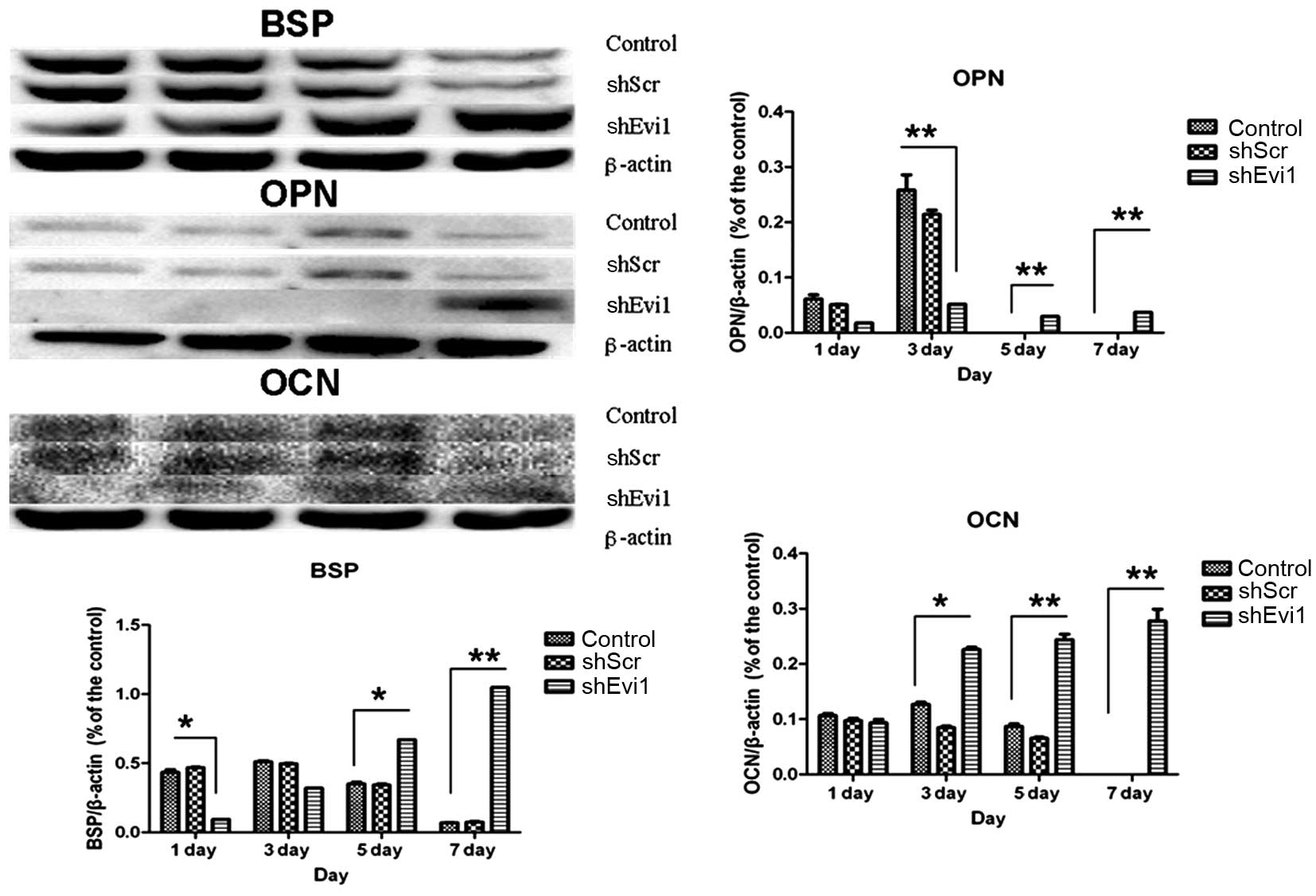
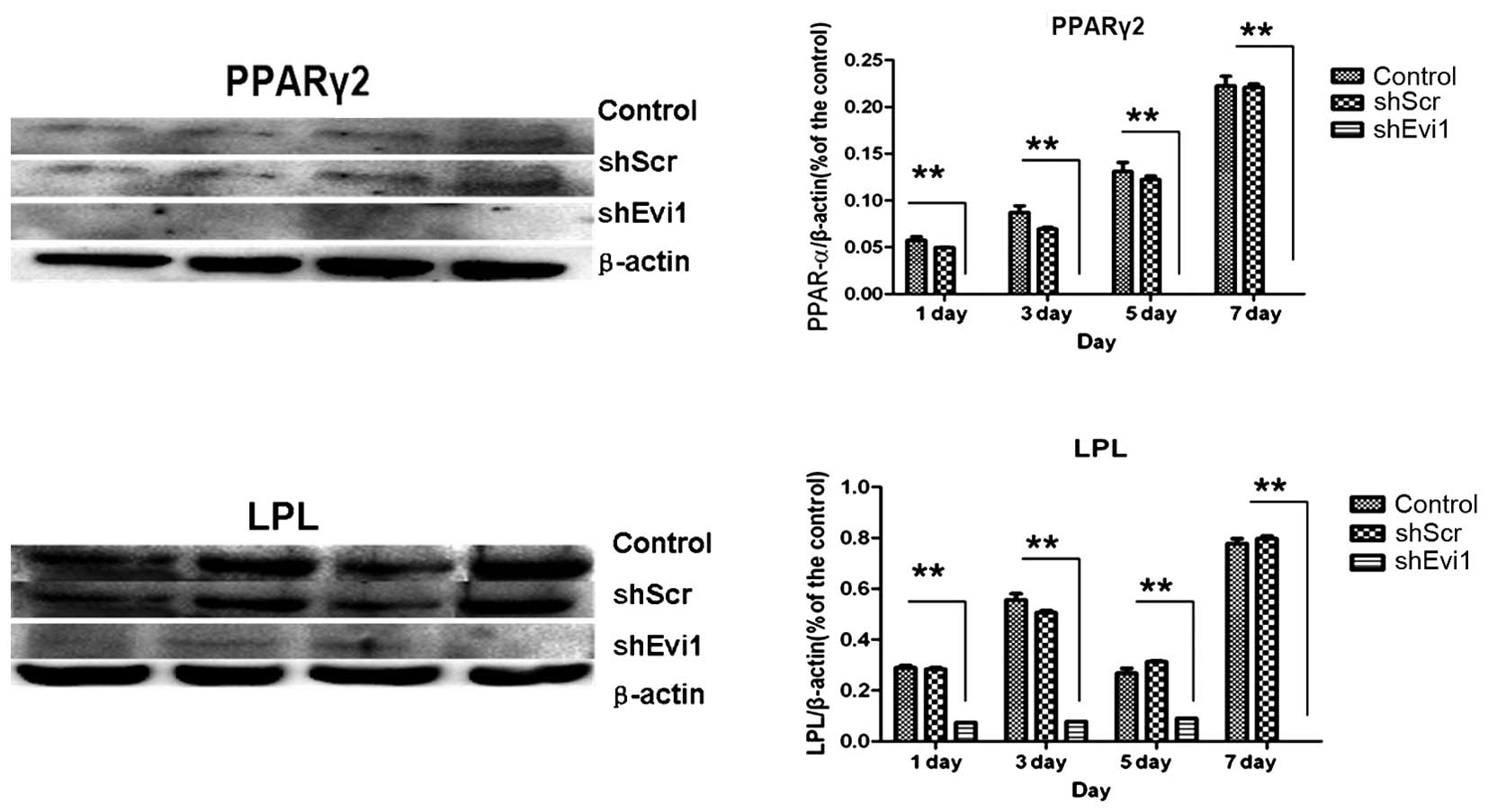
|
1
|
Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Parfitt AM and
Manolagas SC: Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of
apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids.
Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J Clin
Invest. 102:274–282. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morrison NA, Qi JC, Tokita A, Kelly PJ,
Crofts L, Nguyen TV, Sambrook PN and Eisman JA: Prediction of bone
density from vitamin D receptor alleles. Nature. 367:284–287. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seeman E: Bone quality: The material and
structural basis of bone strength. J Bone Miner Metab. 26:1–8.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pietschmann P, Rauner M, Sipos W and
Kerschan-Schindl K: Osteoporosis: An age-related and
gender-specific disease - a mini-review. Gerontology. 55:3–12.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kassem M and Abdallah BM: Human
bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Biological
characteristics and potential role in therapy of degenerative
diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 331:157–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Egermann M, Heil P, Tami A, Ito K, Janicki
P, Von Rechenberg B, Hofstetter W and Richards PJ: Influence of
defective bone marrow osteogenesis on fracture repair in an
experimental model of senile osteoporosis. J Orthop Res.
28:798–804. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Rodriguez JP, Astudillo P, Rios S and Pino
AM: Involvement of adipogenic potential of human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in osteoporosis. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 3:208–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uejima S, Okada K, Kagami H, Taguchi A and
Ueda M: Bone marrow stromal cell therapy improves femoral bone
mineral density and mechanical strength in ovariectomized rats.
Cytotherapy. 10:479–489. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ocarino Nde M, Boeloni JN, Jorgetti V,
Gomes DA, Goes AM and Serakides R: Intra-bone marrow injection of
mesenchymal stem cells improves the femur bone mass of osteoporotic
female rats. Connect Tissue Res. 51:426–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lien CY, Chih-Yuan Ho K, Lee OK, Blunn GW
and Su Y: Restoration of bone mass and strength in
glucocorticoid-treated mice by systemic transplantation of CXCR4
and cbfa-1 co-expressing mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res.
24:837–848. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Park S-H, Sim WY, Min B-H, Yang SS,
Khademhosseini A and Kaplan DL: Chip-based comparison of the
osteogenesis of human bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells under mechanical stimulation. PLoS One.
7:e466892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Recent progress
on tissue-resident adult stem cell biology and their therapeutic
implications. Stem Cell Rev. 4:27–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rodríguez JP, Garat S, Gajardo H, Pino AM
and Seitz G: Abnormal osteogenesis in osteoporotic patients is
reflected by altered mesenchymal stem cells dynamics. J Cell
Biochem. 75:414–423. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ishibashi J, Firtina Z, Rajakumari S, Wood
KH, Conroe HM, Steger DJ and Seale P: An Evi1-C/EBPβ complex
controls peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ2 gene
expression to initiate white fat cell differentiation. Mol Cell
Biol. 32:2289–2299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yue B, Lu B, Dai KR, Zhang XL, Yu CF, Lou
JR and Tang TT: BMP2 gene therapy on the repair of bone defects of
aged rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 77:395–403. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fu L, Tang T, Miao Y, Zhang S, Qu Z and
Dai K: Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation and inhibition of
adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells by
alendronate via ERK and JNK activation. Bone. 43:40–47. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang J, Liu C, Qiao A, Cui Y, Zhang H,
Cui A, Zhang S, Yang Y, Xiao X, Chen Y, et al: MicroRNA-29a-c
decrease fasting blood glucose levels by negatively regulating
hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Hepatol. 58:535–542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manolagas SC: Birth and death of bone
cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the
pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 21:115–137.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khosla S: Minireview: The OPG/RANKL/RANK
system. Endocrinology. 142:5050–5055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwartzman J and Yazici Y: Denosumab in
postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med.
354:2390–2391; author reply 2390–2391. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Watts NB, Roux C, Modlin JF, Brown JP,
Daniels A, Jackson S, Smith S, Zack DJ, Zhou L, Grauer A, et al:
Infections in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with
denosumab or placebo: Coincidence or causal association? Osteoporos
Int. 23:327–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Sobacchi C, Frattini A, Guerrini MM,
Abinun M, Pangrazio A, Susani L, Bredius R, Mancini G, Cant A,
Bishop N, et al: Osteoclast-poor human osteopetrosis due to
mutations in the gene encoding RANKL. Nat Genet. 39:960–962. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
James AW, Pang S, Askarinam A, Corselli M,
Zara JN, Goyal R, Chang L, Pan A, Shen J, Yuan W, et al: Additive
effects of sonic hedgehog and Nell-1 signaling in osteogenic versus
adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells.
Stem Cells Dev. 21:2170–2178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pei L and Tontonoz P: Fat's loss is bone's
gain. J Clin Invest. 113:805–806. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gimble JM and Nuttall ME: The relationship
between adipose tissue and bone metabolism. Clin Biochem.
45:874–879. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Devlin C, Leboy
PS and Owen ME: Evidence for an inverse relationship between the
differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow
stromal cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 102:341–351. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ho PA, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Pollard JA,
Hirsch B, Raimondi SC, Cooper T, Gamis AS and Meshinchi S: High
EVI1 expression is associated with MLL rearrangements and predicts
decreased survival in paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia: A report
from the children's oncology group. Br J Haematol. 162:670–677.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|