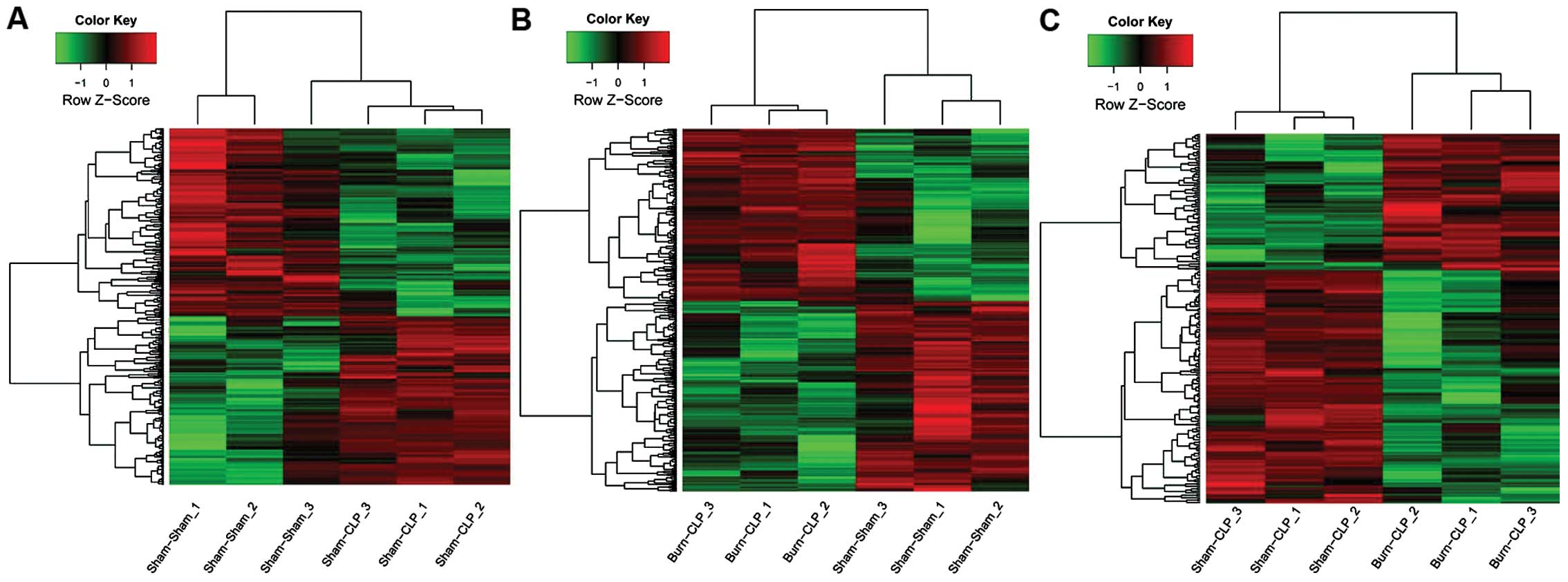
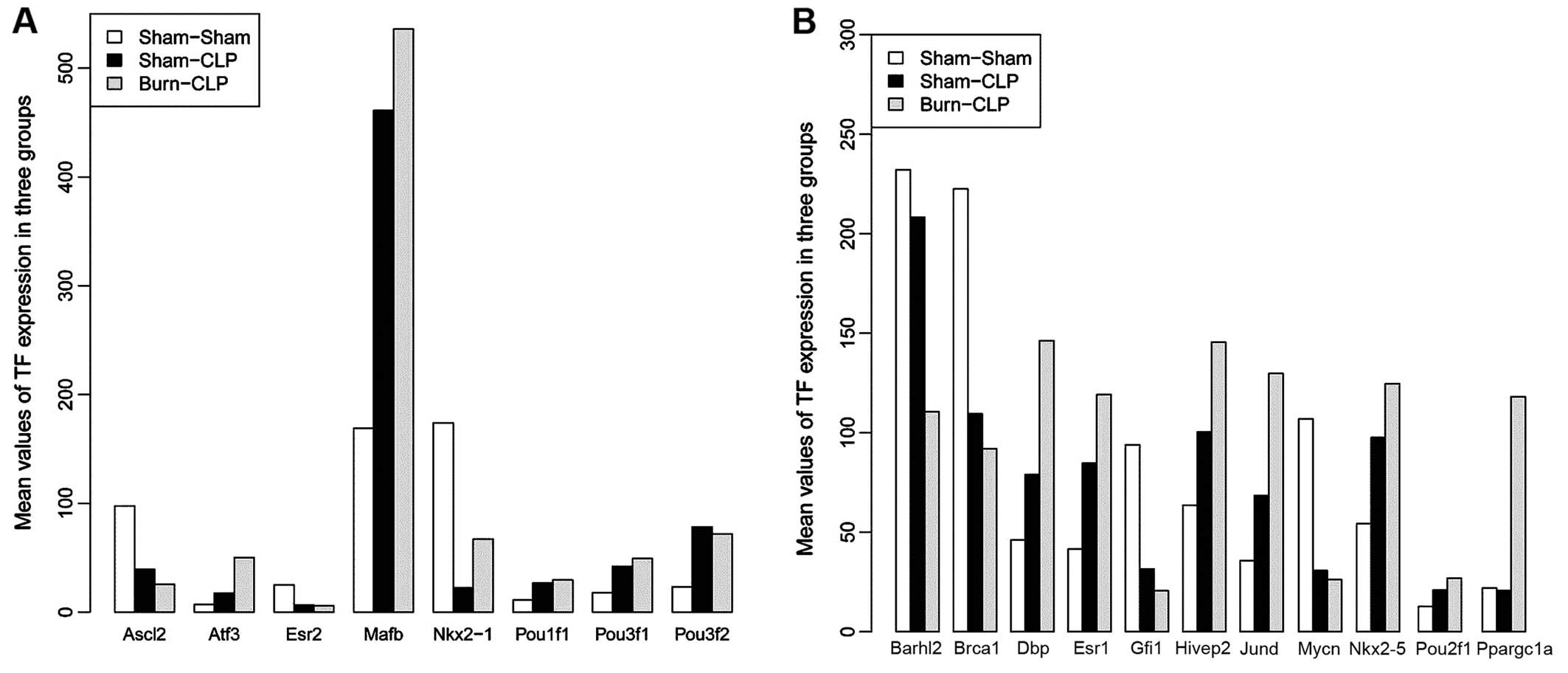
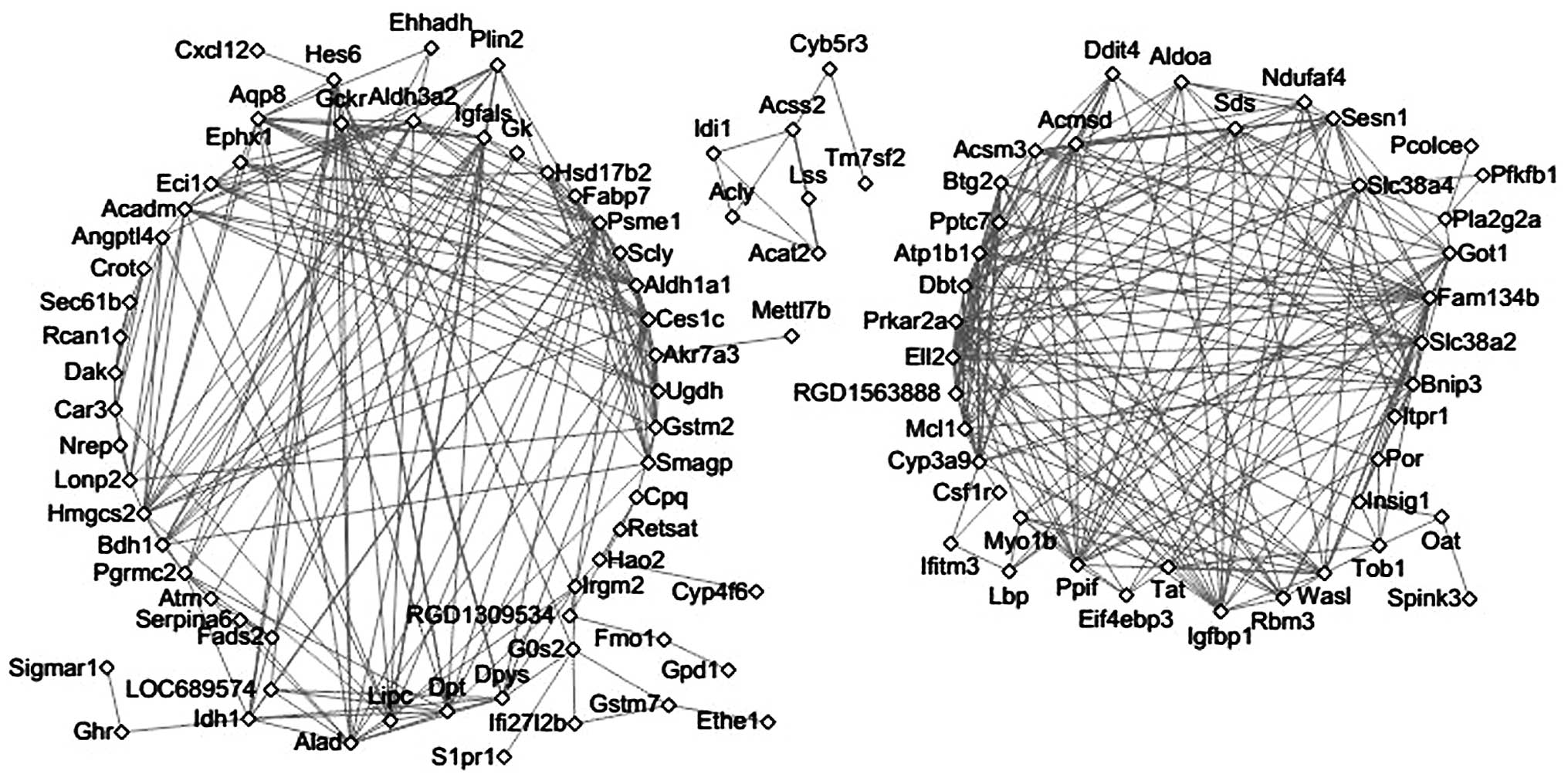
|
1
|
Taylor FB Jr, Kinasewitz GT and Lupu F:
Pathophysiology, staging and therapy of severe sepsis in baboon
models. J Cell Mol Med. 16:672–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Church D, Elsayed S, Reid O, Winston B and
Lindsay R: Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 19:403–434.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beffa DC, Fischman AJ, Fagan SP, Hamrahi
VF, Paul KW, Kaneki M, Yu YM, Tompkins RG and Carter EA:
Simvastatin treatment improves survival in a murine model of burn
sepsis: Role of interleukin 6. Burns. 37:222–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kraft R, Herndon DN, Finnerty CC, Cox RA,
Song J and Jeschke MG: Predictive value of IL-8 for sepsis and
severe infections after burn injury - A clinical study. Shock.
43:222–227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zu H, Li Q and Huang P: Expression of Treg
subsets on intestinal T cell immunity and endotoxin translocation
in porcine sepsis after severe burns. Cell Biochem Biophys.
70:1699–1704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Banta S, Vemula M, Yokoyama T, Jayaraman
A, Berthiaume F and Yarmush ML: Contribution of gene expression to
metabolic fluxes in hypermetabolic livers induced through burn
injury and cecal ligation and puncture in rats. Biotechnol Bioeng.
97:118–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Afsari B, Geman D and Fertig EJ: Learning
dysregulated pathways in cancers from differential variability
analysis. Cancer Inform. 13(Suppl 5): 61–67. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bolstad B: preprocessCore: A collection of
pre-processing functions. R package version 1. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Matys V, Fricke E, Geffers R, Gössling E,
Haubrock M, Hehl R, Hornischer K, Karas D, Kel AE, Kel-Margoulis
OV, et al: TRANSFAC: Transcriptional regulation, from patterns to
profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:374–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering
C, et al: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with
increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Saito R, Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J,
Wang PL, Lotia S, Pico AR, Bader GD and Ideker T: A travel guide to
Cytoscape plugins. Nat Methods. 9:1069–1076. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schmidt MV, Paulus P, Kuhn AM, Weigert A,
Morbitzer V, Zacharowski K, Kempf VA, Brüne B and von Knethen A:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-induced T cell
apoptosis reduces survival during polymicrobial sepsis. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 184:64–74. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiang MC, Cheng YC, Lin KH and Yen CH:
PPARγ regulates the mitochondrial dysfunction in human neural stem
cells with tumor necrosis factor alpha. Neuroscience. 229:118–129.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Singer M: The role of mitochondrial
dysfunction in sepsis-induced multi-organ failure. Virulence.
5:66–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Kim JJ and Miura R: Acyl-CoA
dehydrogenases and acyl-CoA oxidases. Structural basis for
mechanistic similarities and differences. Eur J Biochem.
271:483–493. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Houten SM, Denis S, Argmann CA, Jia Y,
Ferdinandusse S, Reddy JK and Wanders RJ: Peroxisomal
L-bifunctional enzyme (Ehhadh) is essential for the production of
medium-chain dicarboxylic acids. J Lipid Res. 53:1296–1303. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hecker M, Sommer N, Voigtmann H, Pak O,
Mohr A, Wolf M, Vadász I, Herold S, Weissmann N, Morty RE, et al:
Impact of short-and medium-chain fatty acids on mitochondrial
function in severe inflammation. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr.
38:587–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Calamita G, Ferri D, Gena P, Liquori GE,
Cavalier A, Thomas D and Svelto M: The inner mitochondrial membrane
has aquaporin-8 water channels and is highly permeable to water. J
Biol Chem. 280:17149–17153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang JQ, Zhang L, Tao XG, Wei L, Liu B,
Huang LL and Chen YG: Tetramethylpyrazine upregulates the aquaporin
8 expression of hepatocellular mitochondria in septic rats. J Surg
Res. 185:286–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schulte J, Struck J, Köhrle J and Müller
B: Circulating levels of peroxiredoxin 4 as a novel biomarker of
oxidative stress in patients with sepsis. Shock. 35:460–465. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marchissio MJ, Francés DEA, Carnovale CE
and Marinelli RA: Mitochondrial aquaporin-8 knockdown in human
hepatoma HepG2 cells causes ROS-induced mitochondrial
depolarization and loss of viability. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
264:246–254. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Banasik K, Justesen JM, Hornbak M, Krarup
NT, Gjesing AP, Sandholt CH, Jensen TS, Grarup N, Andersson A,
Jørgensen T, et al: Bioinformatics-driven identification and
examination of candidate genes for non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. PLoS One. 6:e165422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Andrades MÉ, Morina A, Spasić S and
Spasojević I: Bench-to-bedside review: sepsis - from the redox
point of view. Crit Care. 15:2302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dare AJ, Phillips AR, Hickey AJ, Mittal A,
Loveday B, Thompson N and Windsor JA: A systematic review of
experimental treatments for mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis and
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Free Radic Biol Med.
47:1517–1525. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lowes DA and Galley HF: Mitochondrial
protection by the thioredoxin-2 and glutathione systems in an in
vitro endothelial model of sepsis. Biochem J. 436:123–132. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ito M, Imai M, Muraki M, Miyado K, Qin J,
Kyuwa S, Yoshikawa Y, Hosoi Y, Saito H and Takahashi Y: GSTT1 is
upregulated by oxidative stress through p38-MK2 signaling pathway
in human granulosa cells: Possible association with mitochondrial
activity. Aging (Albany NY). 3:1213–1223. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Yang CS, Kim JJ, Lee HM, Jin HS, Lee SH,
Park JH, Kim SJ, Kim JM, Han YM, Lee MS, et al: The AMPK-PPARGC1A
pathway is required for antimicrobial host defense through
activation of autophagy. Autophagy. 10:785–802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hato T, Tabata M and Oike Y: The role of
angiopoietin-like proteins in angiogenesis and metabolism. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 18:6–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo L, Ai J, Zheng Z, Howatt DA, Daugherty
A, Huang B and Li XA: High density lipoprotein protects against
polymicrobe-induced sepsis in mice. J Biol Chem. 288:17947–17953.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|