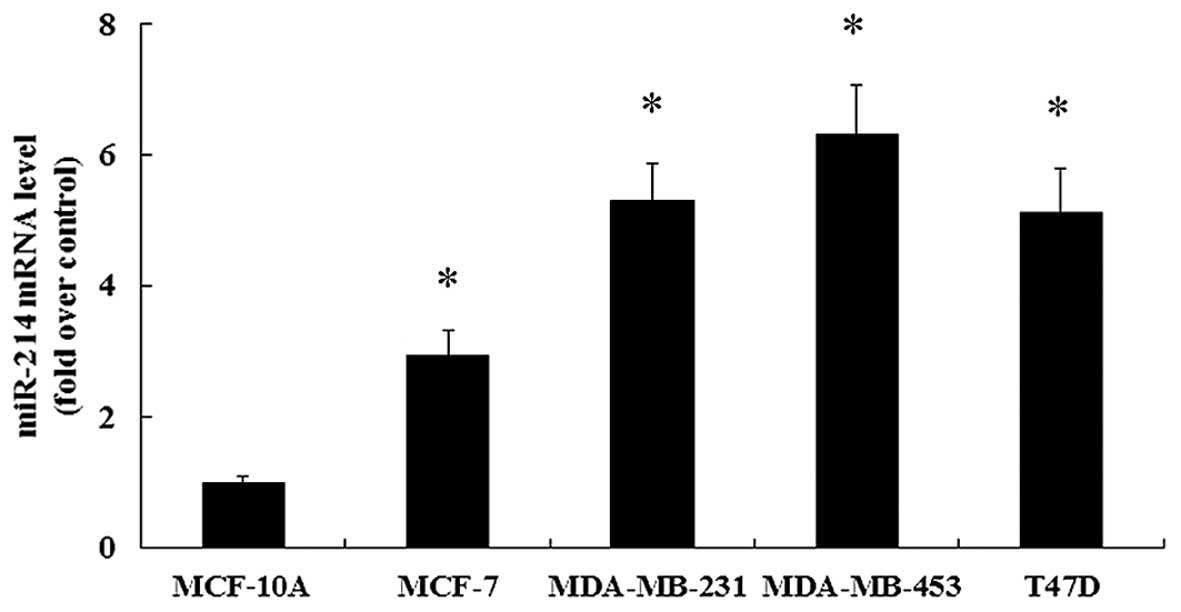
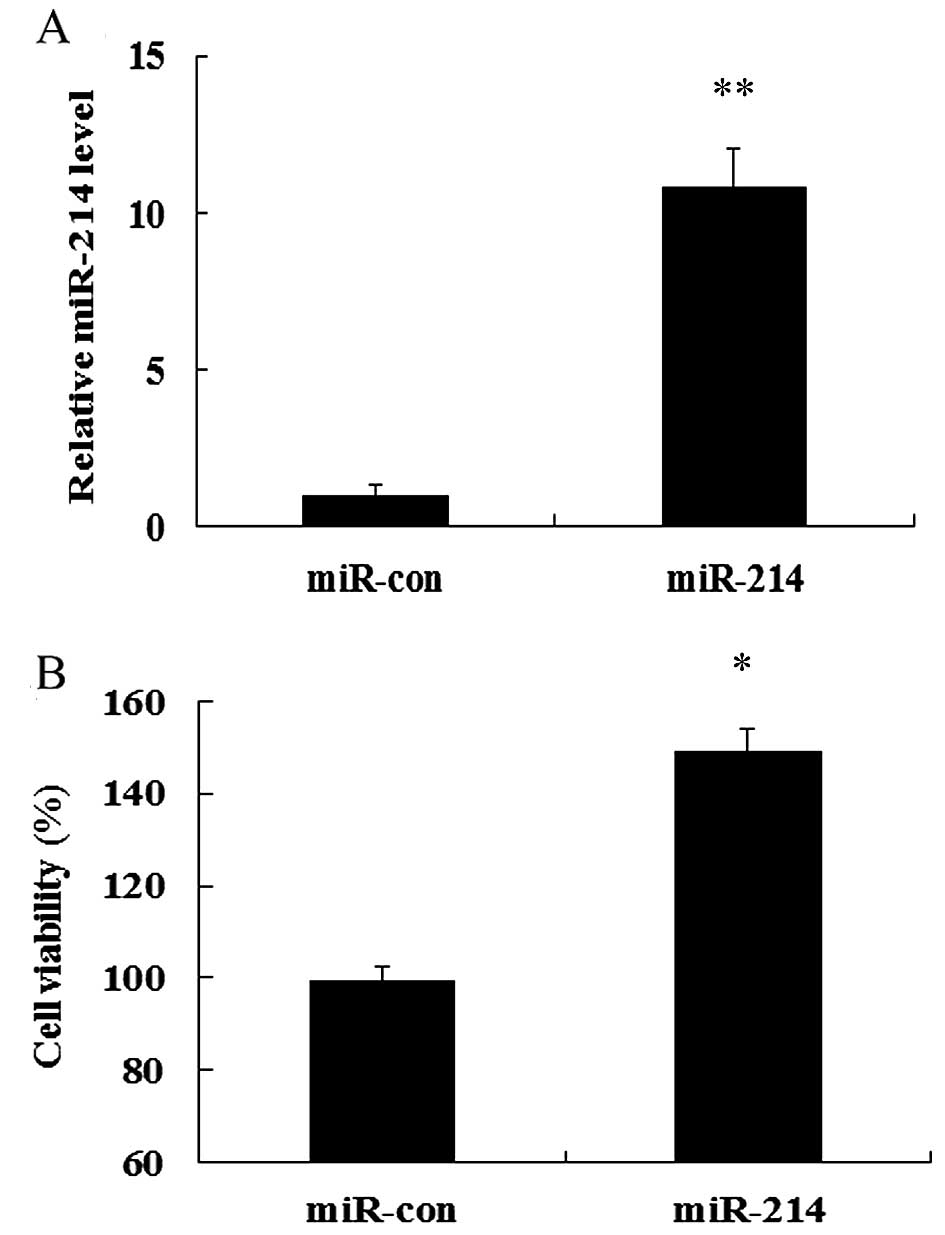
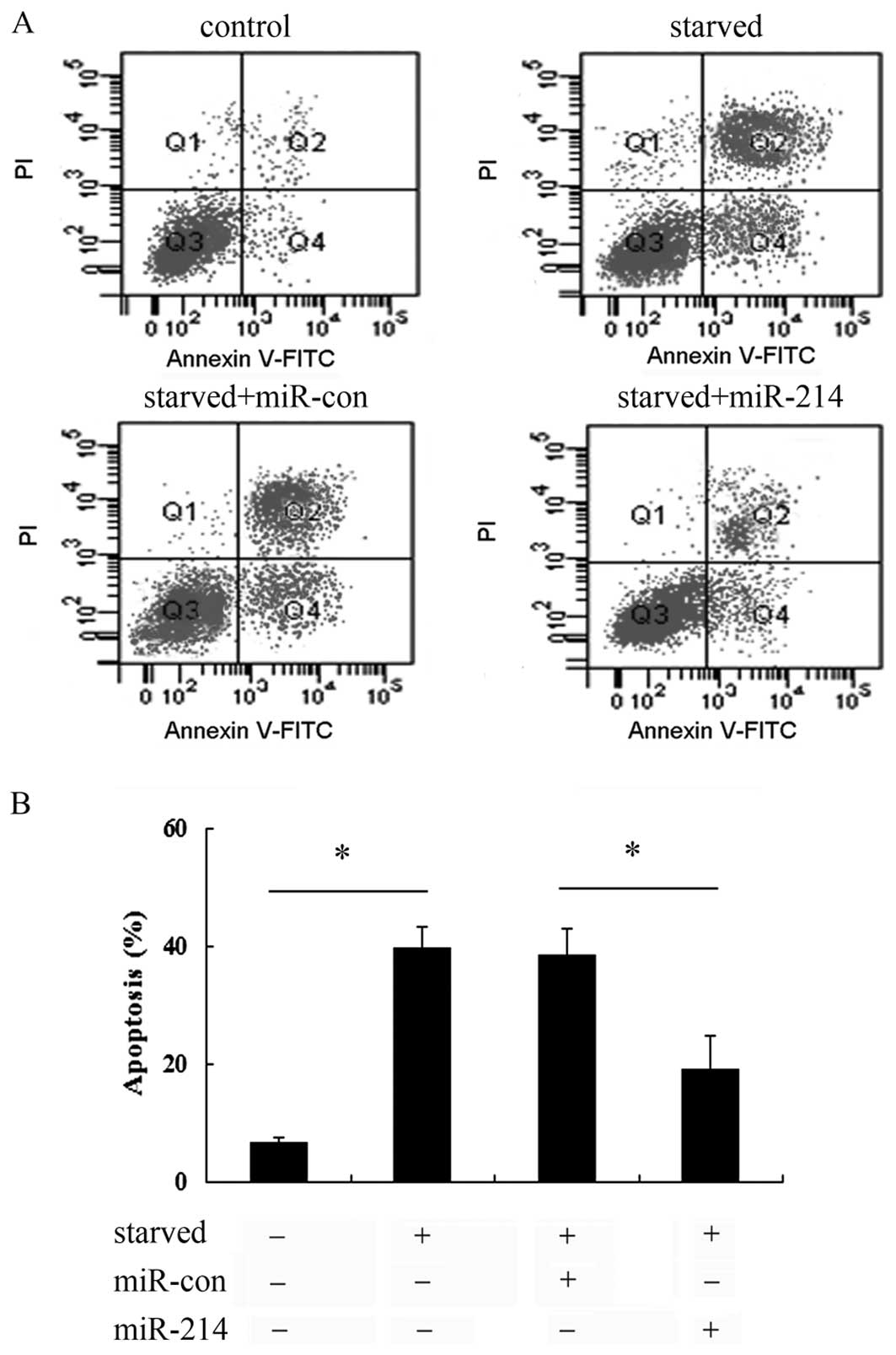
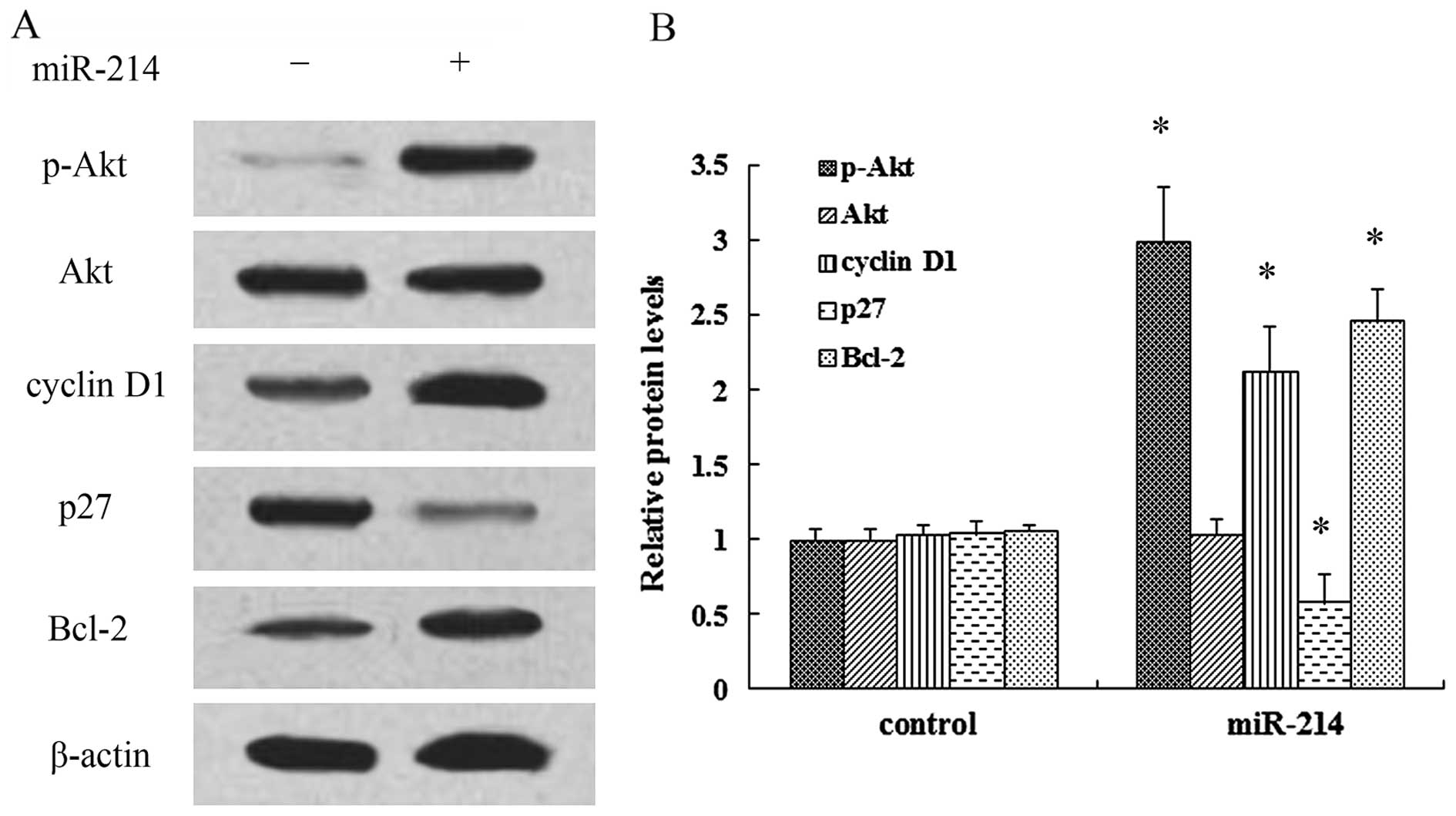
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benson JR and Jatoi I: The global breast
cancer burden. Future Oncol. 8:697–702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van Rooij E and Olson EN: MicroRNA
therapeutics for cardiovascular disease: opportunities and
obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:860–872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai R and Ahmed SA: MicroRNA, a new
paradigm for understanding immunoregulation, inflammation, and
autoimmune diseases. Transl Res. 157:163–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang J, Lyu H, Wang J and Liu B: MicroRNA
regulation and therapeutic targeting of survivin in cancer. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:20–31. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H,
Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR and Zhang W:
Circulating plasma miR-141 is a novel biomarker for metastatic
colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 6:e177452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fornari F, Milazzo M, Chieco P, Negrini M,
Marasco E, Capranico G, Mantovani V, Marinello J, Sabbioni S,
Callegari E, et al: In hepatocellular carcinoma miR-519d is
up-regulated by p53 and DNA hypomethylation and targets CDKN1A/p21,
PTEN, AKT3 and TIMP2. J Pathol. 227:275–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Penna E, Orso F, Cimino D, Tenaglia E,
Lembo A, Quaglino E, Poliseno L, Haimovic A, Osella-Abate S, De
Pittà C, et al: microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour
progression through suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 30:1990–2007.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamada Y, Hidaka H, Seki N, Yoshino H,
Yamasaki T, Itesako T, Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Tumor-suppressive
microRNA-135a inhibits cancer cell proliferation by targeting the
c-MYC oncogene in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:304–312.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shih TC, Tien YJ, Wen CJ, Yeh TS, Yu MC,
Huang CH, Lee YS, Yen TC and Hsieh SY: MicroRNA-214 downregulation
contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the
hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J Hepatol.
57:584–591. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z and Cai H, Lin L, Tang M and Cai H:
Upregulated expression of microRNA-214 is linked to tumor
progression and adverse prognosis in pediatric osteosarcoma.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:206–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Li J, Wang X, Zheng C and Ma W:
Downregulation of microRNA-214 and overexpression of FGFR-1
contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 439:47–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schwarzenbach H, Milde-Langosch K,
Steinbach B, Müller V and Pantel K: Diagnostic potential of
PTEN-targeting miR-214 in the blood of breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:933–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li B, Han Q, Zhu Y, Yu Y, Wang J and Jiang
X: Down-regulation of miR-214 contributes to intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma metastasis by targeting Twist. FEBS J.
279:2393–2398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moon S-H, Kim D-K, Cha Y, Jeon I, Song J
and Park K-S: PI3K/Akt and Stat3 signaling regulated by PTEN
control of the cancer stem cell population, proliferation and
senescence in a glioblastoma cell line. Int J Oncol. 42:921–928.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abdulaziz S, Al-Shahid M and Al-Thenayan
E: A 49-year-old man with acute pulmonary hypertension post lung
transplantation. Chest. 144:704–707. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baumjohann D, Kageyama R, Clingan JM,
Morar MM, Patel S, de Kouchkovsky D, Bannard O, Bluestone JA,
Matloubian M, Ansel KM and Jeker LT: The microRNA cluster MIR-17~92
promotes TFH cell differentiation and represses
subset-inappropriate gene expression. Nat Immunol. 14:840–848.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Y, Xiong M, Niu J, Sun Q, Su W, Zen
K, Dai C and Yang J: Secreted fibroblast-derived miR-34a induces
tubular cell apoptosis in fibrotic kidney. J Cell Sci.
127:4494–4506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zha R, Guo W, Zhang Z, Qiu Z, Wang Q, Ding
J, Huang S, Chen T, Gu J, Yao M and He X: Genome-wide screening
identified that miR-134 acts as a metastasis suppressor by
targeting integrin β1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e876652014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yau WL, Lam CSC, Ng L, Chow AK, Chan ST,
Chan JY, Wo JY, Ng KT, Man K, Poon RT and Pang RW: Over-expression
of miR-106b promotes cell migration and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition process. PLoS One. 8:e578822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Josson S, Gururajan M, Hu P, Shao C, Chu
GY, Zhau HE, Liu C, Lao K, Lu CL, Lu YT, et al: miR-409-3p/-5p
promotes tumorigenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and
bone metastasis of human prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:4636–4646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Slomovitz BM and Coleman RL: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5856–5864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yulyana Y, Ho IA, Sia KC, Newman JP, Toh
XY, Endaya BB, Chan JK, Gnecchi M, Huynh H, Chung AY, et al:
Paracrine factors of human fetal MSCs inhibit liver cancer growth
through reduced activation of IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol Ther.
23:746–756. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vo BT, Morton D Jr, Komaragiri S, Millena
AC, Leath C and Khan SA: TGF-β effects on prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion are mediated by PGE2 through activation of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Endocrinology. 154:1768–1779. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yakes FM, Chinratanalab W, Ritter CA, King
W, Seelig S and Arteaga CL: Herceptin-induced inhibition of
phosphati-dylinositol-3 kinase and Akt is required for
antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action.
Cancer Res. 62:4132–4141. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumar P, Miller AI and Polverini PJ: p38
MAPK mediates γ-irradiation-induced endothelial cell apoptosis, and
vascular endothelial growth factor protects endothelial cells
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biol
Chem. 279:43352–43360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Song MS, Salmena L and Pandolfi PP: The
functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:283–296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mulholland DJ, Tran LM, Li Y, Cai H, Morim
A, Wang S, Plaisier S, Garraway IP, Huang J, Graeber TG and Wu H:
Cell autonomous role of PTEN in regulating castration-resistant
prostate cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 19:792–804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee S, Choi EJ, Jin C and Kim DH:
Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by PTEN reduction and PIK3CA mRNA
amplification contributes to cisplatin resistance in an ovarian
cancer cell line. Gynecol Oncol. 97:26–34. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|