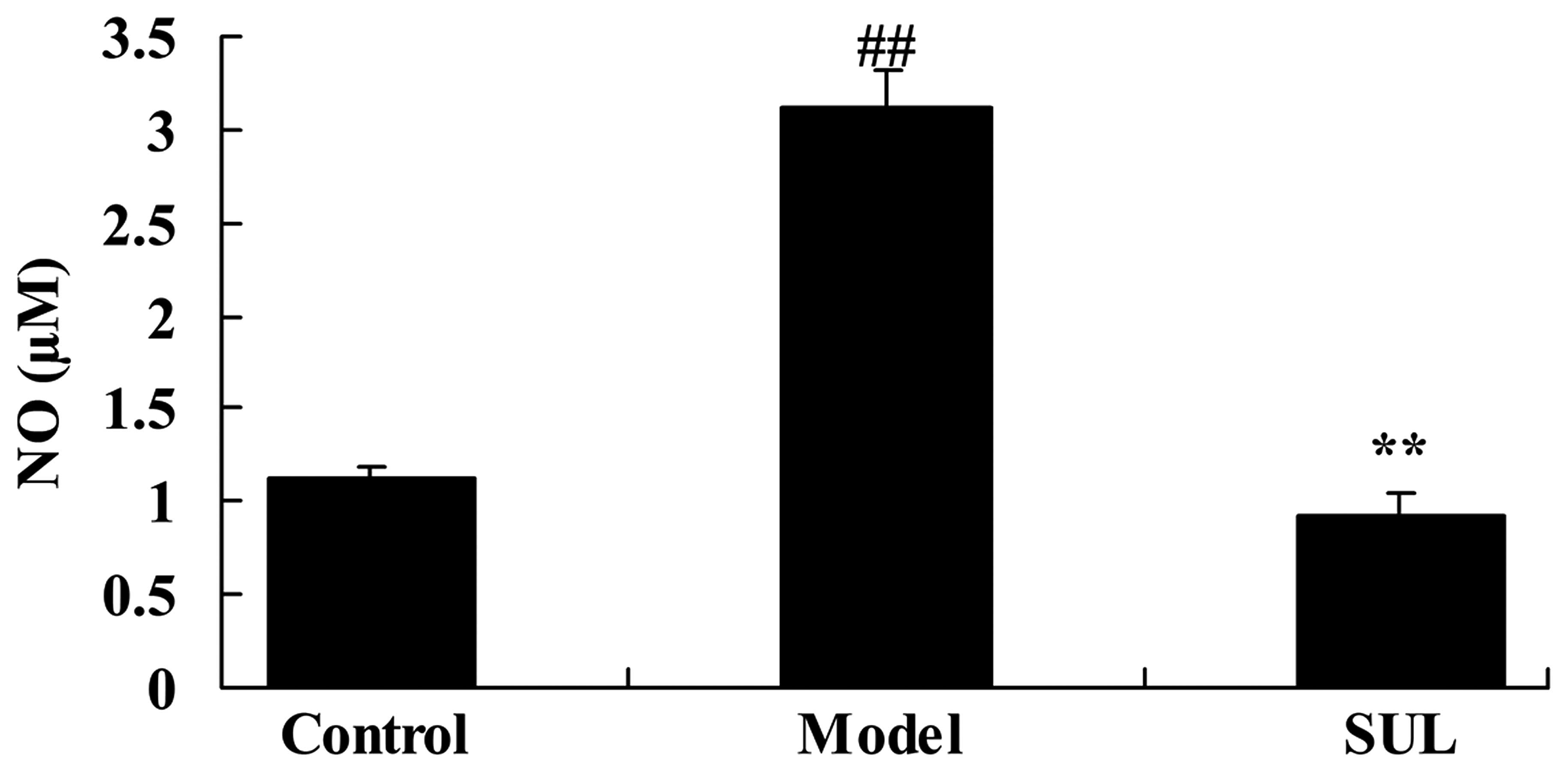
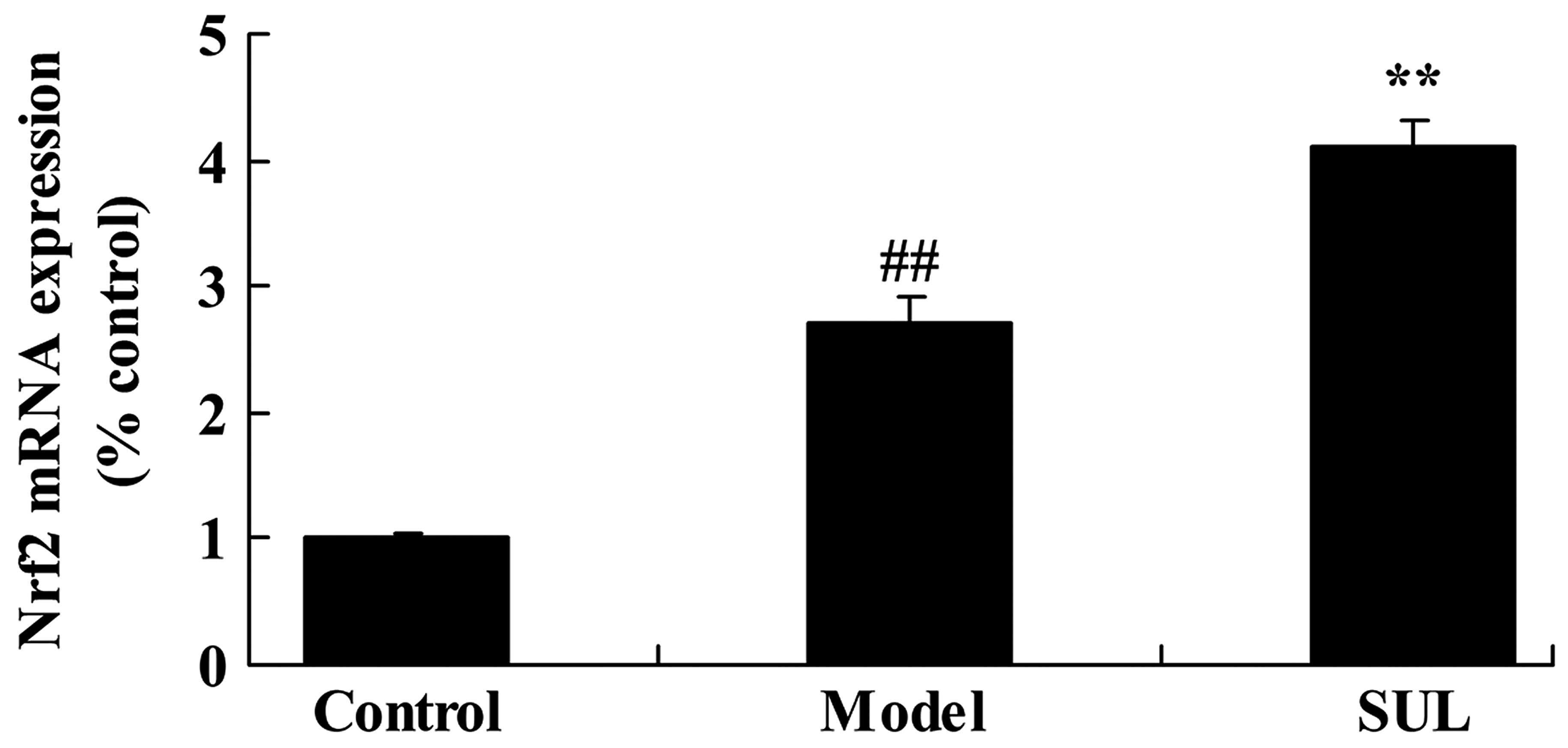
|
1
|
Emr BM, Roy S, Kollisch-Singule M, Gatto
LA, Barravecchia M, Lin X, Young JL, Wang G, Liu J, Satalin J, et
al: Electroporation-mediated gene delivery of Na+,
K+-ATPase, and ENaC subunits to the lung attenuates
acute respiratory distress syndrome in a two-hit porcine model.
Shock. 43:16–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang L, Taneja R, Wang W, Yao LJ,
Veldhuizen RA, Gill SE, Fortin D, Inculet R, Malthaner R and Mehta
S: Human alveolar epithelial cells attenuate pulmonary
microvascular endothelial cell permeability under septic
conditions. PLoS One. 8:e553112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ather JL, Alcorn JF, Brown AL, Guala AS,
Suratt BT, Janssen-Heininger YM and Poynter ME: Distinct functions
of airway epithelial nuclear factor-kappaB activity regulate
nitrogen dioxide-induced acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 43:443–451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Fard N, Saffari A, Emami G, Hofer S,
Kauczor HU and Mehrabi A: Acute respiratory distress syndrome
induction by pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury in large animal
models. J Surg Res. 189:274–284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang B, Huang W, Han J and Liang Z: Study
of the role of epidermal growth factor on lung fluid transport in
rabbits with acute lung injury caused by endotoxin. Exp Ther Med.
4:611–614. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan YM, Li YD, Song XL, Liu M, Diao F,
Wang Y, Sun Y, Wang ZH and Lu J: Therapeutic effects of inhaling
aerosolized surfactant alone or with dexamethasone generated by a
novel noninvasive apparatus on acute lung injury in rats. J Trauma
Acute Care Surg. 73:1114–1120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhandary YP, Velusamy T, Shetty P, Shetty
RS, Idell S, Cines DB, Jain D, Bdeir K, Abraham E, Tsuruta Y, et
al: Post-transcriptional regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator receptor expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:288–298. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Zhang L, Duan W, Liu B, Gong P,
Ding Y and Wu X: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide by
inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in a murine model. Mol Med Rep. 10:447–452. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmidt AE and Adamski J; Education
Committee of the Academy of Clinical Laboratory Physicians and
Scientists: Pathology consultation on transfusion-related acute
lung injury (TRALI). Am J Clin Pathol. 138:498–503. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang ZY, Wu SN, Zhu ZZ, Yang BX and Zhu X:
Inhaled unfractionated heparin improves abnormalities of alveolar
coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation in endotoxemia-induced
lung injury rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:318–324. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Zhang JZ, Liu Z, Liu J, Ren JX and Sun TS:
Mitochondrial DNA induces inflammation and increases TLR9/NF-κB
expression in lung tissue. Int J Mol Med. 33:817–824.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Irwin DC, Baek JH, Hassell K, Nuss R,
Eigenberger P, Lisk C, Loomis Z, Maltzahn J, Stenmark KR,
Nozik-Grayck E and Shetty S: Hemoglobin-induced lung vascular
oxidation, inflammation, and remodeling contribute to the
progression of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and is attenuated in
rats with repeated-dose haptoglobin administration. Free Radic Biol
Med. 82:50–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dominguez-Perles R, Medina S, Moreno DA,
Garcia-Viguera C, Ferreres F and Gil-Izquierdo A: A new ultra-rapid
UHPLC/MS/MS method for assessing glucoraphanin and sulforaphane
bioavailability in human urine. Food Chem. 143:132–138. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chi X, Zhang R, Shen N, Jin Y, Alina A,
Yang S and Lin S: Sulforaphane reduces apoptosis and oncosis along
with protecting liver injury-induced ischemic reperfusion by
activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Hepatol Int. 9:321–329. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin W, Wu RT, Wu T, Khor TO, Wang H and
Kong AN: Sulforaphane suppressed LPS-induced inflammation in mouse
peritoneal macrophages through Nrf2 dependent pathway. Biochem
Pharmacol. 76:967–973. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benedict AL, Mountney A, Hurtado A, Bryan
KE, Schnaar RL, Dinkova-Kostova AT and Talalay P: Neuroprotective
effects of sulforaphane after contusive spinal cord injury. J
Neurotrauma. 29:2576–2586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang CT, Zhang L, Wu HW, Wei L, Xu B and
Li DM: Doxycycline attenuates acute lung injury following
cardiopulmonary bypass: Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7460–7468. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Chevalier S, Cury FL, Scarlata E, El-Zayat
E, Hamel L, Rocha J, Zouanat FZ, Moussa S, Scherz A, Elhilali M and
Anidjar M: Endoscopic vascular targeted photodynamic therapy with
the photosensitizer WST11 for benign prostatic hyperplasia in the
preclinical dog model. J Urol. 190:1946–1953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Joo Choi R, Cheng MS and Shik Kim Y:
Desoxyrhapontigenin up-regulates Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1
expression in macrophages and inflammatory lung injury. Redox Biol.
2:504–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reddy SA, Shelar SB, Dang TM, Lee BN, Yang
H, Ong SM, Ng HL, Chui WK, Wong SC and Chew EH: Sulforaphane and
its methylcarbonyl analogs inhibit the LPS-stimulated inflammatory
response in human monocytes through modulating cytokine production,
suppressing chemotactic migration and phagocytosis in a NF-κB- and
MAPK-dependent manner. Int Immunopharmacol. 24:440–450. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nallasamy P, Si H, Babu PV, Pan D, Fu Y,
Brooke EA, Shah H, Zhen W, Zhu H, Liu D, et al: Sulforaphane
reduces vascular inflammation in mice and prevents TNF-α-induced
monocyte adhesion to primary endothelial cells through interfering
with the NF-κB pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 25:824–833. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Arslan S, Korkmaz Ö, Özbilüm N and Berkan
Ö: Association between NF-κBI and NF-κBIA polymorphisms and
coronary artery disease. Biomed Rep. 3:736–740. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mankan AK, Lawless MW, Gray SG, Kelleher D
and McManus R: NF-kappaB regulation: the nuclear response. J Cell
Mol Med. 13:631–643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang D, Sun Y, Shen Y, Li F, Song X, Zhou
E, Zhao F, Liu Z, Fu Y, Guo M, et al: Shikonin exerts
anti-inflammatory effects in a murine model of
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the
nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
16:475–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trapani L, Segatto M, Ascenzi P and
Pallottini V: Potential role of nonstatin cholesterol lowering
agents. IUBMB Life. 63:964–971. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ethridge RT, Chung DH, Slogoff M, Ehlers
RA, Hellmich MR, Rajaraman S, Saito H, Uchida T and Evers BM:
Cyclooxygenase-2 gene disruption attenuates the severity of acute
pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury.
Gastroenterology. 123:1311–1322. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Santos LA, Ribeiro EL, Barbosa KP, Fragoso
IT, Gomes FO, Donato MA, Silva BS, Silva AK, Rocha SW, França ME,
et al: Diethylcarbamazine inhibits NF-κB activation in acute lung
injury induced by carrageenan in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
23:153–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shan Y, Wu K, Wang W, Wang S, Lin N, Zhao
R, Cassidy A and Bao Y: Sulforaphane down-regulates COX-2
expression by activating p38 and inhibiting NF-kappaB-DNA-binding
activity in human bladder T24 cells. Int J Oncol. 34:1129–1134.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grantham CJ, Izumi T, Lewis DH and Bakhle
YS: Effects of endotoxin-induced lung injury on the
pharmacokinetics of pros-taglandin E2 and adenosine in
rat isolated lung. Circ Shock. 26:157–167. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Jia Z, Liu G, Zhou L, Liu M, Yang B
and Yang T: PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone suppresses renal
mPGES-1/PGE2 pathway in db/db Mice. PPAR Res. 2013:6129712013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kono K, Toda S, Hora K and Kiyosawa K:
Direct hemoperfusion with a beta2-microglobulin-selective adsorbent
column eliminates inflammatory cytokines and improves pulmonary
oxygenation. Ther Apher Dial. 13:27–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Choi YJ, Lee WS, Lee EG, Sung MS and Yoo
WH: Sulforaphane inhibits IL-1β-induced proliferation of rheumatoid
arthritis synovial fibroblasts and the production of MMPs, COX-2,
and PGE2. Inflammation. 37:1496–1503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Menezes LG, Uzuelli JA, Tefé-Silva C,
Ramos SG, Santos JE and Martinez JA: Acute lung injury induced by
the intravenous administration of cigarette smoke extract. J Bras
Pneumol. 39:39–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qi B, Chen HL, Shang D, Dong Y, Zhang GX
and Yu L: Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 on alveolar-capillary barrier disruption and
lung edema in rat models of severe acute pancreatitis-associated
lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 8:899–906. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim KH, Burkhart K, Chen P, Frevert CW,
Randolph-Habecker J, Hackman RC, Soloway PD and Madtes DK: Tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 deficiency amplifies acute lung
injury in bleomycin-exposed mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
33:271–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mao L, Wang HD, Wang XL, Qiao L and Yin
HX: Sulforaphane attenuates matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression
following spinal cord injury in mice. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 40:354–360.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu H, Liang X, Wang D, Zhang H, Liu L,
Chen H, Li Y, Duan Q and Xie K: Combination therapy with nitric
oxide and molecular hydrogen in a murine model of acute lung
injury. Shock. 43:504–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu D, Niu W, Luo Y, Zhang B, Liu M, Dong
H, Liu Y and Li Z: Endogenous estrogen attenuates hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension by inhibiting pulmonary arterial
vasoconstriction and pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells
proliferation. Int J Med Sci. 10:771–781. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin HJ, Wang CT, Niu KC, Gao C, Li Z, Lin
MT and Chang CP: Hypobaric hypoxia preconditioning attenuates acute
lung injury during high-altitude exposure in rats via up-regulating
heat-shock protein 70. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:223–231. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Brandenburg LO, Kipp M, Lucius R, Pufe T
and Wruck CJ: Sulforaphane suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in
primary rat microglia. Inflamm Res. 59:443–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shan Y, Akram A, Amatullah H, Zhou DY,
Gali PL, Maron-Gutierrez T, González-López A, Zhou L, Rocco PR,
Hwang D, et al: ATF3 protects pulmonary resident cells from acute
and ventilator-induced lung injury by preventing Nrf2 degradation.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:651–668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yu JB, Shi J, Gong LR, Dong SA, Xu Y,
Zhang Y, Cao XS and Wu LL: Role of Nrf2/ARE pathway in protective
effect of electroacupuncture against endotoxic shock-induced acute
lung injury in rabbits. PLoS One. 9:e1049242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|