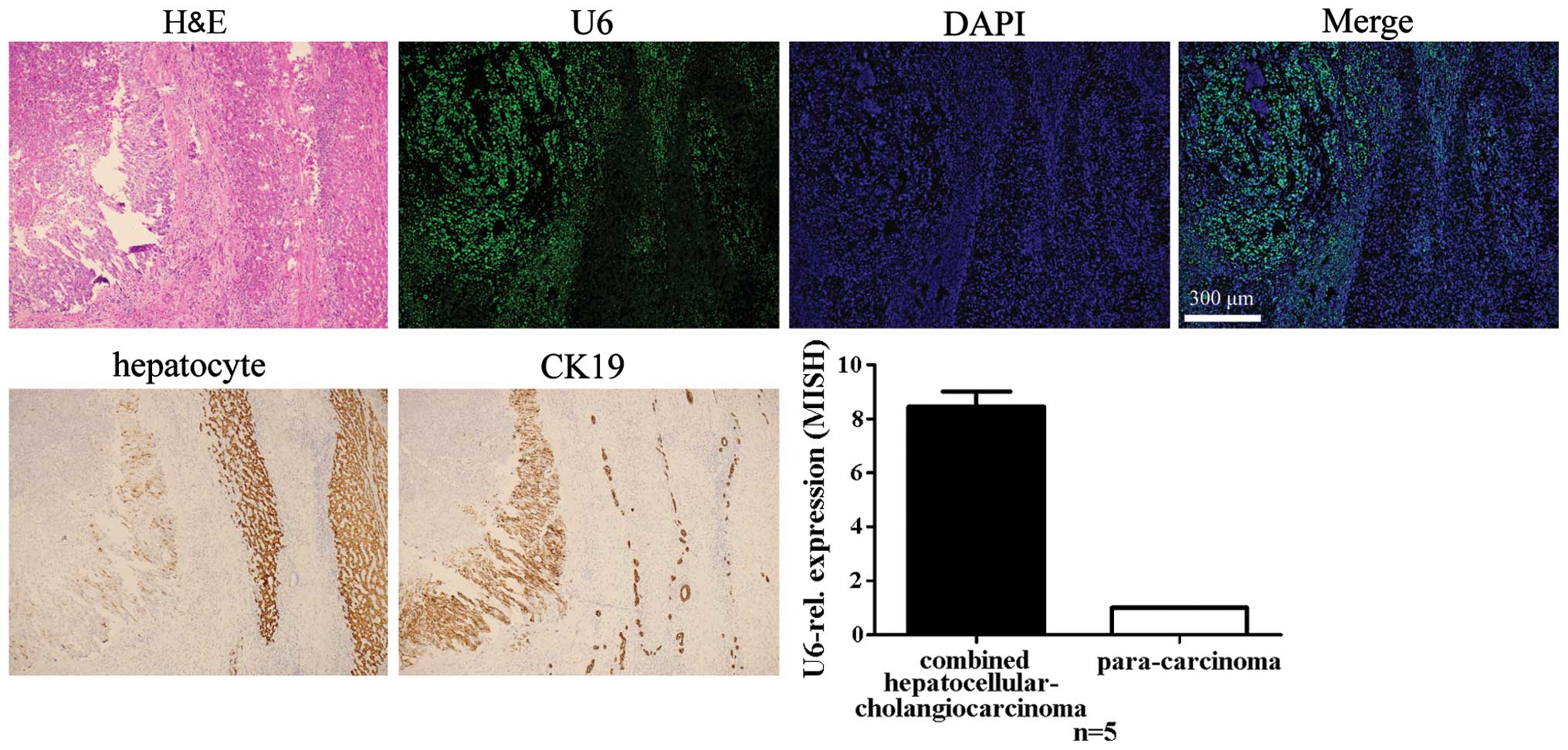
|
1
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner MO: miRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Listowski MA, Heger E, Bogusławska DM,
Machnicka B, Kuliczkowski K, Leluk J and Sikorski AF: microRNAs:
Fine tuning of erythropoiesis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 18:34–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 774:1–20. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luzna P, Gregar J, Uberall I, Radova L,
Prochazka V and Ehrmann J Jr: Changes of microRNAs-192, 196a and
203 correlate with Barrett's esophagus diagnosis and its
progression compared to normal healthy individuals. Diagn Pathol.
6(114)2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mao ZG, He DS, Zhou J, Yao B, Xiao WW,
Chen CH, Zhu YH and Wang HJ: Differential expression of microRNAs
in GH-secreting pituitary adenomas. Diagn Pathol. 5(79)2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nelson KM and Weiss GJ: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Past, present, and potential future. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:3655–3660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP and Chen CZ: Micromanagers of
gene expression: The potentially widespread influence of metazoan
microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 5:396–400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nana-Sinkam SP and Croce CM: MicroRNAs as
therapeutic targets in cancer. Transl Res. 157:216–225. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gattolliat CH, Thomas L, Ciafrè SA,
Meurice G, Le Teuff G, Job B, Richon C, Combaret V, Dessen P,
Valteau-Couanet D, et al: Expression of miR-487b and miR-410
encoded by 14q32.31 locus is a prognostic marker in neuroblastoma.
Br J Cancer. 105:1352–1361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu G, Tang JQ, Tian ML, Li H, Wang X, Wu
T, Zhu J, Huang SJ and Wan YL: Prognostic values of the miR-17-92
cluster and its paralogs in colon cancer. J Surg Oncol.
106:232–237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Liao H, Deng Z, Yang P, Du N,
Zhanng Y and Ren H: miRNA-205 affects infiltration and metastasis
of breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:139–143. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang S, Li H, Wang J and Wang D:
Expression of microRNA-497 and its prognostic significance in human
breast cancer. Diagn Pathol. 8(172)2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ouyang M, Li Y, Ye S, Ma J, Lu L, Lv W,
Chang G, Li X, Li Q, Wang S, et al: MicroRNA profiling implies new
markers of chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS
One. 9:e962282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peltier HJ and Latham GJ: Normalization of
microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays:
Identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and
cancerous human solid tissues. RNA. 14:844–852. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Davoren PA, McNeill RE, Lowery AJ, Kerin
MJ and Miller N: Identification of suitable endogenous control
genes for microRNA gene expression analysis in human breast cancer.
BMC Mol Biol. 9:76–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lamba V, Ghodke-Puranik Y, Guan W and
Lamba JK: Identification of suitable reference genes for hepatic
microRNA quantitation. BMC Res Notes. 7:1292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ,
Wagner I, Miller K, Kilic E, Erbersdobler A, Weikert S and Jung K:
Reference miRNAs for miRNAome analysis of urothelial carcinomas.
PLoS One. 7:e393092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mortarino M, Gioia G, Gelain ME, Albonico
F, Roccabianca P, Ferri E and Comazzi S: Identification of suitable
endogenous controls and differentially expressed microRNAs in
canine fresh-frozen and FFPE lymphoma samples. Leuk Res.
34:1070–1077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li D, Liu H, Li Y, Yang M, Qu C, Zhang Y,
Liu Y and Zhang X: Identification of suitable endogenous control
genes for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of miRNA in bovine solid
tissues. Mol Biol Rep. 41:6475–6480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang KH, Mestdagh P, Vandesompele J,
Kerin MJ and Miller N: MicroRNA expression profiling to identify
and validate reference genes for relative quantification in
colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 10(173)2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Genovesi LA, Anderson D, Carter KW, Giles
KM and Dallas PB: Identification of suitable endogenous control
genes for microRNA expression profiling of childhood
medulloblastoma and human neural stem cells. BMC Res Notes.
5(507)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McDermott AM, Kerin MJ and Miller N:
Identification and validation of miRNAs as endogenous controls for
RQ-PCR in blood specimens for breast cancer studies. PLoS One.
8:e837182013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K,
Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R and Haqq C:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5(24)2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kent OA, McCall MN, Cornish TC and
Halushka MK: Lessons from miR-143/145: The importance of cell-type
localization of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:7528–7538. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Selvakumar T, Gjidoda A, Hovde SL and
Henry RW: Regulation of human RNA polymerase III transcription by
DNMT1 and DNMT3a DNA methyltransferases. J Biol Chem.
287:7039–7050. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin BR and Natarajan V: Negative
regulation of human U6 snRNA promoter by p38 kinase through Oct-1.
Gene. 497:200–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Veras I, Rosen EM and Schramm L:
Inhibition of RNA polymerase III transcription by BRCA1. J Mol
Biol. 387:523–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu P, Samudre K, Wu S, Sun Y and Hernandez
N: CK2 phosphorylation of Bdp1 executes cell cycle-specific RNA
polymerase III transcription repression. Mol Cell. 16:81–92. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rollins J, Veras I, Cabarcas S, Willis I
and Schramm L: Human Maf1 negatively regulates RNA polymerase III
transcription via the TFIIB family members Brf1 and Brf2. Int J
Biol Sci. 3:292–302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marshall L and White RJ: Non-coding RNA
production by RNA polymerase III is implicated in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 8:911–914. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cabarcas S, Watabe K and Schramm L:
Inhibition of U6 snRNA transcription by PTEN. Online J Biol Sci.
10:114–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hilcenko C, Simpson PJ, Finch AJ, Bowler
FR, Churcher MJ, Jin L, Packman LC, Shlien A, Campbell P, Kirwan M,
et al: Aberrant 3′ oligoadenylation of spliceosomal U6 small
nuclear RNA in poikiloderma with neutropenia. Blood. 121:1028–1038.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mroczek S and Dziembowski A: U6 RNA
biogenesis and disease association. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
4:581–592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|