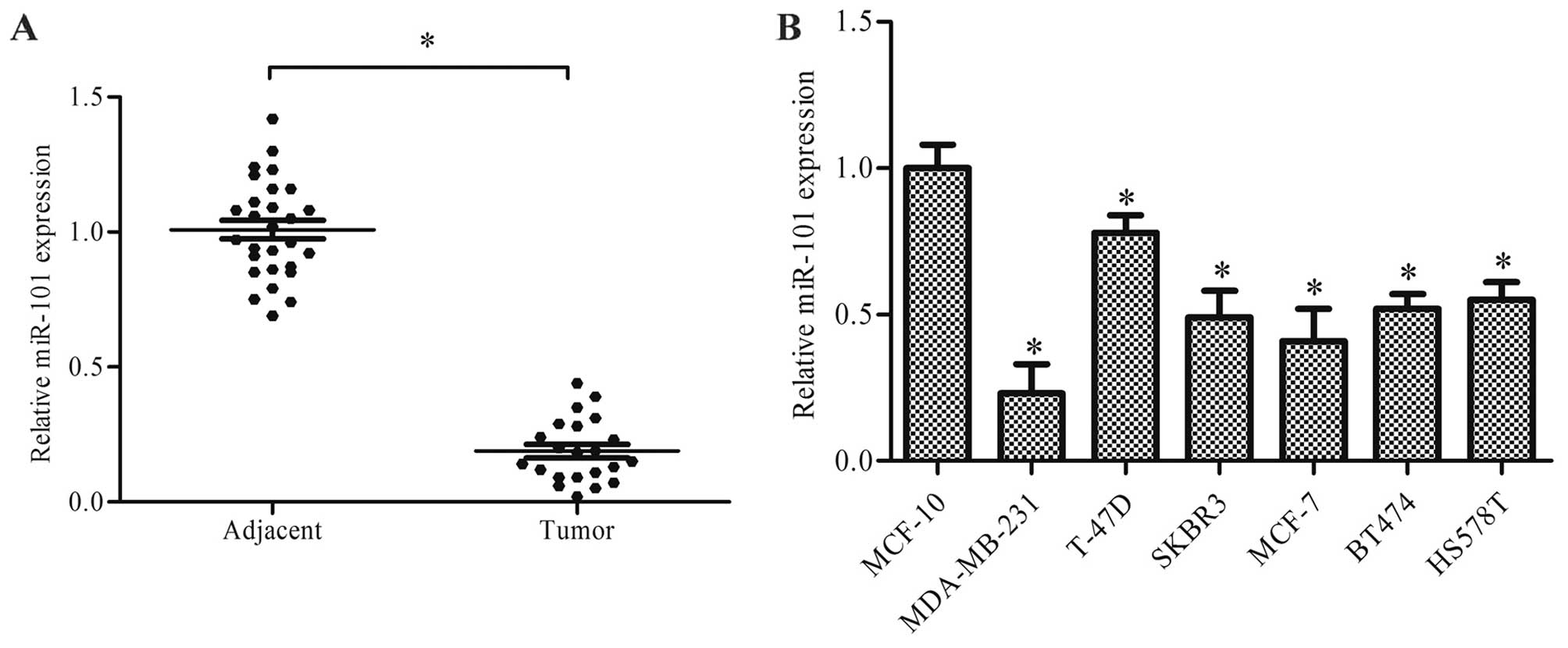
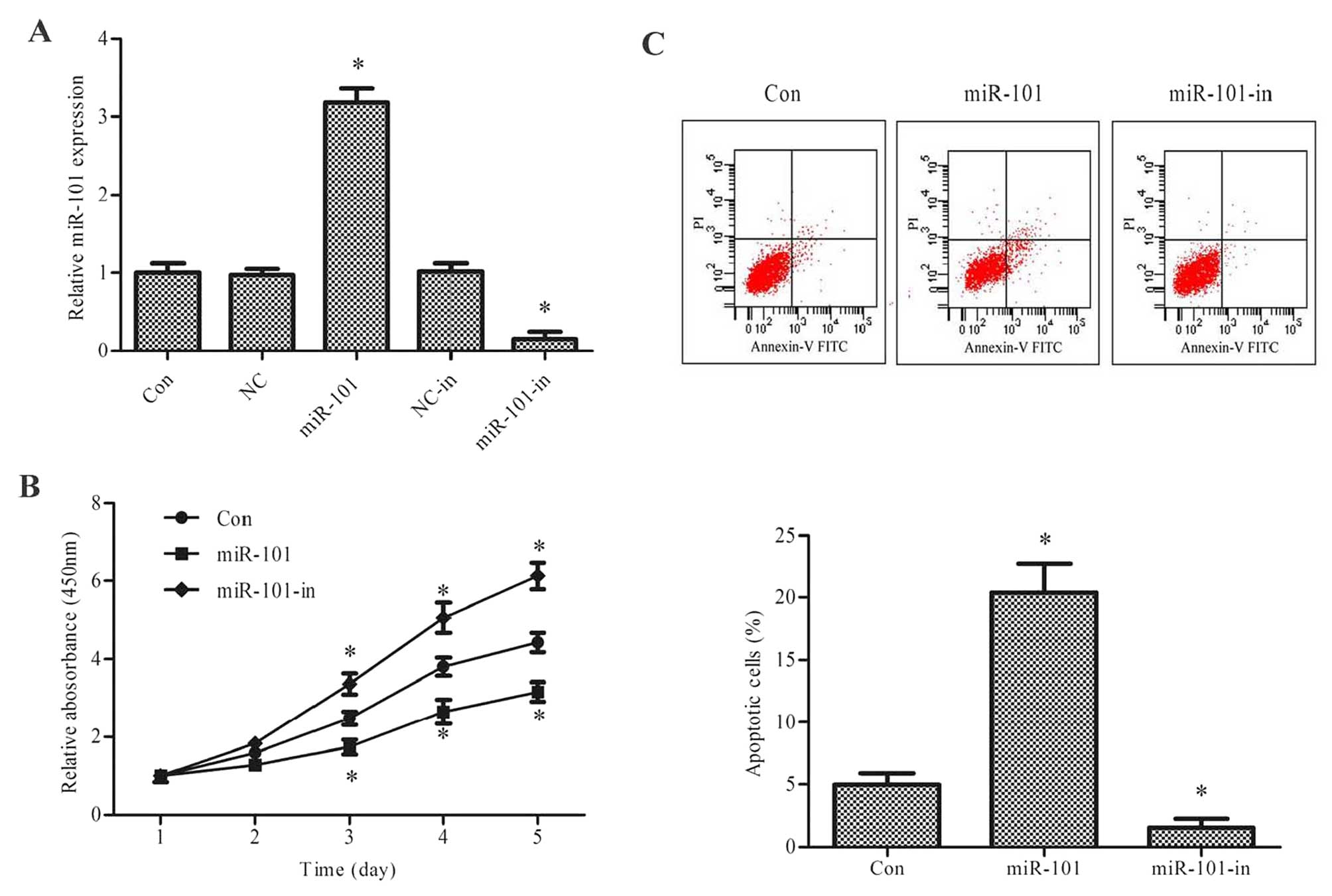
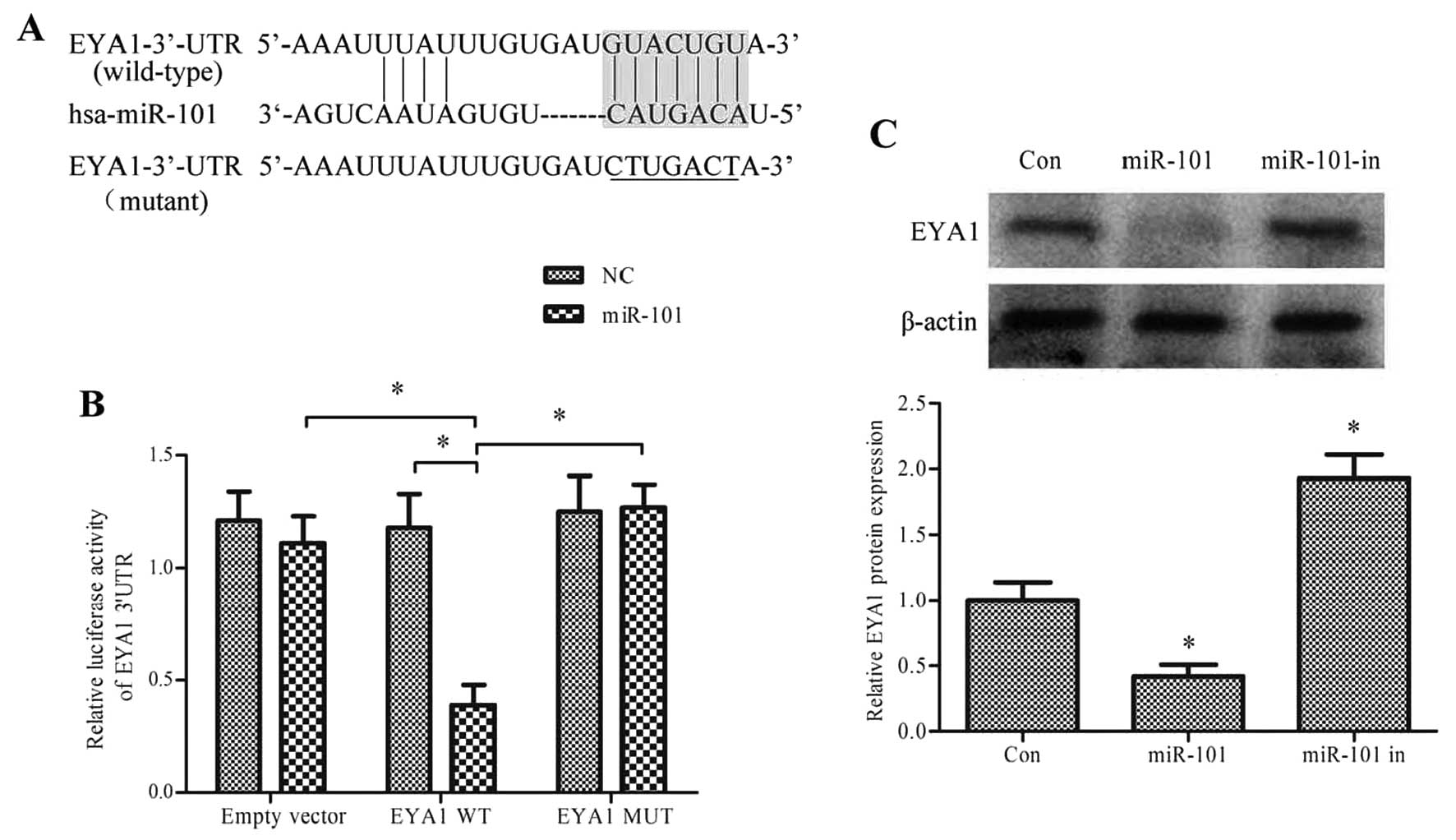
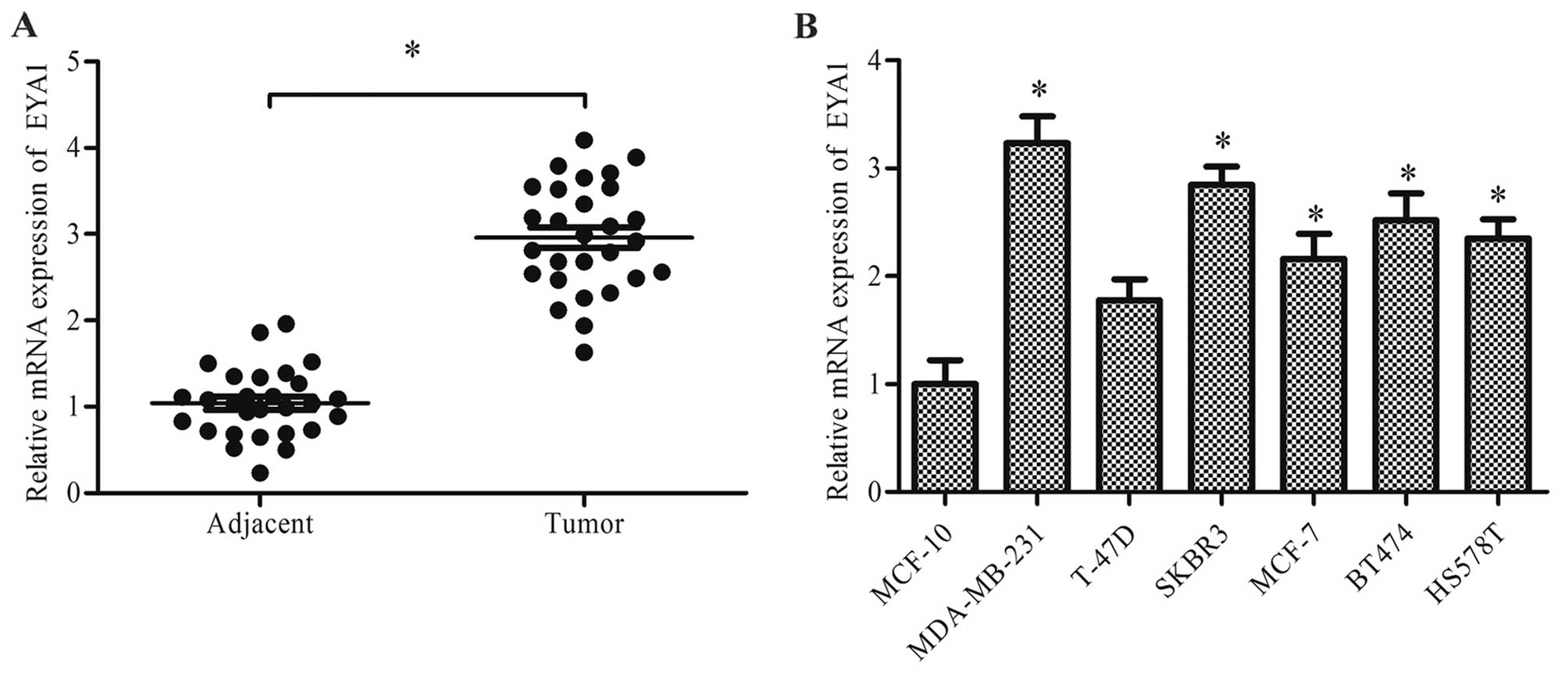
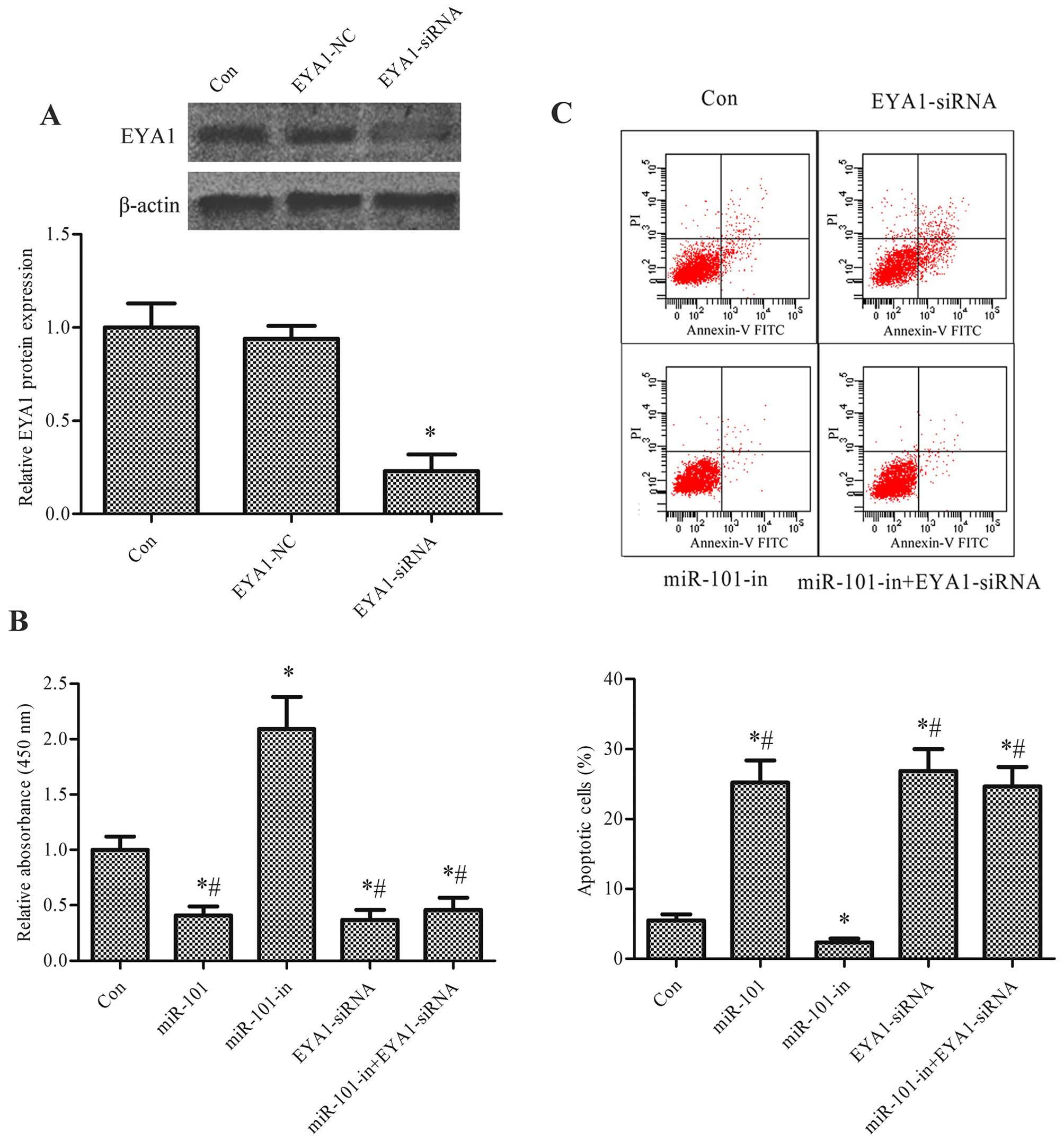
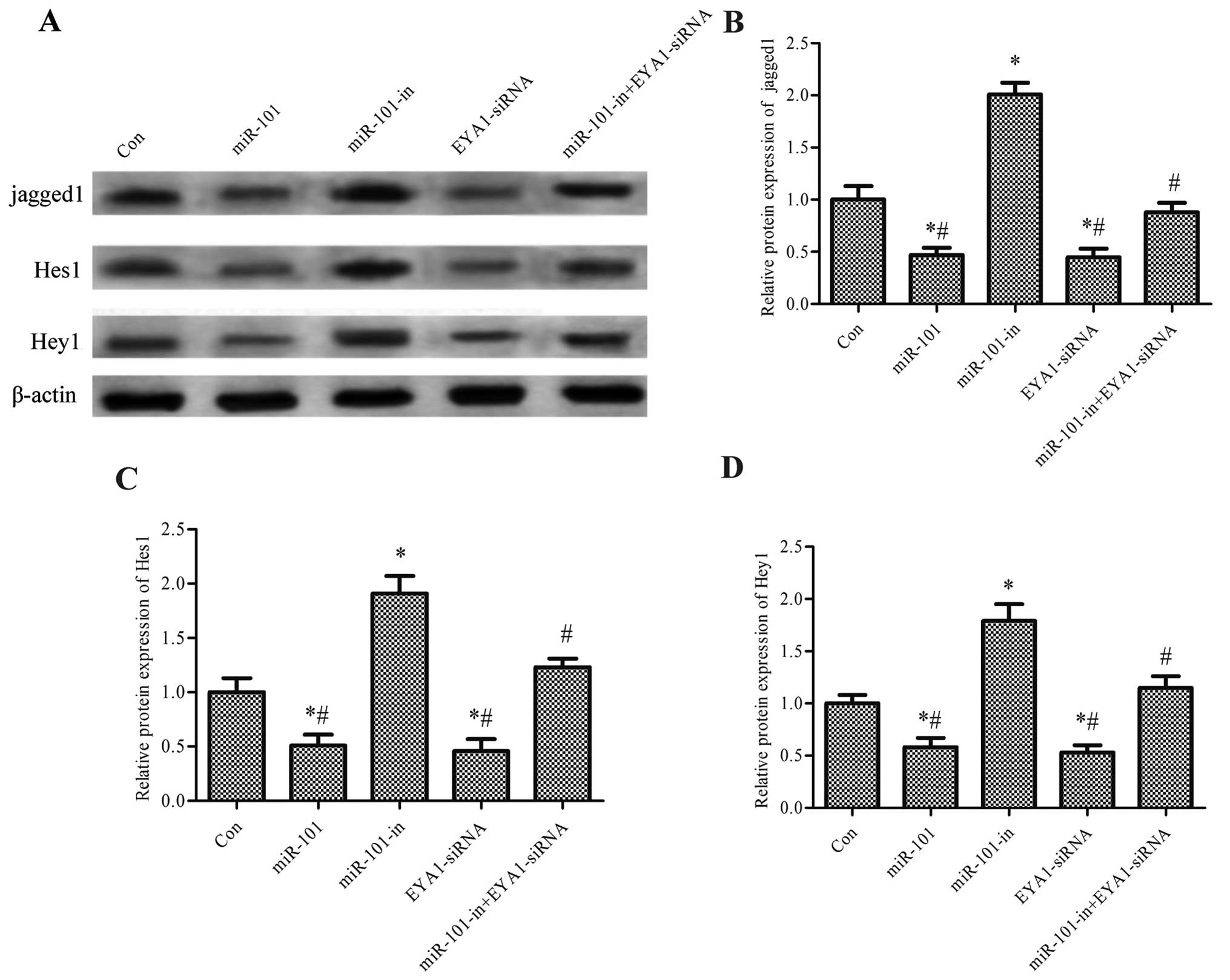
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rhodes DJ, O'Connor MK, Phillips SW, Smith
RL and Collins DA: Molecular breast imaging: a new technique using
technetium Tc 99m scintimammography to detect small tumors of the
breast. Mayo Clin Proc. 80:24–30. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gompel A: Breast cancer incidence rates in
US women are no longer declining. Climacteric. 14:690–691.
2011.
|
|
4
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96(Suppl
96): R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen
S, Bateman A and Enright AJ: miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets
and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:D140–D144. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Griffiths-Jones S: The microRNA Registry.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D109–D111. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Blenkiron C, Goldstein LD, Thorne NP,
Spiteri I, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Barbosa-Morais NL, Teschendorff AE,
Green AR, Ellis IO, et al: MicroRNA expression profiling of human
breast cancer identifies new markers of tumor subtype. Genome Biol.
8:R2142007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frezzetti D, De Menna M, Zoppoli P, Guerra
C, Ferraro A, Bello AM, De Luca P, Calabrese C, Fusco A, Ceccarelli
M, et al: Upregulation of miR-21 by Ras in vivo and its role in
tumor growth. Oncogene. 30:275–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang M, Shen H, Qiu C, Ni Y, Wang L, Dong
W, Liao Y and Du J: High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts
recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer.
Eur J Cancer. 49:604–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shibuya H, Iinuma H, Shimada R, Horiuchi A
and Watanabe T: Clinicopathological and prognostic value of
microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in colorectal cancer. Oncology.
79:313–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong
C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J and Song E: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Corney DC, Hwang CI, Matoso A, Vogt M,
Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, Kamat AA, Sood AK, Ellenson LH,
Hermeking H and Nikitin AY: Frequent downregulation of miR-34
family in human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1119–1128.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang R, Ma J, Wu Q, Xia J, Miele L, Sarkar
FH and Wang Z: Functional role of miR-34 family in human cancer.
Curr Drug Targets. 14:1185–1191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y and Naoe T: let-7
microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon
cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:903–906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: microRNA
involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1126–1133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu C-G, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lei Q, Shen F, Wu J, Zhang W, Wang J and
Zhang L: MiR-101, downregulated in retinoblastoma, functions as a
tumor suppressor in human retinoblastoma cells by targeting EZH2.
Oncol Rep. 32:261–269. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei X, Xiang T, Ren G, Tan C, Liu R, Xu X
and Wu Z: miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x
protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 3A. Cell Signal. 25:439–446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luo C, Merz PR, Chen Y, Dickes E, Pscherer
A, Schadendorf D and Eichmüller SB: MiR-101 inhibits melanoma cell
invasion and proliferation by targeting MITF and EZH2. Cancer Lett.
341:240–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Popov VM, Wu K, Zhou J, Powell MJ, Mardon
G, Wang C and Pestell RG: The Dachshund gene in development and
hormone-responsive tumorigenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
21:41–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Voas MG and Rebay I: Signal integration
during development: Insights from the Drosophila eye. Dev Dyn.
229:162–175. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Yang N, Huang J, Buckanovich RJ,
Liang S, Barchetti A, Vezzani C, O'Brien-Jenkins A, Wang J, Ward
MR, et al: Transcriptional coactivator Drosophila eyes absent
homologue 2 is up-regulated in epithelial ovarian cancer and
promotes tumor growth. Cancer Res. 65:925–932. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Z, Hu J, Sun Y, Li S, Pestell RG and Wu
K: EYA promotes proliferation through up-regulation of cyclin D1.
Cancer Res. 71(Suppl 8): abs. 2942 Proceedings: AACR 102nd Annual
Meeting 2011, April 2–6 2011; http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/71/8_Supplement/2942.short.
|
|
28
|
Pignoni F, Hu B, Zavitz KH, Xiao J,
Garrity PA and Zipursky SL: The eye-specification proteins So and
Eya form a complex and regulate multiple steps in Drosophila eye
development. Cell. 91:881–891. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kumar JP and Moses K: EGF receptor and
Notch signaling act upstream of Eyeless/Pax6 to control eye
specification. Cell. 104:687–697. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li C-M, Guo M, Borczuk A, Powell CA, Wei
M, Thaker HM, Friedman R, Klein U and Tycko B: Gene expression in
Wilms' tumor mimics the earliest committed stage in the metanephric
mesenchymal-epithelial transition. Am J Pathol. 160:2181–2190.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu K, Li Z, Cai S, Tian L, Chen K, Wang J,
Hu J, Sun Y, Li X, Ertel A and Pestell RG: EYA1 phosphatase
function is essential to drive breast cancer cell proliferation
through cyclin D1. Cancer Res. 73:4488–4499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun Y, Kaneko S and Li X and Li X: The
PI3K/Akt signal hyperactivates Eya1 via the SUMOylation pathway.
Oncogene. 34:2527–2537. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nikpour P, Emadi-Baygi M, Emadi-Andani E
and Rahmati S: EYA1 expression in gastric carcinoma and its
association with clinicopathological characteristics: A pilot
study. Med Oncol. 31:9552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sassen S, Miska EA and Caldas C: MicroRNA:
implications for cancer. Virchows Arch. 452:1–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang HJ, Ruan HJ, He XJ, Ma YY, Jiang XT,
Xia YJ, Ye ZY and Tao HQ: MicroRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric
cancer and involved in cell migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer.
46:2295–2303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Howe
TM, Petrocca F, Wallace TA, Liu CG, Volinia S, Calin GA, et al:
Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated
microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6162–6170.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Strillacci A, Valerii MC, Sansone P,
Caggiano C, Sgromo A, Vittori L, Fiorentino M, Poggioli G, Rizzello
F, Campieri M and Spisni E: Loss of miR-101 expression promotes
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway activation and malignancy in colon
cancer cells. J Pathol. 229:379–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Smits M, Nilsson J, Mir SE, van der Stoop
PM, Hulleman E, Niers JM, de Witt Hamer PC, Marquez VE, Cloos J,
Krichevsky AM, et al: miR-101 is down-regulated in glioblastoma
resulting in EZH2-induced proliferation, migration, and
angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 1:710–720. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Xu L, Beckebaum S, Iacob S, Wu G, Kaiser
GM, Radtke A, Liu C, Kabar I, Schmidt HH, Zhang X, et al:
MicroRNA-101 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma progression
through EZH2 downregulation and increased cytostatic drug
sensitivity. J Hepatol. 60:590–598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S,
Wang X, Ateeq B, Laxman B, Cao X, Jing X, Ramnarayanan K, et al:
Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone
methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science. 322:1695–1699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Buechner J, Tømte E, Haug BH, Henriksen
JR, Løkke C, Flægstad T and Einvik C: Tumour-suppressor microRNAs
let-7 and miR-101 target the proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell
proliferation in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer.
105:296–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Graziussi DF, Suga H, Schmid V and Gehring
WJ: The 'eyes absent' (eya) gene in the eye-bearing hydrozoan
jellyfish Cladonema radiatum: conservation of the retinal
determination network. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol. 318:257–267.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li X, Wang S and Schor N: Methylase meets
phosphatase: roles of PRMT and EYA1 in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res.
74(Suppl 19): abs. 464. 2014.
|
|
45
|
Wang J, Cai S, Chen K, Li S, Pestell R and
Wu K: Regulation of AR transcriptional activity and prostate cancer
cellular proliferation by DACH1/Eya1/Six1 pathway. Cancer Res.
73(Suppl 8): abs. 1319. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Bolós V, Grego-Bessa J and de la Pompa JL:
Notch signaling in development and cancer. Endocr Rev. 28:339–363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Allenspach EJ, Maillard I, Aster JC and
Pear WS: Notch signaling in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:466–476.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Miele L, Golde T and Osborne B: Notch
signaling in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:905–918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D, Ahmad A,
Nogueira V, Hay N and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Notch-1 and
Jagged-1 inhibits prostate cancer cell growth, migration and
invasion, and induces apoptosis via inactivation of Akt, mTOR, and
NF-kappaB signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 109:726–736.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kiaris H, Politi K, Grimm LM, Szabolcs M,
Fisher P, Efstratiadis A and Artavanis-Tsakonas S: Modulation of
notch signaling elicits signature tumors and inhibits hras1-induced
oncogenesis in the mouse mammary epithelium. Am J Pathol.
165:695–705. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Stylianou S, Clarke RB and Brennan K:
Aberrant activation of notch signaling in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:1517–1525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|